Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Ibrahim Ali Al Baher*
Received: June 17, 2024; Published: June 24, 2024
*Corresponding author: Ibrahim Ali Al Baher, Academic lecturer, University of the People, Assistant Professor, Islamic University of Minnesota, USA, Expert, Asian Institute of Research, Malaysia, Expert, Canadian Center of Science and Education, Canada
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2024.57.008957
The current study aimed to reveal the level of social intelligence among school principals in Bani Kinana District in Jordan, and its relationship to the level of their professional competencies. The researcher used the descriptive analytical method, where the study sample consisted of (98) individuals. To achieve the objectives of the study a “questionnaire” was prepared and used to collect its data after verifying its validity and reliability and using the SPSS program to analyze its data. The results of the study showed: The level of social intelligence among the principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana District, from their viewpoint was at medium level. And the level of professional competencies came at medium level. There is a positive, statistically significant correlation at the level (α ≤ 0.05) between the average estimates of the sample members on the social intelligence level scale and their estimates on the professional competency scale. There are no statistically significant differences at the level (α ≤ 0.05) between the average estimates of the sample members on all areas of the level of social intelligence & professional competencies among the principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana District according to the different study variables (gender, educational qualification, years of administrative experience). In light of the results, the study came out with several recommendations, including: - Number of training courses and programs for the development and activation of social intelligence among school principals. - Work to develop the professional competencies of school principals so that they can perform their duties and work tasks with distinction and mastery, which is positively reflected on the outputs that achieve the desired and desired goals of the educational process.
Keywords: Social Intelligence; Professional Competencies; Administrators
The world is currently experiencing a state of change in various aspects of its economic, social and political life, especially the educational ones, which bear the bulk of this change in order to keep up with the rapid developments in the field of knowledge. Technology and its various technologies, which reflects positively on the work of the rest of the sectors. Based on this change, new concepts and terminology have emerged in the field of intelligence to keep pace with this change These include: emotional and emotional intelligence, digital intelligence, social intelligence, and others. (Al Khazaleh, Al Omari [1]) mention that the school, as an educational institution that works to refine generations capable of contributing to the progress and development of society, needs a highly qualified leadership; A competent principal is an effective principal who uses his skills, experience and abilities in applying humane and social methods that are commensurate with the nature of his administrative work in accordance with the laws and regulations governing educational work. From here, social intelligence is one of the characteristics that must be distinguished by the school principal, whose importance lies in the effective and mutual social relations between him and teachers, students and other cadres working in the school, and related to the educational-learning process. Social intelligence has a significant positive impact on the success of the manager in his social life and his interaction with the surrounding environment in progress and effectiveness.
Therefore, social intelligence is considered one of the important aspects of the administrator’s personality. Because it is linked to his ability to deal with others, and to form successful social relationships. The importance of studying social intelligence is evident in the fact that it represents a kind of cognitive abilities necessary for positive interaction between it and other individuals working in the educational institution, and for human interaction in general, and interaction in the educational field in particular. Therefore, the more social the school principal is, the better his job performance, and this is reflected first and foremost on the quality of the educational institution’s outputs. The concept of social intelligence indicates that it is the ability to communicate with others, and to build relationships of love and moral commitment with them. Where it is formed as a result of a person’s understanding of himself first, through his ability to control his emotions, and therefore it is closely related to emotional intelligence, Emotional intelligence covers several aspects related to emotional awareness, and how a person manages the different aspects of his life before sharing it with others.
But the role of social intelligence begins with the individual’s ability to master the processes of communication and communication with others within his environment and surrounding society. As a person needs to employ social intelligence skills; Such as the ability to express, constructive dialogue, good listening, reconciliation with oneself and others, .... and others. Social intelligence is one of the acquired skills that the individual acquires and develops with the passage of time, and the change of places and environments in which he lives and coexists with its members. Among the most important basic social intelligence skills, (Al Taie, [2]) mentions the following:
1. Speaking and dialogue skill: A socially intelligent person is distinguished by his ability to talk to different people in a decent and polite manner. As he possesses the so-called skills of adaptation and social expression, and eyes are always directed towards him in social sessions.
2. Knowledge of social customs and norms: a socially intelligent person has the ability to deal with various social situations, whether they require formal or informal dealings. This is because he is fully aware of the rules that govern social attitudes within different environments.
3. Good listening skill: A socially intelligent person is characterized by the ability to master the process of listening to others and listening to them, so others feel comfortable and satisfied by communicating with him.
4. Feeling for others: A socially intelligent person has the ability to understand and feel for others, so he can help them overcome their problems and grief.
5. The skill of switching roles: or the skill of social competence, as a socially intelligent person does not face difficulty in dealing with different personalities and ages, which reflects positively on his self-confidence.
6. The ability to leave a good impression: It is one of the most complex social intelligence skills, as a socially intelligent person is characterized by his ability to leave a good impression on others without pretending or fabricating.
7. Avoiding controversy: A socially intelligent person accepts other people’s points of view with open arms, even if they contradict his personal opinions or beliefs. It is preferable to avoid arguments.
In view of the benefits of social intelligence, we find that it has multiple benefits for the individual and those who coexist with him within his environment, as Daniel mentions (Daniel, [3]) that it works to improve the immune system, Increasing the ability to combat diseases, strong relationships contribute to avoiding feelings of fatigue, depression, and various diseases caused by loneliness. Cohesive relationships reflect positively on all areas of life. From family to work.
When talking about how to develop social intelligence, we note that good social relationships contribute to communication in achieving happiness and success. Therefore, work on improving social intelligence skills is necessary, and the following are the most important methods that can be followed to develop social intelligence skills. (Asiri, [4]) mentions the following:
1. Emotional awareness: If a person is looking to develop his social intelligence, he must start with awareness of his emotional state and realize the physical signs that appear on him when he is emotional, such as his heartbeat, breathing rate, and the degree of sweating, in order to help him control his external behavior and emotions.
2. Respect for others: A person should avoid making prejudices about others, given that these judgments push a person to deal with others based on the image he has drawn of them in his mind, not what they really are, so a person should be careful to accept others and open up to their ideas.
3. Putting oneself in the place of others: A person must put himself in the place of others; to recognize their difficulties, limitations, desires, and situations, this would enable the person to understand the social background of the other party, and contribute to improving empathy and understanding skills during communication.
4. Diplomacy in dealing: This is because people in any social apparatus, whether a company, an institution, or an occasion, are linked together within a hierarchy that defines each person’s relationship with this apparatus, Therefore, it is necessary to know the nature of these links. For a person to adjust his responses and act wisely and consciously.
5. The ability to analyze body language: A person cannot document his relationships with others without understanding the reality of their feelings, so the ability to analyze body language is important to understand their deep feelings without verbal communication, It lies in understanding nonverbal behaviors; such as facial expressions, gestures, and reactions.
Competency-based education is a type of education that emerged in the United States at the end of the sixties, as a response to intertwined political, social, educational and technical pressures to improve the teacher preparation system in terms of professionalism. Professional competencies in administrative work in the school are important, as administration and administrative work are considered an essential element in educational work and the educational process in general. On it depends the success or failure of the work, and the administrative occupies the forefront among the factors on which the success of education depends on achieving its goals and desired objectives. Considering that the obligations and responsibilities of the manager cannot be separated from the fundamental changes that take place in the surrounding society, Most of the educational problems stem from the schools’ lack of effective and successful management. Therefore, every administrator in the educational field must have professional competencies that help him to be compatible professionally and socially. And make him feel psychologically satisfied with his performance. The concept of professional competence in the educational field refers to a set of knowledge, concepts, skills and attitudes that guide administrative and educational behavior in educational work in general. It helps the educational cadres, especially the administration, to perform its work inside and outside the school with distinction and a certain and good level of mastery in choosing the appropriate administrative method that keeps pace with recent developments in its dealings with the teacher, the student, and the rest of the employees in the educational institution. Each adequacy can be measured according to its own criteria agreed upon in cooperation and partnership with the bodies regulating administrative ( Abu Yunus, [5]).
Looking at the types of professional competencies for teachers, we note that there are four types of professional competencies needed by the teacher, they are as follows (Omran, [6]):
- Cognitive competencies: refer to the information and mental skills necessary for the performance of the teacher in the various fields of their work.
- Emotional competencies: They refer to the teacher’s preparations, inclinations, attitudes, values, and beliefs. These competencies cover multiple aspects such as: the sensitivity of the working individual, his self-confidence, and his attitude towards the educational profession.
- Performance competencies: They refer to the educational performance competencies demonstrated by the teacher, including psychomotor skills such as the use of means and technology, and the performance of these skills depends on what the individual (the teacher) previously acquired in terms of cognitive competencies.
- Productive competencies: refer to the impact of the teacher’s performance on previous competencies in the field, i.e. the impact of competencies on the performance of teachers and students, and the extent of their adaptation in their future learning or in their professions.
There are also special competencies that must be possessed by the principal of the school. Where these competencies can be identified and classified into: technical competencies, human competencies, administrative and technical competencies that must be available to the school principal to carry out his job duties. An important role in identifying needs, through it, the extent of their needs is measured. It was classified according to (Othman, [7]) into three competencies as follows:
- Technical competencies: Technical competencies have been defined; They are competencies that the school principal should possess in order to carry out some of the tasks entrusted to him, such as setting the budget, staffing, scheduling administrative work and other administrative responsibilities.
- Human competencies: Human competencies were defined; They are the competencies that refer to the personal skills that a school principal needs to work successfully with people regardless of their social status and status.
- Administrative competencies: As for administrative competencies; They are the competencies needed by the principal of the school, to see the overall picture and the relationships between the different parts.
- Technological competencies: which refer to the ability of the administrator to introduce technology and its modern techniques within the duties and tasks of his work. (Khresat, [8]). Reference can be made here to the possibility of mastering the previous competencies through training the manager to perform them using programs and courses on the subject of administrative competencies.
Study Problem and Questions
The high or low level of social intelligence among school principals is an important aspect of their personality, as it is related to the abilities and skills in dealing with others. This is to form successful human social relationships, and therefore social intelligence is of great importance. It represents a kind of cognitive abilities necessary for constructive positive interaction between the individual and other individuals. It is human interaction in general, and in the educational field in particular (Al-Khazaleh, Al Omari [1]). It has become clear that there is an important and essential role for social intelligence in solving the many, many problems and challenges that educational cadres in schools suffer from, led by school principals of all levels. Because of the lack of interest in him and the activation of his role; This is what I felt through my work as a principal of schools at different levels, and accordingly the problem of the study was represented by answering the following questions:
- The first question: What is the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District in Irbid Governorate-Jordan?
- The second question: What is the level of professional competencies of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District in Irbid Governorate-Jordan?
- The third question: Is there a statistically significant relationship at the level (α ≥ 0.05)) between social intelligence and vocational competencies of male and female principals of public schools in Bani Kinana District in Irbid Governorate-Jordan?
- The fourth question: Are there statistically significant differences at the level (α ≥ 0.05)) in the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in Bani Kinana District in Irbid Governorate due to the study variables (gender, educational qualification, years of administrative experience)?
The Importance of Studying
The importance of the study is highlighted by the importance of its topic, which deals with the concept of social intelligence and its relationship to the professional competencies possessed by administrators in public schools. As well as by being one of the studies that enable researchers in its field to rely on when conducting their research.
Objectives of the Study
The current study aimed to:
1. Identifying the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana district of Irbid Governorate- Jordan.
2. Identifying the level of vocational competencies of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinanah district of Irbid Governorate- Jordan.
3. Detection of differences in the level of social intelligence among public school principals due to the variables of gender, years of administrative experience and educational qualification.
4. Exploring the relationship between social intelligence and professional competencies among principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana district of the Irbid Education Directorate in Jordan. Terminology of Study
* Social Intelligence (Idiomatically): Social intelligence is the ability to communicate with others, and to build relationships dominated by love and commitment. It is formed as a result of a person’s understanding of himself, and his ability to control his emotions, and therefore it is very related to emotional intelligence. As emotional intelligence covers several aspects related to emotional awareness, and how a person manages his life before sharing it with others, While the role of social intelligence begins with communicating with others; Where a person needs to employ social intelligence skills; Such as expression, dialogue, listening, reconciliation, and others (Othman, [7]).
* Social Intelligence (Procedurally): It is the process through which the two processes of communication and effective communication are mastered between school principals on the one hand, and the cadres working in them, including teachers, students, and others in the schools of the Bani Kinana District.
* Professional Competencies (Idiomatically): adequacy refers to a willingness to be able to perform certain actions and acquired knowledge, which may be embodied in the individual’s ability to produce well and quickly, creation and creativity, and good judgment on matters, and fair and transparent evaluation (Khreisat , [8]).
* Professional Competencies (Procedural): It is one of the contemporary and modern educational strategies in the administrative and educational process, which is based on a positive approach in identifying and formulating the elements of educational activity.
* School Principals: They are the leaders in charge of administrative work from the principals of governmental schools (males and females) in the Bani Kinana District in Irbid Governorate - Jordan.
Study Limits and Obstacles
A. The limits of the study:
- Spatial limitations: The study was limited to public schools in Bani Kenana District, Irbid Governorate, Jordan.
- Limits of Objectivity: The study was limited to identifying the level of social intelligence and its relationship to the professional competencies of school principals in Bani Kenana District - Jordan.
- Human limits: The sample of the study was limited to principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District in Irbid Governorate- Jordan.
- Temporal limits: The study was applied during the first semester of the academic year (2021/2022).
Related Previous Studies and The Location of The Current Study, Including
This part of the chapter includes the following studies related to its subject, arranged in descending order:
Al-Khazaleh and (Al Omari, [1]) conducted a study aimed at determining the level of social intelligence and job performance among secondary school principals in the Directorate of Education of Irbid District, from the teachers’ point of view, And revealing the extent to which there are statistically significant differences at the level of significance (0.05) or less in the averages of the sample’s estimation of the level of social intelligence and job performance of secondary school principals in the Directorate of Education of Irbid District, due to the variables (sex, educational qualification, and years of service), To achieve the objectives of the study and to answer its questions, the descriptive-relational approach was used, and the study sample was chosen by the simple random method, representing (7%) of the study population, during the academic year (2019/2020), The results showed that the level of social intelligence of secondary school principals in the Directorate of Education of Qasaba Irbid from the point of view of teachers was high. The results also showed that the level of job performance of secondary school principals in the Directorate of Education of Qasaba Irbid from the point of view of teachers was significant. The results also showed that there is a correlation between social intelligence and job performance among secondary school principals in the Directorate of Education of Qasaba Irbid from the point of view of teachers.
(Asiri, [4]) conducted a study aimed to identify the effect of using the project method in teaching citizenship and social studies on the social intelligence and achievement among intermediate level students in Riyadh, where the study included two main questions to detect the effect of using the project method in teaching citizenship and social studies on the students’ social intelligence levels (oral, and behavioral ), and on the achievement of intermediate level students in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. In order to achieve these questions; the study used the experimental method (quasi-experimental). The results revealed a statistically significant differences at the level of significance (0.05), between the mean scores of the experimental group and the control group according to the social intelligence scale in the post test in favor of the experimental group, as well as a statistically significant differences at the level of significance (0.05 ) between the mean scores of the experimental group in social intelligence between the two tests (pre and post) in favor of the post test , and the results showed a statistically significant differences at the significance level (0.05) between the average test scores for the experimental and the control group in favor of the experimental group, and finally the results of the study showed a statistically significant differences in achievement at the significance level (0.05) between the mean scores of the experimental group in the pre and post tests in favor of the post test.
(Ali, [9]) conducted a study aimed to identify the extent of the use of social media and its relationship to the administrative responsibility of kindergarten principals. The study was conducted on a sample of (108) kindergarten principals in governmental and private kindergartens affiliated to the six directorates of education in Baghdad for the academic year (2018-2019), The researcher built two scales, one to measure the extent of social media use, consisting of (28) items, and the other to measure administrative responsibility, consisting of (32) items. This is after extracting the statistical characteristics of the scales; After applying the standards to the research sample, the results were shown There are significant differences in the extent of using social media, in favor of the sample average. And there are no significant differences in the extent of using social media according to the variable of specialization. And there are no significant differences in the extent of using social media between the private and governmental directors of Riyadh, and there are significant differences in administrative responsibility in favor of the sample average. And there are no significant differences in administrative responsibility according to the specialization variable. And the absence of significant differences in administrative responsibility between female principals in Riyadh according to the variable of kindergarten type (governmental and private), and it was found that there is a weak and non-statistical correlation between the variables of the study.
(Al Khazala, [10]) conducted a study aimed to determine the level of social intelligence and job performance of secondary-school principals in the educational directorate of Irbid and to reveal the extent of the presence of statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α=0.05) in the averages of the sample members’ assessment of the level of social intelligence and job performance of secondary- school principals in the educational directorate of Irbid attributed to the variables of (gender, educational qualification and years of service). To achieve the goals of the study and answer its questions, a descriptive, correlational approach was used and the study sample was chosen by the simple random method to represent 7% of the study population during the academic year (2019/2020), where (200) questionnaires were distributed. The sample consisted of (189) male and female teachers. The results showed that the level of social intelligence among secondary-school principals in the educational directorate of Irbid from the teachers’ point of view was high and the level of job performance of secondary-school principals in the educational directorate of Irbid from the teachers’ point of view was high. In light of the study results, the study recommended maintaining and reinforcing this degree through holding an integrated program of different courses and training programs, aa well as specialized workshops in this aspect.
(Al Maghribi, [11]). conducted a study aimed at measuring the relationship of social intelligence with the professional competence of secondary school teachers in the city of Makkah Al-Mukarramah. The study also showed that there is a correlation between social intelligence and the components of professional competence among teachers. The study recommended conducting more research and studies in the field of professional competence, in addition to the need to spread the culture of social intelligence in all its forms among workers Universities, schools and educational institutes. (Omran, [6]) conducted a study aimed to seek about the relationship between professional competence and o moral intelligence in kindergarten female teachers. Using a sample of 128 (one hundred and twenty-eight) kindergarten female teachers, from the (Rural) Bandar Damanhour Educational Administration and the (Urban) Damanhour Educational Administration, the study employs an analytical method based upon certain variables, in order to identify such correlation between professional competence and moral intelligence. It also builds upon two research tools: the Professional Competence Scale as developed by Hanaa (Abdul Karim, [12]) conducted a study aimed to identify the relationship between social intelligence and leadership competences of educational institutions headmasters. Method of the study: The research has used the descriptive correlational approach in conducting this study. Tools of the study: Scale of social intelligence by (Ali, [9]).
Scale of leadership competency. Sample of the study: The sample of this study is composed of 859 headmasters (males and females) who are working in educational institutions in M’sila city during the academic year 2021/2022. Result of the study: The study has revealed the following results : The level of social intelligence of educational institutions headmasters is average level. The most available leading competency of headmasters of educational institutions is the competency of strategic thinking , then leadership competency to change, then the competency of leading the employees and developing their abilities respectively . The absence of effects that show related functions between gender , years of experience , and educational level on social intelligence of headmasters of educational institutions or on any of its sub-dimensions . The absence of effects that show related functions between gender and years of experience on leadership competencies of headmasters of educational institutions. There is a correlative relationship between social intelligence and leadership competency of headmasters of educational institutions as followed: - Between the overall degree of the social intelligence and that of the leadership competency in the level of signification 0.01 - Between the overall degree of social intelligence and strategic thinking competency, improving and developing employees skills competency, then leadership competency to change in the level of signification 0.01. - Between the overall degree of leadership competency and the dimensions of the social intelligence (analysis of social information, social skills, social awareness, social self, social passion, and solving social problems) in the level of signification 0.01 [13].
We can predict the leadership competency of the headmaster through the overall degree of social intelligence and some of its dimensions as follows: - More predictable overall degree of social intelligence of strategic thinking competency, then social skills dimension, then solving social problems dimension and last analysis of social information dimension with the least impact, and it is with statistical significance at less than (0.01) level of significance. - More predictable overall degree of social intelligence of improving and developing employee’s skills competency, and it is followed by social competencies dimension, and finally analyzing social information dimension the least impactful and it has a statistical significance at less than (0.01). - The more predictable overall degree of social intelligence of leadership competency to change; then social problems dimension, and finally the least predictable social self-dimension and it has a statistical significance at less than (0.01).
Method and Procedures
This part of the study includes a description of the study methodology, its sample, its community, the instrument used, its validity and stability, and the correction of the instrument, its variables, and its procedures. The following is an overview of that:
• Study Methodology: The researcher used the descriptive correlational approach to achieve the objectives of the study and to answer its questions, in order to describe, analyze and interpret the results of the respondents’ responses about the level of social intelligence and the level of professional competencies of school principals in Bani Kinana District.
• Study Population: The study population consisted of the principals of public schools in the schools of the Bani Kenana District in the first semester of the academic year (2020/2021), and their number was (98) principals.
• Study sample: The study sample chosen by the researcher consisted of all members of the community. Where the number reached (98) male and female principals in the public schools affiliated to the Bani Kinana District, distributed according to the variables (gender, educational qualification, and years of administrative experience), and the following Table 1 explains this:
To achieve the objectives of the study, a measure of social intelligence and a questionnaire of professional competencies were used, which were developed by the researcher. This can be explained as follows:
• The study tools: The researcher prepared and built two tools,
• The First: To measure the social intelligence of school principals.
• The Second: To measure their professional competencies; The first included (28) items within four domains, and the second included (20) items within five domains of the main professional competencies.
• First: Social Intelligence Scale Tool: The scale consists of (28) items distributed on dimensions as follows:
- The first dimension: social competence. It consists of paragraphs (1-7).
- The second dimension: social tolerance. It consists of paragraphs (8-13).
- The third dimension: emotional participation. It consists of paragraphs (14-20).
- The fourth dimension: social skills. It consists of paragraphs (21-28).
• Second: Professional competency measurement tool: The scale consists of (20) items distributed as follows:
- Cognitive Competencies: It includes paragraphs (1-4).
- Emotional Competencies: These include paragraphs (5-8).
- Human competencies: they include paragraphs (9-12).
- Production competencies: it includes paragraphs (13-16).
- Technological competencies: it includes paragraphs (17- 20).
The validity of the two tools of the study: After designing the two scales “the two questionnaires” in their initial form, they were presented to a group of (10) arbitrators with specialization and experience from faculty members in the departments of the faculties of education in Jordanian universities. The first tool included (28) items. The second tool included (20) paragraphs, and the arbitrators were asked to judge the quality of the paragraphs’ content. And expressing an opinion on the linguistic formulation and its integrity, the suitability of the paragraph for the field under which it was included, and the linguistic accuracy, in addition to any other opinions that they may deem appropriate, whether by deletion, addition or modification. The arbitrators made many remarks, as some paragraphs were modified, and the opinion of the majority (85%) was adopted.
The Stability of The Two Study Tools
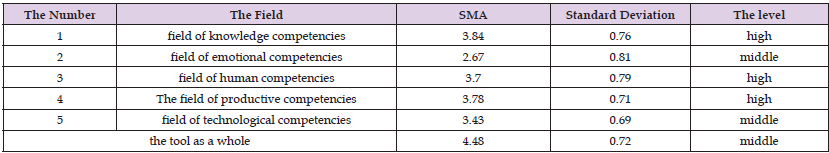
To verify the stability of the two study tools, the stability coefficients were calculated for them, in two ways: the first is the test and re-test method, as they were applied to an exploratory sample of the study population (principals of schools in the Bani Kinana Brigade) who were not members of the household and they numbered (25) male and female principals. By applying them twice, with an interval between the first application and the second application of two weeks. Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated between the results of the two applications, as the stability coefficients for the domains of the two tools ranged between (0.83 - 0.87), The value of the total correlation coefficient was (0.87). As for the second method, the Cronbach alpha method was used to identify the internal consistency of the paragraphs, where the values of the stability coefficients for the domains of the two tools ranged between (0.86 - 0.90) and (0.91) for the domains as a whole, they are acceptable values for conducting such a study. Tables 2 & 3 show that:
Table 2: Shows the values of the recurrence stability coefficients and the internal consistency for each domain of the scale.
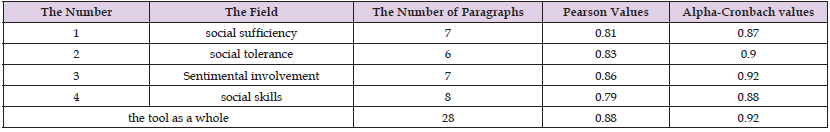
Table 3: Shows the values of the recurrence stability coefficients and the internal consistency for each domain of the scale.
Correction of the two study tools: A five-point Likert scale was used for approval scores for both tools, as follows: very high (5) degrees, high (4) degrees, average (3) degrees, low (2 degrees), very low (1 degree( , To estimate the level of social intelligence and its relationship to the professional competencies of school principals in Bani Kenana District - Jordan. The following statistical grading was used to deal with the arithmetic averages of the respondents’ estimates, according to the category length formula as follows:
category length = upper limit - lower limit / Number of categories 5-1 / 5 = 1.33 .
Therefore, it is:
1 + 1.33 = 2.33, the lowest is the lowest level
2.34 to 3.67 average level
3.68 and above is high
Study Variables
The study included the following variables:
1. Independent Variables: These include the following:
- The main independent variable: the social intelligence of school principals in the Bani Kenana District - Jordan. Secondary
- Independent Variables:
* Gender: It has two levels (male and female).
* Academic Qualification: It has two levels (high diploma, master’s, doctorate).
* Years of Management Experience: It has two levels: (less than 5 years, from 5 years to less than 10, and more than 10 years).
2. The Dependent Variable: the professional competencies of school principals in the Bani Kenana district - Jordan.
Study Procedures
The study was carried out according to the following procedures:
1. Two study tools were designed.
2. The study tool was presented to a number of arbitrators from the faculty members in the Jordanian universities in the departments of the faculties of education.
3. The study tool has been produced in its final form.
4. The study subjects were identified.
5. The questionnaire was distributed to all members of the study.
6. (98) questionnaires were distributed to school principals, and when reviewed, the data were complete, so they were all subjected to statistical analyses.
7. After completing the application of the study, the data were stored on the computer.
8. The appropriate statistical processing of the data was carried out using the statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) program on the computer to obtain the results.
9. The study questions were answered by presenting, analyzing and discussing the results in light of the theoretical literature and previous studies.
Statistical Analyzes
The researchers used the following statistical analyzes:
1. Pearson coefficient, and Cronbach-alpha equation.
2. Arithmetic means and standard deviations.
3. Multiple analysis of variance test (MANOVA).
Presentation and Discussion of the Results of the Study
This part includes a presentation of the results that were reached, after the researcher collected the data using the study tool, and presented it according to the study questions.
The Results Related to the First Question
What is the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District of the Directorate of Education of Irbid Governorate in Jordan?
To answer this question: The arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates were calculated on the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view, as they were shown in the following Table 4:
Table 4: Shows the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates on the domains of the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view, arranged in descending order.
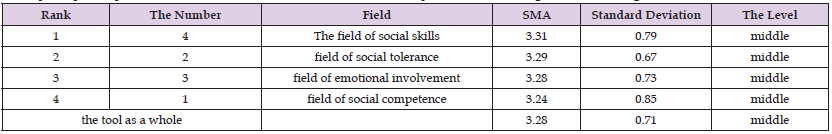
Note: Maximum score out of (5)
Table 4 above shows that the “Social Skills field” ranked first with an arithmetic mean (3.31) and a standard deviation (0.79) and an average level, The field of social tolerance came in second place, with an arithmetic mean (3.29) and a standard deviation (0.67), with an average level. The “Social Competence field” came last, with an arithmetic mean (3.24) and a standard deviation (0.85), with an average level. The arithmetic mean of the sample’s estimates on the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view as a whole was (3.28) with a standard deviation of (0.71), And at an average level The arithmetic means and standard deviations of the estimates of the study sample were calculated on the areas of estimating the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view in the Bani Kinana District, as they were as follows:
The First Field: The Field of Social Competence
Arithmetic means and standard deviations were calculated for the study sample’s estimates of the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view in the Bani Kinana District on the items of this field. Where they were as shown in the following Table 5. Table 5 above shows that the arithmetic averages ranged between (3.14 - 3.87) and that paragraph (1), which stipulated “I have the ability to communicate with others from the first meeting,” ranked first with an arithmetic mean (3.87) and a standard deviation (0.91) with a level of high, Paragraph (5), which reads “I find myself in different social situations,” ranked last, with an arithmetic mean (3.14) and a standard deviation (0.76) at an average level. The total arithmetic mean of the respondents’ estimates on the paragraphs of this domain as a whole was (3.45) and a standard deviation (0.85), at an average level. This may be due to the nature of the surrounding work conditions and to the prevailing organizational climate, and this may be due to the form of hierarchical communication.
Table 5: Shows the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates on the items in the field of social competence, arranged in descending order.
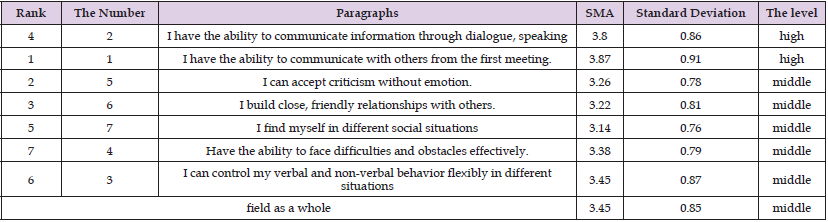
Note: high score out of (5).
The Second Field: The Field of Social Tolerance
The arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates of the level of social intelligence level of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana District were calculated from their point of view in the Bani Kenana District on the items of this field, as they were as shown in the following Table 6. Table 6 shows that the arithmetic means ranged between (2.74 - 3.81), and paragraph (13), which stipulated “I care more about points of agreement with others than disagreement,” ranked first with an arithmetic mean (3.81) and a standard deviation (0.97) with a high level. Paragraph (8), which reads “I respect any decision taken by others to solve their problems,” ranked second, with an arithmetic mean (3.05) and a standard deviation (0.70) at an average level. The arithmetic mean of the sample’s estimates on the paragraphs of this field as a whole was (3.29) and a standard deviation (0.67), at an average level. This may be due to the nature of socialization that surrounds the parties to the educational process.
Table 6: Shows the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates on social tolerance items, arranged in descending order.
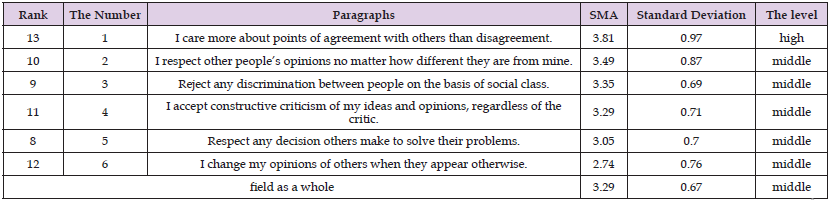
Note: high score out of (5).
The Third Field: The Field of Emotional Participation
Arithmetic means and standard deviations were calculated for the study sample’s estimates of the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view on the items in this field, as they were as shown in the following Table 7. Table 7 shows that the arithmetic averages ranged between (3.74 - 2.70) and paragraph (15) which stipulated “I can recognize the feelings of others even if they try to hide them” ranked first with an arithmetic mean (3.74) and a standard deviation (0.84) with a high level, While I occupied Paragraph (17), which stated: “I value the feelings of others and put myself in their shoes.” The last place, with an arithmetic mean (2.70) and a standard deviation (0.73), with an average level, the arithmetic mean of the respondents’ estimates on the paragraphs of this field as a whole was (3.27) and the standard deviation was (0.73), at an average level.
Table 7: Shows the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates on the paragraphs of the field of emotional participation, arranged in descending order.
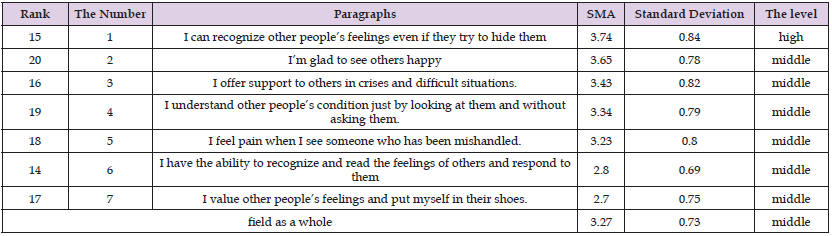
Note: high score out of (5).
The Fourth Field: The Field of Social Skills
The arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates of the level of social intelligence of the principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District were calculated from their point of view on the items of this field, as they were shown in Table 8. Table 8 shows that the arithmetic averages for this field ranged between (2.63 - 3.85) and that paragraph (28), which stipulates “I can lead a team and teamwork in a project,” ranked first with an arithmetic mean (3.85) and a standard deviation (0.73) with a level of high, Paragraph (27), which states “I can predict the behavior of others in different situations,” ranked last, with an arithmetic mean (2.63) and a standard deviation (0.80) and an average level. The arithmetic mean of the respondents’ estimates on the items of this domain as a whole was (3.31) and a standard deviation (0.79), at an average level. This may be due to the poor communication capabilities of the parties to the educational process. Results related to the second question: What is the level of professional competencies of school principals in Bani Kinana District from their point of view? To answer this question; Arithmetic means and standard deviations were calculated for the estimates of the study sample on the items of the scale of the level of professional competence of school principals in the Bani Kinana District from their point of view, and each of its fields. This is shown in the following Table 9.
Table 8: Shows the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study sample’s estimates on the field of social skills, arranged in descending order.
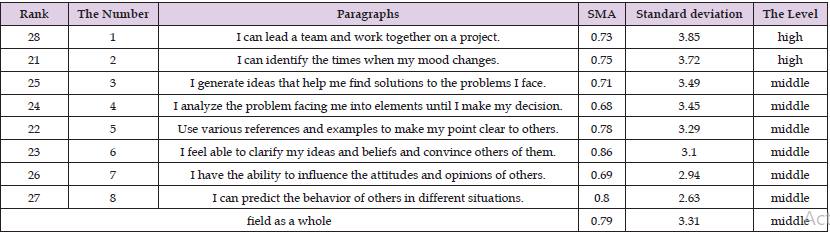
Note: high score out of (5).
Table 9: The arithmetic means and standard deviations of the estimates of the study sample on the paragraphs of the scale of the level of professional competence of school principals and their assistants from their point of view, and each of its fields is arranged in descending order
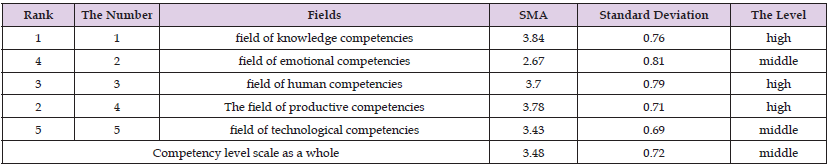
Table 10: Shows the arithmetic means, standard deviations, and the level of the sample’s estimates on the items of each domain.
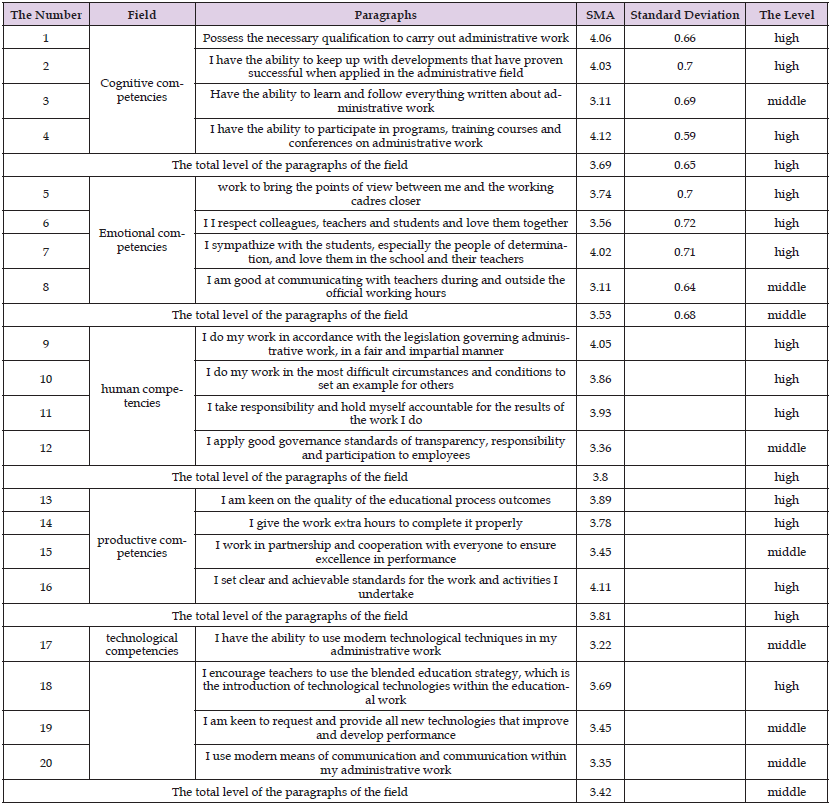
It is noted from Table 9 above that the level of professional competencies of school principals and their assistants in the Bani Kinana district, from their point of view, was at an average level; And with an arithmetic mean (3.48) and a standard deviation (0.72), Arithmetic means and standard deviations were calculated for the study sample’s estimates on the items of professional competencies (cognitive competencies, emotional competencies, human competencies, productive competencies, and technological competencies). The principals of public schools in the Bani Kinana District have their point of view, which is illustrated in the following Table 10. It is clear from Table 10 above that the overall mathematical averages of the estimates of the sample personnel in the fields of the level of professional competencies among school principals; It ranged between (3.42 - 3.81), where the field of “production competencies” ranked first and in my mid -account (3.81). The field of “human competencies” came second and in the midst of my total account (3.80), and the field of “cognitive competencies” came at the third rank in my account (3.74), and the field of “emotional competencies” came fourth and in the midst of my total account (3.53), Finally, in the fifth rank, the field of “technological competencies” came and in my account (3.42), and this may be due to the shape and nature of the prevailing school administration and the administrative style that it believes in.
Results related to the third major question: Is there a statistically significant relationship at α 0.05)) between social intelligence and professional competencies among the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade in the Erbd-Jordan Governorate? To answer this question; Pearson’s correlation transactions were calculated between the average estimates of the sample members at the level of social intelligence and their estimates on the professional competencies of the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade, and the following Table 11 shows this. It is clear from Table 11 the existence of a positive correlation with a statistically significant significance at the level of significance (α 0.05) between the averages of estimates of the level of social intelligence and their estimates on the professional competencies of the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade. The results related to the fourth question: “Are there statistically significant differences at the level of (α 0.05) in the level of social intelligence among the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade in the Arbad Governorate, due to the gender variables, the scientific qualification and years of administrative experience? To answer this question: the mathematical averages, standard deviations, the value of the test (T) and the level of indication of the estimates of the sample members were calculated in the areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and directors of government schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade, Depending on the different study variables: gender (male, female), the scientific qualification (high diploma, master, doctorate), the variable years of administrative experience (less than 5 years, from 5 years to less than 10 years, 10 years or more), which clarifies Table 12 Next.
Table 11: Pearson’s correlation transactions show between the average estimates of members of the study sample at the level of social intelligence and their estimates on professional competencies of the directors and directors of government schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade.
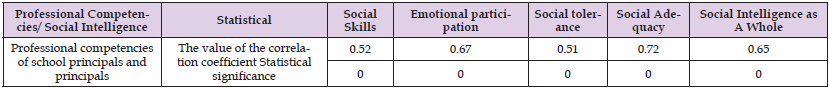
Note: It is statistically significant at the level of significance (∝≤0.05).
Table 12: Shows the mathematical averages and standard deviations of the degrees of members of the study sample on the total mark and in the areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and directors of government schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade according to the variables of the study.
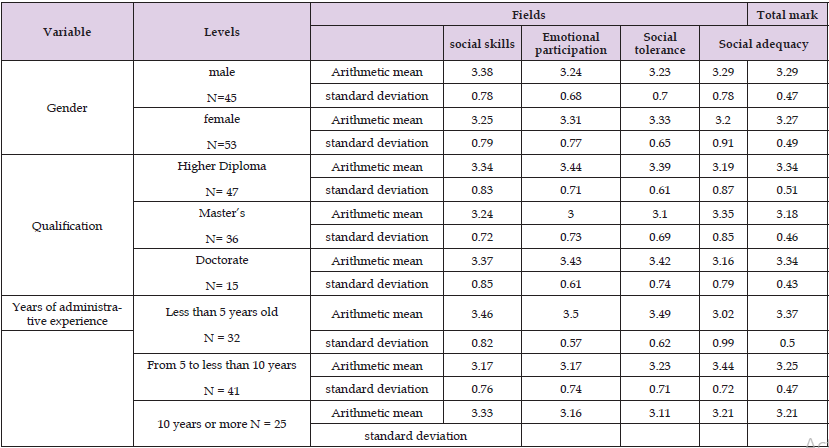
It is noticed from Table 12 the existence of apparent differences between the estimates of the members of the study sample on the total mark of the scale, and the four areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade, According to the independent study variables (gender, scientific qualification and years of administrative experience), and to reveal the significance of these differences in mathematical averages, MANOVA is used using the “Lambda” test “Lambda” at the significance level (0.05 ≥ α). Table 12 shows the results of the Wilkes test for the principle and the results of the multi -variable contrast analysis.
Table 13: Shows the results of the multiple contrast analysis test between the estimates of the sample members in the areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade and the total brand depending on the different gender variables, the scientific qualification and years of administrative experience.
Note: Statistically significant at the level of statistical significance (α0.05).
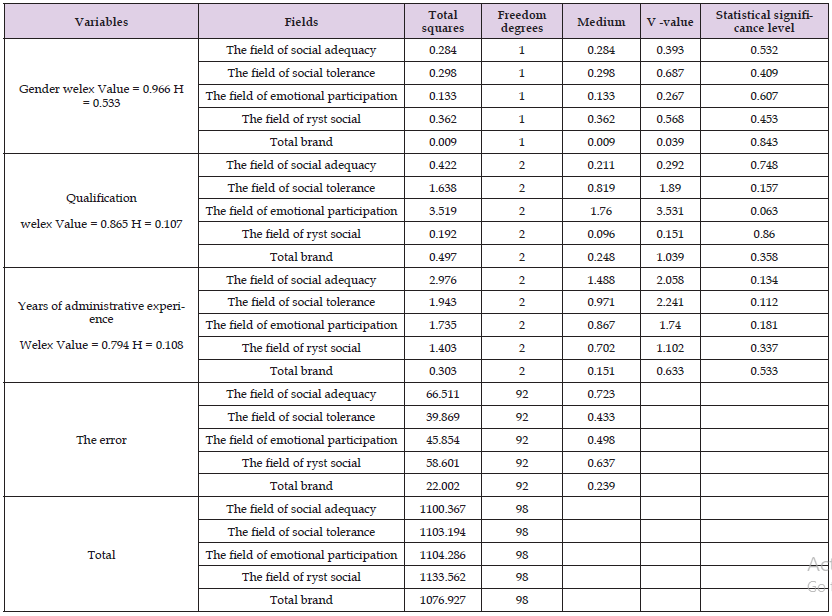
It is mentioned from Table 13 above the following:
1. There are no statistically significant differences at the level of statistical significance (α≤0.05) between the average estimates of the sample personnel in all areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and principals of government schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade and the total brand depending on the difference in the gender variable.
2. There are no statistically significant differences at the level of statistical significance (α ≤ 0.05) between the average estimates of the sample members in all areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and directors of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade and the total brand according to the difference in the variable of the educational qualification.
3. There are no statistically significant differences at the level of statistical significance (α ≤ 0.05) between the average estimates of the sample personnel in all areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade and the total brand depending on the difference in the variable years of experience.
* The level of social intelligence among the directors and principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade from their point of view as a whole came at an average level.
* The level of professional competencies among the directors and principals of public schools in the Bani Kananah Brigade, from their point of view, came at an average level.
* The existence of a positive correlation with statistically significant at the level of significance (α 0.05) between the averages of estimates of the level of social intelligence and their estimates on the professional competencies of the directors and principals of public schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade.
* The absence of statistically significant differences at the level of statistical significance (α≤0.05) between the average estimates of the sample members in all areas of the level of social intelligence among the directors and principals of government schools in the Bani Kenana Brigade and the total brand depending on the different variables of the study (gender, scientific qualification, number of years administrative experience).
- The number of courses and training programs to develop and activate social intelligence among school administrators.
- Working to develop professional competencies among school principals so that they can perform their duties and the tasks of their work with excellence and mastery, which reflects positively on the outputs that achieve the desired and desirable goals of the educational pro.


