Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Rajiv Choudhary, Nandigana V R Vishal* and K Srinivasa Reddy
Received: January 08, 2026; Published: February 05, 2026
*Corresponding author: Nandigana V R Vishal, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai 600036, India
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2026.64.010073
In this paper, we study integrated digital fluidic circuit. We measure the pressure of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. We measure the mass of KCl inside the packaged purchased bottle and measurement cup using precision mass balance. The integrated fluidic circuit are fabricated with components KCl inside the flat container, electrical wirings, electronic ON/OFF switch, digital pressure transmitter, battery and multimeter. The hydrostatic pressure of KCl of two concentrations are measured using digital pressure transmitter. We measure the pressure for continuous 1 hour. The experiments are carried out at room temperature measured using digital temperature sensor. We obtain the average pressure of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre inside the flat container is 150 Pa. The flat container have length 21 cm, width 12 cm and height 2 cm. We obtain the average pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre inside the flat container. The value is 210 Pa. The dimensions of the flat container are the same. We perform computer aided design (CAD) design simulation for bottle, measurement cup and flat container having KCl. We perform Ansys simulations to understand the hydrostatic pressure of KCl inside the flat container. The density details are available. The simulations match the experiments. We perform theoretical modeling to understand the pressure of KCl inside the flat container. The theory matches the experiments.
Abbreviations: CAD: Computer Aided Design; PCB: Printed Circuit Board; SMPS: Switched-Mode Power Supply; IFC: Integrated Fluidic Circuit; PVC: Polyvinyl Chloride; FD: Fluid Displays
The research on fluid based circuits are new in science. The technology evolved with fluid flow inside the pipe that have options to control and manipulate [1-2]. The applications have purpose to use the fluid flow inside the pipe to connect to valves, channels for bio science, medical devices, chemical analysis, chemical synthesis, pumps, mixing, separation and sensor devices. The circuit for the fluid is different from pipe flow where the fluid inside the pipe are controlled using electrokinetic, electric field driven, printed circuit board (PCB), switched-mode power supply (smps) and electrical power supply [3]. The fluidic circuits have applications in soft robotics, lab on chip, organ on chip, industrial manufacturing devices, medical devices and toys [4]. The fabrication of fluid based circuits are challenge owing to the manufacturing of new design methods. The integration of fluid based circuits with microelectronics to form microfluidic devices are researched in detail for many years [5-7]. The devices are heavily applied in sensors and environment sensors [8]. They operate in reduced power consumption from the size factors. The reliability of the devices with water and electrolytes are studied in detail over the past decade [8]. The integration have evolved with 3D Integrated circuit (IC) chip technology, power based supplies from electronics, batteries and motors [9]. The sensors and devices with AR/VR, computer vision [10], AI based software integration, AI hardware computer components and chips [11] are new.
The combined software and hardware integration in the fluidic circuits with AI and computers are scope for the future work. The fluidic circuits are environment safe and energy efficient [12]. In this paper we fabricate the integrated fluidic circuit (IFC). The fabrication is different compared to existing methods. The liquid KCl electrolyte is considered in the flat container. The electrical wirings are used. The pressure transmitter is digital. The battery is input power supply. The electronic ON/OFF switch and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ON/ OFF switch are connected to electrical wirings. The electrical wirings are connected to battery and multimeter. The electrical wirings are connected to pressure transmitter. The readings are digitized. We fabricate digital integrated fluidic circuit for the first time. The surface pressure, forces, attraction relation with gas, liquid and solid contact surfaces are studied in detail for sensor applications [13,14]. Figure 1 shows the schematic of the pressure measurement of KCl inside the flat container. The integrated fluidic circuit can find applications in fluid displays (FD), google maps, soft robotics, fluidic computing, toys and precision manufacturing of objects. The integrated fluidic circuits are different from integrated electronic circuit chips. The difference is electronics are the motion of electrons inside the electrical wires. The electrical wires are cylindrical shape made of insulating materials. The electrical wire have another cylindrical thin film made of copper in typical [9].
The inside of the electrical wire have copper only or copper and air. The electrons flow inside the copper thin film resulting in the electrical conduction phenomenon. The transport of electrons are well studied. The formula for electron flow inside the copper, electron flow inside the copper and air are well studied. The end caps of the electrical wires having copper are connected to another controllers, valves and electrical wirings. The formula based on electrical connections, valves, controllers, wirings, electrical channels are available to sensor, pumping DC motor, electrical plugs, mobiles and many other applications. The devices are fabricated using precision manufacturing. The liquid and fluid in the integration circuit chips have liquid motion based electronics with wide applications [15- 19]. The humidity and environment sensors applications on the integrated digital fluidic circuit are the scope for the future work. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 discusses the experimental details. Section 3 provides the theory. The detailed governing equations are given in section 4. The discussion of the pressure of the electrolyte inside the flat container is presented in section 5. Finally, conclusions are presented in Section 6.
The flat containers are purchased from Omega glassware, India. ength of the flat container is 21 cm, width 12 cm and height are 4.5 cm. The KCl of concentration of 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre are purchased from Kesari Chemicals, India. The purchase volume are 0.5 litre for both the KCl of concentration of 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. The digital pressure transmitter are purchased from IPS Automation, India. The pressure transmitter has input power supply with DC voltage varying from 10.5 V to 42 V. The current can vary from 4 mA to 20 mA. The pressure are available from -100 kPa to 600 kPa in the sensor. The precision mass balance are purchased from Merck, Germany. The maximum mass to measure are 1200g. The precision of the mass are 0.01 g. The battery is purchased from Shah, India. The battery voltage is 12 V. The multimeters are purchased from Mercy electronics, India. The digital temperature sensor are purchased from Industry buying, India. The digital vernier caliper are also purchased from Industry buying, India.
We develop GUI to model the volume, surface potential inside the empty bottle, measurement cup and flat container, respectively. The model calculates the mass of KCl, concentration of KCl, mole of KCl, number of KCl inside the flat container, measurement cup and bottle respectively. Figure 2 shows the GUI. In this study, the surface potential are zero for container, cup and bottle, respectively.
Volume of KCl in the Package Bottle
The volume of the bottle having KCl is the volume of the cylinder having KCl given in Eq. (1).
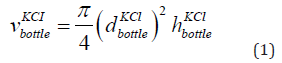
where
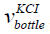 is the volume of the bottle having KCl,
is the volume of the bottle having KCl, 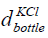 is the
diameter and
is the
diameter and 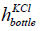 is the
is the
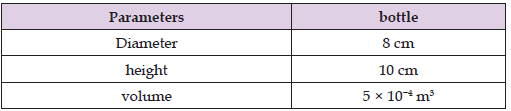
height of the bottle having KCl. The parameters are given in Table 1. The diameter is 8 cm and the height is 10 cm. The volume of the KCl in the bottle is 5 × 10−4 m3.
Table 1: Parameters of the bottle having KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively.
Mass of KCl in the Bottle
The mass of KCl in the bottle is given in Eq. (2).
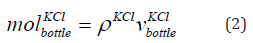
where 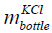 is the mass of the KCl in the bottle and
is the mass of the KCl in the bottle and 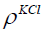 is the
density of the KCl. The parameters are given in Table 2. The mass of
KCl in the bottle is 0.52 kg.
is the
density of the KCl. The parameters are given in Table 2. The mass of
KCl in the bottle is 0.52 kg.
Mole of KCl in the Bottle
The mole of KCl in the bottle is given in Eq. (3).

where 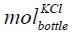 is the mole of KCl in the bottle,
is the mole of KCl in the bottle, 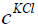 is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 1 mol/litre. This
is equal to concentration of KCl 1000 mM. That is 1 M KCl. The mole of
KCl in the bottle is 0.5 mol.
is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 1 mol/litre. This
is equal to concentration of KCl 1000 mM. That is 1 M KCl. The mole of
KCl in the bottle is 0.5 mol.
Number of KCl in the Bottle
The number of KCl in the bottle is given in Eq. (4).
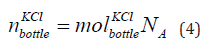
where 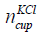 is the number of KCl in the bottle of concentration 1
mol/litre and NA is the Avogadro number. The number of KCl in the
bottle are 3 × 1023 elements for concentration of 1 mol/litre.
is the number of KCl in the bottle of concentration 1
mol/litre and NA is the Avogadro number. The number of KCl in the
bottle are 3 × 1023 elements for concentration of 1 mol/litre.
CAD Modeling of Bottle
The bottle height till 500 ml KCl solution is 10 cm. The height of the top frustum in the bottle is 5 cm. The diameter of the top frustum is 3 cm. The height of the neck in the bottle is 0.8 cm. The diameter of the neck is same as the diameter of the top frustum that is 3 cm. The measurements of the bottle are same for KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. We draw the bottle and the solution of KCl as cylinder in the bottle.
Volume of KCl in the Package Bottle
The volume of the bottle having KCl is the volume of the cylinder having KCl given in Eq. (5).
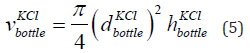
where
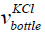 is the volume of the bottle having KCl,
is the volume of the bottle having KCl, 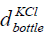 is the
diameter and
is the
diameter and 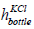 is the height of the bottle having KCl of concentration
0.01 mol/litre. The diameter is 8 cm and the height is 10 cm. The
volume of the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the bottle is 5 ×
10−4 m3.
is the height of the bottle having KCl of concentration
0.01 mol/litre. The diameter is 8 cm and the height is 10 cm. The
volume of the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the bottle is 5 ×
10−4 m3.
Mole of KCl in the Bottle
The mole of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the bottle is given in Eq. (6).
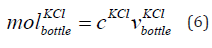
where 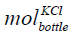 is the mole of KCl in the bottle, cKCl is the concentration
of KCl that is 0.01 mol/litre. This is equal to concentration
of KCl 10 mM. The mole of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the
bottle is 0.005 mol.
is the mole of KCl in the bottle, cKCl is the concentration
of KCl that is 0.01 mol/litre. This is equal to concentration
of KCl 10 mM. The mole of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the
bottle is 0.005 mol.
Number of KCl in the Bottle
The number of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the bottle is given in Eq. (7).
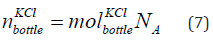
where 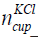 is the number of KCl in the bottle of concentration
0.01 mol/litre. The number of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in
the bottle are 3 × 1021 elements for concentration of 0.01 mol/litre
(Figures 3 & 4).
is the number of KCl in the bottle of concentration
0.01 mol/litre. The number of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in
the bottle are 3 × 1021 elements for concentration of 0.01 mol/litre
(Figures 3 & 4).
Here we measure the mass of KCl in the bottle using mass balance. Figure 5 shows the mass of the KCl in the bottle of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. Figure 5(a) shows the mass of the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the bottle is 570.51 grams. The mass of the bottle with the cap is 64.3 grams. The mass of the bottle without the cap is 52.7 grams. The mass of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre is 506.21 grams. In this study we understand the measured density from mass measurements and compare them with the provided specification details for density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre only. The mass of the KCl in the bottle for concentration 1 mol/litre is 588.37 grams. The mass of the bottle with the cap is 64.3 grams. Figure 5 (b) shows the mass of KCl in the bottle for concentration of 1 mol/litre. The mass of KCl for concentration of 1 mol/litre is 524.07 grams. The calculated density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/ litre from our experiments is given in Eq. (8).

where 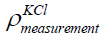 is the density of the KCl of concentration 1
mol/litre obtained from the indirect measurement of mass of KCl in
the bottle.
is the density of the KCl of concentration 1
mol/litre obtained from the indirect measurement of mass of KCl in
the bottle. 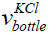 is the volume of the KCl in the bottle obtained earlier
in the discussion. The volume of the KCl in the bottle is 5× 10−4 m3.
The density of the KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is 1048 kg/m3. The
method is matching with the specification details of density of KCl of
concentration 1 mol/litre given as
is the volume of the KCl in the bottle obtained earlier
in the discussion. The volume of the KCl in the bottle is 5× 10−4 m3.
The density of the KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is 1048 kg/m3. The
method is matching with the specification details of density of KCl of
concentration 1 mol/litre given as 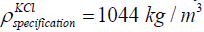 [20].
[20].
Volume of KCl in the Measurement Cup
The volume of the measurement cup having KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is given in Eq. (9).
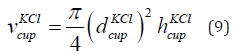
where 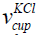 is the volume of the measurement cup having KCl,
is the volume of the measurement cup having KCl,
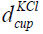 is the diameter and
is the diameter and 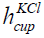 is the height of the cup having KCl.
The parameters are given in Table 3. The diameter is 69 mm and the
height is 67 mm. The volume of the KCl in the cup is 2.5 × 10−4 m3.
is the height of the cup having KCl.
The parameters are given in Table 3. The diameter is 69 mm and the
height is 67 mm. The volume of the KCl in the cup is 2.5 × 10−4 m3.
Mass of KCl in the Cup
The mass of KCl in the cup is given in Eq. (10).

where 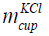 is the mass of the KCl in the cup and
is the mass of the KCl in the cup and 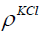 l is the
density of the KCl. The parameters are given in Table 4. The density
of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is 1044 kg/m3. The mass of KCl in
the cup is 0.26 kg.
l is the
density of the KCl. The parameters are given in Table 4. The density
of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is 1044 kg/m3. The mass of KCl in
the cup is 0.26 kg.
Mole of KCl in the Cup
The mole of KCl in the cup is given in Eq. (11).
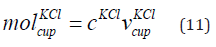
where 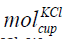 is the mole of KCl in the cup, cKCl is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 1 mol/litre. This is
equal to concentration of KCl 1000 mM. That is 1 M KCl. The mole of
KCl in the cup is 0.25 mol.
is the mole of KCl in the cup, cKCl is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 1 mol/litre. This is
equal to concentration of KCl 1000 mM. That is 1 M KCl. The mole of
KCl in the cup is 0.25 mol.
Number of KCl in the Cup
The number of KCl in the cup is given in Eq. (12).
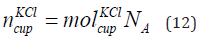
where
 is the number of KCl in the cup and NA is the Avogadro
number. The number of 𝑐𝑢𝑝 𝐴KCl in the cup are 1.5 × 1023 elements.
is the number of KCl in the cup and NA is the Avogadro
number. The number of 𝑐𝑢𝑝 𝐴KCl in the cup are 1.5 × 1023 elements.
CAD Modeling of Measurement cup
We draw the cup as cylinder. The KCl is another cylinder inside the cup.
Volume of KCl in the Measurement Cup
The volume of the measurement cup having KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre is given in Eq. (13).
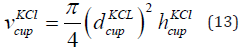
where  is the volume of the measurement cup having KCl,
is the volume of the measurement cup having KCl,
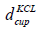 is the diameter and
is the diameter and 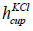 is the height of the cup having KCl. The
diameter is 69 mm and the height is 67 mm. The volume of the KCl in
the cup is 2.5 × 10−4 m3.
is the height of the cup having KCl. The
diameter is 69 mm and the height is 67 mm. The volume of the KCl in
the cup is 2.5 × 10−4 m3.
Mole of KCl in the Cup
The mole of KCl in the cup is given in Eq. (14).
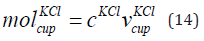
where
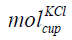 is the mole of KCl in the cup, cKCl is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 0.01 mol/litre. That
is 10 mM KCl. The mole of KCl of concentration
0.01 mol/litre in the cup is 0.0025 mol.
is the mole of KCl in the cup, cKCl is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 0.01 mol/litre. That
is 10 mM KCl. The mole of KCl of concentration
0.01 mol/litre in the cup is 0.0025 mol.
Number of KCl in the Cup
The number of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the cup is given in Eq. (15).
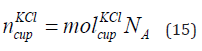
where 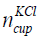 is the number of KCl in the cup and NA is the Avogadro
number. The number of KCl in the cup are 1.5 × 1021 elements.
Figure 6 shows the KCl in the measurement cup of concentration 0.01
mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. We use two cups to transfer
the bottle having KCl because the bottle having KCl has volume 500
ml and the cup having KCl has volume 250 ml. This is same for KCl of
concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre. The density of KCl for
concentration of 0.01 mol/litre in measurement is scope for future
work. Figure 7 shows the CAD model of the KCl filled in the measurement
cup.
is the number of KCl in the cup and NA is the Avogadro
number. The number of KCl in the cup are 1.5 × 1021 elements.
Figure 6 shows the KCl in the measurement cup of concentration 0.01
mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. We use two cups to transfer
the bottle having KCl because the bottle having KCl has volume 500
ml and the cup having KCl has volume 250 ml. This is same for KCl of
concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre. The density of KCl for
concentration of 0.01 mol/litre in measurement is scope for future
work. Figure 7 shows the CAD model of the KCl filled in the measurement
cup.
Here we measure the mass of KCl in the measurement cup. We consider two measurement cups to measure the mass of KCl that is available in the bottle. Figure 8 shows the mass of the KCl in the cup of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. Figure 8 (a) shows the mass of the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the cup is 279.57 grams. The mass of the cup is 32.1 grams. The mass of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre is 247.47 grams. In this study we understand the measured density from mass measurements and compare them with the provided specification details for density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre only. The mass of the KCl in the cup for concentration 1 mol/litre is 287.33 grams. The mass of the cup is 32.1 grams. Figure 8 (b) shows the mass of KCl in the cup. The mass of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is calculated as 255.23 grams. The calculated density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre from our experiments is given in Eq. (16).

where  is the density of the KCl of concentration 1
mol/litre obtained from the indirect measurement of mass of KCl in
the cup.
is the density of the KCl of concentration 1
mol/litre obtained from the indirect measurement of mass of KCl in
the cup. 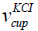 is the volume of the KCl in the cup obtained earlier in
the discussion. The volume of the KCl in the cup is 2.5 × 10−4 m3. The
density of the KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is 1021 kg/m3. The
method is matching with the specification details of density of KCl of
concentration 1 mol/litre given as
is the volume of the KCl in the cup obtained earlier in
the discussion. The volume of the KCl in the cup is 2.5 × 10−4 m3. The
density of the KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre is 1021 kg/m3. The
method is matching with the specification details of density of KCl of
concentration 1 mol/litre given as 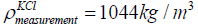 [20].
[20].
Volume of KCl in the Flat Container
We use two cups to transfer the KCl from the cup to the flat container. This is because the cup having KCl has volume 250 ml. The flat container has to be filled with KCl from the bottle having KCl that has volume 500 ml. Hence two cups are used. The flat container having KCl has volume 500 ml. This is same for KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre. The volume of the flat container having KCl is given in Eq. (17). The length of the flat container is 21 cm, width is 12 cm and height having KCl is 2 cm.
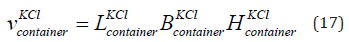
Where
 is the volume of the container having KCl,
is the volume of the container having KCl, 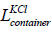 is the length,
is the length, 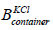 is the width and
is the width and  is the height of the container
having KCl. The parameters are given in Table 5. The volume of
the KCl in the flat container is 5 × 10−4 m3. We study concentration of
KCl is 1 mol/litre. The density is 1044 kg/m3.
is the height of the container
having KCl. The parameters are given in Table 5. The volume of
the KCl in the flat container is 5 × 10−4 m3. We study concentration of
KCl is 1 mol/litre. The density is 1044 kg/m3.
Mass of KCl in the Flat Container
The mass of KCl in the container is given in Eq. (18).
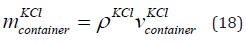
where  is the mass of the KCl in the container and
is the mass of the KCl in the container and 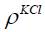 is the density of the KCl. The parameters are given in Table 6. The
mass of KCl in the container is 0.52 kg.
is the density of the KCl. The parameters are given in Table 6. The
mass of KCl in the container is 0.52 kg.
Mole of KCl in the Flat Container
The mole of KCl in the container is given in Eq. (19).
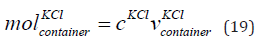
where 𝑚 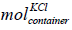 is the mole of KCl in the container, cKCl is
the concentration of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 1 mol/
litre. This is equal to concentration of KCl 1000 mM. That is 1 M KCl.
The mole of KCl in the container is 0.5 mol.
is the mole of KCl in the container, cKCl is
the concentration of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 1 mol/
litre. This is equal to concentration of KCl 1000 mM. That is 1 M KCl.
The mole of KCl in the container is 0.5 mol.
Number of KCl in the Container
The number of KCl in the container is given in Eq. (20).

where  is the number of KCl in the container and NA is the
Avogadro number. The number of KCl in the container are 3 × 1023
elements.
is the number of KCl in the container and NA is the
Avogadro number. The number of KCl in the container are 3 × 1023
elements.
CAD Modeling of Flat Container
We draw the flat container as cuboid. The top plane is open. The KCl solution is drawn as cuboid inside the flat container.
Volume of KCl in the Flat Container
The volume of the flat container having KCl is given in Eq. (21). The length of the flat container is 21 cm, width is 12 cm and height having KCl is 2 cm.
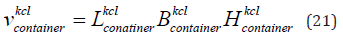
where
 is the volume of the container having KCl,
is the volume of the container having KCl,  is the length,
is the length,  is the width and
is the width and 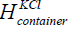 is the height of the
container having KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre. The volume of
the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the flat container is 5 × 10−4
m3.
is the height of the
container having KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre. The volume of
the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the flat container is 5 × 10−4
m3.
Mole of KCl in the Flat Container
The mole of KCl in the container is given in Eq. (22).
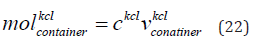
where  is the mole of KCl in the container,
CKCl is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 0.01 mol/litre.
The mole of KCl in the container is 0.005 mol.
is the mole of KCl in the container,
CKCl is the concentration
of KCl. We consider concentration of KCl is 0.01 mol/litre.
The mole of KCl in the container is 0.005 mol.
Number of KCl in the Container
The number of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the container is given in Eq. (23).
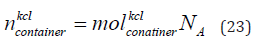
where  is the number of KCl in the container. The number
of KCl in the container are 3 × 1021 elements. Figure 9 shows the KCl
in the flat container of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre,
respectively. Figure 10 shows the CAD model of the KCl filled in the
flat container.
is the number of KCl in the container. The number
of KCl in the container are 3 × 1021 elements. Figure 9 shows the KCl
in the flat container of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre,
respectively. Figure 10 shows the CAD model of the KCl filled in the
flat container.
In this study we theoretically calculate the pressure of KCl in the flat container. Firstly we consider KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre. The hydrostatic pressure of KCl in the flat container is given by Eq. (24).
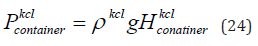
where  is the hydrostatic pressure and 𝑔 is the gravity. Here, the density
is the hydrostatic pressure and 𝑔 is the gravity. Here, the density 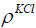 is given 1044 kg/m3. The length of the flat
container is 21 cm, width is 12 cm and height having KCl is 2 cm. The
hydrostatic pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre in the flat
container is 205 Pa.
is given 1044 kg/m3. The length of the flat
container is 21 cm, width is 12 cm and height having KCl is 2 cm. The
hydrostatic pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre in the flat
container is 205 Pa.
The hydrostatic pressure (P) distribution of KCl is given by the partial differential equation (PDE) (25).
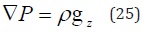
where gz is the gravity acting download in the z direction that is from the top surface to the bottom surface of the flat container filled with KCl. The simulations are performed for density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre.
Experiments of Pressure of KCl of Concentration 0.01 mol/ Litre and 1 mol/Litre in the Flat Container Here we measure the pressure of KCl in the container. Figure 11 shows the integrated fluidic circuit. The circuit has KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the container, pressure transmitter, electrical wirings, electronic ON/OFF switch, battery and multimeters. Figure 12 shows the integrated fluidic circuit. The circuit has KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre in the container. Figure 13 shows the pressure of the KCl in the container of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/ litre, respectively. Figure 13 shows the pressure of the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the container is varying between 100 Pa to 185 Pa. The readings are taken for 70 minutes. The average pressure of KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre in the container is 150 Pa. In this study we understand the measured density from pressure measurements and compare them with the provided specification details for density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre only. Figure 13 shows the pressure of the KCl in the container for concentration 1 mol/litre is varying from 100 Pa to 320 Pa. The readings are taken for 70 minutes. The average pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre in the container is 210 Pa. The calculated density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre from our pressure experiments are given in Eq. (26).

where 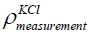 is the density of the KCl of concentration 1
mol/litre obtained from the indirect pressure method of KCl in the
container. The average pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre
in the container is 210 Pa
is the density of the KCl of concentration 1
mol/litre obtained from the indirect pressure method of KCl in the
container. The average pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre
in the container is 210 Pa  from the experiment are already
discussed. The height of the KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre in the
flat container is 2 cm as informed. The density of the KCl of concentration
1 mol/litre is 1071 kg/m3. The pressure method is matching
with the specification details of density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/
litre given as
from the experiment are already
discussed. The height of the KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre in the
flat container is 2 cm as informed. The density of the KCl of concentration
1 mol/litre is 1071 kg/m3. The pressure method is matching
with the specification details of density of KCl of concentration 1 mol/
litre given as 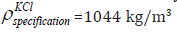 [20] Figure 14 shows the polyvinyl
chloride based ON/OFF switch with electrical wirings. Figure 15
shows the digital temperature sensor with the reading showing the
room temperature of 33.2 ◦C. Figure 16 shows the digital vernier caliper
to measure the length, width, height of the flat container. Similarly
to measure the diameter and height of the measurement cup. Also the
digital vernier calipers are used to measure the small diameter, large
diameter, height, frustum height and neck height of the bottle.
[20] Figure 14 shows the polyvinyl
chloride based ON/OFF switch with electrical wirings. Figure 15
shows the digital temperature sensor with the reading showing the
room temperature of 33.2 ◦C. Figure 16 shows the digital vernier caliper
to measure the length, width, height of the flat container. Similarly
to measure the diameter and height of the measurement cup. Also the
digital vernier calipers are used to measure the small diameter, large
diameter, height, frustum height and neck height of the bottle.
Simulation Details
Figure 17 shows the Ansys simulation result of pressure of KCl of concentration 1 mol/litre inside the flat container. The density of KCl for concentration of 1 mol/litre is 1044 kg/m3 and viscosity is 0.0011 Pa·s [20]. Figure 17 shows the pressure value shown in red is the bottom surface and the blue is the top surface of the container. The value is 200 Pa matches the experiments. The results are grid independent.
In conclusion we build integrated fluidic circuit. The fluidic circuit has components flat container, measurement cup, bottle, KCl solution, electrical wirings, electronic ON/OFF switch, polyvinyl chloride ON/ OFF switch, digital pressure transmitter, battery, multimeter and digital circuit measurements. We measure the pressure of the KCl of concentration 0.01 mol/litre and 1 mol/litre, respectively. We measure the mass of KCl of two concentrations separately using digital mass balance. We measure the temperature using digital temperature sensor. We measure the dimensions using digital vernier caliper. We measure the battery input voltage using multimeter. We measure the input power supply that includes the voltage and current for the digital pressure transmitter. The pressure readings of the KCl of two concentrations are matched with theory and simulations. We develop CAD model for the flat container, cup and bottle.
There is no funding for this work.
Rajiv Choudhary: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, writing – original draft Nandigana V. R. Vishal: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing – original draft, writing – review and editing. K. Srinivasa Reddy: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, software, supervision, visualization, writing – review and editing.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
The data from the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.


