Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Juan Carlos Salazar Conde* and Giselle Adriana Arcos Streber
Received: January 10, 2024; Published: January 24, 2024
*Corresponding author: Juan Carlos Salazar Conde, Médico Especialista en Anestesiología, Profesor titular, Curso de Anestesiología en el Hospital General de Naucalpan, Mexico
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2024.54.008583
Osteoarthritis (OA) is definitely a major public health problem due to the large proportion of the population affected, the duration of the evolution and the lack of treatment. The main causes are traumatic inflammation, aging, metabolic syndrome and biomechanical misalignment. Recently, a close connection between intestinal inflammation and chronic joint inflammation was demonstrated; It may be associated with microbiome dysbiosis, which corresponds to an imbalance between pathogenic and commensal bacteria resulting from stress, dietary components, drugs such as antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Objective: To demonstrate functional improvement three months after ingesting Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C in patients with gonarthrosis symptoms.
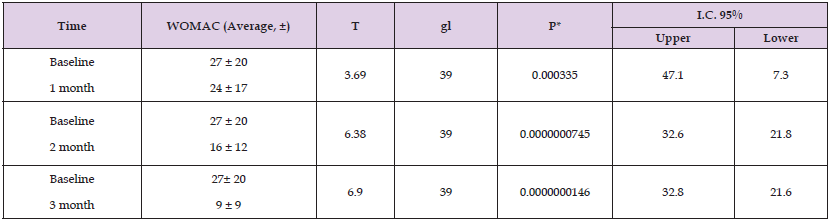
Results: The consumption of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 for 3 months, assessing joint function using the WOMAC scale, is statistically significant with a value of p<0.05 (p= 0.0000000146).
Conclusions: The use of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C for three months in patients with OA decreased the WOMAC Scale p=0.0000000146 and VAS p=0.0000000204, both p<0.05, which are statistically significant, which translates into recovery of joint function and reduction of pain, presenting an improvement in the quality of life of patients subjected to the consumption of this dietary supplement.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is definitely a major public health problem due to the large proportion of the population affected, the duration of the evolution and the lack of treatment. OA is a whole joint disease that affects both articular and periarticular tissues, but OA can have different clinical phenotypes. The main phenotypes described in the literature are traumatic inflammatory, aging, metabolic syndrome and biomechanical misalignment. Each of these could require a specific intervention and/or treatment. Currently available interventions aim to reduce symptoms (i.e. pain, inflammation and impairment of joint functionality), but none of them are capable of maintaining or restoring joint structures. So far, all recommendations refer to symptom control. New treatment alternatives are necessary aimed at the structural changes associated with OA [1]. It has been estimated that the prevalence of OA in Mexico is 10.5% (95% CI 10.1 to 10.9), being more common in women (11.7%) than in men (8.7%), although it varies enormously in different regions of the country. country; In Chihuahua the prevalence is 20.5%, in Nuevo León 16.3%, in Mexico City 12.8%, in Yucatán 6.7% and in Sinaloa 2.5% (p < 0.01). Worldwide, the prevalence is 43.3% (95% CI 42.7-42.9) in the hand, 23.9% (95% CI 23.6-24.2) in the knee, and 10.9% (95% CI 10.6-11.2) in the hip [1].
Recently, a close connection between intestinal inflammation and chronic joint inflammation was demonstrated, opening new therapeutic perspectives. This relationship is now documented for spondyloarthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and OA. Two main hypotheses have been proposed to explain the relationship between inflammation and the mucosal immune system. The first refers to bacterial translocation, which corresponds to an increase in the permeability of the lumen of the intestinal wall and the exposure of the immune system to commensal microbiota that is not physiologically linked to a disease. The second suggests that chronic inflammatory arthritis could be associated with microbiome dysbiosis, which corresponds to an imbalance between pathogenic and commensal bacteria resulting from stress, dietary components, drugs such as antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or inflammatory bowel diseases [2-3]. This second mechanism involves the recruitment of lymphocytes from the intestine or activated macrophages to the joints and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The content of LPS depends on the nature of the microbiome and its biological activity requires the toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway [3]. (Figure 1) Finally, and interestingly, it was suggested that the administration of probiotics could not only act to reduce inflammation and pain, but also modulate the effectiveness of an anti-OA treatment [4].
Together, these findings suggest that measures that could correct intestinal permeability and/or joint microinflammation could be effective modalities for treating or preventing chronic arthritis such as OA. One approach is the administration of a cocktail of metabolites derived from probiotics. Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 has recently been characterized and shown to promote the growth of bifidobacteria. This specific strain has been selected for its action on the immune response and possible applications in inflammatory disorders. This strain was shown to colonize the lower parts of the intestine where they reduce bacterial translocation. Furthermore, it was shown that the tested product, when administered orally, reduces the translocation as well as the spread of bacteria (WO 2004/093898 and WO 2006/040485) [5]. Vitamin C is necessary for the growth and repair of tissues in all parts of the body. It is necessary to produce collagen, being involved in the generation of skin, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels. Promotes wound healing and forms scar tissue. Repairs and maintains cartilage, bones and teeth [6]. A useful tool to assess joint function is the modified WOMAC (The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) scale. The modified scale went from 24 to 32 items, in the pain dimension it has nine items, ten in the rigidity dimension and 13 in physical function; evaluated on an ordinal scale and submitted to the assessment of the panel of experts through a five-step Likert scale, in which they ratified the importance they attributed to each item.
Descriptive measures were calculated, among which 4.33 and 5.0 stand out as average. Each indicator was given a score from zero to four, so the scale showed a minimum of zero and a maximum of 128 points, the lowest value obtained (0) refers to those patients who are not affected, and the The highest (128) corresponds to the most symptomatic patients or those with the most difficulties [7,8].
Demonstrate functional improvement three months after ingesting Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C in patients with gonarthrosis symptoms.
• Determine the efficacy of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C in patients with gonarthrosis symptoms.
• Evaluate the effectiveness of the product using the WOMAC scale.
• Examine the improvement in pain using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS).
Type of Study
• Type of research: Clinical trial.
• According to the researcher's intervention: Quasi-experimental.
• According to the moment in which the data will be produced: prospective and longitudinal.
• Place of study: Workers and family members of a company.
• Study population: Patients with gonarthrosis symptoms.
Sample Size
A total of 40 patients were entered into the study, among whom with mild to moderate gonarthrosis symptoms.
Inclusion Criteria
• Signing of informed consent.
• Patients aged 30 to 75 years.
• Any weight, indistinct sex.
• With or without comorbidities (controlled).
• Not suffer from rheumatoid arthritis.
Exclusion Criteria
• Patients over 75 and under 30 years of age. • Having received any type of intra-articular treatment. • Having previously had knee surgery. • Have sequelae of intra-articular fracture,• Having third degree genu valgus or superior varus, having knee arthroplasty, decompensated gout, untreated osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis or some type of cancer.
Elimination Criteria
• Patients in whom planned measurements are performed.
• By voluntary withdrawal of the patient.
Development of the Study
• 40 patients with symptoms of gonarthrosis, company workers and their relatives interested in participating in the study, signed informed consent for their participation for three months.
• An intake evaluation of the modified WOMAC scale and VAS was performed to determine the degree of pain, stiffness, and physical function of the knee joint.
• The study participants were given a monthly dose corresponding to one month for consumption every 24 hours, which will be refilled monthly in the follow-up consultation with the appropriate completion of the questionnaire containing the WOMAC scale.
• The WOMAC scale was evaluated for 3 months to determine the effectiveness of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C.
• All information was recorded in the data collection tool and will be concentrated in an Excel database.
• Subsequently, the information was collected and concentrated in a database in the statistical analysis program SPSS V.23 IBM CORP.
The descriptive statistics of the demographic variables were presented in tables and graphs; for quantitative variables, they were calculated with measures of central tendency (mean and median) and dispersion (standard deviation); For qualitative variables, frequencies and percentages were calculated; Box graphs, bars or frequency histograms were made depending on the case; The results were compared using Student's T for quantitative numerical variables when they have a normal distribution; A p value less than 0.05 was considered statistical significance; The statistical analysis will be carried out in the statistical analysis package SPSS V.23 IBM CORP.
40 patients with symptoms of gonarthrosis were studied for three months, with an average age of 51 ± 12 years, body mass index of 27.6 ± 4.2 (Table 1), with an average baseline VAS of 3.8 ± 1.99 and baseline WOMAC of 19.07. ±20.5. Of the participants studied, 70% (n=28) were female and 30% (n=12) were male. 32.5% of the patients (n=13) had normal weight, 50% were overweight (N=40), 1 was obese 7.5% (n=3), 2 were 7.5% obese (n=3), 3 were obese. 2.5% (n=1) (Graph 1). In the comparison of the behavior of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C in the assessment of joint function using the WOMAC scale consuming the food supplement for three months, it was observed that between the baseline measurement compared to the intermediate measurements there were variations in which observed a progressive decrease in the WOMAC scale between the baseline and intermediate measurements, being statistically significant with a value of p<0.05; However, between the comparison of the measurement at baseline and at the end of drug consumption after three months, statistically significant differences were found with p=0.0000000146 (Table 2). The maximum value of the baseline WOMAC scale was 84 with a minimum value of 2, with a mean of 27. 25 and a median of 20; The WOMAC observed 3 months after consumption of the dietary supplement, the maximum value was 9, with a minimum of 0, with a mean of 9.3 and a median of 7 (Graph 1).
Table 2: Comparison of the behavior of the WOMAC scale during three months of consumption of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C.
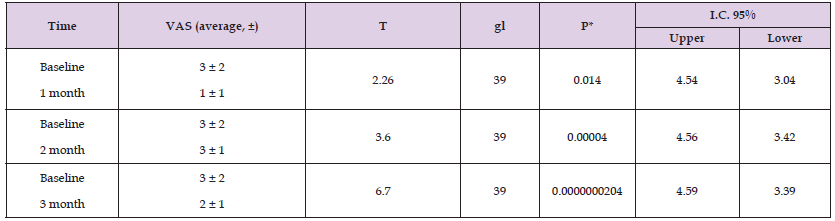
In the comparison of the behavior of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C in the assessment of pain using the VAS scale consuming the food supplement for three months, it was observed that between the baseline measurement compared to the intermediate measurements, there were variations in which it was observed a progressive decrease in the VAS scale between the baseline and intermediate measurements, being statistically significant with a value of p<0.05; However, between the comparison of the measurement at baseline and at the end of consumption of the product at three months, statistically significant differences were found with a p = 0.0000000204 (Table 3). The maximum value of the baseline VAS scale was 9, with a minimum value of 1, with a mean of 3.8, and a median of 24; The VAS observed three months after consumption of the product had a maximum value of 6, with a minimum of 0, with a mean of 1.7, and a median of 1.5 (Graph 2).
Table 3: Comparison of the behavior of the VAS scale during three months of consumption of Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C.
There are few studies on taking Bifidobacterium longum CBI0703 plus vitamin C in human patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis; the study by Juan Chen et.al. reports that this bifidobacteria colonizes the intestinal microbiota in a period of 3 months and that the symptoms decrease in patients with osteoarthritis. Compared to our study, the period of colonization of the intestinal microbiota is corroborated and with which we obtained encouraging results in the recovery of joint mobility and decreased pain. It is recommended to carry out more studies with this dietary supplement in the future to expand the sample of patients and obtain more significant results, because there was a significant improvement in the quality of life of the patients.
The intake of Bifidobacterium longum CBi0703 plus vitamin C for three months in patients with OA decreased the WOMAC Scale p=0.0000000146 and VAS p=0.0000000204, both p<0.05, which are statistically significant, which translates into progress in joint function and reduction in pain, presenting an improvement in the quality of life of patients subjected to the consumption of this dietary supplement.
According to the Official Mexican Standard NOM-004-SSA3-2012, of the clinical medical record, which establishes the criteria for the execution of research projects for health in human beings and the Official Mexican Standard NOM-006-SSA3-2011, of the practice of Anesthesiology, published in the Official Gazette of the Federation, these documents consider in detail the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association on ethical principles for medical research in human beings, According to the regulations of the General Health Law regarding health research, article 17 provides information on the risk that patients may present during research. The probiotic Bifidobacterium longum CBi0703 plus vitamin C was donated by Solidfarma.


