Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Junrong Xu and Bin Zhao*
Received: January 23, 2024; Published: January 31, 2025
*Corresponding author: Bin Zhao, School of Science, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2025.60.009452
With the rapid development of economy and technology, as well as the improvement of people’s quality of life
and the acceleration of their pace of life, the demand for cars is increasing day by day, which poses challenges to
their repair technology. The traditional maintenance methods are increasingly unable to meet the requirements
of car maintenance, so some new types of maintenance equipment have emerged, such as lifting machines that
lift cars. The emergence of these devices has made car maintenance faster and more efficient. For car maintenance,
a lift should not only be safe and reliable, but also easy to operate. Compared with other lifts, hydraulic
lifts have the advantages of compact structure, safety and reliability, easy operation, and small footprint However,
due to the inability of existing pure electric vehicle technology to completely solve problems such as short
range, long charging process, and large grid impact, its widespread promotion still faces difficulties. The use of
battery swapping technology to replace the power battery pack of electric vehicles has gradually gained attention
from automotive and power companies as a feasible solution to the above-mentioned problems. Analysis
has found that existing battery swapping technologies typically require the occupation of fixed land to establish
swapping stations, which incurs high land costs and cannot be implemented on a large scale; The distributed
battery swapping mode can effectively utilize urban underground parking lots for battery swapping, and can
effectively solve problems such as site construction costs.
The research on battery swapping technology under distributed battery swapping mode has good application
prospects. Therefore, based on the analysis of the application scenarios of electric vehicle battery swapping stations,
this article conducted a relevant analysis of the hydraulic device of hydraulic elevators, and analyzed the
force conditions of column lifting mechanisms for electric vehicle lifting.
Keywords: Hydraulic Cylinder; Battery Replacement Station; Column Lifting Mechanism
With the continuous development of the economy and the improvement of living standards, people’s demand for cars continues to rise. At the end of 2019, the number of civilian cars in China reached 260 million, with a year-on-year growth rate of 8.83%. However, with the improvement of residents’ automobile consumption ability, the exhaust emissions of fuel vehicles have caused a large amount of environmental pollution. Under the limited global oil reserves, the scarcity of oil will also limit the development of traditional fuel vehicles. As an important direction for the transformation and upgrading of the automotive industry, electric vehicles have received high attention from countries around the world. In recent years, they have developed rapidly and many countries have put the comprehensive implementation of electric vehicles on their agenda. Although electric vehicles are a major alternative to fuel vehicles, which can reduce their negative impact on the environment and dependence on petroleum energy, there are still several issues with their widespread promotion, including:
1) Limited energy density of power batteries and short driving range of vehicles;
2) The price of power batteries is expensive, and the cost of purchasing a car is high;
3) Slow battery charging speed;
4) The charging process has a significant impact on the power grid load [1,2]. In order to solve the bottleneck faced by the largescale promotion of electric vehicles on the basis of existing technology, the electric vehicle battery swapping operation model has emerged. In the electric vehicle battery swapping operation mode, the cost of the power battery is borne by the operator [3]. When the electric vehicle runs out of power, the vehicle owner enters the battery swapping station to replace the battery and pays for the battery replacement cost. At present, the battery swapping mode has been applied to a certain scale in countries such as Denmark, Israel, and Canada. At the same time, companies such as State Grid, Southern Power Grid, NIO, and BAIC New Energy have carried out corresponding demonstration constructions in China.
Explanation
The main function of hydraulic cylinders is to convert the pressure energy of hydraulic systems into mechanical energy in the form of linear reciprocating motion. It has a simple structure and reliable operation, and is widely used in various mechanical hydraulic systems [4]. As the actuator in the hydraulic system, the hydraulic cylinder is responsible for converting hydraulic energy into actual working pressure, thrust, and tension. The magnitude and speed of its output force can be precisely controlled through the control components of the hydraulic system. Specifically, hydraulic cylinders are widely used in engineering, such as various action hydraulic cylinders in construction machinery, to achieve various complex mechanical actions [5]. In agricultural machinery, hydraulic cylinders also play an important role, such as being used for lifting, lowering, flipping and other operations of agricultural tools. In addition, with the development of modern technology, the types and performance of hydraulic cylinders are constantly improving to meet the needs of different fields.
Analysis
The driving device set for the scissor lift mechanism is hydraulic drive, and in the analysis process, it should be calculated based on the minimum length, minimum stroke, and maximum load of the hydraulic cylinder [6]. The relevant data of the hydraulic actuator components will be calculated in the following text to make choices for each component Hydraulic actuators are mainly composed of hydraulic cylinders responsible for achieving linear motion and hydraulic pumps responsible for achieving rotary motion [7]. According to the scope of application of both, the following table can be listed (Table 1).
The Model
In the Figure, the different physical meanings of different symbols are as follows. Fw represents the external load on the piston rod, Fm represents the sealing resistance between the piston and the cylinder arm, as well as between the piston rod and the guide sleeve, Fg represents the working load, Fa represents the inertial load, and Ff represents the load generated between the piston and the guide rail. The working load is the maximum load of the piston rod, usually determined by factors such as the length of the piston rod and the weight of the load (Figure 1). It constantly changes in different scenarios and needs to be determined according to the actual situation [8]. The piston of hydraulic cylinders with direct acting installation usually has guide rails to fix its operation and prevent it from deviating from direction. When the friction load Ff of the guide rail is very small compared to the total load, this term can be ignored. Inertial load
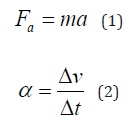
Among them, Δv refers to the change in speed, Where Δt refers to the starting or braking time of the machine. For general mechanical Δt = 0.1 ~ 0.5s , the small value is taken for low-speed moving parts under mild load, and the large value is taken for high-speed parts under heavy load [9]. Walking machinery generally takes 0.5~1.5 seconds. In addition to external loads, there is also a sealing resistance Fm between the seals of the piston and cylinder arm, as well as between the piston rod and the guide sleeve (Table 2). Based on empirical values, the general formula for estimating the sealing resistance is
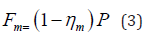
The magnitude of system pressure is an important data that needs to be followed when selecting hydraulic cylinders, which is mainly determined by the type of equipment and the size of the load it is subjected to, while also considering the actual situation such as the assembly space of the executing components. The working pressure is usually related to the size of the actuator, which also affects the accuracy of the pump cylinder valve components [10]. The selection of system pressure can refer to the following Table . When the design object is used to lift batteries, it belongs to the category of small construction machinery in terms of mechanism type, with a working pressure level of 10-18Mpa.When the working pressure of the system is greater than 14Mpa, the ratio of the piston rod to the inner diameter of the hydraulic cylinder is 0.7, and the calculation formula for the diameter of the hydraulic cylinder should be as follows.
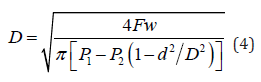
After determining the calculated diameter, round it according to the standard value of the hydraulic cylinder bore to comply with national standards [11]. In terms of selecting hydraulic pumps and motors, it is usually necessary to determine them based on the maximum working pressure of the hydraulic pump, and the determination principle is as follows:
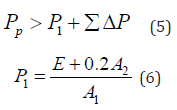
ΣΔP refers to the pipeline loss from the outlet of the hydraulic pump to the inlet of the hydraulic cylinder, and its empirical value data is as follows. The minimum overflow rate refers to the situation in a water pump system where, when the flow rate falls below a certain set value, the system automatically activates the overflow device to maintain a certain flow rate [12]. This minimum flow rate value is known as the minimum overflow rate. The setting of minimum over flow volume is crucial for the stable operation of the system and the protection of equipment. Definition and function of minimum overflow volume [13]. The minimum overflow rate is an important parameter for the water pump system during low flow operation. When the system flow rate is lower than this set value, the overflow device will automatically open to ensure that the system will not be damaged due to low flow rate (Table 3). This can protect the water pump and other related equipment from malfunctions caused by dry running or cavitation. The minimum overflow volume is generally taken as 0.5×10- 4m3/s. After determining the above parameters, a hydraulic pump can usually be selected and the driving power of the hydraulic pump can be determined. The calculation formula is as follows.
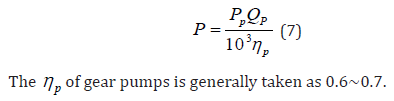
Hydraulic cylinders have important application significance in electric vehicle battery swap·ping platforms. In the mechanical operation of the battery swapping platform, hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role. They ensure the smooth progress of the battery swapping process by providing stable output force and self-locking function. For example, hydraulic cylinders can be used to operate the lifting mechanism of the battery swapping platform, achieve height adjustment of the vehicle, and facilitate battery replacement. In addition, hydraulic cylinders can be used for battery disassembly and installation during the process of replacing electric vehicles. By precisely controlling the movement of the hydraulic cylinder, smooth movement and accurate docking of the battery module can be achieved, ensuring efficient and safe battery replacement. The application of hydraulic cylinders in terms of platform stability and safety can also improve the stability and safety of the battery swapping platform. By adjusting the pressure and flow rate of the hydraulic system, the stability of the battery swapping platform during operation can be ensured, avoiding faults or accidents caused by external forces.
In this article, the selection of relevant parameters for hydraulic cylinders is mainly analyzed, and how to determine different types of pumps under different load conditions is discussed. According to the schematic diagram of the hydraulic system, the external load, sealing resistance, working load, inertial load and other data on the piston in the oil cylinder were explained and how to determine these parameters were explained. From the above, it can be seen that when selecting a hydraulic system, we should consider factors such as load and hydraulic cylinder formation. In addition, attention should be paid to the different roles of different types of pumps in different application scenarios..


