Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Glushchenko AG1*, Glushchenko VA2 and Glushchenko AA3
Received: May 15, 2024; Published: May 23, 2024
*Corresponding author: Alexander Glushchenko AG, Department of Physics Povolzhsky State University of Telecommunications and Informatics, Samara, Russia
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2024.56.008896
Reflection and refraction of waves is a fundamental physical process observed in nature and widely used in studies of the interaction of waves with surfaces and technical devices for various purposes. The laws of reflection and refraction are well studied for stationary conditions. Of interest is the nature of changes in these laws under non-stationary conditions. By solving wave equations, the nature of the change in the law of refraction on the surface of moving media is considered. Analytical relations are obtained for calculating the angle of refraction, the angle of total internal reflection and the angle of total polarization depending on the speed and direction of motion of the media.
Keywords: Motion of Media; Angle of Refraction; Total Polarization; Internal Reflection
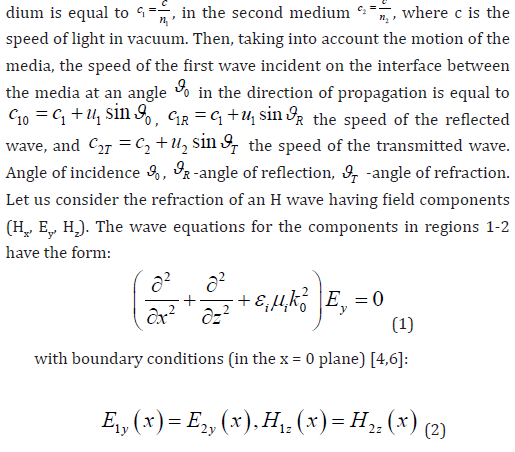
Waves are the most common physical process. Almost all natural processes take place with the participation of waves of various natures, the basic properties of which are largely similar [1]. During the interaction of waves propagating in media at the interfaces, reflection and refraction of waves arise - a fundamental phenomenon of physics, which has found great application in various fields of technology and in natural processes. Wave reflection occurs when waves are reflected from the interface between media, propagate in the same medium and change their direction without changing the parameters of the medium [2]. In this case, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, the incident and reflected rays lie in the same plane with the normal to the surface. Wave refraction occurs when waves move from one medium to another with different parameters and at the same time change their speed and direction. According to the law of refraction, the wave vector of the refracted wave lies in the same plane with the wave vector of the incident wave and the normal to the interface drawn at the point of incidence. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is equal to the ratio of the velocities of sound waves in the first and second media c1 and c2 (Snell’s law). When a wave passes from a medium with a higher density (lower speed of wave propagation) to a medium with a lower density (accordingly, with a higher speed of wave propagation at a certain angle of incidence, it may not pass into the second medium and be completely reflected from the interface between the media. This effect is called total internal reflection and is widely used in optical technology for channeling optical radiation. The laws of reflection and refraction are well studied for stationary parameters of contacting media [3,4]. In the nonstationary state of the parameters of the adjacent media, there are features of the laws of reflection and refraction that must be taken into account in measuring technology [5-7]. This paper examines the influence of the motion of adjacent media parallel to the interface between media on the laws of reflection and refraction.
The passage of waves through the interface of two media moving
along the interface 0z (for simplicity, we assume that 0 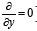 )
(Figure 1) in the general case with different velocities u1 and u2 is considered.
The speed of propagation of waves in the first stationary
)
(Figure 1) in the general case with different velocities u1 and u2 is considered.
The speed of propagation of waves in the first stationary
The solution for the incident, reflected and transmitted waves in each of the regions is sought in the form of functions:

where in the general case, the wave numbers of the forward and backward waves in the first medium and the forward wave in the second semi-infinite medium differ due to the difference in the velocities of these waves, which is created by the movement of the media: where in the general case, the wave numbers of the forward and backward waves in the first medium and the forward wave in the second semi-infinite medium differ due to the difference in the velocities of these waves, which is created by the movement of the media:
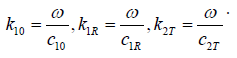
Substitution of the field components into the boundary conditions for Ey leads to the relation:
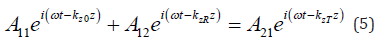
where z – components of wave numbers are determined by the relations:
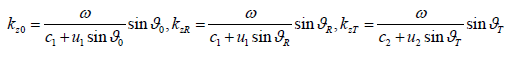
since the boundary conditions must be satisfied at any point z, then.
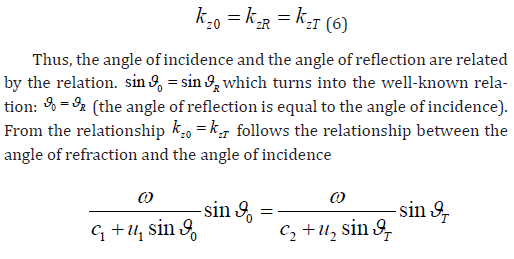
The angle of refraction is determined through the angle of incidence by the relation.

which in the absence of mutual displacement of the adjacent media ( u1 = u2 ) transforms into the known relation [1-3]:
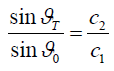
Thus, the law of reflection does not change, but the law of refraction is transformed, which is associated with a change in the ratio of wave velocities in media during their relative motion. Figure 2 shows the dependence of the angle of refraction on the angle of incidence for various ratios of media parameters.
When a wave passes an interface from a denser medium to a less
dense one (for example, from moving water into air), the critical angle
of total internal reflection at
 is determined by the relation.
is determined by the relation.
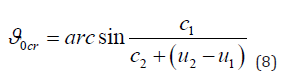
and depends on the relative difference in the velocities of the media
to the wave speed c1.2 in a denser layer (in Figure 3). An increase
in the angles of total internal reflection is observed when the direction
of motion of the medium changes. The movement of the adjacent
media also affects the polarization effect upon reflection. The angle
of total polarization (Brewster angle from the condition T 0 2
π
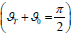 ) is
determined from the equation.
) is
determined from the equation.
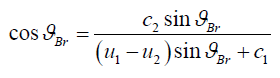
A change in the Brewster angle due to the movement of media is observed when the difference in media velocities changes. For example, changing from -0.2 to 0.2 changes the Brewster angle from 1.05 to 1.15 rad.
The movement of media adjacent to the interface does not lead to a change in the law of wave reflection, but significantly changes the law of refraction, the angle of total internal reflection and the Brewster angle, which can be used to control these parameters or to measure the velocities of media.


