Abstract
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are highly prevalent worldwide. Urinary tract infections
(UTIs) are the inflammatory disorders of the urinary tract caused by the abnormal
growth of pathogens. The purpose of this study was to determine the most frequent
bacterial pathogens responsible for UTIs, to evaluate antibiotics used to treat
such infection, to detect and evaluate the incidence of infection & to review the current
evidence of diagnosis, management of UTIs from the patients. A descriptive type
of cross-sectional study design was used. The survey was carried out from November
2019 to February 2020, among 50 patients in the Urology Department of Chattogram
Medical College Hospital (CMCH), Chattogram. According to this survey the highest
proportion of patient’s age range was from 21-30 years which was 28%. 68% of patients
were male and the remaining 32% were female patients. 64% of patients were
married and the remaining 36% were unmarried. The highest proportion of patients
was illiterate regarding 46%. The highest proportion of patients was from rural area
which was 60%.
The highest proportion of patients had frequency or urgency of urination with less
urine output which was 32%. The highest proportion of patients had done USG of KUB
diagnosis for UTI which was 20%. The highest proportion of patients had taken antibiotic
therapy only during hospitalization which was 48%. The highest proportion of
patients had not taken any antibiotic which was 30%. The highest proportion of patients
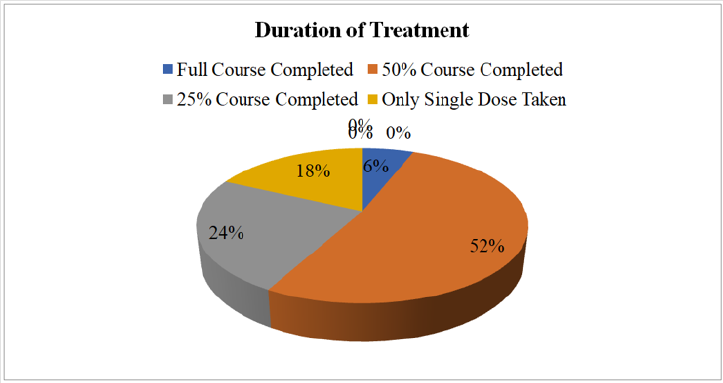
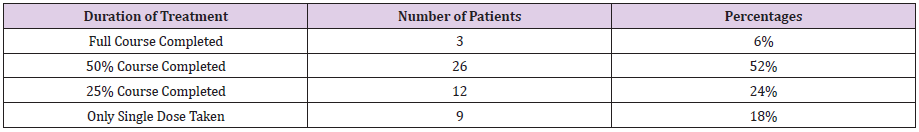
had completed 50% course of treatment which was 52%. The highest proportion
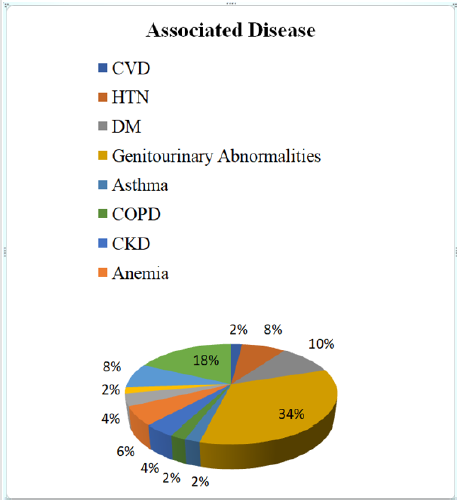
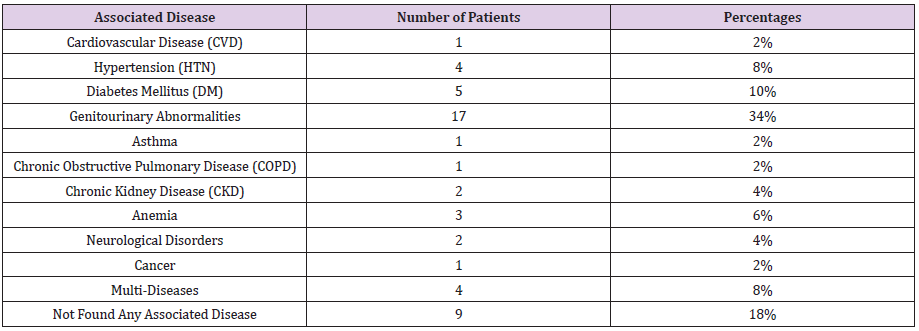
of patients had genitourinary abnormalities as associated disease with UTI which was
34%. In this research work, awareness program was carried out among the students of
different teaching institutes, where the information about prevention and treatment of
UTI had provided.
Keywords: Urinary tract infections; Survey; Chattogram
Introduction
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are highly prevalent worldwide [1]. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the inflammatory disorders of the urinary tract caused by the abnormal growth of pathogens [2,3]. Urinary tract infection is known to cause short-term morbidity in terms of fever, dysuria, and lower abdominal pain (LAP) and may result in permanent scarring of the kidney [4,5]. Urinary tract infections may be asymptomatic, acute, chronic, and complicated or uncomplicated, and the clinical manifestations of UTIs depend on the portion of the urinary tract involved, the etiologic organisms, the severity of the infection, and the patient’s ability to mount an immune response to it. Both asymptomatic and symptomatic UTIs pose a serious threat to public health care, hence reducing the quality of life and resulting into work absenteeism [6]. UTIs are most often due to bacteria (95%), but may also include fungal and viral infection [7]. Several authors around the world have been reported the Gram negative bacteria of E.coli and Klebsiella spp. being the most frequent organisms causing UTIs [8-12]. E.coli causes 70-95% upper and lower UTIs [13]. About 150 million people suffer from UTIs each year globally [14]. Urinary surgery or an exam of your urinary tract that involves medical instruments can both increase risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
Materials and Method
Design
A descriptive type of cross-sectional study design was used. All the data were collected through structured format in questionnaires. The sample sizes were statistically desirable, feasible and satisfactory and were approached randomly. The recording system was almost adequate and no other persons were engaged in collecting the data except the researcher so that the quality of the overall data was reliable.
Place of Study
The survey was carried out in the Urology Department of Chattogram Medical College Hospital (CMCH), Chattogram.
Data Collection Period
From November 2019 to February 2020.
Survey Protocol
For prospective cross-sectional encounter, pre-prepared questions were asked among 50 patients regarding UTI from Chattogram Medical College Hospital (CMCH), Chattogram, who agreed to participate were selected randomly. The patients were asked the questions by researcher herself which she filled in the questionnaire form. The questionnaire was to collect information on age, gender, marital status, level of education, residence, signs and symptoms, diagnostic test, antibiotic therapy, used antibiotic, duration of treatment and associated disease. The data from questionnaire were processed anonymously. Data were analyzed.
Data complication and processing
After complication of raw data, we stoned out and prepared a master table manually, keeping in view the objectives and variables.
Data analysis and report writing
Data were processed with the help of MS Excel and MS Word.
Results and Discussion
Age range
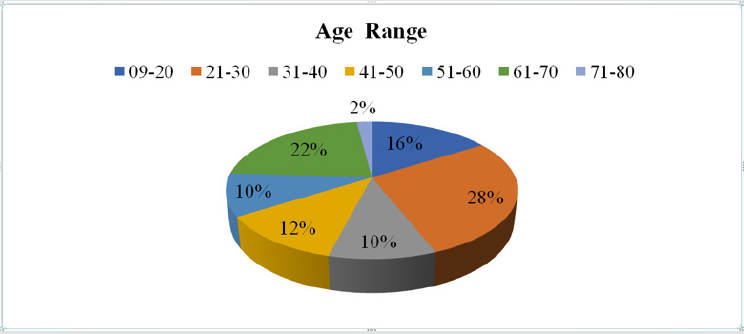
a. Comment: (Table 1) (Figure 1)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of
patient’s age range was from 21-30 years which was 28% and the
least proportion of patient’s age range was from 71-80 years which
was only 2%. Among the remaining 22% of patient’s age range was
from 61-70 years, 16% of patient’s age range was from 09-20 years,
12% of patient’s age range was from 41-50 years, 10% of patient’s
age range was from 31-40 years and 10% of patient’s age range was
from 51-60 years.
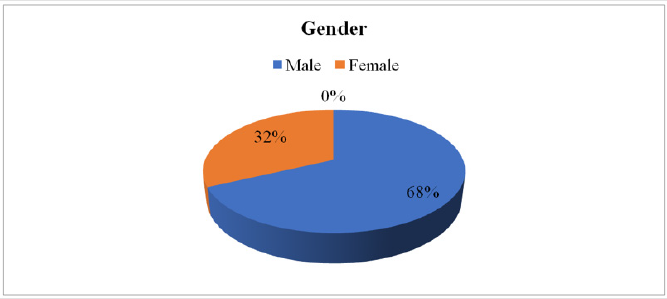
Gender
a. Comment (Table 2) (Figure 2)
From the above figure it was seen that 68% of patients were male and the remaining 32% were female patients.
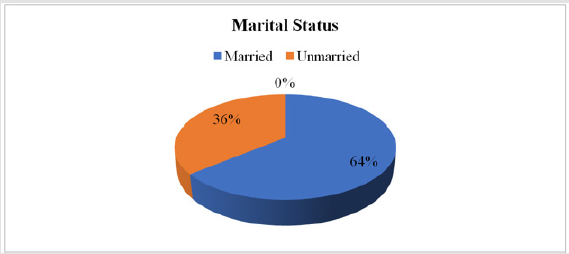
Marital Status
a. Comment (Table 3) (Figure 3)
From the above figure it was seen that 64% of patients were married and the remaining 36% were unmarried.
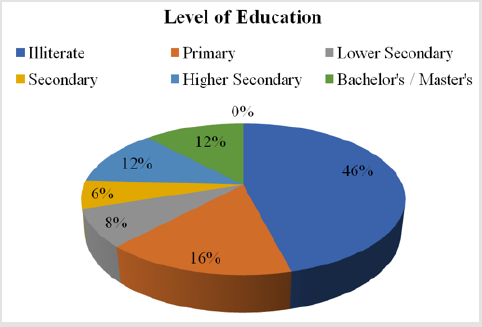
Level of Education
a. Comment (Table 4) (Figure 4)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients was illiterate regarding 46% and the least proportion had secondary education which was 6%. Among the remaining, 16% of patients were educated with primary education, 12% had a bachelor’s/ master’s degree, 12% were educated with higher secondary education and 8% were educated with lower secondary education.
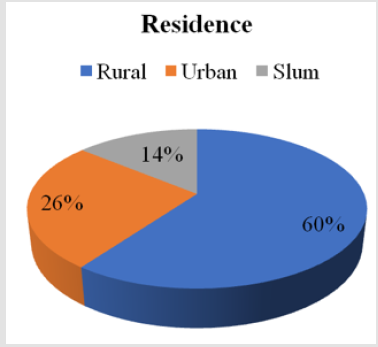
Residence
a. Comment (Table 5) (Figure 5)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients was from rural area which was 60% and the least proportion was from slum area which was 14%. The remaining 26% patients were from urban area.
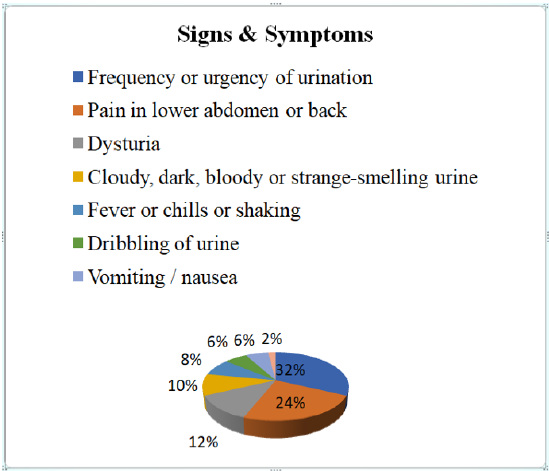
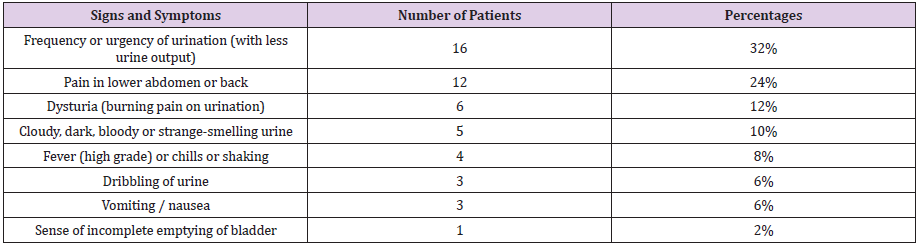
Signs and Symptoms
a. Comment (Table 6) (Figure 6)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients had frequency or urgency of urination with less urine output which was 32% and the least proportion had sense of incomplete emptying of bladder which was only 2%. Among the remaining 24% patients had pain in lower abdomen or back , 12% patients had dysturia (burning pain on urination), 10% patients had cloudy, dark, bloody or strange-smelling urine, 8% patients had fever (high grade) or chills or shaking, 6% patients had dribbling of urine and 6% patients had vomiting / nausea.
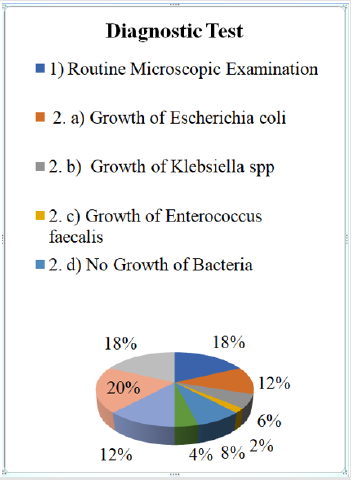
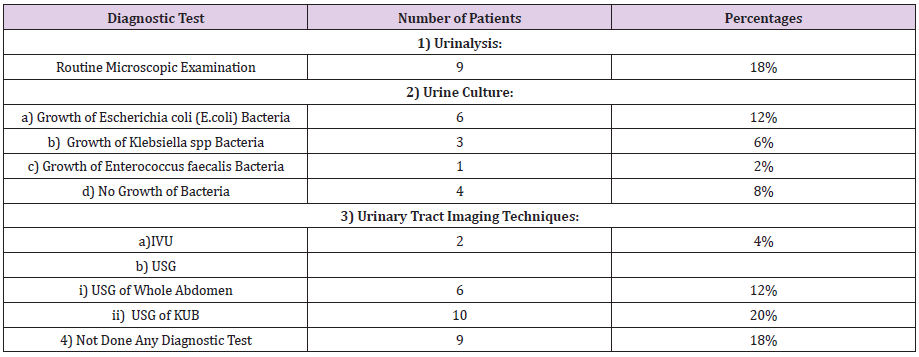
Diagnostic Test
a. Comment (Table 7) (Figure 7)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients had done USG of KUB diagnosis for UTI which was 20% and the least proportion had done urine culture test in which the growth of Enterococcus faecalis bacteria was found which was only 2%. Among the remaining 18% patients had done routine microscopic examination, 12% patients had done urine culture test in which the growth of Escherichia coli (E.coli) bacteria was found, 6% patients had done urine culture test in which the growth of Klebsiella spp bacteria was found, 8% patients had done urine culture test in which no growth of bacteria was found , 4% patients had done IVU test,12% patients had done USG of whole abdomen and 18% patients had not done any diagnostic test for UTI.
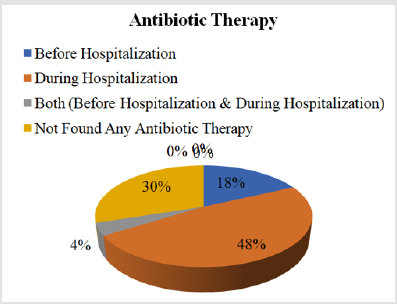
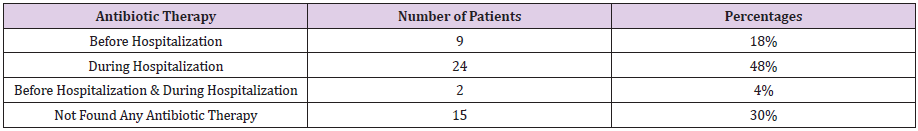
Antibiotic Therapy
a. Comment (Table 8) (Figure 8)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients had taken antibiotic therapy only during hospitalization which was 48% and the least proportion had taken antibiotic therapy before hospitalization & during hospitalization which was only 4%. Between the remaining 18% patients had taken antibiotic therapy before hospitalization and 30% patients had not taken any antibiotic therapy.
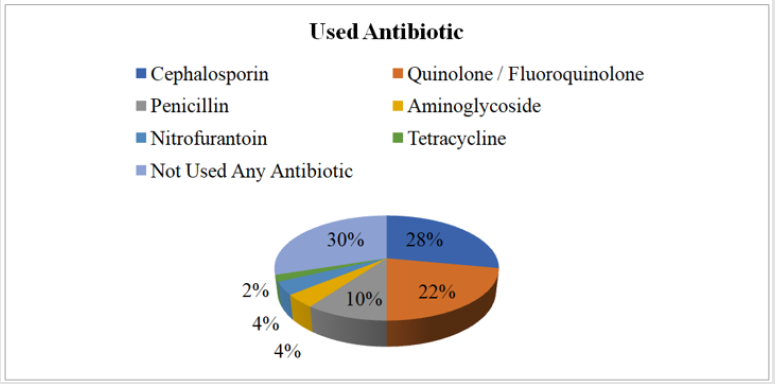
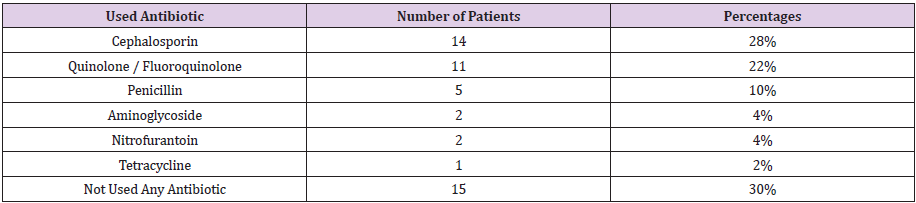
Used Antibiotic
a. Comment (Table 9) (Figure 9)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients had not taken any antibiotic which was 30% and the least proportion had taken antibiotic related to tetracycline drug class which was only 2%. Among the remaining 28% patients had taken antibiotic related to cephalosporin drug class, 22% patients had taken antibiotic related to quinolone or fluoroquinolone drug class, 10% patients had taken antibiotic related to penicillin drug class, 4% patients had taken antibiotic related to aminoglycoside drug class, and 4% patients had taken antibiotic related to nitrofurantoin drug class.
Duration of Treatment
a. Comment (Table 10) (Figure 10)
From the above figure it was seen that the highest proportion of patients had completed 50% course of treatment which was 52% and the least proportion had completed full course of treatment which was only 6%. Between the remaining 24% patients had completed 25% course of treatment and 18% patients had taken only a single dose.
Associated Disease
a. Comment (Table 11) (Figure 11)
abnormalities as associated disease with UTI which was 34% and the least proportion had cardiovascular disease (CVD), asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cancerwhich was only 2% each. Among the remaining 8% patients had hypertension (HTN), 10% patients had diabetes mellitus (DM), 4% patients had chronic kidney disease (CKD), 6% patients had anemia, 4% patients had neurological disorders, 8% patients had multi-diseases and 18% patients had not found any associated disease with UTI.
Awareness Program
a. Place: The awareness program was carried out around 500 students of different teaching institutes like Buetech academics, Probaha coaching center, Retina coaching center and Udvash coaching center.
b. Provided information:
I. Briefing to the students about the definition of UTI.
II. Asking to the students if they have any knowledge about
the signs and symptoms of UTI.
III. Explaining them how to prevent UTI.
IV. Specifying that the Urologists are the specialists for UTI
treatment.
Conclusion
There has been a lot of concern about increasing the rate of UTI patients in last few years. According to this survey the highest proportion of patient’s age range was from 21-30 years which was 28% and the least proportion of patient’s age range was from 71-80 years which was only 2%. 68% of patients were male and the remaining 32% were female patients. 64% of patients were married and the remaining 36% were unmarried. The highest proportion of patients was illiterate regarding 46% and the least proportion had secondary education which was 6%. The highest proportion of patients was from rural area which was 60% and the least proportion was from slum area which was 14%. The highest proportion of patients had frequency or urgency of urination with less urine output which was 32% and the least proportion had sense of incomplete emptying of bladder which was only 2%. The highest proportion of patients had done USG of KUB diagnosis for UTI which was 20% and the least proportion had done urine culture test in which the growth of Enterococcus faecalis bacteria was found which was only 2%. The highest proportion of patients had taken antibiotic therapy only during hospitalization which was 48% and the least proportion had taken antibiotic therapy before hospitalization & during hospitalization which was only 4%. The highest proportion of patients had not taken any antibiotic which was 30% and the least proportion had taken antibiotic related to tetracycline drug class which was only 2%. The highest proportion of patients had completed 50% course of treatment which was 52% and the least proportion had completed full course of treatment which was only 6%. The highest proportion of patients had genitourinary abnormalities as associated disease with UTI which was 34% and the least proportion had cardiovascular disease (CVD), asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cancer which was only 2% each. In this research work, awareness program was carried out among the students of different teaching institutes, where the information about prevention and treatment of UTI had provided.
References
- Lichtenberger P, Hooton TM (2008) Complicated urinary tract infections. Curr Infect Dis Rep10: 499-504.
- D Prakash, RS Saxena (2013) Distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of bacterial pathogens causing urinary tract infection in Urban Community of Meerut City, India. ISRN Microbiologyvol 2013: 749629.
- O Amali, MD Indinyero, EU Umeh, NO Awodi (2009) Urinary tract infections among female students of the university of agriculture, Makurdi, Benue State, Nigeria. Internet Journal of Microbiology 7(2): 1-5.
- A Hoberman, M Charron, RW Hickey, M Baskin, DH Kearney, et al. (2003) Imaging studies after a first febrile urinary tract infection in young children. New England Journal of Medicine 348(3): 195-202.
- V Camacho, M Estorch, G Fraga, Mena E, Fuertes J, et al. (2004) DMSA study performed during febrile urinary tract infection: A predictor of patient outcome. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 31(6): 862-866.
- O Olowe, B OjoJohnson, O Makanjuola, R Olowe, V Mabayoje (2015) Detection of bacteriuria among human immuno deficiency virus seropositive individuals in Osogbo, south-western Nigeria,” European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology 5(1): 126-130.
- Cattell WR (1996) Infections of the Kidney and Urinary Tract. Oxford University Press p. 1-26.
- Obiogbolu CH, Okonko IO, Anyamere CO, AO Adedeji, A Ogun, et al. (2009) Incidence of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) among pregnant women in Akwa metropolis, Southeastern Nigeria. Sci Res Essays 4: 820-824.
- Behzadi P, Behzadi E (2008) The Microbial Agents of Urinary Tract Infections at Central Laboratory of DrShariati Hospital, Tehran, IRAN. Turk Klin Tip Bilim28:445-449.
- Ayhan N, Basbug N, Ozturk S (1998) Causative agents of urinary tract infections and sensitivity to antibiotics. Microbiol Bull 22: 215-221.
- Ebie MY, Kandakai Olukemi YT, Ayanbadejo J (2001) Urinary tract infections in a Nigerian Military Hospital. Nig J Microbiol 15: 31-37.
- Garofalo CK, Hooton TM, Martin SM, Stam WE, Palermo JJ, et al. (2007) Escerichia coli from Urine of Female Pateints with Urinary Tract Infections is Competent for Intracellular Bacterial Community Formation. Infect Immun 75: 52-60.
- Stamm WE (2001) An Epidemic of Urinary Tract Infections? N Engl J Med 345:1055-1057.
- WE Stamm, SR Norrby (2001) Urinary tract infections: disease panorama and challenges. Journal of Infectious Diseases 183(s1): S1-S4.

 Research Article
Research Article