Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Valeria Brichetti1, Tamara Rubilar2,3*, Julieta Tejada1, Priscila Montecino1, Augusto Crespi-Abril2,3, Marisa Avaro2, Gabriela De Larrañaga, Clara Volonteri3, María Rosa Nuñez5, Javier Iriarte-Vasquez5, Mariana Jajati5, Martín Sivori5, Carlos Alberto Mangone6 and Fernando Saldarini1
Received: October 07, 2024; Published: October 22, 2024
*Corresponding author: Tamara Rubilar, Instituto Patagónico del Mar (IPaM), Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y de la Salud (FCNyCS), Universidad Nacional de la Patagonia San Juan Bosco (UNP), Bv. Almte Brown 3051, U9120 Puerto Madryn, Chubut, Argentina
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2024.59.009252
Introduction: The global impact of COVID-19 has resulted in a long COVID syndrome, which is defined by persistent symptoms and a significant decline in patients’ quality of life. To address this challenge, we conducted a multicenter, double-blind, randomized study to assess the effects of Echinochrome A, the active principle from sea urchin found in the dietary supplement Echa Marine®, on health-related quality of life and inflammatory biomarkers in 50 long-term COVID patients. Baseline characteristics were similar between groups.
Methods: Adult men and non-pregnant women aged 18 to 60 diagnosed with long COVID were randomly assigned to the intervention or control groups. For three months, patients were given daily doses of EchA Marine®, a dietary supplement made from sea urchin eggs, or a matching placebo. The effects of EchA Marine® were assessed using the EuroQol 5-Dimension (EQ-5D) questionnaire and serum parameter measurements.
Discussion: Consumers of EchA Marine®exhibited significant reductions in pain, improved mobility, enhanced overall quality of life, and improved inflammation biomarkers. These findings suggest that Echinochrome A, due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, effectively alleviates long COVID symptoms, particularly pain and mobility. The results underscore the potential of EchA Marine® as a safe and natural remedy for long COVID patients, warranting further research with larger cohorts to consolidate its efficacy.
Keywords: COVID-19; Spinochromes; Antioxidants; Oxidative Stress; Sequelae; Pain; Cytokines
Abbreviations: EQ-5D-3L: EuroQol 5 Dimensions 3 Levels; VAS: Visual Analog Scale; TTO: Time Trade-Off; BMI: Body Mass Index
The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been profound, affecting the health of millions worldwide. The aftermath of SARSCoV- 2 infection is characterized by persistent symptoms lasting weeks or even longer, leading to what is commonly known as long COVID or COVID sequelae [1-3]. Current literature has not settled on a definitive term for this syndrome, also referred to as ‘post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection’ (PASC) and ‘post-acute COVID syndrome’ (PACS) [2]. While the clinical description of long COVID is still evolving, it is often characterized by a range of symptoms persisting beyond 12 weeks from the initial infection or diagnosis, which cannot be explained by alternative diagnoses [3-6]. Common symptoms include fatigue, difficulty breathing, headaches, loss of smell and taste, brain fog, and muscle pain [4-7]. Long COVID syndrome is a multi-organ, multi-system disease that is still poorly understood, creating an unmet need in medical care and patient health [2,6-8]. Some indications of the underlying mechanisms include oxidative stress and glutathione depletion [9], cellular inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction [9], the presence of microclots [10,11] or diverse auto-antibody [12,13], persistent SARS-CoV-2 reservoirs and/or Epstein- Barr [14- 18] virus reactivation, and immune perturbation [19].
Individuals suffering from long COVID often feel ignored and are eager for research findings to be translated into clinical trials. According to ClinicalTrials.gov, there are 581 clinical trials investigating interventions for long COVID syndrome, with only four having reported results as of May 2024. Among these trials, 82 are interventional, and 31 involve the use of nutraceuticals, vitamins, or probiotics as interventions. Various approaches for drug or nutraceutical interventions include modulation of immunity or inflammation, SARS-CoV-2 protection, gut microbiota modulation, and improvements in mitochondrial function, symptom relief, cognitive function, and pain management [20]. Individuals with long COVID experience a significant decrease in their quality of life, making them particularly vulnerable to the syndrome’s various negative effects [2,7,8,20-23]. Efforts have been made to understand the impact of long COVID on patients’ quality of life, as health-related quality of life assessments are essential for understanding the total impact of COVID-19 and guiding clinical and policy decisions. One commonly used tool to measure health-related quality of life is the EuroQol 5-Dimension (EQ-5D) questionnaire, which assesses five dimensions of health: mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression.
The EuroQol is widely used in clinical and economic studies due to its brevity and simplicity, allowing for comparison of results across different diseases and treatments [24]. Additionally, it includes a visual analog scale (VAS) that measures overall health perception. Based on these attributes, several studies have implemented the EuroQol questionnaire to evaluate the health-related quality of life in patients with long COVID [22,25-27]. Overall, the EuroQol has proven to be a valuable tool for assessing quality of life in a wide range of medical conditions and appears to be particularly useful for assessing the quality of life in patients with long COVID-19 [22,25-29]. With specific reference to long COVID, the EuroQol has been able to detect the decrease in health-related quality of life and has been able to demonstrate that long COVID involves a significantly higher disability rate than that which is seen in the general population [21,30-32].
Echinochrome A is a 1,4-naphthoquinone polyhydroxylated pigment derived from sea urchin shells, spines, gonads, and eggs, with over 40 years of research and more than 90 scientific publications examining its physiological, pharmacological, and clinical effects [33]. This compound has demonstrated potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, the ability to modulate interleukins, increase glutathione production [34], and improve mitochondrial function [35]. Echinochrome A is the active molecule in the clinically approved drugs Histochrome®, used to treat myocardial infarction, and Gistochrome ®, used to treat glaucoma [36]. Therefore, we conducted a double-blind, multicenter randomized trial to assess the supplementation of patients with EchA Marine®, a commercial dietary supplement based on sea urchin eggs rich in Echinochrome A, evaluating its impact on health-related quality of life and inflammatory biomarkers.
Population Data
A total of 50 long COVID patients were recruited for this multicenter, double-blind, randomized study from September 2021 to December 2022. Twenty-two patients received a placebo, twenty-four received treatment with EchA Marine®, and four patients did not complete the protocol. Both the placebo and treatment groups had similar distributions of age, sex, and BMI (Table 1).
Note: BMI: body mass index.
Quality of Life
The multivariate result was not significant for treatment at the start (Basal) of the trial (Pillai’s Trace = 0.22, F = 1.552, df = (7), p = 0.180), indicating no statistical differences in the response of the EuroQol 5-D 3L Questionnaire between placebo and Echa Marine groups (Table 2). All patients reported a decrease in quality of life in some of the five dimensions, with values of 2 and 3 being the most frequent (Figure 1). Three months of treatment with the dietary supplement resulted in a significant decrease in the values of two of the five EuroQol dimensions (Figure 1, Table 2). The multivariate results were significant for treatment at the end (Final) of the trial (Pillai’s Trace = 0.323, F = 2.205, df = (8), p = 0.048). The univariate F tests showed there was a significant difference between placebo and Echa Marine values for mobility (F = 6.738, df = (1), p = 0.013), pain and discomfort (F = 8.863, df = (1), p = 0.005), VAS (F = 5.632, df = (1), p =0.022) and TTO values (F = 9.746, df = (1), p =0.003). The most significant effect was observed in the reduction of pain and discomfort, where the placebo had no effect. In fact, patients who consumed the dietary supplement did not have values of 3 in any dimension at the end of the treatment, whereas patients in the placebo group still had values of 3, indicating a positive resolution of symptoms when consuming EchA Marine®. TTO and VAS also improved after treatment (Figure 2), indicating an improvement in overall quality of life after treatment.
Table 2: MANOVA results summary of the EuroQol 5D-3L. Factors: Treatment (Echa Marine vs Placebo), Time (Basal vs Final).
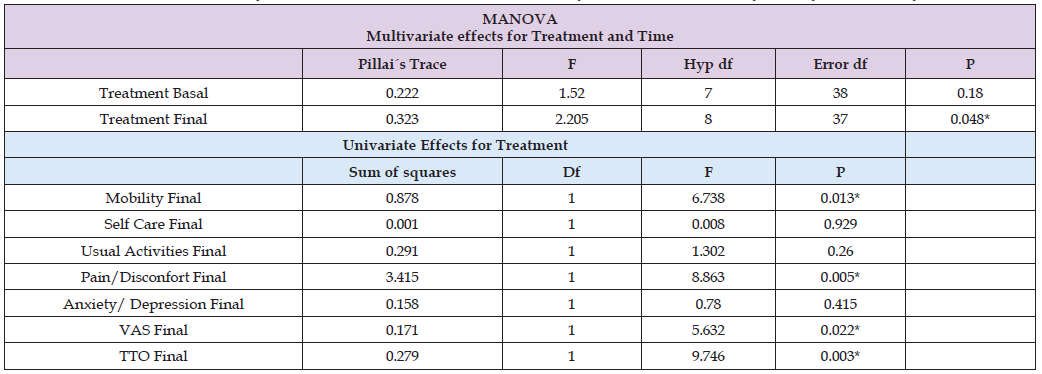
Note: VAS: visual analog scale. TTO: time trade-off. * Significative differences at 5%.
Serum Cytokines Biomarkers
There were no significant differences between groups in terms of any cytokine values at the start (Basal) of the trial (Table 3). Three months of treatment with the dietary supplement, however, resulted in a significant decrease in IL-2 mean values (Placebo mean: 90.03 pg/ml ± 14.99; Echa Marine® mean: 84 pg/ml ± 11.20) and a significant increase in IL-10 mean values (Placebo mean: 12.43 pg/ml ± 3.14; Echa Marine® mean: 15.48 pg/ml ± 4.60). The values of IL-6 and TNF-α, on the other hand, did not differ significantly (Figure 3, Table 3).
Note: IL-6: interleukin type 6. IL-10: interleukin type 10. TNF-𝛂𝛂: tumoral necrosis factor alpha type. IL-2: interleukin type 2. * Significative differences at 5%.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant number of cases of long COVID syndrome, which can persist for months and substantially impact patients’ quality of life [2,3,7,8,23]. Treatment of long COVID can be challenging, and existing options have had limited success [7,37]. The intervention in this study demonstrated that the dietary supplement EchA Marine® can significantly enhance the quality of life of these patients, particularly as regards pain and discomfort, notably improving their quality of life and ability to have better mobility. Although values were not significant in other dimensions, it can be observed that the group of patients who consumed the dietary supplement did not have values of 3 at the end of the study, while patients with placebo still had these values. This suggests that the supplement improved all dimensions studied, as evidenced by TTO and VAS values, and that continued use of the supplement may reduce values in other dimensions. Considering that, despite the small sample size, the results were statistically significant and can be seen to be robust, offering promising implications for the treatment of long COVID patients. Furthermore, this suggests that with a larger number of patients, the results could be even more solid and promising.
This indicates that EchA Marine® is an effective and natural treatment option for improving the quality of life of long COVID patients. These findings are especially encouraging in light of the supplement’s safety and natural origins, as well as the real need in patients and the limited options with results thus far. Importantly, the prolonged consumption of the supplement may further improve values in other dimensions. The mechanism underlying these improvements may be linked to the nature of Echinochrome A, the active ingredient in the sea urchin eggs in the dietary supplement, and its two main actions in our bodies: antioxidant and antiinflammatory. The most significant effect of this molecule at the cellular level is its ability to improve cellular function. This is a small molecule of 260 kDa that enters the cell easily in its salt form and performs a dual function: it inhibits free radicals, balancing oxidative stress, and generates large amounts of hydrogen peroxide, mimicking the SOD enzyme and activating glutathione metabolism, generating energy through mitochondrial activation and increased mass, as well as cellular oxygenation [33,38-41]. Even though we did not test ROS in plasma, there is a lot of evidence to support this benefit in relation to Echinochrome A consumption.
This molecule has also been proposed to alleviate the Cytokine Storm Syndrome39, since there is evidence that it is able to inhibit the synthesis of pro-inflammatory interleukins such as IL-1B, IL-6, and IL-8, as well as reduce pro-inflammatory factors such as TNFα and INFγ, resulting in reduced cellular inflammation and modulation of the immune response in humans [36,42,43] and increase the baseline secretion level of the anti-inflammatory interleukin IL-10 37,44. Our findings showed that after three months of EchA Marine® treatment, patients with long COVID have lower levels of pro-inflammatory interleukins like IL-2 and higher levels of anti-inflammatory interleukins like IL-10, indicating an improvement in inflammation biomarkers. All the results presented in this work support the working hypothesis that Echinochrome A can effectively improve cellular function and, consequently, organ function, thereby contributing to improving the quality of life of long COVID patients. With an ever-evolving disease like COVID-19, the identification of effective treatments for long COVID is a priority, and compounds like Echinochrome A offer a promising alternative to existing treatments.
Our findings indicate that a dietary supplement based on sea urchin egg extract rich in Echinochrome A is an effective treatment option for long COVID patients, and its efficacy could be strengthened with more research and larger sample sizes. EchA Marine® has the potential to make a significant impact on the fight against the pandemic and improve the lives of those affected by long COVID by providing a safe and natural solution. Because the medical and scientific communities are dealing with a multiorgan, multisystem disease for which there is currently no treatment, the findings of this study are critical.
Study Design
The study is a prospective, randomized, double-blind, multi-hospital clinical trial with intervention. The Ethical Committees of the three participating Hospitals approved and authorized the study, Hospital General de Agudos Donación Francisco Santojanni (Registration code 5832), Hospital de Infecciosas Francisco Javier Muñiz (Registration code 5240) and Hospital General de Agudos José María Ramos Mejía (Registration code 5196). All detailed information regarding this medical trial can be found at Trial Registry: www.clinicaltrials. gov; Identifier: NCT05531019 Date: 07/09/2022.
Inclusion Criteria
Positive diagnosis of COVID-19 in at least the last 12 weeks; diagnosis of long COVID; adult men or non-pregnant adult women between the ages of 18 and 60.
Exclusion Criteria
Patients who did not want to give their informed consent or those who, in the opinion of the doctor, evidenced some form of an advanced organic dysfunction that would not make participation appropriate.
Participants
We carefully and prospectively selected 50 patients of both sexes, between 18 and 60 years, with the long COVID syndrome, who came to our center (Hospital Donación Santojanni y Hospital de Agudos Ramos Mejía, City of Buenos Aires, Argentina) between September 2021 and October 2022. Four of them did not finish the protocol.
Treatment
Patients in the treatment group received two doses per day of 3 ml each for 90 days of the dietary supplement EchA Marine® with a concentration of 0.025% of Echinochrome A, obtained from sea urchin egg extraction and purification, according to Vasileva45. HPLC and spectrophotometry were used to assess the purity and concentration of the formulation, which was compared to the Russian standard of Echinochrome A used to produce Thymarin (https://tifarm. su/en#rec166058765). Patients consumed 1.5 mg of Echinochrome A per day. The placebo group received an equivalent solution without Echinochrome A.
Outcome Variables
The primary outcome variable was the improvement in patients’ quality of life, analyzed on the basis of its 5 dimensions and 3 levels and the levels of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory biomarkers. The safety and efficacy of the product were also evaluated. The study compared the efficacy of the dietary supplement Echinochrome A with a placebo in patients with long COVID symptoms.
Health-Related Quality of Life (EQ-5D-3L)
Patients completed the EuroQol questionnaire in the hospital at which they were recruited during an interview with a physician belonging to the study team. These interviews were held at the beginning and end of the study. The questionnaire was administered in paper format. The data was subsequently uploaded to the OcusMed telemedicine platform (Ocus Cloud) to make it available for statistical analysis. The EuroQol EQ-5D-3L questionnaire was used to assess health-related quality of life and consisted of two sections: a visual analog scale (VAS) and a descriptive system covering five dimensions (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/ depression) [44]. Each dimension is evaluated on a three-level scale, allowing patients to be classified into 243 different health states. The scores of the dimensions have different meanings, with 3 representing the least positive state and 1 the best [45]. The values obtained for Argentina in the study by Augustovski [46] were applied to assign quality of life scores and used time trade-off (TTO) and contingent valuation with regression analysis (VAR) techniques. The EuroQol dimensions were measured, and the TTO and VAS techniques were used to evaluate patient quality of life before and after treatment [47,48].
Interview Description
EuroQol surveys were undertaken face-to-face at the start of the study and, again, after three months. Day 1 is the day of the first intake of EchA Marine®. The objective and design of the study were carefully explained, and a brochure with information regarding the clinical trial and the nutraceuticals was provided to the patient. It was mandatory that the patient formally confirm their acceptance of the express informed consent by signing the informed consent.
Serum Cytokines Measurements
To analyze the inflammation state of the body, pro-inflammatory biomarkers such as Tumoral Necrosis factor-α, interleukins type 2 and 6, and anti-inflammatory interleukin type 10 were measured by ELISA technique from patients’ serum samples. The measurements were performed at basal and final conditions. The analyses were performed by using commercial kits (ThermoFisher Scientific, Bender MedSystem GMbH/Campus Vienna Biocenter 2/1030 Vienna, Austria) and following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the controls, calibrators, white sample, and patient´s sample were analyzed using a 96-well plate. Each well was washed with a washing buffer and then filled with 50 uL of assay buffer and 100 uL of each calibrator/sample/etc, 50 uL of Biotin-Conjugate was added, and the plate was incubated for 2 h at room temperature. Streptavidin-HRP and TMB-Substrate were used to reveal the plate by reading absorbance at 450 nm.
Sample Size
In this analysis, we assume a success rate that is 20% (0.20) higher in the treatment group compared to the placebo group, warranting the use of a one-tailed test to assess significance. The significance level is set at 5% (α=0.05), and the statistical power at 90% (1-β=0.90). To consider the success rate in both the treatment and placebo groups, it is assumed that the improvement rate with placebo is 10% (p1=0.1), and with the treatment is 30% (p2=0.3). Thus, a total of 50 patients per group will be included.
Randomization
Patients were randomly assigned to each group (placebo and treatment) following a double-blind pattern. The R software was used to perform permuted block randomization with a sequential mixed block size of 6. Sequentially numbered, identical containers were administered serially to each participant. Randomization was overseen by a statistics specialist who was a member of the scientific team and was specifically designated for this purpose. This individual did not participate in any patient-related activities. This individual coordinated the delivery of the nutraceutical product to the patients. The randomization results were blinded for the remainder of the research team, the medical doctors who recruited the patients, and for the patients. The product and placebo were optically indistinguishable.
Data Analysis
Data was downloaded from the OcusMed platform into Excel spreadsheets and then analyzed using the SPSS statistical software version 25. Accounting for the lack of adherence, the Per Protocol Analysis (PP) was used. It means that only the complete data sets were included in the analysis. Quality of life scores were calculated for each dimension of EuroQol and for the VAS scale. A multivariate analysis of variance was used to compare quality of life scores between patients in the treatment group and the placebo group. Two-way analysis of variance was used to compare Interleukin values between the basal and final conditions of each group. A p-value <0.05 was red statistically significant in all statistical tests.
Demographic and Clinical Information
Patients also provided sociodemographic information, such as sex, age, weight, and height.
Informed Consent
Patients provided their informed consent prior to initiating any study procedures. Study duration: The study was conducted for a total of 90 days.
Ethical Considerations
The researchers adhere to national and international bioethical standards, including ANMAT 5330/97 disposition, the Nuremberg Code, the Helsinki Declaration (2008 version and its amendments), the Universal Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights (UNESCO, 2005), the International Declaration on Human Genetic Data (UNESCO, 2003), the Universal Declaration on Bioethics and Human Rights, and the Guide for Human Health Research (GISH), resolution 1480/2011 MSN. Approval for this study has been obtained from the Ethics Committees of Santojanni, Ramos Mejia, and Muñiz hospitals.
Confidentiality in Argentina
Personal information is protected by Law No. 25,326 on Personal Data Protection, ensuring the comprehensive safeguarding of data in both public and private files. Patient rights are further addressed by Law No. 26,529, effective since February 2010, regulating relationships between patients, doctors, and health institutions.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the CONICET institutional repository. [https://ri.conicet. gov.ar/handle/11336/199122].
This work was funded by the grant “PICTO Sequelas COVID-19 00009” from the National Agency for the Promotion of Research, Technological Development, and Innovation. EchA Marine® supplements for the complete clinical trial were donated by Erisea S.A.
Dr Rubilar is co-founder of StartUp Erisea S.A. which produced and provided the Dietary Supplement for the Clinical Trial. Dr Volonteri is an employee of StartUp EriSea S.A. They had no role in volunteers selection, conduction of the trial and collection of data sets. The rest of the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.


