Abstract
A 46-year-old woman suffered from significant chronic pain, depression, insomnia, non-restorative sleep, chronic fatigue, irritable bowel syndrome, abdominal trouble, and dizziness. Blood test was negative for rheumatic disorders. The patient was diagnosed with Fibromyalgia Syndrome (FMS). She was treated intravenously with Placental Extract (PE)-containing 5% glucose solution once a week for 9 weeks. She experienced significantly improved fatigue, pain, and health-related quality of life by the successive intravenous administration of PE. The treatment effects of PE were parallel with the fatigue reduction. This case implies that PE administration is a safe and feasible tool to treat FMS patients.
Keywords: Fibromyalgia; Placental Extract; Intravenous Infusion; Fatigue; Pain; Quality of Life
Abbreviations: PE: Placental Extract; FMS: Fibromyalgia Syndrome; FSS: Fatigue Severity Scale
Introduction
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is a condition characterized by chronic widespread pain and fatigue which brings about a serious fall of quality of life in patients. Its pathophysiology still remains a mystery. Diverse treatment strategy including pharmacological therapies, non-pharmacological conventional therapies, and complementary and alternative medicine therapies has been used for the management of FMS.Previously, we reported acupuncture point injection of placenta extract (PE) in FMS patients relieved pain, ameliorated sleep disorder, and increased daily productive time[1].Experimental studies on the effect of PE on behavior and physical condition in the animal model showed decrease in symptoms of fatigue and increased resistance to physical stress [2]. PEs were also demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory effects in both animals and humans [3,4]. Numerous reports on intravenous infusions of pharmacological agents and nutrients to FMS patients have presented a substantial pain relief in the patients [5,6]. We describe for the first time the case of intravenous administration of PE to woman who was diagnosed for FMS. This case report deals with improvement of fatigue, pain, and quality of life by the continual systemic administration of PE.
Case Presentation
A 46-year-old female patient was admitted to our clinic because of debilitating chronic pain and fatigue. On admission, she had been reporting pain in various parts of her body for 7 years. She complained of significant pain in cervical spine and radiating pain in her left shoulder blade up to left upper arm. She had lumbar/ sacral pain radiating to left leg reaching to left ankle. She had pain in all major joints, particularly left jaw and left shoulder. The patient also described uncomfortable abdominal trouble as if irregular or obscure compartment inside the abdomen was dragged inward and downward from time to time. She had suffered irritable bowel syndrome to date. The patient complained that the pain was exacerbated by physical and mental stress. Her mood was said to be depressive and she experienced weakness and uselessness. She expressed problems falling and staying asleep irrespective of pain. She expressed herself in a serious state of tiredness. She said she felt an uncontrollable feeling of never being rested and a ghastly sensation of being totally drained of every fiber of energy. She reported dizziness with dull feeling on her head more than once a day. She described an unpredictable choky feeling on her throat and lost her breath several times a day. Laboratory investigations of routine blood test including liver function, renal function, electrolyte concentration, thyroid function, and cortical hormone were all within the normal limits. No serum markers were detected for tumor and rheumatic disorders.
Result
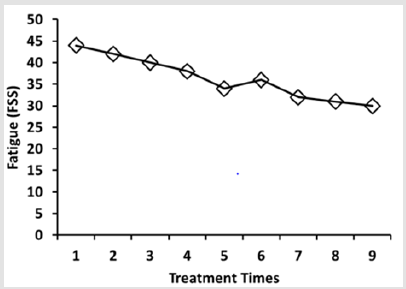
As a result of medical examination, she was diagnosed with FMS according to the 1990 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria [7]. We administered PE in 5% glucose solution to the patient by an intravenous route with her consent. The infusion cocktail contained 5 ampules (2ml/ampule) of PE (Green Cross Wellbeing, Korea) in 250 ml of 5% glucose solution (Green Cross Wellbeing, Korea). She completed the Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS) [8]to assess the degrees of fatigue. Self-reported level of fatigue was scored from one to 7, and high scores indicate severer tiredness. The fatigue index of the patient was improved following the beginning of treatment. At 9-week assessment, a decrease in FSS scores from 44 to 30 was observed (Figure 1). Pain score was recorded by the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) where the score of zero meant that the patient has no pain and the score of 10 was the worst pain. The patient was asked to indicate her feelings of pain by drawing a vertical line on a 10 cm VAS before and after every week of PE administration.
Figure 1: Effects of PE infusion on fatigue index. Fatigue index was calculated from the result of self-reported FSS questionnaire after the PE infusion at each week. PE infusion was carried out once a week for 9 weeks.
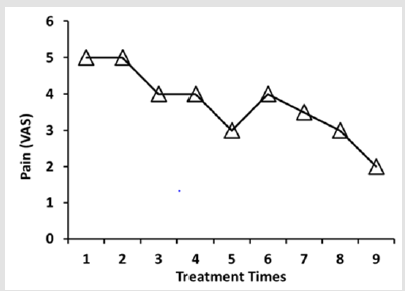
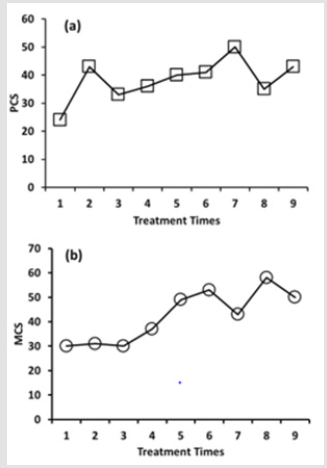
In the first week of her admission, the patient reported inconsistent pain (VAS 5) accompanied by episodes of several pain in same as the before of the treatment (Figure 2). After that, there was an increasingly clear improvement in pain symptom. At the end of the PE treatment, pain was decreased to VAS 2 (Figure 2). SF-12 Health Status Inventory (SF-12) [9]was used to evaluate the healthrelated quality of life. The SF-12 is a shorter form of SF-36, a generic health status measure. SF-12 expresses two summary measures of health status, Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS). Based on the checklist of SF-12, the impairment caused by the physical and mental symptoms was assessed. The PCS includes scales assessing physical functioning, role functioning difficulties caused by physical problems, bodily pain, and general health. The MCS includes scales assessing vitality, social functioning, role functioning difficulties caused by emotional problems and mental health. The larger scores of PCS and MCS indicate better-health state.Before the treatment of PE, the values of PCS and MCS were 24 and 30, respectively (Figure 3a & 3b).
Figure 2: Effects of PE infusion on pain. The severity of pain was expressed by VAS. PE infusion was carried out once a week for 9 weeks.
Figure 3: Effects of PE infusion on health-related quality of life. Based on the self-reported SF-12, PCS and MCS were calculated from the software officially provided. PE infusion was carried out once a week for 9 weeks.
After 9 weeks of PE infusion, each value of PCS and MCS was increased to 43 and 50 (Figure 3a & 3b). She reported feeling that she was responding well to the treatment. She experienced herself filled with higher energy than before the treatment. Before discharge, she was satisfied with her progress. However, the abdominal discomfort and dizziness occurred from time to time, not much different from the before treatment.
Discussion
In this case report, we demonstrated the intravenous
administration of PE ameliorated pain and health-related quality
of life in accordance with refinement of fatigue. Placenta is a
storehouse of potent biogenic stimulators and its extracts were
verified to contain wide range of peptides, proteins, minerals,
amino acids, nucleotides, carbohydrates, and steroid hormones.
Placebo-controlled clinical studies on the human PE demonstrated
a considerable improvement of fatigue [10,11]. PE was verified
to decrease symptoms of fatigue and increase the resistance to
physical stress in animals and humans [2,12]. Besides, we observed
the acupuncture point injection of PE ameliorated pain and quality
of life in knee arthritis and FMS patients [1,13]. Studies in FMS
patients demonstrated that chronic persistent pain, poor sleep
quality, depressed mood, anxiety, and combinations of these were
associated with fatigue [14,15].
We identified that the symptoms changes of the female patient
interrelated with the change in the condition of fatigue. As a
continual intravenous infusion of PE was conducted, indexes of
fatigue, pain, and quality of life from the FMS patient were shifted
from unhealthy to healthy state. The therapeutic effects seen in this
trial are commensurate with other modalities considered promising.
We previously confirmed the long-term administration of PE was
safe and effective in a complex regional pain syndrome patient [16].
Intravenous infusions of pain-relieving pharmaceuticals have some
side effects at doses required for pain control [17]. However, the
systemic use of PE was efficacious to control pain and secure not
to evoke any adverse effect in this study. Further investigation is
needed to evaluate clinical significance of PE infusion therapy to
treat FMS.
Conflict of interest
I declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Park KM, Cho TH (2020) Acupuncture point injection with placental extract improves pain and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Physiother Res Rep 3: 1-4.
- Moon PD, Kim KY, Rew KH, Kim HM, Jeong HJ (2014) Anti-fatigue effects of porcine placenta and its amino acids in a behavioral test on mice. Can J PhysiolPharmacol 92: 937-944.
- Lee KH, Kim TH, Lee WC, Kim SH, Lee SY (2011) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of human placenta extract. Nat Prod Res 25: 1090-1000.
- Agarwal N, Kulshrestha V, Kriplan A (2010) Clinical efficacy of placentrex injection in pelvic inflammatory disease. J Indian Med Assoc 108(2): 117-118.
- Kosharskyy B, Almonte W, Shaparin N, Pappagallo M, Smith H (2013) Intravenous infusions in chronic pain management. Pain Physician 16(3): 231-249.
- Massey PB (2007) Reduction of fibromyalgia symptoms through intravenous nutrient therapy: results of a pilot clinical trial. Altern Ther Health Med 13(3): 32-34.
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C,et al. (1990) The American college of rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis Rheum 33(2): 160-172.
- Tang S, Calkins H, Petri M (2004)Neurally mediated hypotension in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(5): 609-614.
- Ware J, Kosinski M, Keller SD (1996) A 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey: construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med Care 34(3): 220-233.
- Park SB, Kim KN, Sung E, Lee SY, Shin HC (2016) Human Placental Extract as a Subcutaneous Injection Is Effective in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Multi-Center, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Biol Pharm Bull 39(5): 674-679.
- Lee KK, Choi WS, Yum KS, Song SW, Ock SM, et al. (2012) Efficacy and safety of human placental extract solution on fatigue: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012: 130875.
- Park SB, Kim KN, Sung E, Lee SY, Shin HC (2016) Human placental extract as a subcutaneous injection is effective in chronic fatigue syndrome: a multi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Biol Pharm Bull 39(5): 674-679.
- KM Park, TH Cho (2017) Therapeutic effect of acupuncture point injection with placental extract in knee osteoarthritis. J Integr Med 15(2): 135-141.
- Nicassio PM, Moxham EG, Schuman CE, Gevirtz RN (2002) The contribution of pain, reported sleep quality, and depressive symptoms to fatigue in fibromyalgia. Pain 15: 271-279.
- Finan PH, Zautra AJ (2010) Fibromyalgia and fatigue: central processing, widespread dysfunction. PM R15: 431-437.
- Cho TH, Park KM (2014) Complex regional pain syndrome type 1 relieved by acupuncture point injections with placental extract. J Acupunc Meridian Stud 7(3): 155-158.
- TremontLukats IW, Challapalli V, McNicol ED, Lau J, Carr DB (2005) Systemic administration of local anesthetics to relieve neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. AnesthAnalg 101:1738-1749.

 Case Report
Case Report