Abstract
Herein for the first time the quantitative determination of seven heavy metal ions i.e., Fe, Cu, Pb, Cd, Cr, Mn and Zn in the water samples of village Toke district Kalat Balochistan, Pakistan have been carried out by using atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Calibrations were constructed for the seven metals using standard solution. The analysis showed that the concentrations of Pb, Cd and Cr are moderately high in the water samples of determine the concentration of trace and heavy metals in drinking water of village Toke district Kalat Balochistan. Whereas Zn and Cu have no significant difference while, Fe, Cd, Pb, and Cr have moderately high value compared to standard given by WHO.
Keywords: Heavy Metals; Kalat Balochistan; Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric; Environment
Introduction
Water is the most important element for the living organisms
without water it would be impossible to maintain life on earth [1-
3]. Water pollution has become a very important field of global
research due to the direct impact on climate and humans being
[4-6]. Heavy metals are considered to be one of the main sources
of pollution in the environment, since they have a significant effect
on its ecological quality [7,8]. Human activity leads to increasing
levels of heavy metal contamination in the environment. Heavy
metals owing to atmospheric and industrial pollution accumulate
in the water and influence the ecosystem nearby [9]. Surface water
contamination with heavy metals is a serious environmental
problem. The determination of heavy metal in water samples is
very important in monitoring environmental pollution [9,10].
Zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), cadmium (Cd),
Lead (Pb) and chromium (Cr) etc., were chosen as representative
trace metals whose levels in the environment represent a reliable
index of environmental pollution. Metals like zinc, iron, manganese,
and copper are essential metals since they play an important role
in biological systems, whereas Pb, Cr and Cd are non-essential
metals as they are toxic even in traces [11-13]. While the essential
metals can also produce toxic effects when the metal intake is
excessively elevated. Recently, both international and Pakistan
studies have drawn attention to the metal pollution of water [14-
18]. But such a study has not been yet carried out in village Toke
district Kalat which is back word area of Balochistan, Pakistan. Here
water is mainly used by the people for drinking and agriculture
purpose. Current study is almost first report on determination of trace and heavy metals in drinking and agriculture water of Toke
Kalat, Balochistan. The aim of this study is to determine the mean
concentrations of heavy metals including Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, Cd, Pb,
and Cr in water. Heavy metals concentrations were determined by
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS). The relationships between
the metal levels in samples collected from areas of the village and
physicochemical parameters were assessed.
Methods
Experimental
Reagents and Solutions: Analar (AR grade) samples of Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, Cd, Pb and Cr, Zinc Nitrate, Ferrous Sulphate, Manganese chloride, Copper Nitrate, Lead Nitrate, Chromium Chloride and Nitric acid, were purchased from Merck, Marker. All reagents are of Analar grade and triply distilled water were used throughout the study. The apparatus and the glassware’s were thoroughly washed and dried in oven. Pre concentration of the samples were carried out and the residue was leached with 0.1M HNO3 acid (Analar) solution. This solution was used for the determination of Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, Cd, Pb and Cr using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS).
Instrumentation
Elico SL 163 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer is used to analyze the concentration of heavy metals with hollow cathode lamps of different metals and a flame of air-acetylene. The calibration curves were constructed using standard solution of the metal ions by following the procedure given in the manual using appropriate detectors in the wavelength range suitable for the concentration range. Five replicates of each experiment are carried out. The calibrations are precise and accurate as demonstrated by % RSD being less than 2.
Collection of Sample
Five different water samples were collected from different areas of Toke Kalat district Table 1. To avoid possible contamination, these samples were collected in one liter capacity polypropylene bottles i.e. pre acid washed and then 0.5 mL of conc HNO3 were added to 75 mL of each sample I in order to avoid the microbial activities. The water samples were then boiled or evaporated up to one-fourth of original volume. The samples were then kept in a refrigerator for two weeks to stabilize the metals. From the pool 100 mL water sample was filtered and concentrated to about 60mL in 100mL standard flask to which 5.0 mL of conc. HNO3 was added. This was made up to the mark with de-ionized water. After digestion, samples were analyzed for Zn, Fe, Mn , Cu, Cd, Pb and Cr using atomic absorption spectrophotometer according to standard methods as described in the manual supplied along with the atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
Results and Discussion
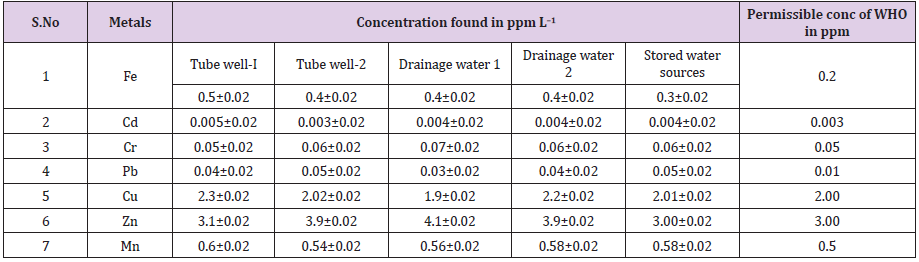
The analysis of water from the study area showed that water samples have no color and odor. The analytical results of metals in the samples of water are shown in the Table 2. This data showed that the concentration of Fe, Cd, Cr Zn, Mn, and Pb, are found to be present moderately high in the samples of Toke kalat district, where as Cu, and Cr concentration in all the study areas had no significant difference of concentrations when compared with WHO data . The table shows the results of analysis together with the permissible range of metal ions as defined by WHO. After analysis, the obtained results (ppm L–1) for Zn, Fe, Cd, Mn, Cu, Pb, and Cr are shown in Table 2.
Conclusion
The presence of heavy metals with moderate high concentrations in the water samples of Toke Kalat district indicates that there can be a chance of damage 9 to water and animal kingdom including human beings. Hence continual assessment and enlightenment is highly essential.
Conflict of Interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
References
- Mustafa S, N Baloch, S Muhammad, Y Malik, T Khan(2017) Determination of trace and heavy metals in drinking water of JhalMagsi district of Balochistan Pakistan. Pure Applied Biology 6(1): 9.
- Hussain J, J Shah,I Khan, D Lopes, R Souza,(2012) Determination of trace elements in the drinking water of mardan district KPK Pakistan. EurasiaJ Agre Environ Sci 12:1091-1094.
- Kulkarni S, S Dhokpande, J Kaware (2015) A Review On Spectrophotometric Determination Of Heavy Metals With Emphasis On Cadmium And Nickel Determination By UV Spectrophotometry. Int J Adv Eng Res Sci 2: 34-36.
- Ezemonye L, A Enuneku (2005) Evaluation of acute toxicity of cadmium and lead to amphibian tadpoles (Toad: Bufo maculatus and frog: Ptychadena bibroni) Journal of aquatic Sciences 20: 33-38.
- Kulkarni S J, S R Dhokpande, D J P Kaware ( 2013) Studies on flyash as an adsorbent for removal of various pollutants from wastewater. Int J Eng Res Technol 2(5): 1190-1195.
- Kulkarni S J (2013) Removal of organic matter from domestic waste water by adsorption. Int J Sci Eng Technol Res 2(10): 1836-1839.
- Sastre J, ASahuquillo, M Vidal, G Rauret (2002) Determination of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in environmental samples: microwave-assisted total digestion versus aqua regia and nitric acid extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta 462(1): 59-72.
- Kulkarni S J, S R Dhokpande, D J P Kaware (2014) A Review on Studies on Effect of Heavy Metals on Man and Environment. Int J Res Appl Sci Engi Technol 2: 227-229.
- AlRadady, A B Davies, M French (1994) Distribution of lead inside the home: case studies in the North of England. Sci Envt 145: 143-156.
- Zhou C, MWong, L Koh, Y Wee (1997) Soil lead and other metal levels in industrial, residential and nature reserve areas in Singapore. Environl Monit Assesst 44: 605-615.
- Nahid P, Y Rohan (2011) Spectrophotometric determination of some environmental samples. J Envi Res Devel 6(1): 57-62.
- Sarker K C, R Ullaha (2013) Determination of Trace Amount of Cu (II) Using UV-VisSpectrophotometric Method. Int J Chem Studie 1: 5-14.
- Heghedűş-Mîndru, R C Heghedűş-Mîndru, P Negrea, D S Ştef, R L Şumălan et al. (2013) Quantitative determination by atomic absorption spectrometry for macro elements of mineral waters from Romania. Revi Agri Rural Devel 2: 245-251.
- Soylak M, O Türkoglu (1999) Trace metal accumulation caused by traffic in an agricultural soil near a motorway in Kayseri Turkey. J Trace Microprobe Tech 17: 209-217.
- Beck J N, J Sneddon (2000) Metal concentrations in soils and sediments in Southwest Louisiana. Anal. Lett.
- Tüzen M (2003) Determination of heavy metals in soil, mushroom and plant samples by atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem J 74(3): 289-297.
- Ahmad M, S Muhammed, N Jahan, S U Jan, Qureshi (2014) Anti-dermatitis, anxiolytic and analgesic effects of Rhazya stricta from Balochistan. Pak J Pharma Sci 27(3): 45-48.
- Kawatra B, P Bakhetia (2008) Consumption of heavy metal and minerals by adult women through food in sewage and tube-well irrigated area around Ludhiana city (Punjab, India). J Human Ecol 23(4): 351-354.

 Research Article
Research Article