Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Janos Vincze* and Gabriella Vincze Tiszay
Received: June 26, 2023; Published: July 05, 2023
*Corresponding author: Janos Vincze, Health Human International Environment Foundation, Budapest, Hungary
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2023.51.006053
Stress is a complicated concept just as its special literature looks like. For the sake to keep the everyday physical balance, the healthy man creates mentally that stress-level interval which, despite its fluctuations, represents the proper ratio of the equilibrated state. The long-lasting unsuccess may generate failure on other fields whether similar or different and the protracted negative status may call in action itself a process of query. The observation, perception, experience of the stress and the adaptation, sufferance to it, forming of defensive mechanisms jointly appear but not in the same time. The research and application field of psychosomatics, due to the new interdisciplinary aspect has been developed to a new trend. The biological stress is a long succession of active, interactive mutual effect. Psychical stressors are those which come into being independently from the man’s will and destroy – as social factors – psychic and organic components taking place in the response, the organism consequently get tired. Action comes into being when it is threatened by an external factor or mediates such adequate, essential information towards the system that has to be replied. Creativity can be considered as the highest level of the expression of the operational polivalency of the human psyche.
Keywords: Psychological Balance; Psychosomatics; Creativity
Stress is a complicated concept just as its special literature looks like. For the sake to keep the everyday physical balance, the healthy man creates mentally that stress-level interval which, despite its fluctuations, represents the proper ratio of the equilibrated state. Motivation is one of its facilitating factors composed of intrinsic as well as extrinsic constituents. Both set an adaptation process in the individual, first by imagination, later put into the practice whatsoever step by step. Although the unsuccess, failure, lack of self-confidence, delay of recognition, uncertain existence, insecure status are negative judgment forms they may also stimulate to search for new variations. In this case drawing a lesion from the failure one must take another course, prepare another strategy accordingly and apply it gradually. The solution of the question depends upon how long a person can tolerate the mass of negative influences, when does a lethargic state ensue resulting in stagnation.
Stress is a complicated concept just as its special literature looks like. For the sake to keep the everyday physical balance, the healthy man creates mentally that stress-level interval which, despite its fluctuations, represents the proper ratio of the equilibrated state. Motivation is one of its facilitating factors composed of intrinsic as well as extrinsic constituents. Both set an adaptation process in the individual, first by imagination, later put into the practice whatsoever step by step. [1] Although the unsuccess, failure, lack of self-confidence, delay of recognition, uncertain existence, insecure status are negative judgement forms they may also stimulate to search for new variations. In this case drawing a lesion from the failure one must take another course, prepare another strategy accordingly and apply it gradually. The solution of the question depends upon how long a person can tolerate the mass of negative influences, when does a lethargic state ensue resulting in stagnation.
In the natural sciences even with physical phenomena, it is a known fact the summation of small effects the time interval of which we cannot suspect, it is person-dependent. The long-lasting unsuccess may generate failure on other fields whether similar or different and the protracted negative status may call in action itself a process of query. [2] Stress is similar so far to other stimuli as to elicit a lot of somatic responses. We should primarily understand the somatic functions in order to get nearer to the essence of the stress. Alarm reactions originate from the conception of Cannon: once the person is confronted with any kind of difficulty, emotional experience to overcome problems, there happen automatically a long row of somatic changes and although the struggle is mental in the beginning, changes are notwithstanding similar to some kind of „flight”.
The usage flight is symbolically general, nothing else but a mental preparedness carrying out the voluntary action to come which is a purposeful activity. The perceptible part of the stress is the internal restlessness preparing with its pulsation the accomplishment of the conceived action. The organic and psychotic behavioural changes don’t run parallelly and on the same frequency whereas they appear simultaneously despite the shift. The physiological activation processes are parts of the psychical emotional mechanisms, these processes are intensity indicators, markers of the behaviour and aren’t any criteria in directional relation. The born and learnt behaviour as forms are composed in an imperfectly connected system in complicated interaction with each other. The born and the learned behavioural reactions evolve during the long-term effect of the stimulus and do not by the chaotic short, low intensity appearances. There is no correlation between two somatic variables. But correlations are modified in functions of more than two variables; such influencing factors are the cultural surrounding, the intelligence level, tradition, national customs, manner of life (conduct), family structure, etc. The observation, perception, experience of the stress and the adaptation, sufferance to it, forming of defensive mechanisms jointly appear but not in the same time. In consequence of stress producing stimuli, many physiological processes go into action, probably through different paths in close connection; the response is, therefore, an interaction between the organism and his environment [3].
The different somatic processes have got different role in performing the behaviour, the interaction is of different dimension and of temporal order. The different attitudes of stimuli induce different somatic patterns of response being so the cause of the psychosomatic illnesses. Individuals inclined to produce psychosomatic symptoms possess of different and characteristic attitudes. Also the different emotional states result in deviating physiological response patterns or even when stimuli are unaltered these bring about different subjective states, experiences. The pattern derives from the attitude, expectation of the person. From the complex responses of behaviour, from the complex states of stimuli, one cannot separate the essential factors neither to determine the interactions between the somatic response reactions nor estimate them in advance. Also the emotional component takes part in the response reactions through the somatic effect of which it influences the behaviour.
The research and application field of psychosomatics, due to the new interdisciplinary aspect has been developed to a new trend. It searches and treats the human physical and psychical symptoms in their connection and by settled common features, psychosomatic and somatopsychic correlations has been established because of their various etiology which is of primary importance in creating symptoms. [4] It deals of course with genetic factors, too, built into the person’s environment, into its involved effects which makes this aspect mutually unambiguous interactive. As far as sicknesses are concerned the loosened homeostasis takes place on the basis of bed, deficient or weak adaptation caused by outer environmental effects: the different neurotic disharmonies, high blood pressure and its circulatory and organ consequences, gastric and duodenal ulcer, articular and rheumatic complaints, renal illnesses, asthma, allergies etc. In such quality and enlightening, resp. each of them can be appraised as independent, adaptational illness. The biological stress is a long succession of active, interactive mutual effect. This relation which always consists of the difference of value-power-intensity is, like an example of today, a chain of action of two fighter during which they get the offensive and defensive conduct in exchanged role.
The fortune is also changing, the winner prevails but the victory’s price is that he must use up suddenly more of the given adaptative reserve than with the soft harmonic balanced daily conduct [5]. Every struggle induces a biological change. It is most often still a reversible state and apparently will be equalized through different compensatory processes. As psychical stressors there are of significant effect: losing a person or the danger to lose him, the loss of a thing, wounded, injured person, life-danger, threatened state, protracted injustice, legal delay of jurisdiction, precariousness of existence, isolation, overtax of information, sensorial deprivation, leading role or high rank hanged upon an immature personage. Psychical stressors are those which come into being independently from the man’s will and destroy – as social factors – psychic and organic components taking place in the response, the organism consequently get tired. During the harmonic life gradually all human psycho-organic components shall get exhausted. My interdisciplinary aspect suggests me that some greater stress or protracted negative circumstance invades the weakest organ of the body and the interaction the uniform chain-reaction within the organism and its co-operation loosens. In this unbalanced health condition intervene compensating processes but their efficiency varies by organs.
Whilst in the first case ensues harmonic organ and psychical aging in the second case, on the other hand, a stormy struggle between the organism and the psychical defence? The similarity between the symptoms of the somatic diseases and those organic ones caused by psychical tension is misleading. [6] The reactions of the organism, its reaction capacity, the general capability of resistance exert influence on consciousness of the disease and its course. To the mental shock it is generally typical the psycho-somatic change. It is a disease from the point of view of the person and the physician alike in this appeared formation – because the internal regeneration to bring about or restore an equilibrium is a fruitless attempt – the diseased condition has been elicited about whether by corporeal or by spiritual stress, it needs already external medical intervention [7].
The inner life is a multidimensional and at the same time a uniform system. From the point of view of the human individual life the psyche (psychism) is a subsystem. If still we take it out of this relationship with investigational aim then we have to consider it a system. In this respect the human psychism unifies in itself the attributes of integrity, the openness, the complexity of the synthetic character, the probabilisticity, the self-organization i.e. the (active and passive) homing guidance and the self-regulation so we can draw a picture of the highest grade cybernetic system [8]. This is to explain that in the course of searching the human psyche one have to use the general system theory, the internetics and the dimensions of the control regulation. Quite apart from our morphological, functional or spiritual approximation we have to emphasize first of all the internetical connections of its components and peculiar features, those of organization, information delivery, controllability, expediency. The psychology represents a non-substantial, essentially functional system the fundamental role of which is governing and control: referring to the internal conceptual world of the man and by the interest to insure mutual balance as well between the man’s attitude and the outside world [9].
One can establish that the physical system is an isomorphic superstructure of material, energetical and informational cycles of events originating from the in- and outside of the organism and realized in the peculiar alphabet of the logical network of the nervous system. This superstructure evolves place through the self-organization of abstract co¬des created in the course of the juncture of the reflexion- rised imaginal and of the symbolic one. We can plainly say that the spiritual life in cybernetic respect is nothing else but an entropy device subjected to the preservation task of the human-specific psychophysiological homeostasis. The psychical system in organizational viewpoint is of developing character because it forms and develops within the frame of interaction between the man and his environment. It is, therefore, a self-organizing, developing system.The organization of the psychical system is subordinated to the domination areas of the universal laws of the evolution and it is directed also by such particular principles which accentuate more concrete its organizational mechanisms and variants. Out of these let’s mention some: the Le-Chatelier principle, the weakest chain-loop, the efficiency of the energy consumption, the ranking, avalanche-effect, the compensation, the principle of action. [10] In reference to the Le-Chatelier principle: if on a system in rest is operative such an external input which changes one of the conditions resulting the equilibrium state then the system evades in the direction reducing the outcome of the effect.
The principle of the weakest chain-link declares that during a change-over from a given organization to the new one the modification determined by the effect of the directing factors take place mainly in the vulnerable points or chain-loops of the system. For the energy consumption an excellent example is the formation of dynamic stereotypes. Ranking happens when simultaneously more factors affect the living system. The avalanche-effect is well illustrated by the „it’s hit or miss” law of the nervous system in the case of the stimulus-answer reaction. The compensation principle is realized in the living organism in every case of the negative feedback regulation. [11] Action comes into being when it is threatened by an external factor or mediates such adequate, essential information towards the system that has to be replied. According to the system theory, from the of viewpoint of the steering circumstances in the systems the process of the guiding communication takes its course in compliance with the divergency- convergency principle. [12,13] Creativity can be considered as the highest level of the expression of the operational polivalency of the human psyche.
The distance between reality and model the effort and the possibility is such an indicator which determines the real self implementation level of the personality. Since these indicators determine the entity of the psychical organization by their help one can estimate the general development level of the personality which expresses the conformity of the behaviour towards the nature and sense of the external effects. [14] This can be estimated by completing the phase profile of the psychical system on the basis of the main psychical indicators which can be expressed in the form of the following relation:
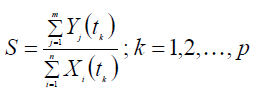
where: