Abstract
Routine health check-up can help to find problems early for better treatment and cure. Balanced diet and proper lifestyle would keep our body running like a well-tuned engine, which would prevent diseases, suffering, morbidity and mortality in the long run. So, it became customary for everyone to have a yearly check-up even if someone is feeling perfectly well. The paper deals with routine physicals, screening tests, and good health tips for healthy & asymptomatic adults.
Keywords: BMI; Echocardiogram; HbA1c; SGPT; PAP Smear Test; C- Reactive Protein
a) Visual Disorders: Glaucoma, Cataracts, Diabetes and Hypertension related eye disease.
b) Dental Disorders: Gum disease, Dry mouth, Tooth decay, Plaque formation.
c) Lung Disorders: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease loss of lung volume. (COPD),
d) Cardiovascular Disorders: Heart attacks, Conge peripheral artery disease, Constive heart failure, Irregular heart rhythm, Hypertension, Atherosclerosis.
e) Gastrointestinal Disorders: Stomach ulcers, Colon inflammation orcolitis from infection or ischemic, dysphasia, constipation, bowel incontinence, hemorrhoids.
f) Kidney Disorders: Kidney or renal disease from long standing diabetes and hypertension, Stone in kidney or gallbladder.
g) Musculoskeletal Disorders: Osteoarthritis, Osteoporosis, and Gout.
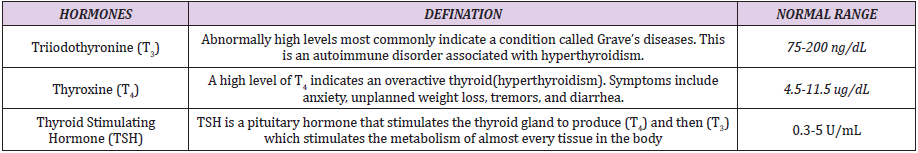
h) Hormonal Disorders: Diabetes, Menopause, Thyroid dysfunction.
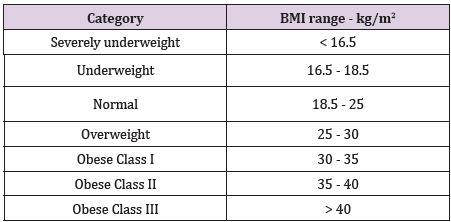
Body weight and BMI test
The body weight based on BMI values for adults. It is used for both men and women, age 18 or older [1] (Table 1).Eye Tests
Eyesight tends to deteriorate with age. Serious eye conditions such as Glaucoma, Cataracts, Diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration are more common with age.
a) Eye Pressures: Eye pressure testing (Tonometry) is one of the ways we watch for Glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness.
b) Visside Vision: Visual field testing (measuring side vision) is another way we watch for Glaucoma.
c) Dilated Retinal Examination [2]:
i. By evaluating the eye’s natural lens, we can detect signs of cataracts.
ii. By looking for changes in the optic nerve, we may be able to tell if glaucoma is present.
iii. Damage to the eye’s arteries and veins (blood vessels) can give us clues about the presence of diabetes.
d) Slit lamp (microscope): For Dry eyes, Eyelid disease etc other eye care.
Dental Check Up
a) Scaling and Cleaning: Scaling and cleaning involve the removal of built-up debris from the teeth. This may include food particles, soft plaque or hard calculus.
b) Fissure sealants: Sealants protect teeth from decay.
Lung Test
a) Breathing Tests [3]:
(Spirometry): This test measures how much air you can breathe in and out. It also measures how fast you can blow air out. The test helps to detect diseases like asthma and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). Pulmonary fibrosis (scarring of the lung tissue).b) Lung Diffusion Capacity: This test measures how well oxygen passes from your lungs to your bloodstream.
c) Tests to Measure Oxygen Level: Pulse Oximetry and arterial blood gas tests show how much oxygen is in your blood.
d) Lung Volume Measurement: Body Plethysmography is a test that measures how much air is present in your lungs when you take a deep breath. It also measures how much air remains in your lungs after you breathe out fully. Spirometry can show whether you have: A blockage (obstruction) in your airways. This may be a sign of asthma, COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), or another obstructive lung disorder.
Cardiac Tests
a) Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) [4]: An electrical activity and show certain problems such as abnormal heartbeats or damage to the heart. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that can record your heart’s electrical impulse.
b) Chest x-ray: A chest x-ray provides a picture of the lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and the diaphragm.
c) Blood Pressure Test: To check the blood pressure in sphygmomanometer. Normal blood pressure level is 120/80 mm Hg.
d) Echocardiogram: An Echocardiogram uses sound waves to create a moving picture of your heart. It provides information about the size and shape of your heart and how well your heart chambers and valves are functioning.
e) Heart Rate: It is the speed of the heartbeat, specifically the number of heartbeats per unit of time. The normal adult human heart rate ranges from 60–100 bpm.
f) Pulse Rate: older, and adults (including seniors): 60 - 100 beats per minute.
g) Creatine phosphokinase-MB (CPK-MB): CPK-MB is a cardiac marker use to assist diagnoses of an acute myocardial infarction. The normal adult human range 5 to 25 IU/L
h) Troponin: A Troponin test measures the levels troponin T or troponin I proteins in the blood. There proteins are released when the heart muscle has been damaged, such as occurs with the heart attack. The normal adult human range less than 0.01 ng/mL
Blood Tests
A fasting glucose test that checks your blood sugar level to screen for diabetes. Normal blood sugar level is
a) Fasting Blood Glucose: Less than or equal to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
b) 2 hours after eating (postprandial)
I. Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) for people age 50 and younger.
II. Less than 150 mg/dL (8.3 mmol/L) for people ages 50– 60.
III. Less than 160 mg/dL (8.9 mmol/L) for people age 60 and older.
c) HbA1c blood test [5]
HbA1c is a marker that can determine your average blood sugar (glucose) levels over the previous 3 months. [Range 4.5 % to 7.1%].
d) Lipid profile test
A fasting lipid panel to check your cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
I. Normal level of cholesterol is not less than 130-250 mg/ dL.
II. Normal level of HDL is in between 50-60 mg/dL.
III. Normal level of LDL cholesterol is lower than 100 mg/dL.
IV. Normal level of triglyceride is lower than 150 mg/dL
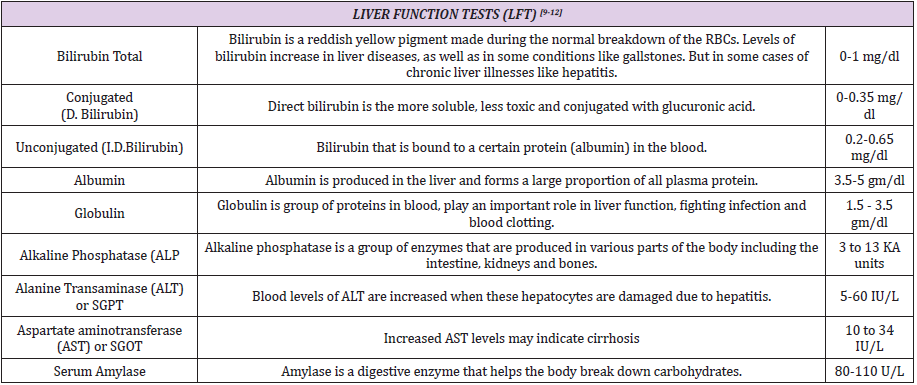
e) Haemogram [6-8]: A complete blood count (CBC) gives important information about the kinds and numbers of cells in the blood, especially red blood cells, white blood cells , and platelets [9-12].
a. Normal range of WBC: 5,000–10,000 WBCs per cubic millimeter (mm3).
b. Normal range of WBC cell types(differential)
Neutrophils: 50%–62% Band neutrophils: 3%–6% Lymphocytes: 25%–40% Monocytes: 3%–7% Eosinophils: 0%–3%c. Normal range of RBC: 4.5–5.5 million RBCs per mcL.
d. Normal range of Haemoglobin: 14–17.4 g/dL Platelet (thrombocyte) count: 140,000–400,000 platelets per mm3 (Table 2).
Kidney Tests
a) Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) test [13]: This test, which is used to evaluate kidney function, diagnose kidney problems. This test measuring the level of nitrogen in the urea of the blood.
1. The normal range for this test is 7 to 20 mg/dL.
b) Creatinine Test: Creatinine (Cr) forms when a substance found in muscle tissue breaks down. A high level of creatinine in the blood may indicate kidney damage caused by kidney infection, kidney stones, or decreased blood flow to the kidneys.
1. The normal range for this test is 0.8 to 1.4 mg/dL.
c) Calcium Test: This test, which measures the level of calcium in the blood, can be used to screen patients for kidney disease.
1. The normal range for this test is 8.5 to 10.2 mg/dL.
d) Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test [14,15]:
I. This test may be used in men to screen for prostate cancer (beginning at the age of 50 or at age 40 if at higher risk) and to monitor prostate cancer treatment. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland.
II. For most men-
III. The normal range for the PSA test is lower than 4.0 ng/ mL. Men at increased risk for prostate cancer may be retested if their level is higher than 2.5 ng/mL.
IV. Normally, the protein PSA can be found in two forms in the blood either attached to other proteins or “free” (unattached). The free PSA test measures the amount of PSA that is unattached [16-19] (Table 3).
Test for Women [20]
a) Breast Test:
a. Mammography: It is the process of using low-energy x-rays (usual around 30 kVp) to examine the women breast and it use as a diagnostic and a screening tool.
b) Abdomen Test:
b. Ultrasonography: Above 40 women, suffer uterine cyst, so to check it Ultrasonography is used.
c) PAP smear test: It is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially pre-cancerous and cancerous processes in the endocervical canal.
Blood Tests for Infertility
a) FSH (Follicle-stimulating Hormone) [21]: It helps a women’s menstrual cycle and the production of egg maturation. Normal range 5-20 IU/L (Third day of Menstrual Period)
b) LH (Luteinizing Hormone): In women, luteinizing hormone (LH) is link to ovarian hormone production and egg maturation. Normal range 24-40 mlU/ml (24-36 hours before ovulation)
c) Ovarian Reserve (AMH) test [22]: The level of AMH (Anti-Mullerian Hormone) in an women’s blood is generally a good indicator of her ovarian reserve. Normal range 1.35-4 ng/ mL [23,24] (Table 4).
Conclusion
Go for routine health check-up & balanced diet for keep your smile healthy
Good Health Tip
a. Balanced diet
b. Regular Exercise, Walking & Jogging
c. Routine screening tests
d. Preventive measures
e. Tension free mind
f. Early to bed at night
g. Early morning Rise
h. Keep smiling always
Conclusion
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prochazka AV, Lundahl K, Pearson W, Oboler SK, Anderson RJ, et al. (2005) Support of evidence-based guidelines for the annual physical examination: a survey of primary care providers. Arch Intern Med 165(12): 1347-1352.
- Boulware LE, Marinopoulos S, Phillips KA, Hwang CW, Maynor K, et al. (2007) Systematic review: the value of the periodic health examination. Ann Intern Med 146(4): 289-300.
- Dubey V, Mathew R, Katyal S, Iglar K (2011) Preventive Care Checklist Forms. Mississauga, ON: College of Family Physicians of Canada 25-31.
- Dubey V, Mathew R, Iglar K, Moineddin R, Glazier R, et al. (2006) Improving preventative service delivery at adult complete health check-ups: The Preventive health Evidence-based Recommendation Form (PERFORM) cluster randomized trial. BMC Fam Pract 7: 44.
- Dubey V, Glazier R (2006) Preventive Care Checklist form. Evidence-based tool to improve preventive health care during complete health assessment of adults. Can Fam Physician 52: 48-55.
- Iglar K, Katyal S, Matthew R, Dubey V (2008) Complete health checkup for adults: update on the Preventative Care Checklist Form. Can Fam Physician 54(1): 84-88.
- Jackson RD, LaCroix AZ, Gass M, Wallace RB, Robbins J, et al. (2006) Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and the risk of fractures. N Engl J Med 354(7): 669-683.
- Papaioannou A, Morin S, Cheung AM, Atkinson S, Brown JP, et al. (2010) clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada: summary. CMAJ 182(17): 1864-1873.
- (2009) Health Canada [website] Health concerns. Nicotine replacements and medications for quitting smoking.Ottawa, ON: Health Canada, 30 Nov 2011.
- Lau DC, Douketis JD, Morrison KM, Hramiak IM, Sharma AM, et al. (2006) Canadian clinical practice guidelines on the management and prevention of obesity in adults and children. Executive summary. CMAJ 176(8): 1-4.
- Padwal RS, Hemmelgarn BR, Grover S, McKay DW, Wilson T, et al. (2009) The 2009 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 1-diagnosis and assessment of risk. Can J Cardiol 25(5): 279-286.
- Khan NA, Hemmelgarn BR, Herman RJ, Bell CM, Mahon JL, et al. (2009) The 2009 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 2-therapy. Can J Cardiol 25(5): 287-298.
- Genest J, McPherson R, Frohlich J, Anderson T, Campbell N, et al. (2009) 2009 Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease in the adult-2009 recommendations. Can J Cardiol 25(10): 567-579.
- (2007) National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) Statement on conjugate meningococcal vaccine for serogroups A, C, Y and W135. An Advisory Committee Statement (ACS) Can Commun Dis Rep 33(ACS-3): 1-23.
- (2008) National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) Statement on the recommended use of pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine in homeless persons and injection drug users. An Advisory Committee Statement (ACS) Can Commun Dis Rep 34(ACS-5): 1-12.
- (2010) National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) Statement on seasonal trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (TIV) for 2010–2011. An Advisory Committee Statement (ACS) Can Commun Dis Rep 36(ACS-6): 1-49.
- (2010) National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) Statement of the recommended use of herpes zoster vaccine. An Advisory Committee Statement (ACS) Can Commun Dis Rep 36(ACS-1): 1-19.
- Reid RL, Blake J, Abramson B, Khan A, Senikas V, et al. (2009) Menopause and Osteoporosis Update 2009. Bone health. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 31(1): S34-41.
- Bischoff HA, Stähelin HB, Dick W, Akos R, Knecht M, et al. (2003) Effects of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on falls: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res 18(2): 343-351.
- Ladwig KH, Marten Mittag B, Löwel H, Döring A, Koenig W, et al. (2003) Influence of depressive mood on the association of CRP and obesity in 3205 middle aged healthy men. Brain Behav Immun 17(4): 268-275.
- McElroy SL, Kotwal R, Malhotra S, Nelson EB, Keck PE, et al. (2004) Are mood disorders and obesity related? A review for the mental health professional. J Clin Psychiatry 65(5): 634-651.
- (2010) Canadian Obesity Network Canadian obesity network. Edmonton, AB: Canadian Obesity Network.
- Dent R, Habib R, Soucy L, Bissada H (2007) 2006 Canadian clinical practice guidelines on the management and prevention of obesity in adults and children. 7. Psychiatric issues in the management of obesity. CMAJ 176(8): 40-44.
- Vallis M (2006) Canadian clinical practice guidelines on the management and prevention of obesity in adults and children. 10. Behaviour therapy. CMAJ 176(8): 54-56.

 Mini Review
Mini Review