Abstract
Introduction: Professors’ communication skill is one of the main factors guaranteeing the improvement of education quality. Therefore, regarding this significant role and the special role of the students in evaluation of the professors’ performance and the effect of the communication of the professor and the students on the evaluation scores, this research has investigated the relationship between the faculty members’ communication skills and the results of evaluation of them by the students in Iran University of Medical Sciences.
Research Method: The current study is a descriptive-analytical one of crosssectional type conducted on 10 education groups of Iran University of Medical Sciences in the academic year 2016-2017. The data collection tools were Queendom communication skill questionnaire and the scores of the evaluation of the professors’ performance by the students. The SPSS13 software and statistical tests such as Pearson’s correlation coefficient and variance were used for analyzing the data.
Findings: The data analysis indicated that the mean score of the total communication skill was 117.77. The mean score of the evaluation of the professors was 16.68. The highest mean score of evaluation belonged to the orthopedic group (18.41), and the lowest mean score belonged to the gynecology group (15.82). Pearson’s correlation coefficient indicated a direct significant relationship between the score of communication skill and the score of the evaluation by the students (p≤0.05). The variance analysis indicated that there is a significant difference between the mean scores of evaluation and communication skill of the groups (p≤0.05).
Conclusion: Paying attention to the issue of communication skill of the medical sciences professors requires a special look. Therefore, it is necessary to apply appropriate planning in order to upgrade and educate this skill, especially in clinical fields, so that we can guarantee the learners’ satisfaction and the education quality.
Keywords: Communication Skills; Evaluation; Faculty Members; Medical Education
Introduction
Education system is a fully human organization and all its essence aspects originate from human, are accompanying and for humans. So, the skill of human relations depends on the faculty members’ skills in communicating. The faculty members of every university are the main elements of transfer of knowledge and science to the students. Therefore, the credit of every university is depending on the scientific activities of the professors and the students [1]. One of the factors influencing the professors’ teaching ability is their communication skill [2]. So that, in teaching process, not only the teacher’s experiences and scientific viewpoints are effective, but also learning takes place by the effective communication of the teacher and the learner [3]. There have been different definitions of communication. However, in the education process, “communication” is defined as the relation between two or more people, subjects, or thinking. In other words, communication is referred to mutual understanding and common thoughts of the teacher and the learner. In simple words, interpersonal relationship is the process of exchanging information, emotions, and beliefs by verbal and nonverbal messages [4]. Thoughts and information exchanges should be done between the students and the professor, so that the full perception and learning takes place properly. The more this communication, the student’s self-confidence and learning motivation is increased, and consequently, the education quality is promoted. If this interaction is not done properly, even spending a lot of time and money cannot have the expected results [5].
On the other hand, the most usual method for determining the
professors’ success in the educational purposes is the evaluation of
the professors by the students [6]. Sensitivity about the process of
education and learning in the universities increases the necessity
of evaluation, because it will lead to the improvement of the
education quality and consequently improvement of efficiency and
effectiveness of education system of thecountry[7]. The proper
execution of the evaluation requires collecting the necessary
information about educational activities and choosing criteria for
comparing the gathered information by them and then, making
judgement about the professors’ success in teaching. In this regard,
using the students’ opinions in evaluation of the professors’
performance is one of the common and convenient methods used
by many reputable universities of the world [8]. Some researchers
believe that this evaluation method can be effective in improvement
of teaching methods and helping the students in taking credits [9].
Students’ feedbacks are considered as a major part of the cycle
of quality improvement and this successful quality guarantees
learning and teaching [10]. In some researchers, it has been stated
that communication skills can make the teacher look good or bad
[4]. For example, according to the study conducted by Yousefi et al.
one of the factors having a positive correlation with the evaluation of
the professors by the students is the interpersonal relationships of
the students and the professors [11]. Also, in the study conducted by
Amini et al. it was found that the faculty members’ communication
skill is one the effective factors in the evaluation scores [2].
However, there are studies suggesting different results.
For example, the study conducted by Norouziniya indicates no
relationship between the professors’ communication skills and
their evaluation scores [12]. Therefore, regarding these different
results, the significant role of communication skills in achieving
the education goals and improvement of teaching quality, and the
important role of the students in evaluating the professor and the
effects of the communication between the professor and the student
on evaluation scores, this research has investigated the relationship
between the faculty members’ communication skills (regarding the
5 scales of ability to perceive or understand verbal and nonverbal
messages, regulating the emotions, listening skills, having insight
to the communication process, and communication decisiveness)
and the results of their evaluation by the students of Iran University
of Medical Sciences. The current study is a descriptive-analytical
one of cross-sectional type conducted at Iran University of Medical
Science in academic year 2016-2017. The population of this
research consists of the faculty members of Iran University of
Medical sciences. 76 people of the professors of medical faculty
with at least 5 years of teaching experience in the university sere
selected and enter the study by convenient sampling method.
In order to measure the relationship between communication
skills and the results of evaluation of the professors, Queendom
communication skill questionnaire (CSTR) was used. This scale
included 34 questions and is published by Queendom institute
(2004). It covers five subscales of the ability to perceive and
understand verbal and nonverbal messages, regulating the
emotions, listening skill, having a insight to the communication
process, and communication decisiveness. The responding scale is 5
point Likert scale. In order to fill the questionnaire, the respondent
should specify the level of correspondence of his/her current
situation with each item on a five-point scale from 1 (never) to 5
(always). First, the questionnaires were filled by the professors.
Then, according to the codes considered for each professor (for
the privacy of the collected information), the results of evaluation
of them were measured by the results of communication skill
questionnaires filled by the students for each professor in order to
study the effectiveness of the professors’ communication skills and
the students-professor relationship on the results of evaluating the
professors.
In 2005, Hossein Chari and Fadakar reported validity and
reliability of this questionnaire equal to 0.69 by Cronbach’s alpha
method, and this suggests its internal consistency. This value was
equal to 0.71 for the university student subjects and 0.66 for the
high school students. In order to study the construct validity of the
communication skill test and the structure of the communication
skill factors, the analytical statistic method was used in the
mentioned research in which the numerical value of KMO index
was equal to 0.71 and the numerical value of the X2 index was equal
to 2318.01 in Bartlett’s test of sphericity. This value was significant
at 0.001 level. Also in 2006, Yousefi reported the total validity of
communication skills scale equal to 0.81 by Cronbach’s alpha method and equal to 0.77 by split-half method. After data collection,
the data were entered in SPSS software version 13. Descriptive
statistics such as mean, Pearson correlation test, and variance
analysis (with significance level of P≤0.05) were calculated.
Findings
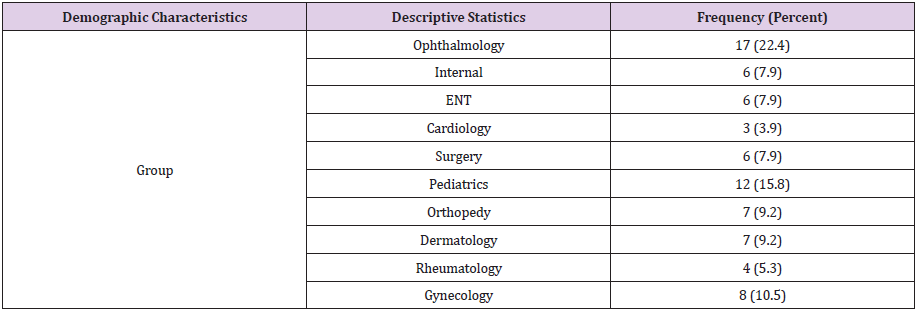
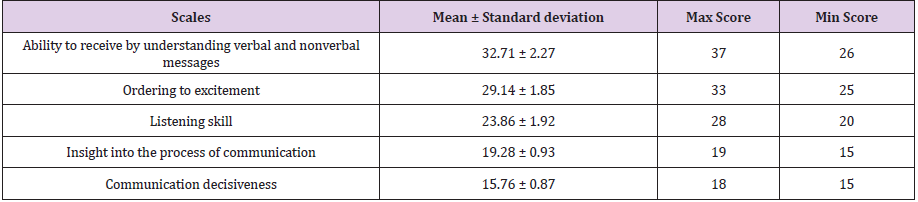
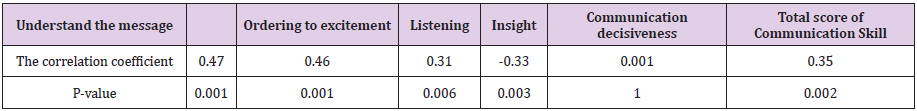
In this study, 76 faculty members from 10 educational groups of clinical sciences of Iran University of Medical Sciences participated. The highest number was related to Ophthalmology group (22.4%) and the lowest number was related to Cardiology group (3.9%) (Table1).Data analysis indicated that the mean score of total communication skills was equal to 117.77. The score of the professors’ communication skill was at the highest level in the scale of the ability to perceive and understand verbal and nonverbal messages (32.71) and at the lowest level in the scale of communication decisiveness (15.76) (Table 2). The mean score of the evaluation of professors was 16.88. The highest mean evaluation score was belonged to Orthopedy group (18.41) and the lowest mean score belonged to women’s group (15.52). Pearson correlation coefficient showed a direct significant relationship between the scores of communication skill and students’ evaluation (p≤0.05). In the study of the evaluation score in the four scales of communication skill including ability to perceive or understand verbal and nonverbal messages, regulating the emotions, listening skills, and having insight to the communication process, a significant correlation relationship was observed (Table3). Regarding the normality of distribution in Kolmogrov-Smirnov test, ANOVA was used for studying the significance of the difference between evaluation scores and communication skill scores of the groups. As presented in tables 4 and 5, there was a significant difference between the mean scores of evaluation and communication skill of the groups (p≤0.05). The results of Scheffe post hoc test indicated that the difference between scores of the evaluation of the gynecology a Orthopedy groups and also the difference between heart and Orthopedy groups was significant (p≤0.05).
Discussion and conclusion
This study was conducted on 76 people of faculty members of
Iran University of Medical Sciences to investigate the relationship
between communication skill and evaluation score. The results
indicated that there is a direct significant relationship between the
scores of communication skill and evaluation. According to the study
conducted by Yousefi et al. one of factor having a positive correlation
with the scores of evaluations of the professors by the students is
the interpersonal relationship between professor and student [11].
In the study conducted by Amini et al. it was found that the faculty
members’ communication skill is one of the effective factors on the
professors’ evaluation score (2) and this is correspondent to the
result of the current study. The study conducted by Norouziniya
et al. contradicts the results of the current study [12] and suggest
no relationship between the professors’ communication skills
and their evaluation scores. As mentioned in some studies,
proper relationship between the professor and the student lead
to the students’ increased self-confidence and motivation and
consequently, it will facilitate the learning process. So, the student
having a good relationship with their professors will have better
scientific achievements. Therefore, all mentioned factors cal lead
to more satisfaction of the students with the professors and giving
higher scores in evaluation.
The current study indicated that the mean score of
communication skills of the professors was 117.77 out of 170. In the
study conducted by Peyman et al, this mean value was equal to 106,
and in the study conducted by Norouziniya, this value was reported
equal to 123.93 [12,13]. Also, in the study conducted by Rezaeiyan
et al. the total communication skills of the faculty members of
Rafsanjan was evaluated at a medium level [5]. Regarding the
fact that the professors’ communication skills are influenced by
different factors such as professional competence, scientific ability,
their communication style, educational and ethical characteristics,
etc, the difference between various universities and professors can
highlight the role of these factors.
In the current study, the mean score of evaluation of the
professors was 16.88. The highest mean score of evaluation belonged
to orthopedy group (18.41) and the lowest mean score belonged
to the gynecology group (15.82). Also, there was a significant
difference the mean scores of evaluation and communication skill of
the groups. This difference of evaluation scores was also significant
between the Cardiology and orthopedy groups. This difference
can be due to difference expectation of the students from different
groups. When entering different sections, the students have
different goals, and they try to achieve them during the education
period. Their success or failure can influence their viewpoints and
scores. In addition, sometimes these differences may be due to the
factors which are mentioned as evaluation problems in the articles.
As mentioned in some studies, the students may be not honest in
evaluation, or maybe they have not spent adequate attention and
time for evaluation. Even, the evaluation can be influenced by other
factors such as lack of sense of responsibility and awareness. The
issue of the professors’ communication skills requires a special
attention, especially in medical sciences in which the professors
have different roles including teacher, leader, physician, etc.
Therefore, appropriate planning is required to be applied for
promotion and education of this skill, especially in clinical fields, so
ensure the learners’ satisfaction and our education quality.
References
- Oskouhi F, MovahedMohammadi SH, Rezvanfar A (2014) Relationship between Communication Skills of Faculty Members, Educational- Research Performance at Sari University of Agricultural and Natural Resources. Journal of Agricultural Education Administration Research6(30):89-100.
- Amini M, Honardar M (2008) The view of faculties and medical students about evaluation of faculty teaching experiences. Koomesh9(3):171-178.
- Sharifirad GH R, Rezaeian M, Jazini A, Etemadi Z S (2011) The Knowledge, Attitude and Performance of the Academic Members towards Effective Communication Skills in education. Health System Research6(2):217-25.
- Attarha M, Shamsi M, akbary Torkestani N (2012) Faculty Members’ Communication Skills in Educational Process inArak University of Medical Sciences. Iranian Journal of Medical Education12(9):676-685.
- Rezaeian M, ZareBidaki M, Bakhtar M, Kargar S (2013) A Survey on Communication Skills of Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences Faculty Members in 2013. J RafsanjanUniv Med Sci14(5): 417-426.
- Derakhshan A, Darabee M R, Saeedi M, Kiani M A (2014) Assessment of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences facultys' opinions about the criteria of a good educator. Journal of Medical Ethics7(26):159-182.
- Fakhri M, Yaghoobian M, Mohseni Bandpei M A, Enayati A A, Ahmad Shirvani M, et al. (2012) Reliability of the Teaching Evaluation Instrument of the Instructors Working. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci21(86):38-46.
- Bastani P, Rouhollahi N, Tahernejad A (2015) Validity and Reliability of Teachers` Evaluation Questionnaires from Students Point of View in Tehran University of Medical Sciences 3(1):7-14.
- Mahdavi S, Zare S, Naeimi N (2014) Comparison between Student Evaluation and Faculty Self-Evaluation of Instructional Performance. Rme6(2):51-58.
- Aburawi E, McLean M, Shaban S (2014) Are medical students and faculty on the same page? Sultan Qaboos University Med J14(3):361-368.
- Yousefi Afrashteh M, soltani arabshahi S K, bigdeli S, sedigh maroofi S (2015) Analysis of structural relationships of variables associated with evaluation of teaching by students in medical education. Iranian Journal of Medical Education15:393-404.
- Norouzinia R, Noorisepehr M, Heidari A, Kabir K (2014) Communication skills of Academic members and it’s relation with theri evaluation outcome in Alborz university of Medical Sciences. Development Strategies in Medical Education1(1):64-71.
- Peyman H, Yaghoubi M, Sadeghifar J, Sayehmiri K, AlizadehM, et al. (2012) Assessment of Interpersonal Communication Skill Levels in Lecturers of Ilam University of Medical Sciences: A Case Study. IJME 11(9):1436-1442.

 Review Article
Review Article