Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Saad M Saad1, Fahim A Shaltout1*, Hashim F Mohammed2 and Amal AA Farag1
Received:November 18, 2022; Published:November 28, 2022
*Corresponding author: Fahim A Shaltout, Department of Food Control, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Benha Univerisity, Egypt
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2022.47.007478
A total 45 fish samples (Tilapia, Claris) were collected from EL-Bagoria, EL-Menofi drainage and Bahr Shibin for detection and determination of organophosphorus pesticides (diazinon, Malathion and chlorpyrifos). Organophosphorus pesticides could not be detected in Bahr Shibin No diazinon in Tilapia from EL-Bagoria but mean value of of Malathion 5.50±2.0, chlorpyrifos 5.0±1.66but from EL-Menofi drainage mean level of diazinon 3.33±0.65, Malathion 4.98±1.22 and chlorpyrifos3.0±0.71but in Claris samples, there were no diazinon, no Malathion, no chlorpyrifos from EL-Bagoria canal but from EL-Menofi drainage, mean value of diazinon 6.8±1.42, Malathion 4.64±0.81 and chlorpyrifos4.0±0.96. Pesticides are one the main contaminants of water sources which are considered the natural environment of fish. on the other hand, fish could be contaminated by pesticides either directly by gills breathing or indirectly through contamination of feeding items, so it is very important to analyze fish samples to detect to what extent the rate of accumulation of pesticides residues in fish flesh and organs.
Keywords: Organophosphorus; Diazinon; Malathion; Chlorpyrifos
Fish is low-fat high-quality protein. Fish is filled with omega-3. Fatty acids and vitamins such as D and B2(riboflavin). Fish is rich in calcium and phosphorus and great source of iron, zinc, iodine, magnesium, and potassium. The American Heart Association recommends eating fish at least two times per week as part of a healthy diet. Fish is packed with protein, vitamins and nutrients that can lower blood pressure and help to reduce the risk of a heart attack or stroke. Fish are known to be highly nutritious and excellent sources of animal protein which are consumed by larger percentage of the world’s population because of its availability and palatability (Shaltout, et al. [1-3]). Fish and fish products are in the forefront offood safety and quality improvement because they are among the most internationally traded food commodities. Fish and fish products are one of the most important food stuffs as they are one of the cheapest sources of animal protein. Fish are enriched with essential minerals, vitamins and unsaturated fatty acids (Shaltout, et al. [4-8]). Today, the environmental pollution is considered one of the most serious problems in the world. The deleterious effect of the environmental pollution of pesticides is one of the principal research activities 1962.contamination of food at animal origin with Organochlorine compounds and their metabolites has been reported in various countries (Neumann, et al. [9-10]).
(Choudhary, et al. [11]): reported that Organophosphorus pesticides causes burning/stinging of eyes, blurred vision, skin redness and itching, excessive sweating and shortness of breath, dry sore throat and burning of nose among spray farmers of Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh India, who sprayed pesticides by themselves and therefore were directly exposed to pesticides. When people come into contact with large quantities of pesticide, this may cause acute poisoning or long-term health effects, including cancer and adverse effects on reproduction (FAO, WHO [12]). Fish and aquatic animals are exposed to pesticides in three primary ways, the first way was through dermal by direct absorption through the skin by swimming in pesticide contaminated waters, the second is breathing by direct uptake of pesticide through the gills during respiration and the third way is oral by drinking pesticide contaminated water or feeding on pesticide contaminated preys. Poisoning of human being occur by consumption of poisoned fish, which termed (secondary poisoning) (Johnson, et al. [13]) Priyadharshini et al. (2017): reported that indiscriminate use and improper handling of synthetic pesticides in agriculture have resulted in serious problems such as asthma, wheeze and chronic bronchitis among the farmers.
This study is made for detection and determination organophosphorus in Nile Tilapia and Claris samples from ELBagoria canal, El-Menofi drainage and Bahr Shibin in Menofia Governorate.
45fish samples of Tilapia and Claris from EL-Bagoria canal, EL-Menofi drainage and Bahr Shibin in Menofia Governorate for detection and determination of organophosphorus (Malathion, Diazinon and chlorpyrifos). The collected samples were packed separately and transferred to laboratory for analysis. Samples were extracted according to AOAC [14]. and Pesticide Analytical Manual [15]. Fifty grams of samples were grinded with 100 gram of anhydrous sodium sulphate in prescence of 150gram of 40-60petroleum ether for 2 minutes then extract was decanted through 500ml Buchnov funnel containing two wattman filter papers number 1/2 The extract was poured through 40ᶍ25mm column of anhydrous sodium sulphate and elutent was collected in 500ml flask. Extraction and clean up by acetonitrile partitioning. Clean up by florisil column was firstly carried out by eluting the column with 200ml of 50 petroleum ether /diethyl ether (v/v). The elute was concentrated by rotator evaporator to dry film which was dissolved by 2ml n-hexane for HPLC determination.
(Figures 1 & 2, Tables 1-4)
Table 1. Statistical Analysis of Organophosphorus Residues (ppb, Wet Weight) in Examined Tilapia Samples.

Table 2. Mean Residue Levels of Organophosphorus Pesticides (ppb, wet weight) in Examined Tilapia Samples from EL-Bagoria Canal and El-Menofi Drainage.
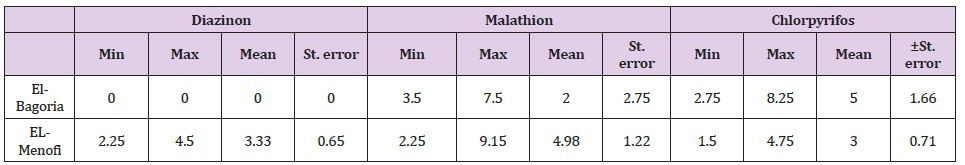
Table 3. Statistical Analysis of Organophosphorus Residues (ppb, Wet Weight) in Examined Claris Samples.
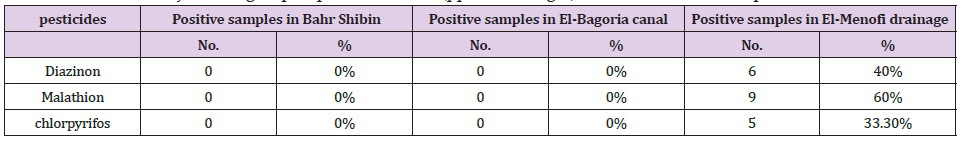
Table 4. Mean Residue Levels of Organophosphorus Pesticides (ppb, Wet Weight) in Examined Claris Samples from EL-Bagoria Canal and El-Menofi Drainage.
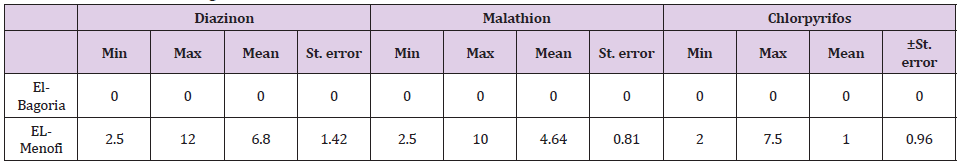
There were no organophosphorus pesticides in Bahr Shibin. The results on the and revealed that no diazinon in Tilapia from EL-Bagoria but mean level of malathion5.50±2.0, chlorpyrifos 5.0±1.66but from EL-Menofi drainage, mean level of diazinon 3.33±0.65, Malathion 4.98±1.22 and chlorpyrifos 3.0±0.71. in Claris samples there was no diazinon, no Malathion, no chlorpyrifos while from EL-Menofi drainage, mean value of diazinon 6.8±1.42, 4.0±0.96.The results of diazinon in Tilapia from EL-Menofi drainage were higher than that detected by (Ibigbami, et al. [16] and (Yahia, et al.[17]).The results of Malathion in Tilapia from EL-Bagoria canal and from EL-Menofi drainage were higher than that detected by (Soumis, et al. [18-19]) and (Yahia, et al. [17]). The results of chlorpyrifos in Tilapia from EL-Menofi drainage were equal to that detected by (Soumis, et al. [18]) but in Tilapia from EL-Bagoria canal were higher than that detected by (Soumis, et al. [18]) and (Yahia, et al. [17]). The results of diazinon in Claris from EL-Menofi drainage were higher than that detected by (Ibigbami, et al. [16]) and (Yahia, et al. [17]). The results of Malathion in Claris from ELMenofi drainage were higher than that detected by (Soumis, et al. [18]) and (Yahia, et al. [17]) The results of chlorpyrifos in Claris from EL-Menofi drainage were higher than that detected by (Soumis, et al. [18]) (0,3 ± 0,3) and (Yahia, et al. [17]).
Organophosphorus Pesticides are one the main contaminants of water sources which are considered the natural environment of fish. on the other hand, fish could be contaminated by Organophosphorus pesticides either directly by gills breathing or indirectly through contamination of feeding items, so it is very important to analyze fish samples to detect to what extent the rate of accumulation of Organophosphorus pesticides residues in fish flesh and organs.


