Abstract
Background and purpose: Studies on the relationship between the Salvia Officinalisextracts and tumor characteristics are relatively rare. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of Salvia Officinalis extracts on the level of tumor associated marker called Carcinoembryonic Antigen in male rats.
Methods: In this experiment 20 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups of control, normal saline recipients, and Salvia Officinalis extract recipients (100 and 200 mg/kg body weight), each including 5 rats. Samples were subjected to laboratory experiments for seven weeks. Thereafter, blood samples were collected through cardiac puncture method, and following serum collection, the serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen was measured using radioimmunoassay method. Ultimately, the data was statistically analyzed and compared among distinct groups using one-way analysis of variance technique.
Results : The results indicated that the serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen in the Salvia Officinalis extracts recipient group (200 mg / dl) was significantly lower than that of the control group (P = 0.007), although the serum levels of this antigen showed no significant variation in the group receiving Salvia Officinalis extracts with the dosage of 100 comparing to control.
Conclusion: In general, the results of this study demonstrated that Salvia officinalis extract with appropriate dosage can reduce the serum levels of carcinoembryonic antigen. Accordingly, the pharmacological application of Salvia officinalis extract seems to be beneficial in treatment of cancers with elevated levels of this tumor marker.
Keywords: Salvia officinalis; Carcinoembryonic Antigen; Rat
Introduction
Salvia is a perennial plant of the mint family, Lamiaceae, and is commonly referred to as Salvia officinalis. This genus consists of nearly 900 species and hence, is the largest genus is the mint family. This plant is mostly found in natural regions, in the Mediterranean, and in parts of Europe and Iran [1,2]. Salvia officinalis is exploited as a flavor in foods and beverages and is also employed in herbal medicine production and for therapeutic purposes. One of its major application is in Salvia officinalis (Sage) tea. Two of its extract’s components including Camphor and Alpha-Thujene essence are used for cosmetic purposes [1-6]. Salvia has antimicrobial activity as well [7,8]. Salvia has also application in inflammatory disorders and skin wound healing in traditional medicine [9,10]. An ointment has recently been made of Salvia extract which is effective in wound healing [9]. Moreover, administration of Salvia extract improves perceptual function in young adults mainly though establishing Cholinergic Characteristics [11].
Carcinoembryonic antigen is one of the hallmarks of tumors which is expressed in cancerous tissues and appears as secretions in serum [12]. Carcinoembryonic antigen was first detected in human gastric adenocarcinoma [13-15]. This antigen is a cell membrane glycoprotein [16,17]. Carcinoembryonic antigen molecules are released from the cell surface into the interstitial compartment and subsequently enter the blood circulatory system [18,19]. Carcinoembryonic antigen also protects tumor cells and mediates their survival in blood stream [20]. Studies have shown methanolic extraction of Salvia to have anti-growth activity against cervical cancer, skin cancer and breast cancer cells [21]. Additionally, numerous anti-tumorigenic effects have been attributed to aromatic plants of Salvia Officinalis genus [22]. Salvia Officinalis extracts inhibits colon cancer cells’ growth [23]. Altogether, even though myriad of studies has been conducted regarding various herbs’ extracts effect on tumor markers, studies on those of Salvia Officinalis extracts are quite limited. Therefore, this study investigates the impact of Salvia Officinalis extracts on serum levels of carcinoembryonic antigen in male rats.
Analysis Method
This is an experimental laboratory research through which the data resulting from laboratorial experiments were statistically compared among distinct groups. In this research, adult Wistar male rats weighing 200 ± 24 grams with light-dark period of 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness and with the light period beginning from 8 am were employed. They accessed to limitless sources of nutrients and water (urban water and commercial rat food from Pars Dam Company). Animals were numbered in each group and were adapted to the presence of this project’s conductor. None of the animals had any disease or displayed any sign of disease during the experiment.The methodology of preparation and injection of Salvia Officinalis extracts was adjusted based on previous studies [24-27].In this regard, first, the plant’s leaves were washed, then they were dried while being incubated in the shade for a week. Subsequently, dried leaves were grinded into powder using electric mill and the resulting powder was dissolved in 80% ethanol.After solution filtration, the solvent was separated from the extract using Rotary machine. Eventually after desiccating the extract, the aqueous solution of the extract was prepared through adding normal saline.Rats were divided into 4 groups of 5, including the control,normal saline recipients, and extracts recipients at doses of 100 and 200 mg/kg of body weight.
The extract was injected intraperitoneally. All animals were subjected to blood sampling after seven weeks. Blood samples were prepared using Cardiac Puncture technique. In this method, the samples were relatively anesthetized by the ether, and subsequently, 3 to 5 milliliters of blood were drawn by inserting a syringe needle into the left ventricle. Blood samples were then incubated at laboratory temperature for 15 minutes. Blood samples were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for serum separation, and thereafter the serum samples were stored at -20°C for further carcinoembryonic antigen serum level measurements. Serum level concentration of carcinoembryonic antigen was measured by means of radioimmunoassay technique using (Immunotech A Beckman Coulter/ ref) detection kit. Throughout the study, all international regulations regarding samples rights were complied with based on international standards. Finally, the data was analyzed using SPSS 19 software and one-way analysis of variance technique. In variance analysis, the significance of variations amongst groups was determined using Tukey Test. The variation between probability level less than 0.05 was considered meaningful.
Findings
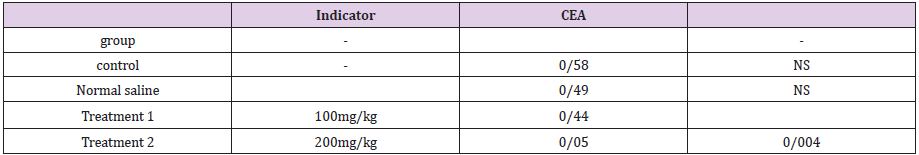
Tables 1& 2displays the concentration of CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) in serum of male rats.Statistical comparison of data between the control group and the normal saline group demonstrated that there was no significant difference between these groups. Accordingly, the feeding method of extract had no impact on the results of the present study. On the other hand, the results showed that CEA concentration in male rats receiving Salvia officinalisextract (200 mg/kg) was significantly lower than that of the control group (P <0.05). In addition, the serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen in rats receiving Salvia officinalis extract at 100 mg/kg dosage did not display significant variation to that of the control group.
Table 1: Concentration CEA in Rat (control and recipient of Maryam flower (Salvia officinalis)).
Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity
Garden sage essence encompasses total phenolic content of 5.276 milligrams of tannic acid per liter of sample. The antioxidant
activity is displayed in table 1 based on IC50, through implementation of DPPH free radical inhibition method, beta-carotene/linoleic
acid emulsion bleaching prevention, and reduction potential, all of which being spectrophotometric strategies. Less IC50 indicates
higher essence antioxidant activity. In all models, the least IC50 belonged to BHT. Here, the necessary amount of garden sage to have
50% inhibitory effect is higher in comparison with that of BHT, which implies higher BHT potential (p<0.005).
Table 2: Antioxidant activity (IC50 ± SD μg/ml) of garden sage essence and BHT in various systems’ model.
*DPPH: radical deterrence potential, BCB: linoleic acid inhibition potential, RP: reduction potential
Discussion and Conclusion
Based on this study, the aqueous extract of Salvia officinalis has resulted in reduction in serum levels of carcinoembryonic antigen, thereby its capability of having anti-tumor activity is plausible. Other studies have also demonstrated that Salvia officinalis extract can inhibit growth and proliferation of colorectal cancer cells in cell culture media [22]. Moreover, it has been indicated in another study that Diterpenoid Quinines extracted from Salvia officinalis have cytotoxic and DNA-damaging effects in colon and liver cancer cells in cell culture media through which they exert their growth-inhibitory effects on tumor cells [23]. Additionally, assessment of Salvia officinalis effect on chicken’s Chorioallantoic membrane indicates its anti-angiogenic and anti-proliferative activity, and since carcinoembryonic antigen tumor marker elevates during proliferation and cellular degradation, reduction in its serum level under these circumstances is expected [28]. In conformance to this research, studies have indicated that alpha terpineol, which is one of the primary compounds in Salvia officinalis extract, can prevent tumor cell growth, and hence, can have inhibitory effects on secretion of carcinoembryonic antigen tumor marker [29].
Furthermore, studies have revealed that some compounds found in Salvia officinalis extract such as Thujene Monoterpenes, Beta-pinene, and Cineol can have anti-cancer therapeutic activity through cell growth inhibition [30]. Moreover, essential fats present in Salvia officinalis extracthave shown anti-tumor activities according to some studies [31,32]. Taken together, it can be concluded that components present in Salvia officinalis extract, particularly alpha terpineol, Thujene Monoterpenes, Beta-pinene, Cineol, and essential fats prevent normal cells’ destruction and also inhibit tumorigenesis in cells, and this serves as a major factor in reduction of carcinoembryonic antigen serum level. Furthermore, although molecular mechanisms underlying some cancers metastasis are yet to be discovered, carcinoembryonic antigen production has been introduced as a major factor in metastasis both clinically and experimentally [20]. Studies have proven to be a close connection between serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen and colorectal cancer metastasis to liver [32].
Based on this, since Salvia officinalis extract has anti-metastatic effects, its decreasing effect on carcinoembryonic antigen serum level is also conceivable in this regard as well [28]. In contrast, some studies cast doubt on this link between serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen and metastasis [33]. In conclusion, the findings of this study demonstrate Salvia officinalis extracts have dwindling effect on serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen. Thus, the anti-metastatic and anti-cancer effects of this plant are substantial and can be considered for clinical applications.This study solely focused on evaluating the changes in serum level of carcinoembryonic antigen following intraperitoneal injection of Salvia officinalis extracts, and assessments on cellular and molecular levels were not intended. Thus, interpretation of the results is only feasible at serum level variations of the tumor marker, and any explication at cellular and molecular levels is beyond the scope of this study.
References
- Imanshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H (2006) The pharmacological effects of Salvia species on the central nervous system. Phytother Res 20(6):427-437.
- Kuzma L, Skrzypek Z, Wysokinska H (2006) Diterpenoids and triterpenoids in hairy roots of salvia sclarea. PCTOC 84(2):171-179.
- JibaoC, Ping L, Xiaolan Z, Qingde S (2006)Comparative analysis of Clary Sage(Salvia sclarea L.) oil volatile by GC FTIR and GC MS. Food Chem 99(2):401-407.
- Pavela R (2005) Insecticidal activity of some essential oils against larvae of SpodopteraIittoralis.Fitoterapia 76(7-8):691-696.
- G Walch S, kuballa T, Stuhlinger W, Lachenmeier D (2011) Determination of the bioilogically active flavor substances thujone and camphor in active flavor substances thujone and camphor in foods and medicines containing sage(Salvia officinalis L). Chem Cent J 5:44.
- Lachenmeier DW, Uebelacker M (2010) Risk assessment of thujone in foods and medicines containing sage and wormwood-evidence for a need of regulatory changes?Regultoxicolpharmacol 58(3):437-443.
- ManFan Wan J, Sit WH, Lee CL, HoiMan fuk, Kwong on Cgan D (2006) Protection of lethal toxicity of endotoxin by Salvia miltiorrhiza BUNGE is viareduction in tumor nectosisfactoralpha release and liver injury. Int Immunopharmacol6(5):750-758.
- Bouaziz M, Yangui T, Sayadi S, Dhouib A (2009) Disinfectant properties of essential oils from Salvia officinalis L. cultivated in Tunisia. Food Chem Toxicol47(11): 2755-2760.
- Suntar I, Akkol EK, Keles H,Oktem A, Baser KH, et al. (2011) A novel wound healing ointment: a formulation of Hypericum perforatumiol and sage and oregano essential oils based on traditional Turkish knowledge. J Ethnopharmacol134(1):89-96.
- Baricevic D, Sosa S, Della Loggia R, Tubaro A, Simonovska B, et al. (2001) Topical anti- inflammatory activity of Salvia officinalis L. leaves: the reletance of ursolic acid. J Ethnopharmacol 75(2-3):125-132.
- Scholey AB, Tidesley NT, Ballard CG, Wenes KA, Tasker A, et al. An extract of Salvia (sage) with anticholinesteraseproperties improves memory andattention in healthy older volunteers.Psychopharnacology (Berl) 198(1):127-139.
- Saeland E, Belo AI, Mongera S,van Die I, Meijer GA, et al. (2011) Differential glycosylation of MUCI and CEACAM5 betweem normal mucosa and tumour tissue of colon cancer patients.Int J Cancer 131(1): 117-128.
- Gold P, Freedman SO (1965) Demonstration of tumor-specific antigens in human colonic carcinomata by immunological tolerance and absorption techniques.JEM121(3):439-462.
- Kar A, Panda S, Bharti S (2002) Relative efficacy of three medicinal plant extracts in the alteration of thytoid hormone concentrations in male mice. J Ethnopharmacol81(2): 281-285.
- Gold P,Krupey J, Ansari H (1970) Position of the carcinoembryonic antigen of the human digestive system in ultrastructure of tumor cell surface.JNCI45(2):219-225.
- Rosenthal KL, Palmer JL, Harris JA, W E Rawls, W A Tompkins (1975) Antibody- induced redistribution of CEA on the cell surface: utilization in separation of CEA and isoantigen A. j Immunol115(4):1049-1053.
- Pignatelli M, Durbin H,Bodmer WF (1990) Carcinoembryonic antigen functions as an accessory adhesion molecule mediating colon epithelial cell- collagen interactions. PNAS 87(4):1541-1545.
- Thomson DM, Krupey J, Freedman SO, P Gold (1969) The radioimmunoassay of circulating carcinoembryonic antigen of circulating carcinoembryonic antigen of the human digestive system. PNAS64(1): 161-167.
- Khan WN, Teglund S,Bremer K, S Hammarstrom (1992) The pregnancy- specific glycoprotein family of the immunoglobulin superfamily: identification of a newmembers and estimation of family size. Genomics12(4):780-787.
- Thomas P, Forse RA, Bajenova O (2011) Carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA) and its receptor hnRNP M are mediators of metastasis and the inflammatory response in the liver. Clin Exp Metastasis 28(8): 923-932.
- Janicsak G, Zupko I,Nikolovac MT, Forgo P, Vasas A, et al. (2011) Bioactivity- guided study of antiproliferative activites of Salvia extracts. Nat prod Commun 6(5):575-579.
- Xavier CP, Lima CF, Fernandes Ferreira M, Pereira Wilson C (2009)Salvia fruticosa, Salvia officinalis, and rosmarinic acid induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation of human colorectal cell lines: the role in MAPK/ERK pathway. NutrCancet61(4):264-271.
- Slamenova D, Masterova I,Labaj J, Horvathova E, Kubala P, Jakubikova J, et al. (2004) Cytotoxic and DNA- damaging effects of diterpenoid quinones from the roots of Salvia officinalis on colonic and hepatic human cells culturedin vitro. Basic Clin PharmacolToxicol94(6):282-290.
- Gold P, Freedman SO (1965) Specific carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system.JEM122(3):467-481.
- Panda S, Kar A (1998) Dual role of betel leaf extract on thyroid function in male mice. Pharmacol Res38(6):493-496.
- Panda S, Kar A (1998) Changes in thyroid hormone concentrations after administration of ashwagandha root extract to adult male mice.J Pharm Pharmacol50(9):1065-1068.
- AlQarawi AA, AlDamagh MA, Elmougy SA (2002) Effect of freeze-dried extract of Olea europea on the pituiary- thyriod axis in rats. Phytother Res16(3):286-287.
- Keshavarz M, Bidmeshkipour A, Mostafaie A, Mansouri K, MohammadiMotlagh HR (2011)Anti-tumor activity of Salvia officinalis is due to its anti- angiogenic, anti-migratory and anti-proliferative effects. Cell Journal (Yakhteh)12(4):477-482.
- Tundis R,Louzzo MR, Menichini F, Bonesi M, Colica C, Menichini F (2011) In vitro cytotoxic activity of extracts and isolated constituents of Salvia leriifoliaBenth against a panel of human cancer cell lines. Chem Biodivers8(6):1152-1162.
- Hassan SB, GaliMuhtasib H, Goransson H, Larsson R (2010) Alpha terpineol:a potential anticancer agent which acts through suppressing NF- kappaB signaling. Anticancer Res30(6):1911-1919.
- Sertel S, Eichhom T, Plinkert PK, Efferth T (2011) Anticancer activity of Salvia officinalis essential oil against HNSCC cell line (UMSCC1). HNP 59(12):1203-1208.
- RLoizzo M, Menicihini F, Tundis R, Bonesi M, Nadjafi F, et al. (2010) Comparative Chemical Composition and Antiproliferative Activity of Aerial Parts of Salvia leriifoliaBenthanlSalvia acetabulosa Essential oils against human tumor cell in vitro models. JMF13(1):62-69.
- Aarons CB, Bajenova O, Andrews C, Heydrick S, Bushell KN, et al. (2007) Carcinoembryonic antigen- stimulated THP-1 mactophagesactibate endothelial cells and increase cell- cell adhesion of colorectal cancer cells. Slin Exp Metastasis 24(3):201-209.
- Gangopadhyay A, Bajenova O, Kellt TM, Thomas P (1996) Carcinoembryonic antigen induces cytokine expression in Kuppfer cells: implications for hepatic metastasis from colorectal cancer. Cancer Res56(20):4805-1480.

 Short Communication
Short Communication