Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Jesús Cuéllar Álvarez1*, Melva García Martínez2 and Yaquelin Gómez Morales3
Received: July 09, 2022; Published: July 15, 2022
*Corresponding author: Jesús Cuéllar Álvarez, Policlinic “José Ramón León Acosta” of Santa Clara, Cuba
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2022.45.007166
The teaching learning with students guarantees in the adolescents the active appropriation and creator of the knowledge and prepares it to solve the problems that are presented in its professional practice. Objective: To design actions with a pedagogic content for the professional motivation with adolescent’s students. Methods: Was carried out a traverse descriptive study in the understood period of October 2020 to November 2021 it was applied a not structured interview and a questionnaire to adolescent’s students, and it was used mathematical methods for the absolute and relative values. Results: It was verified that in the process teaching learning with adolescent’s students. Conclusions: The students recognized not to know how to identify the essential of the pedagogic content; they have difficulties to still apply it before new situations with the books of texts.
Keywords: Developing Learning; Communication; Pedagogy; Professional Motivation
Developed a descriptive transverse study in the period understood between October 2020 and November 2021 in the teaching poly-clinician for the sake of proposing actions as a pedagogic content with adolescent’s students. The universe was conformed for students’ totality with 60 adolescent’s students selected by aleatory simple sampling.
1. Adolescents’ students.
2. That they wish to take voluntarily part in investigation.
1. Students that had requested extra-teaching licenses.
2. That they do not wish to take part in investigation.
The following variable as from the obtained data were utilized: levels the pedagogic content.
They utilized to students for the purpose of obtaining enlarged information like techniques the not structured interview and the questionnaire for the realization of investigation.
The information stored in a data file in SPSS version itself 21,0 and it presents graphics itself. The information was summarized by means of the calculation of the arithmetical mean, standard deviation, absolute frequencies and percents.
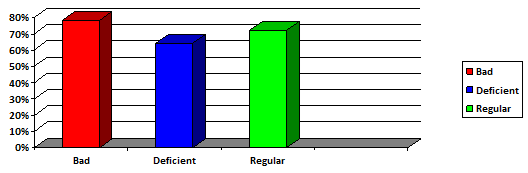
When applying the students, the questionnaire, it became verified that 78 % of these do not know how to identify the heart of the matter of the contents or invariants of knowledge and they tend to learn it by heart, aspect this that does not love one another with the present-day tendencies that you abstain of the learning acquired by memory in the students. 78 % of the students referred that they do not learn from active way, that only they listen to the professor’s explanations and have difficulty applying the knowledge in front of new learning situations. When bearing in mind that the set of knowledge, abilities, habits, and moral values incorporated gradually to culture and the fact that they conform an enormous volume of information constitute contentses, the more important task of teaching is to provide the pupils the experience systematized and organized of humanity, means and methods to take possession of the contentses in order to attain competitions socially determined and to perform efficiently in practice professional. A 72 % intercedes than when they confront the contents, they try to memorize it or to reproduce it mechanically. A teaching with these characteristics cannot guarantee an adequate learning and you drive repeaters that little can operate with what they have learned to students. This bears to that they do not acquire the competitions required like professionals, because the poor person development of the abilities to confront and to give solution to the problems, you impede successes in my whole life social and labor. On the other hand, the 64 % presents that it is difficult for them to establish relations between the contentses and selling of the abstracts, they copy the contentses of the textbook textually. According to the bibliographic realized revision, several investigators discuss this subject matter related with learning developer (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Levels of the pedagogic content for the professional motivation with adolescent’s students.
Note: Source: Own Elaboration.
For example: Garcia Batista [5] presents ten beginnings to have in account for the creation of situations and learning developers they meet between: The possibility to learn through challenging activities that the intrinsic motivations arouse ; Participation and solution in real problems, that they allow exploring, discovering and trying to change the reality; The transformation of the student of recipient in investigator and producer of information; The promotion of auto-knowledge, of the self-appraisal and of the reflection about the process of learning and the valuing of auto-directivity and auto-education like goal. The fact that the competitions do not know some to achieve in the subject of study, the main characters of their learning not take a seat, not always verified itself in the students’ opinions they know how to solve problems it be necessary in the application of it learned and the unspecified textbook’s all epigraphs tend to want to learn the necessary and enough of the contents for his level of formation. Deficiencies in the reasoning of the problems exist, his capabilities of analysis, synthesis, abstraction, and generalization, which is why his active participation is not produced of spontaneous way, are banked which forces the teacher to look for new learning styles in dependence of the groups or individual characteristics of the pupils constantly. In learning developer the student is and the main character of the process take a seat and he does not show up like passive recipient of information, trigger an intense mental activity from a creative perspective; Learning constitutes for him a constant process of quest of significances, of constant contradictions; The pupil is responsible for his own learning as from the commitment with oneself and he sets himself goals and periods to achieve them; It is able to assimilate his errors, capabilities, weaknesses and fortresses, you perceive the effort like a prime factor in his results and you confer a great value to the act to learn like something primary for the personal growth and the affective realization. Learning the developer is an ample and generalizing concept whose end is the development they learn of [6]. In another investigation according to refer Rodríguez López et to the [7] process teaching learning at the universities of medical sciences presents fissures in each one of the three moments of the teaching activity, students the actions do not execute a number enough of times in order that these may happen in abilities in the majority of the occasions, and that way guaranteeing his adequate acquisition. The author agrees with others [8,9] that the fact that today the basic quality of learning of the area constitutes a worry for the clinical teachers of the area presents ; therefore, you are important from the tender age of Medicine’s race to teach how to the students to reason, like preamble of the application of the clinical method that they must utilize in superior years and in practice professional, since the clinic and his method incur in a still bigger value today than in the past and it is the professors’ duty to educate his disciples, with the example and the word, in the debugged utilization and with excellence of the clinical method. That way, in order to teach how to the pupils to reason it is necessary for them to give the contentses of the study programs with the action’s adequate guiding base, the author agrees with Escobar et to the [10], the that they affirm that the lecture is the ideal space to do it.
The difficulties verified in the applied methods are similar to give them another scene, what teachers’ worry has been, and the place has opened into the realization of investigations on this subject matter [11]. The authors of investigation, based in his scientific preparation methodological and his vocational experience, they consider that it is obvious than be prevailing in the aspect on the learning of contentses didactic self-regulating actions that you contribute to a learning of contentses in students of medicine propose the paper of the professor in the activity of orientation of the independent work based in teaching tasks with the use of the educational guides and in his place. Actions educational to develop for the teachers:
1. Applying to new situations the professor’s explanations.
2. Selecting texts, schemata, and photos in the orientated bibliographies.
3. Developing abilities in the search of the information that they allow doing them a reflexive analysis about the reliability of his contentses for the correct realization of the tasks.
4. Establishing linkages between the previous knowledge and the present-day.
5. Answering for reflexive form professor’s questions.
6. Distinguishing in the textbook the concepts that the professor and to examine them offers of critical form.
7. Selecting the figures of book of text that they must observe and accomplishing the schematic performance of the structures.
8. Argumenting the development that the country has attained of late years the utility of the methods and techniques of study of the linked Morbid Anatomy.
9. Establishing a method of self-control answering to the questions of checking that the professor accomplishes
10. Emitting his criteria doing analysis, synthesis, and abstraction about what learned.
11. Accomplishing a critical assessment of the teaching activity, expressing which one’s music his future needs in dependence to the knowledge obtained at the classroom.
12. Evaluating his companions, highlighting the ones that contribute new knowledge according to the scientific advances and the technique.
It I became verified than in the process teaching still the teaching’s acquired by memory features, the pupils utilize learning with adolescents students race themselves they acknowledged not to not knowing how to identify the heart of the matter of the pedagogic contents of knowledge, difficulties to apply it in front of new situations have, it is difficult for them to establish relations between the pedagogic contentses and they copy the contentses of the text book, which is why didactic actions to achieve a learning proposed developer in agreement with the contemporary educational tendencies from an educational center.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.


