Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Qianqian Zhang*
Received: July 29, 2025; Published: August 04, 2025
*Corresponding author: Qianqian Zhang, Graduate School of Education, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2025.62.009808
The application of prompt diagnosis technology (POC) in resource-poor areas faces the dual challenges of technology and human capital. From the perspective of economics of medical education, this paper analyzes the disconnection between industry and education in the promotion of POC technology and proposes that deepening the reform of medical-education synergy through school-enterprise co-establishment of industrial colleges and clinically oriented curriculum development can enhance the penetration rate of the technology. The practice of Chinese vocational colleges and universities shows that “dual-teacher” faculty construction, such as the rotation system of clinical teachers in Suihua University of Health Sciences, and job-embedded training, such as the “base teaching class” in Three Gorges Medical College, can effectively shorten the cycle of technology application.
The application of prompt diagnosis technology (POC) in resource-poor areas faces the dual challenges of technology and human capital. From the perspective of economics of medical education, this paper analyzes the disconnection between industry and education in the promotion of POC technology and proposes that deepening the reform of medical-education synergy through school-enterprise co-establishment of industrial colleges and clinically oriented curriculum development can enhance the penetration rate of the technology. The practice of Chinese vocational colleges and universities shows that “dual-teacher” faculty construction, such as the rotation system of clinical teachers in Suihua University of Health Sciences, and job-embedded training, such as the “base teaching class” in Three Gorges Medical College, can effectively shorten the cycle of technology application.
Table 1: Pathways of support for POC technology implementation in China’s medical school industry-teaching integration model.
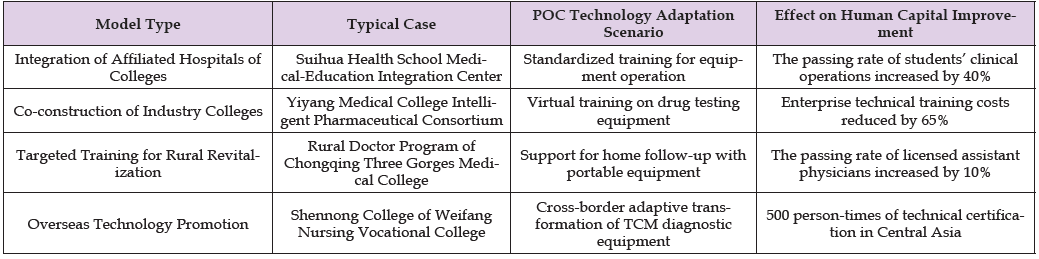
The promotion of tools such as CRISPR-SHERLOCK at the grassroots level is limited by the complexity of operation, whereas Suifang Nursing School, through the clinical apprenticeship point system and students’ 1-week affiliated hospital rotation per semester, enables imaging students to independently operate CT equipment prior to their internships, demonstrating that job-front training can break through the barriers of technological application. The cost of nanopore sequencing has been reduced to $1,000 per sample, but the research of Weifang Nursing Vocational College shows that there is a positive correlation between the utilization rate of the equipment and the clinical experience of teachers. Through the integrated platform of “TCM department-hospital-research base”, the school has transformed the research results of the five movements and six qi into diagnostic teaching modules, which has significantly increased the adoption rate of the technology.
The imbalance in the allocation of educational resources has exacerbated the technology gap. A survey of rural doctors in Chongqing shows that the idle rate of POC equipment reaches 57%, which is mainly due to the lack of continuing education. The university developed a “four-combination” model of government-university collaboration, online and offline, point-to-point coverage, and education and training articulation, and completed 12,000 trainings through catechism and resident mentorship, raising the utilization rate of the equipment to 89%. With regard to the integration of industry and education, although enterprise virtual situation training reduces training costs, fewer POC technology papers in the past five years have dealt with the evaluation of educational interventions (Table 2).
Promote dual-scenario immersion learning with VR simulation operation before class and guidance from enterprise mentors during class. The experience of the Three Gorges Medical College shows that this mode reduces the error rate of electrocardiograph operation by 65%. Developing technical gradient course packages, referring to the mind map of 234 courses of Suihua Health School, and designing POC training modules for nurses, village doctors and inspectors in a hierarchical manner to match the requirements for job skill certification. Establish cross-domain industry-teaching consortiums such as the Chengdu-Chongqing Medicine and Health Vocational Education Alliance and form a sustainable input mechanism through the sharing of equipment among institutions, enterprise donation quotas, and government subsidies to crack the resource fragmentation dilemma.
The realization of the universal value of POC technology needs to be premised on the reconstruction of the medical education ecosystem. The practice of Chinese vocational colleges and universities shows that the integration of the three chains of “education chain - technology chain - industry chain” can significantly reduce the cost of technology application through the model of “building production in the school and growing the school and production together” of Weifang Nursing Vocational College. Future research should focus on the quantitative relationship between vocational education investment and technology penetration rate and provide empirical support for resource optimization in economics.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This study was supported by the Major Project of Humanities and Social Sciences Base of the Ministry of Education, “Industry-Education Integration, Science- Education Integration and High-Quality Talent Cultivation in Chinese Universities” (22JJD80001).


