Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Mehmet Rami Helvaci1*, Mutlu Cihan Daglioglu2, Hulya Halici3, Cigdem Sen4, Alper Sevinc1, Celaletdin Camci1, Abdulrazak Abyad5 and Lesley Pocock6
Received: June 21, 2024; Published: June 27, 2024
*Corresponding author: Mehmet Rami Helvaci, Specialist of Internal Medicine, MD, 07400, ALANYA, Turkey
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2024.57.008976
Background: The hardened red blood cells-induced capillary endothelial damage initiates at birth and terminates with leg ulcers-like atherosclerotic endpoints even at childhood in the sickle cell diseases (SCD).
Methods: All cases with the SCD were included.
Results: We studied 222 males and 212 females with similar mean ages (30.8 vs 30.3 years, p>0.05, respectively). Disseminated teeth losses (5.4% vs 1.4%, p<0.001), ileus (7.2% vs 1.4%, p<0.001), cirrhosis (8.1% vs 1.8%, p<0.001), leg ulcers (19.8% vs 7.0%, p<0.001), digital clubbing (14.8% vs 6.6%, p<0.001), coronary heart disease (18.0% vs 13.2%, p<0.05), chronic renal disease (9.9% vs 6.1%, p<0.05), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (25.2% vs 7.0%, p<0.001), and stroke-like atherosclerotic consequences (12.1% vs 7.5%, p<0.05) were all higher in males.
Conclusion: Infection, medical or surgical emergency, or emotional stress-induced increased basal metabolic rate aggravates the sickling and secondary capillary endothelial inflammation and edema, and terminates with disseminated tissue hypoxia, accelerated atherosclerosis, and multiorgan failures. Although the fibrotic vascular stenoses are irreversible in the leg ulcers, the acute capillary endothelial inflammation and edema can be returned to some extent with aspirin and hydroxyurea. Aspirin plus low-dose warfarin may even increase the legs’ blood supply by preventing recurrent ischemiaes in microcirculation. Thus, anti-inflammatory dose of aspirin plus low-dose warfarin in addition to hydroxyurea may be the optimal treatment regimen of leg ulcers in the SCD at the moment.
Keywords: Sickle Cell Diseases; Capillary Endothelial Inflammation; Capillary Endothelial Edema; Leg Ulcers; Anti-Inflammatory Dose of Aspirin; Low-Dose Warfarin; Hydroxyurea
Abbreviations: BP: Blood Pressure; HT: Hypertension; DM: Diabetes Mellitus; COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease; CHD: Coronary Heart Disease; CRD: Chronic Renal Disease; PAD: Peripheric Artery Disease; SCD: Sickle Cell Diseases; TM: Thalassemia Minors; RBC: Red Blood Cells; HPLC: High Performance Liquid Chromatography; DVT: Deep Venous Thrombosis; MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging; SCA: Sickle Cell Anemia; ACS: Acute Chest Syndrome; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; CIMT: Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness; AF: Atrial Fibrillation; INR: International Normalized Ratio; CVT: Cerebral Venous Thrombosis; VTE: Venous Thrombotic Events; CIMT: Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness
Chronic endothelial damage may be the major cause of aging and death by causing end-organ failures in human being [1]. A much higher Blood Pressure (BP) of the afferent vasculature may be the major accelerating factor by causing recurrent injuries on vascular endothelial cells. Probably, whole afferent vasculature including capillaries are mainly involved in the process. Thus, the term Ven sclerosis is not as famous as atherosclerosis in the literature. Due to the chronic endothelial damage, inflammation, edema, and fibrosis, vascular walls thicken, their lumens narrow, and they lose their elastic natures, those eventually reduce blood supply to the terminal organs, and increase systolic and decrease diastolic BP further. Some of the wellknown accelerating factors of the inflammatory process are physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, animal-rich diet, smoking, alcohol, overweight, chronic inflammations, prolonged infections, and cancers for the development of terminal consequences including obesity, Hypertension (HT), Diabetes Mellitus (DM), cirrhosis, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), Chronic Renal Disease (CRD), stroke, Peripheric Artery Disease (PAD), mesenteric ischemia, osteoporosis, dementia, early aging, and premature death [2,3]. Although early withdrawal of the accelerating factors can delay terminal consequences, after development of obesity, HT, DM, cirrhosis, COPD, CRD, CHD, stroke, PAD, mesenteric ischemia, osteoporosis, and dementia-like end-organ insufficiencies and aging, the endothelial changes cannot be reversed due to their fibrotic natures, completely.
The accelerating factors and terminal consequences of the vascular process are researched under the titles of metabolic syndrome, aging syndrome, and accelerated endothelial damage syndrome in the literature [4-6]. On the other hand, Sickle Cell Diseases (SCD) are chronic inflammatory and highly destructive processes on vascular endothelium, initiated at birth and terminated with an advanced atherosclerosis- induced end-organ insufficiencies in much earlier ages of life [7,8]. Hemoglobin S causes loss of elastic and biconcave disc shaped structures of Red Blood Cells (RBC). Probably loss of elasticity instead of shape is the major problem because sickling is rare in peripheric blood samples of the cases with associated Thalassemia Minors (TM), and human survival is not affected in hereditary spherocytosis or elliptocytosis. Loss of elasticity is present during whole lifespan, but exaggerated with inflammations, infections, and additional stresses of the body. The hardened RBC-induced chronic endothelial damage, inflammation, edema, and fibrosis terminate with tissue hypoxia all over the body [9].
As a difference from other causes of chronic endothelial damage, SCD keeps vascular endothelium particularly at the capillary level [10,11], since the capillary system is the main distributor of the hardened RBC into the tissues. The hardened RBC-induced chronic endothelial damage builds up an advanced atherosclerosis in much earlier ages of life. Vascular narrowing’s and occlusions-induced tissue ischemia and end-organ insufficiencies are the final consequences, so the mean life expectancy is decreased by 25 to 30 years for both genders in the SCD [8].
The study was performed in the Medical Faculty of the Mustafa Kemal University between March 2007 and June 2016. All patients with the SCD were included. The SCD was diagnosed with hemoglobin electrophoresis performed via High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Medical histories including smoking, alcohol, acute painful crises per year, transfused units of RBC in their lives, leg ulcers, stroke, surgical operations, Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT), epilepsy, and priapism were learnt. Patients with a history of one packyear were accepted as smokers, and one drink-year were accepted as drinkers. A complete physical examination was performed by the Same Internist, and patients with disseminated teeth losses (<20 teeth present) were detected. Patients with an acute painful crisis or any other inflammatory event were treated at first, and the laboratory tests and clinical measurements were performed on the silent phase. Checkup procedures including serum iron, iron binding capacity, ferritin, creatinine, liver function tests, markers of hepatitis viruses A, B, and C, a posterior-anterior chest x-ray film, an electrocardiogram, a Doppler echocardiogram both to evaluate cardiac walls and valves, and to measure systolic BP of pulmonary artery, an abdominal ultrasonography, a venous Doppler ultrasonography of the lower limbs, a Computed Tomography (CT) of brain, and a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of hips were performed. Other bones for avascular necrosis were scanned according to the patients’ complaints. So avascular necrosis of bones was diagnosed by means of MRI [12].
Associated TM were detected with serum iron, iron binding capacity, ferritin, and hemoglobin electrophoresis performed via HPLC, since the SCD with associated TM show a milder clinic than the Sickle Cell Anemia (SCA) (Hb SS) alone [13]. Systolic BP of the pulmonary artery of 40 mmHg or higher are accepted as Pulmonary Hypertension (PHT) [14]. The criterion for diagnosis of COPD is a post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity of lower than 70% [15]. Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) is diagnosed clinically with the presence of new infiltrates on chest x-ray film, fever, cough, sputum production, dyspnea, or hypoxia [16]. An x-ray film of abdomen in upright position was taken just in patients with abdominal distention or discomfort, vomiting, obstipation, or lack of bowel movement, and ileus was diagnosed with gaseous distention of isolated segments of bowel, vomiting, obstipation, cramps, and with the absence of peristaltic activity. CRD is diagnosed with a persistent serum creatinine level of 1.3 mg/dL or higher in males and 1.2 mg/ dL or higher in females. Cirrhosis is diagnosed with physical examination findings, laboratory parameters, and ultrasonographic evaluation. Digital clubbing is diagnosed with the ratio of distal phalangeal diameter to interphalangeal diameter of higher than 1.0, and with the presence of Schamroth’s sign [17,18]. An exercise electrocardiogram is performed in cases with abnormal electrocardiogram and/or angina pectoris. Coronary angiography is taken for the exercise electrocardiogram positive cases.
So, CHD was diagnosed either angiographically or with the Doppler echocardiographic findings as movement disorders in the cardiac walls. Rheumatic heart disease is diagnosed with echocardiographic findings, too. Stroke is diagnosed by the CT of brain. Sickle cell retinopathy is diagnosed with ophthalmologic examination in patients with visual complaints. The Mann-Whitney U test, Independent-Samples t test, and comparison of proportions were used as the methods of statistical analyses.
The study included 222 males and 212 females with similar ages (30.8 vs 30.3 years, p>0.05, respectively). Prevalences of associated TM were similar in both genders, too (72.5% vs 67.9%, p>0.05, respectively). Smoking (23.8% vs 6.1%) and alcohol (4.9% vs 0.4%) were higher in males (p<0.001 for both) (Table 1). Transfused units of RBC in their lives (48.1 vs 28.5, p=0.000), disseminated teeth losses (5.4% vs 1.4%, p<0.001), ileus (7.2% vs 1.4%, p<0.001), cirrhosis (8.1% vs 1.8%, p<0.001), leg ulcers (19.8% vs 7.0%, p<0.001), digital clubbing (14.8% vs 6.6%, p<0.001), CHD (18.0% vs 13.2%, p<0.05), CRD (9.9% vs 6.1%, p<0.05), COPD (25.2% vs 7.0%, p<0.001), and stroke (12.1% vs 7.5%, p<0.05) were all higher in males. Although the mean age of mortality (30.2 vs 33.3 years) was lower in males, the difference was not significant, probably due to the small sample size of the study cases (Table 2). On the other hand, mean ages of the other atherosclerotic consequences in the SCD were shown in Table 3.
Table 1: Characteristic features of the study cases.
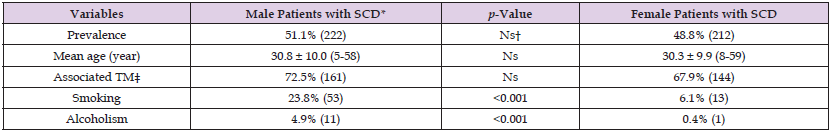
Note: *Sickle cell diseases †Nonsignificant (p>0.05) ‡Thalassemia minors
Table 2: Associated pathologies of the study cases.
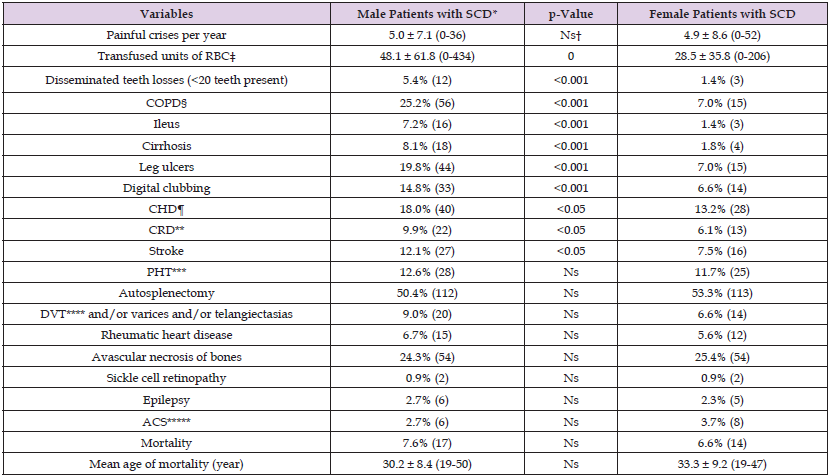
Note: *Sickle cell diseases †Nonsignificant (p>0.05) ‡Red blood cells §Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ¶coronary heart disease **Chronic renal disease ***Pulmonary hypertension ****Deep venous thrombosis *****Acute chest syndrome.
Table 3: Mean ages of the consequences of sickle cell diseases.
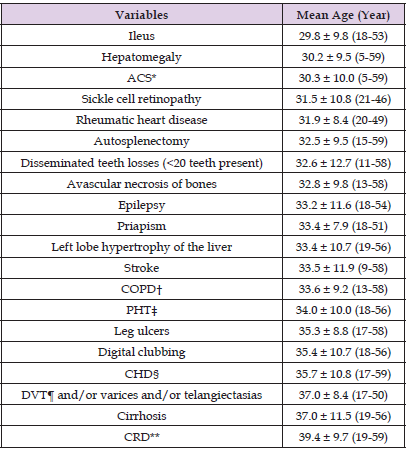
Note: *Acute chest syndrome †Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ‡Pulmonary hypertension §coronary heart disease ¶Deep venous thrombosis **Chronic renal disease.
Leg ulcers are seen in 10% to 20% of the SCD [19], and the ratio was 13.5% in the present study. Its prevalence increases with aging, male gender, and SCA [20]. Similarly, its ratio was higher in males (19.8% vs 7.0%, p<0.001), and mean age of the leg ulcer cases was higher than the remaining patients (35.3 vs 29.8 years, p<0.000) in the present study. Leg ulcers have an intractable nature, and around 97% of them relapse in a period of one year [19]. Similar to Buerger’s disease, leg ulcers occur in the distal segments of the body with a lesser collateral blood flow [19]. The hardened RBC-induced chronic endothelial damage, inflammation, edema, and fibrosis at the capillaries may be the major causes [20].
Prolonged exposure to the hardened bodies due to the pooling of blood in the lower extremities may also explain the leg but not arm ulcers in the SCD. The hardened RBC-induced venous insufficiencies may also accelerate the process by pooling of causative bodies in the legs, and vice versa. Pooling of blood may also be important for the development of venous ulcers, diabetic ulcers, Buerger’s disease, digital clubbing, and onychomycosis in the lower extremities. Furthermore, pooling of blood may be the cause of delayed wound and fracture healings in the lower extremities, again. Smoking and alcohol may also have some additional atherosclerotic effects on the leg ulcers in males. Hydroxyurea is the first drug that was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the SCD [21]. It is an orally administered, cheap, safe, and effective drug that blocks cell division by suppressing formation of deoxyribonucleotides which are the building blocks of DNA [11].
Its main action may be the suppression of hyperproliferative WBC and PLT in the SCD [22]. Although presence of a continuous damage of hardened RBC on vascular endothelium, severity of the destructive process is probably exaggerated by the patients’ own immune systems. Similarly, lower WBC counts were associated with lower crises rates, and if a tissue infarct occurs, lower WBC counts may decrease severity of pain and tissue damage [23]. According to our experiences, prolonged resolution of leg ulcers with hydroxyurea may also suggest that the ulcers may be secondary to increased WBC and PLT counts-induced exaggerated capillary endothelial inflammation and edema instead of the fibrosis, yet. After excess weight, smoking may be the second most common cause of disseminated vasculitis all over the world. It may cause a systemic inflammation on vascular endothelium terminating with an accelerated atherosclerosis-induced end-organ insufficiencies in whole body [24]. Its atherosclerotic effect is the most obvious in COPD and Buerger’s disease [25]. Buerger’s disease is an obliterative vasculitis characterized by inflammatory changes in the small and medium-sized arteries and veins, and it has never been documented in the absence of smoking. Its characteristic findings are acute inflammation, stenoses and occlusions of arteries and veins, and involvements of hands and feet. It is usually seen in young males between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Claudication may be the most common initial symptom of Buerger’s disease.
It is an intense pain caused by insufficient blood flow during exercise in feet and hands, but it may even develop at rest in severe cases. It typically begins in extremities, but it may also radiate to more central areas in advanced cases. Numbness or tingling of the limbs is also common. Raynaud’s phenomenon may also be seen in which fingers or toes turn a white color upon exposure to cold. Skin ulcerations and gangrene of fingers or toes are the final consequences. Gangrene of fingertips may even need amputation. Unlike many other forms of vasculitis, Buerger’s disease does not keep other organs for unknown reasons, yet. Similar to the venous ulcers, diabetic ulcers, leg ulcers of the SCD, digital clubbing, onychomycosis, and delayed wound and fracture healings of the lower extremities, pooling of blood due to the gravity may be important in the development of Buerger’s disease, particularly in the lower extremities. Angiograms of upper and lower extremities are diagnostic for Buerger’s disease. In angiogram, stenoses and occlusions in multiple areas of arms and legs are seen. In order to rule out some other forms of vasculitis by excluding involvement of vascular regions atypical for Buerger’s disease, it is sometimes necessary to perform angiograms of other body regions. Skin biopsies are rarely required, since a biopsy site near a poorly perfused area will not heal completely. Association of Buerger’s disease with tobacco use, particularly cigarette smoking is clear. Although most patients are heavy smokers, some cases with limited smoking history have also been reported.
The disease can also be seen in users of smokeless tobacco. The limited smoking history of some patients may support the hypothesis that Buerger’s disease may be an autoimmune reaction triggered by some constituent of tobacco. Although the only treatment way is complete cessation of smoking, the already developed stenoses and occlusions are irreversible. Due to the clear evidence of inflammation in this disorder, anti-inflammatory dose of aspirin plus low-dose warfarin may probably be effective to prevent microvascular infarctions in fingers or toes at the moment. On the other hand, fasting plasma glucose and high-density lipoproteins may be negative whereas triglycerides, Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL), erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein may be positive acute phase reactants indicating such inflammatory effects of smoking on vascular endothelium [26]. Similarly, it is not an unexpected result that smoking was associated with the lower values of Body Mass Index (BMI) due to the systemic inflammatory effects on vascular endothelium [27]. In another definition, smoking causes a chronic inflammation in the human body. Additionally, some evidence revealed an increased heart rate just after smoking even at rest [28]. Nicotine supplied by patch after smoking cessation decreased caloric intake in a dose-related manner [29]. According to an animal study, nicotine may lengthen intermeal time, and decrease the amount of meal eaten [30]. Smoking may be associated with a postcessation weight gain, but the risk is the highest during the first year and decreases with the following years [31].
Although the CHD was detected with similar prevalences in both genders, prevalences of smoking and COPD were higher in males against the higher prevalences of white coat hypertension, BMI, LDL, triglycerides, HT, and DM in females [32]. Beside that the prevalence of myocardial infarction is increased three-fold in men and six-fold in women who smoked at least 20 cigarettes per day [33]. In another word, smoking may be more dangerous for women about the atherosclerotic endpoints probably due to the higher BMI in them. Several toxic substances found in the cigarette smoke get into the circulation, and cause vascular endothelial inflammation in various organ systems of the body. For example, smoking is usually associated with depression, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), chronic gastritis, hemorrhoids, and urolithiasis in the literature [34]. There may be several underlying mechanisms to explain these associations [35]. First of all, smoking may have some antidepressant properties with several potentially lethal side effects. Secondly, smoking-induced vascular endothelial inflammation may disturb epithelial functions for absorption and excretion in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts which may terminate with urolithiasis, loose stool, diarrhea, and constipation. Thirdly, diarrheal losses-induced urinary changes may even cause urolithiasis [36]. Fourthly, smoking-induced sympathetic nervous system activation may cause motility problems in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts terminating with the IBS and urolithiasis.
Eventually, immunosuppression secondary to smoking-induced vascular endothelial inflammation may even terminate with the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract infections causing loose stool, diarrhea, and urolithiasis, because some types of bacteria can provoke urinary supersaturation, and modify the environment to form crystal deposits in the urine. Actually, 10% of urinary stones are struvite stones which are built by magnesium ammonium phosphate produced during infections with the bacteria producing urease. Parallel to the results above, urolithiasis was detected in 17.9% of cases with the IBS and 11.6% of cases without in the other study (p<0.01) [34]. Acute painful crises are the most disabling symptoms of the SCD. Although some authors reported that pain itself may not be life threatening directly, infections, medical or surgical emergencies, or emotional stress are the most common precipitating factors of the crises [37]. The increased basal metabolic rate during such stresses aggravates sickling, capillary endothelial damage, inflammation, edema, tissue hypoxia, and multiorgan insufficiencies. So, the risk of mortality is much higher during the crises. Actually, each crisis may complicate the following crises by leaving significant sequalae’s on the capillary endothelial system all over the body. After a period of time, the sequalae’s may terminate with sudden end-organ failures and death during a final acute painful crisis that may even be silent, clinically. Similarly, after a 20-year experience on such patients, the deaths seem sudden and unexpected events in the SCD.
Unfortunately, most of the deaths develop just after the hospital admission, and the majority of them are patients without hydroxyurea therapy [38,39]. Rapid RBC supports are usually lifesaving for such patients, although preparation of RBC units for transfusion usually takes time. Beside that RBC supports in emergencies become much more difficult in terminal cases due to the repeated transfusions-induced blood group mismatch. Transfusion of each unit of RBC complicates the following transfusions by means of the blood subgroup mismatch. Due to the significant efficacy of hydroxyurea therapy, RBC transfusions should be kept just for acute events and emergencies in the SCD [38,39]. According to our experiences, simple and repeated transfusions are superior to RBC exchange in the SCD [40,41]. First of all, preparation of one or two units of RBC suspensions in each time rather than preparation of six units or higher provides time to clinicians to prepare more units by preventing sudden death of such high-risk patients. Secondly, transfusions of one or two units of RBC suspensions in each time decrease the severity of pain, and relax anxiety of the patients and their relatives since RBC transfusions probably have the strongest analgesic effects during the crises. Actually, the decreased severity of pain by transfusions also indicates the decreased severity of inflammation all over the body. Thirdly, transfusions of lesser units of RBC suspensions in each time by means of the simple transfusions will decrease transfusion-related complications including infections, iron overload, and blood group mismatch in the future.
Fourthly, transfusion of RBC suspensions in the secondary health centers may prevent some deaths developed during the transport to the tertiary centers for the exchange. Finally, cost of the simple and repeated transfusions on insurance system is much lower than the exchange that needs trained staff and additional devices. On the other hand, pain is the result of complex and poorly understood interactions between RBC, White Blood Cells (WBC), Platelets (PLT), and endothelial cells, yet. Whether leukocytosis contributes to the pathogenesis by releasing cytotoxic enzymes is unknown. The adverse actions of WBC on endothelium are of particular interest with regard to the cerebrovascular diseases in the SCD. For example, leukocytosis even in the absence of any infection was an independent predictor of the severity of the SCD [42], and it was associated with the risk of stroke in a cohort of Jamaican patients [43]. Disseminated tissue hypoxia, releasing of inflammatory mediators, bone infarctions, and activation of afferent nerves may take role in the pathophysiology of the intolerable pain. Because of the severity of pain, narcotic analgesics are usually required to control them [44], but according to our practice, simple and repeated RBC transfusions may be highly effective both to relieve pain and to prevent sudden death that may develop secondary to multiorgan failures on the chronic inflammatory background of the SCD. Hydroxyurea may be the only life-saving drug for the treatment of the SCD.
It interferes with the cell division by blocking the formation of deoxyribonucleotides by means of inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase. Deoxyribonucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Hydroxyurea mainly affects hyperproliferating cells. Although the action way of hydroxyurea is thought to be the increase in gamma-globin synthesis for fetal hemoglobin (Hb F), its main action may be the suppression of leukocytosis and thrombocytosis by blocking the DNA synthesis in the SCD [45,46]. By this way, the chronic inflammatory and destructive process of the SCD is suppressed with some extent. Due to the same action way, hydroxyurea is also used in moderate and severe psoriasis to suppress hyperproliferating skin cells. As in viral hepatitis cases, although presence of a continuous damage of sickle cells on the capillary endothelium, the severity of destructive process is probably exaggerated by the patients’ own WBC and PLT. So, suppression of proliferation of them may limit the endothelial damage-induced edema, ischemia, and infarctions in whole body [47]. Similarly, final Hb F levels in hydroxyurea users did not differ from their pretreatment levels [23]. The Multicenter Study of Hydroxyurea (MSH) studied 299 severely affected adults with the SCA and compared the results of patients treated with hydroxyurea or placebo [48]. The study particularly researched effects of hydroxyurea on painful crises, ACS, and requirement of blood transfusion. The outcomes were so overwhelming in favour of hydroxyurea that the study was terminated after 22 months, and hydroxyurea was initiated for all patients.
The MSH also demonstrated that patients treated with hydroxyurea had a 44% decrease in hospitalizations [48]. In multivariable analyses, there was a strong and independent association of lower neutrophil counts with the lower crisis rates [48]. But this study was performed just in severe SCA cases alone, and the rate of painful crises was decreased from 4.5 to 2.5 per year [48]. Whereas we used all subtypes of the SCD with all clinical severity, and the rate of painful crises was decreased from 10.3 to 1.7 per year (p<0.000) with an additional decreased severity of them (7.8/10 vs 2.2/10, p<0.000) in the previous study [38]. Parallel to our results, adult patients using hydroxyurea for frequent painful crises appear to have reduced mortality rate after a 9-year follow-up period [49]. Although the underlying disease severity remains critical to determine prognosis, hydroxyurea may also decrease severity of disease and prolong survival [49]. The complications start to be seen even in infancy in the SCD. For example, infants with lower hemoglobin values were more likely to have a higher incidence of clinical events such as ACS, painful crises, and lower neuropsychological scores, and hydroxyurea reduced the incidences of them [50]. Hydroxyurea therapy in early years of life may protect splenic function, improve growth, and prevent end-organ insufficiencies. Transfusion programmes can also reduce all of the complications, but transfusions carry many risks including infections, iron overload, and development of allo-antibodies causing subsequent transfusions difficult.
Aspirin is a member of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, inflammation, and acute thromboembolic events. Although aspirin has similar anti-inflammatory effects with the other NSAID, it also suppresses the normal functions of PLT, irreversibly. This property causes aspirin being different from other NSAID, which are reversible inhibitors. Aspirin acts as an acetylating agent where an acetyl group is covalently attached to a serine residue in the active site of the Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. Aspirin’s ability to suppress the production of Prostaglandins (PG) and Thromboxanes (TX) is due to its irreversible inactivation of the COX enzyme required for PG and TX synthesis. PG are the locally produced hormones with some diverse effects, including the transmission of pain into the brain and modulation of the hypothalamic thermostat and inflammation in the body. TX are responsible for the aggregation of PLT to form blood clots. In another definition, low-dose aspirin use irreversibly blocks the formation of TXA2 in the PLT, producing an inhibitory effect on the PLT aggregation during whole lifespan of the affected PLT (8-9 days). Since PLT does not have nucleus and DNA, they are unable to synthesize new COX enzyme once aspirin has inhibited the enzyme. The antithrombotic property of aspirin is useful to reduce the incidences of myocardial infarction, transient ischemic attack, and stroke [51]. Heart attacks are caused primarily by blood clots, and low dose of aspirin is seen as an effective medical intervention to prevent a second myocardial infarction [52].
According to the literature, aspirin may also be effective in prevention of colorectal cancers [53]. On the other hand, aspirin has some side effects including gastric ulcers, gastric bleeding, worsening of asthma, and Reye syndrome in childhood and adolescence. Due to the risk of Reye syndrome, the US Food and Drug Administration recommends that aspirin or aspirin-containing products should not be prescribed for febrile patients under the age of 12 years [54]. Eventually, the general recommendation to use aspirin in children has been withdrawn, and it was only recommended for Kawasaki disease [55]. Reye syndrome is a rapidly worsening brain disease [55]. The first detailed description of Reye syndrome was in 1963 by an Australian pathologist, Douglas Reye [56]. The syndrome mostly affects children, but it can only affect fewer than one in a million children a year [56]. Symptoms of Reye syndrome may include personality changes, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness [55]. Although the liver toxicity typically occurs in the syndrome, jaundice is usually not seen with it, but the liver is enlarged in most cases [55]. Although the death occurs in 20-40% of affected cases, about one third of survivors get a significant degree of brain damage [55]. The cause of Reye syndrome is unknown [56]. It usually starts just after recovery from a viral infection, such as influenza or chicken pox. About 90% of cases in children are associated with aspirin use [56,57].
Inborn errors of metabolism are also the other risk factors, and the genetic testing for inborn errors of metabolism became available in developed countries in the 1980s [55]. When aspirin use was withdrawn for children in the US and UK in the 1980s, a decrease of more than 90% in rates of Reye syndrome was seen [56]. Early diagnosis improves outcomes, and treatment is supportive. Mannitol may be used in cases with the brain swelling [56]. Due to the very low risk of Reye syndrome but much higher risk of death due to the SCD in children, aspirin should be added both into the acute and chronic phase treatments with an anti-inflammatory dose even in childhood in the SCD [58]. Warfarin is an anticoagulant, and first came into large-scale commercial use in 1948 as a rat poison. It was formally approved as a medication to treat blood clots in human being by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1954. In 1955, warfarin’s reputation as a safe and acceptable treatment was bolstred when President Dwight David Eisenhower was treated with warfarin following a massive and highly publicized heart attack. Eisenhower’s treatment kickstarted a transformation in medicine whereby CHD, arterial plaques, and ischemic strokes were treated and protected against by using anticoagulants such as warfarin. Warfarin is found in the List of Essential Medicines of WHO. In 2020, it was the 58th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States. It does not reduce blood viscosity but inhibits blood coagulation. Warfarin is used to decrease the tendency for thrombosis, and it can prevent formation of future blood clots and reduce the risk of embolism.
Warfarin is the best suited for anticoagulation in areas of slowly running blood such as in veins and the pooled blood behind artificial and natural valves, and in blood pooled in dysfunctional cardiac atria. It is commonly used to prevent blood clots in the circulatory system such as DVT and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who have Atrial Fibrillation (AF), valvular heart disease, or artificial heart valves. Less commonly, it is used following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and orthopedic surgery. The warfarin initiation regimens are simple, safe, and suitable to be used in ambulatory and in patient settings [59]. Warfarin should be initiated with a 5 mg dose, or 2 to 4 mg in the very elderly. In the protocol of low-dose warfarin, the target International Normalized Ratio (INR) value is between 2.0 and 2.5, whereas in the protocol of standard-dose warfarin, the target INR value is between 2.5 and 3.5 [60]. When warfarin is used and INR is in therapeutic range, simple discontinuation of the drug for five days is usually enough to reverse the effect and causes INR to drop below 1.5 [61]. Its effects can be reversed with Phyto menadione (vitamin K1), fresh frozen plasma, or prothrombin complex concentrate, rapidly. Blood products should not be routinely used to reverse warfarin overdose, when vitamin K1 could work alone. Warfarin decreases blood clotting by blocking vitamin K epoxide reductase, an enzyme that reactivates vitamin K1. Without sufficient active vitamin K1, clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X decrease clotting ability.
The anticlotting protein C and protein S are also inhibited, but to a lesser degree. A few days are required for full effects to occur, and these effects can last for up to five days. The consensus agrees that patient self-testing and patient self-management are effective methods of monitoring oral anticoagulation therapy, providing outcomes at least as good as, and possibly better than, those achieved with an anticoagulation clinic. Currently available self-testing/self-management devices give INR results that are comparable with those obtained in laboratory testing. The only common side effect of warfarin is hemorrhage. The risk of severe bleeding is low with a yearly rate of 1-3% [62]. All types of bleeding may occur, but the most severe ones are those involving the brain and spinal cord [62]. The risk is particularly increased once the INR exceeds 4.5 [62]. The risk of bleeding is increased further when warfarin is combined with antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel or aspirin [63]. But thirteen publications from 11 cohorts including more than 48.500 total patients with more than 11.600 warfarin users were included in the meta-analysis [64]. In patients with AF and non-end-stage CRD, warfarin resulted in a lower risk of ischemic stroke (p= 0.004) and mortality (p<0.00001) but had no effect on major bleeding (p>0.05) [64]. Similarly, warfarin resumption is associated with significant reductions in ischemic stroke even in patients with warfarin-associated Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH) [65]. Death occurred in 18.7% of patients who resumed warfarin and 32.3% who did not resume warfarin (p= 0.009) [65].
Ischemic stroke occurs in 3.5% of patients who resumed warfarin and 7.0% of patients who did not resume warfarin (p= 0.002) [65]. Whereas recurrent ICH occurred in 6.7% of patients who resumed warfarin and 7.7% of patients who did not resume warfarin without any significant difference in between (p>0.05) [65]. On the other hand, patients with Cerebral Venous Thrombosis (CVT) those were anticoagulated either with warfarin or dabigatran had low risk of recurrent Venous Thrombotic Events (VTE), and the risk of bleeding was similar in both regimens, suggesting that both warfarin and dabigatran are safe and effective for preventing recurrent VTE in patients with CVT [66]. Additionally, an INR value of about 1.5 achieved with an average daily dose of 4.6 mg warfarin, has resulted in no increase in the number of men ever reporting minor bleeding episodes, although rectal bleeding occurs more frequently in those men who report this symptom [67]. Non-rheumatic AF increases the risk of stroke, presumably from atrial thromboemboli, and long-term low-dose warfarin therapy is highly effective and safe in preventing stroke in such patients [68]. There were just two strokes in the warfarin group (0.41% per year) as compared with 13 strokes in the control group (2.98% per year) with a reduction of 86% in the risk of stroke (p= 0.0022) [68]. The mortality was markedly lower in the warfarin group, too (p= 0.005) [68]. The warfarin group had a higher rate of minor hemorrhage (38 vs 21 patients) but the frequency of bleedings that required hospitalization or transfusion was the same in both group (p>0.05) [68].
Additionally, very-low-dose warfarin was a safe and effective method for prevention of thromboembolism in patients with metastatic breast cancer [69]. The warfarin dose was 1 mg daily for 6 weeks and was adjusted to maintain the INR value of 1.3 to 1.9 [69]. The average daily dose was 2.6 mg, and the mean INR was 1.5 [69]. On the other hand, new oral anticoagulants had a favorable risk-benefit profile with significant reductions in stroke, ICH, and mortality, and with similar major bleeding as for warfarin, but increased gastrointestinal bleeding [70]. Interestingly, rivaroxaban and low dose apixaban were associated with increased risks of all-cause mortality compared with warfarin [71]. The mortality rate was 4.1% per year in the warfarin group, as compared with 3.7% per year with 110 mg of dabigatran and 3.6% per year with 150 mg of dabigatran (p>0.05 for both) in patients with AF in another study [72]. On the other hand, infections, medical or surgical emergencies, or emotional stress-induced increased basal metabolic rate accelerates sickling, and an exaggerated capillary endothelial edema-induced myocardial infarction or stroke may cause sudden deaths in the SCD. So lifelong aspirin with an anti-inflammatory dose plus low-dose warfarin may be a life-saving treatment regimen even at childhood both to decrease severity of capillary endothelial inflammation and to prevent thromboembolic complications in the SCD [73]. COPD is the third leading cause of death with various underlying etiologies in whole world [74,75].
Aging, physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, animal-rich diet, smoking, alcohol, male gender, excess weight, chronic inflammations, prolonged infections, and cancers may be the major underlying causes. Atherosclerotic effects of smoking may be the most obvious in COPD and Buerger’s disease, probably due to the higher concentrations of toxic substances in the lungs and pooling of blood in the extremities. Besides smoking, regular alcohol consumption is also important for the pulmonary and systemic inflammatory process of COPD, since COPD was one of the most common diagnoses in alcohol dependence [76]. Furthermore, 30-day readmission rates were higher in the COPD patients with alcoholism [77]. Probably an accelerated atherosclerotic process is the main structural background of functional changes that are characteristics of the COPD. The inflammatory process of vascular endothelium is enhanced by release of various chemicals by inflammatory cells, and it terminates with advanced fibrosis, atherosclerosis, and pulmonary losses. COPD may be the pulmonary consequence of the systemic atherosclerotic process. Besides the accelerated atherosclerotic process of the pulmonary vasculature, there are several reports about coexistence of associated endothelial inflammation all over the body in COPD [78,79]. For example, there may be close relationships between COPD, CHD, PAD, and stroke [80]. Furthermore, two-third of mortality cases were caused by cardiovascular diseases and lung cancers in the COPD, and the CHD was the most common cause in a multi-center study of 5.887 smokers [81].
When the hospitalizations were researched, the most common causes were the cardiovascular diseases, again [81]. In another study, 27% of mortality cases were due to cardiovascular diseases in the moderate and severe COPD [82]. On the other hand, COPD may be the pulmonary consequence of the systemic atherosclerotic process caused by the hardened RBC in the SCD [74]. Digital clubbing is characterized by the increased normal angle of 165° between nailbed and fold, increased convexity of the nail fold, and thickening of the whole distal finger [83]. Although the exact cause and significance is unknown, chronic tissue hypoxia is highly suspected [84]. In the previous study, only 40% of clubbing cases turned out to have significant underlying diseases while 60% remained well over the subsequent years [18]. But according to our experiences, digital clubbing is frequently associated with pulmonary, cardiac, renal, and hepatic diseases and smoking which are characterized with chronic tissue hypoxia [5]. As an explanation for that hypothesis, lungs, heart, kidneys, and liver are closely related organs which affect their functions in a short period of time. On the other hand, digital clubbing is also common in the SCD, and its prevalence was 10.8% in the present study. It probably shows chronic tissue hypoxia caused by disseminated endothelial damage, inflammation, edema, and fibrosis at the capillary level in the SCD. Beside the effects of SCD, smoking, alcohol, cirrhosis, CRD, CHD, and COPD, the higher prevalence of digital clubbing in males (14.8% vs 6.6%, p<0.001) may also show some additional role of male gender in the systemic atherosclerotic process.
Cirrhosis was the 10th leading cause of death for men and the 12th for women in the United States in 2001 [6]. Although the improvements of health services worldwide, the increased morbidity and mortality of cirrhosis may be explained by prolonged survival of the human being, and increased prevalence of excess weight all over the world. For example, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) affects up to one third of the world population, and it became the most common cause of chronic liver disease even at childhood, nowadays [85]. NAFLD is a marker of pathological fat deposition combined with a low-grade inflammation which results with hypercoagulability, endothelial dysfunction, and accelerated atherosclerosis [85]. Besides terminating with cirrhosis, NAFLD is associated with higher overall mortality rates as well as increased prevalences of cardiovascular diseases [86]. Authors reported independent associations between NAFLD and impaired flow-mediated vasodilation and increased mean Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) [87]. NAFLD may be considered as one of the hepatic consequences of the metabolic syndrome and SCD [88]. Probably smoking also takes role in the inflammatory process of the capillary endothelium in liver, since the systemic inflammatory effects of smoking on endothelial cells is well-known with Buerger’s disease and COPD [25]. Increased oxidative stress, inactivation of antiproteases, and release of proinflammatory mediators may terminate systemic atherosclerosis in smokers.
The atherosclerotic effect of alcohol is much more prominent in hepatic endothelium probably due to the highest concentrations of its metabolites there. Chronic infectious or inflammatory processes and cancers may also terminate with an accelerated atherosclerosis in whole body [89]. For example, Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection raised CIMT, and normalization of hepatic function with HCV clearance may be secondary to reversal of favorable lipids observed with the chronic infection [89,90]. As a result, cirrhosis may also be another atherosclerotic consequence of SCD. CRD is also increasing all over the world that can also be explained by aging of the human being, and increased prevalence of excess weight all over the world [91]. Aging, physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, animal-rich diet, excess weight, smoking, alcohol, inflammatory or infectious processes, and cancers may be the major causes of renal endothelial inflammation. The inflammatory process is enhanced by release of various chemicals by lymphocytes to repair the damaged endothelial cells of the renal arteriols. Due to the continuous irritation of the vascular endothelial cells, prominent changes develop in the architecture of the renal tissues with advanced atherosclerosis, tissue hypoxia, and infarcts [92]. Excess weight-induced hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, elevated BP, and insulin resistance may cause tissue inflammation and immune cell activation [93]. For example, age (p= 0.04), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (p= 0.01), mean arterial BP (p= 0.003), and DM (p= 0.02) had significant correlations with the CIMT [91].
Increased renal tubular sodium reabsorption, impaired pressure natriuresis, volume expansion due to the activations of sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin system, and physical compression of kidneys by visceral fat tissue may be some mechanisms of the increased BP with excess weight [94]. Excess weight also causes renal vasodilation and glomerular hyperfiltration which initially serve as compensatory mechanisms to maintain sodium balance due to the increased tubular reabsorption [94]. However, along with the increased BP, these changes cause a hemodynamic burden on the kidneys in the long term that causes chronic endothelial damage [95]. With prolonged weight excess, there is increased urinary protein excretion, loss of nephron function, and exacerbated HT. With the development of dyslipidemia and DM in cases with excess weight, CRD progresses much more easily [94]. On the other hand, the systemic inflammatory effects of smoking on endothelial cells may also be important in the CRD [96]. Although some authors reported that alcohol was not related with the CRD [96], various metabolites of alcohol circulate even in the blood vessels of the kidneys and give harm to the renal vascular endothelium. Chronic inflammatory or infectious processes may also terminate with accelerated atherosclerosis in the renal vasculature [89]. Although CRD is due to the atherosclerotic process of the renal vasculature, there are close relationships between CRD and other atherosclerotic consequences of the metabolic syndrome including CHD, COPD, PAD, cirrhosis, and stroke [97,98].
For example, the most common cause of death was the cardiovascular diseases in the CRD again [99]. The hardened RBC-induced capillary endothelial damage in the renal vasculature may be the main cause of CRD in the SCD. In another definition, CRD may just be one of the several atherosclerotic consequences of the metabolic syndrome and SCD, again [100]. Stroke is an important cause of death and develops as an acute thromboembolic event on the chronic atherosclerotic background in most of the cases. Aging, male gender, smoking, alcohol, and excess weight may be the major underlying causes. Stroke is also a common complication of the SCD [101]. Similar to leg ulcers, stroke is particularly higher in the SCA and cases with higher WBC counts [102]. Sickling-induced capillary endothelial damage, activations of WBC, PLT, and coagulation system, and hemolysis may terminate with chronic capillary endothelial inflammation, edema, and fibrosis [103]. Probably, stroke may not have a macrovascular origin in the SCD, and diffuse capillary endothelial inflammation, edema, and fibrosis may be much more important. Infections, inflammations, medical or surgical emergencies, and emotional stress may precipitate stroke by increasing basal metabolic rate and sickling. A significant reduction of stroke with hydroxyurea may also suggest that a significant proportion of cases is developed due to the increased WBC and PLT counts-induced exaggerated capillary inflammation, edema, and fibrosis [104].
As a conclusion, infection, medical or surgical emergency, or emotional stress-induced increased basal metabolic rate aggravates the sickling and secondary capillary endothelial inflammation and edema, and terminates with disseminated tissue hypoxia, accelerated atherosclerosis, and multiorgan failures. Although the fibrotic vascular stenoses are irreversible in the leg ulcers, the acute capillary endothelial inflammation and edema can be returned to some extent with aspirin and hydroxyurea. Aspirin plus low-dose warfarin may even increase the legs’ blood supply by preventing recurrent ischemiaes in microcirculation. Thus, anti-inflammatory dose of aspirin plus lowdose warfarin in addition to hydroxyurea may be the optimal treatment regimen of leg ulcers in the SCD at the moment.


