Abstract
The problem of modern physical inactivity in children is becoming very relevant. Accelerated technological progress observed in society contributes to a reduction in motor activity not only in children, but also in adults. Improper body position with physical inactivity is accompanied by the formation of muscle imbalance in the human body. The current paper presents a methodology for the physical development of preschool aged children with the use of means of rhythmic gymnastics. Such means include various options for steps, running; simple acrobatic elements; choreographic balances, turns, jumps; gymnastic objects: ropes, balls, hoops. To justify the effectiveness of the experimental technique for the prevention of muscle imbalance, it has been tested some physical qualities in the preschool children. Therefore, it was investigated the following physical qualities: muscles strength endurance of the individual parts of the body, flexibility/mobility of the hip joints and spine, rapidity of action and reaction. The effectiveness of the developed methodology was confirmed using mathematical statistics methods. The obtained results are graphically presented and in the table.
Keywords: Preschool Children; Muscle Imbalances; Rhythmic Gymnastics
Introduction
Currently, under the influence of numerous socio-economic and ecological factors, the health of children and adolescents has deteriorated, and is in critical condition. Incorrect posture, according to many authors, is found in 15-20% of younger children, and 10- 12 years old – every third child is marked. Most postural disorders in school-age children have acquired a functional character. It is known that the conditions of the educational environment are the dominant factor in the formation of the whole range of functional states of the students that reflect a type of “school violations” syndrome in the activities of the life support systems of the body [1]. Nowadays, under the conditions of the scientific and technological revolution (smart phones, tablets), the interest of the children in the knowledge of these “toys” has suddenly increased, which often leads to an increase in the neuropsychological load, significantly reducing the physical activity of the children.
The lack of movement, static positions lead to asymmetry in muscle development and eventually to various posture violations [2]. Today’s children have encountered problems of hypertension, functional disorders of the muscles, muscle imbalance, when some muscle groups are spasmodic and others, on the contrary, too relaxed, which can lead to muscle fatigue, muscle pain, postural disorders. The incorrect position of the body is related to the need to prolong the rescue of the working position, the unilateral muscular weight, the weakness and underdevelopment of the musculoskeletal system, the loss of sight, hearing, creates unfavourable conditions in the functioning of organs and systems. There are adverse effects, especially in the circulatory, respiratory and digestive systems.
Position of body segments in space with forced static hypostases sitting, standing, and conditioned reflex is fixed in an ordinary position, a posture is installed, and curves of the spine are formed. Training, education, and then strengthening is done at 18-20 years. One of the ways to improve violations is the means and methods of physical education and sports applications. The implementation of these tools and techniques creates the conditions for the correct posture formation, its correction and the prophylaxis of disorders [3,4].
Materials and Methods
The purpose of our research involved the appreciation of the possibilities of rhythmic gymnastics funds for the prophylaxis of muscular imbalance in pre-schoolers through rhythmic gymnastics. The research methodology is presented by the methods of theoretical analysis and synthesis of the data of the specialized literature, the analysis of the training process, the method of pedagogical observation, the testing of physical capabilities, the pedagogical experiment, the methods of statistical mathematics. Data analysis of the scientific and methodological literature was performed on the problems of hypo-dynamics and kineto-prophylaxis. It has been studied the problems of the physical development of the children, as well as the means of the sports tests aimed at the physical development were analysed and synthesized.
The synthesis of the literary data allowed us to find that the wide application of the means of rhythmic gymnastics is one of the acceptable conditions for the improvement of the prophylactic process of the muscular imbalance, the formation of the muscle tone, the development of the motor skills of the children, as well as the removal of the stress of the daily life, which is expressed in psychological comfort and safety itself. The analysis of the kineto-prophylactic training process allowed us to establish that its optimization is possible provided the continuous study of new programs and proposals from the scientific body of research in this field. The improvement of the kineto-prophylactic process in the system of rhythmic gymnastics lessons is possible only by the permanent condition of the interest towards the new methods and the forms of organization of the training. Self-enrichment with new information, tendency towards creation, elaboration of new methodologies with the use of different means must increase the effectiveness of the training lessons. The pedagogical observations were carried out with the purpose of multilateral study of the problem interested in us in the process of kineto-prophylactic training. The observations were made on both the activities of the coaches and the activities of the children during the physical exercises. In order to assess the physical abilities of the children were performed the following tests:
A. Assessment of the Strength Endurance of the Different Muscles of the Body
1. Abdominal Muscle – bending of the body (times) from the position lying on the back, legs bent, arms crossed on the chest with hands on shoulders, for 30″.
2. Spine Muscles – lifting the body from the position lying on the abdomen and maintaining this position, hands bent after the head (sec).
3. The Muscles of the Parts of the Body – the child lies on the right (left) side of the body, arms and legs extended; on command, raise the limbs simultaneously and try to maintain the position (sec).
4. Arm Muscles – from the support position lying down, legs extended, the child tries to move forward in the hands (m).
5. The Muscles of the Legs – from the standing position, performing the knee flexions (times).
B. From the “Flexibility/Mobility” Group the Possibilities of the Following Joints were Determined:
1. Coxofemoral Joints – “string” is performed: right (left) – forward and backward extension of the legs, landing on the floor; the front string is made with the legs extended laterally. The distance from the groin area to the floor will be determined (cm).
2. The Backbone – was accomplished in one forward
direction by bending the body from the sitting position on the floor, the legs slightly apart laterally, the arms outstretched (cm).C. Rapidity
1. Of the actions are determined according to VL Marishchuk [5] – performing the beating of the hands (times) over the head and thighs for 20 seconds.
2. Of the reactions are determined after VI Lyah [6]: The trainer holds a gymnastics stick numbered vertically from the upper end with the extended arm. The child holds the open palm near the bottom end of the stick. After 1-2 seconds, the trainer releases the stick, and the examiner must catch it as soon as possible (close the palm). The grip is made with the working hand. It is evaluated by the average distance in cm after three attempts from the bottom end of the stick to the place where the little finger is held.
Subjects
The research was carried out within the sports complex of the State University of Physical Education and Sport and the kindergarten of the municipality of Chisinau. In the pedagogical experiment 20 children participated, divided into two groups: experiment and witness, 10 children each.
Procedures
The pedagogical experiment was carried out through two basic stages. In the first stage, the objectives of systematic means of rhythmic gymnastics were solved, which ensures the development of physical abilities in the examined children. At the present stage, the parameters of the physical capacities have been established. The initial level of exam development was appreciated using the methods of testing the strength, flexibility/mobility and rapidity capabilities, as a result of which the homogeneous groups were evaluated. In the second stage, the control of the effect of the kinetoprophylactic program for the development of physical abilities in the examined children was accomplished.
Statistical Analysis
The processing of the obtained results of the research was
carried out by means of mathematical processing and interpretation
of statistical data: arithmetical mean the mean 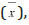 standard deviation
standard deviation 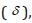 the standard error of the mean values, the reliability
of the differences in the mean values of the two empirical sets was
determined by the Student’s t-criterion.
the standard error of the mean values, the reliability
of the differences in the mean values of the two empirical sets was
determined by the Student’s t-criterion.
Description of the Experiment
The purpose of the physical exercise consists in strengthening the health, increasing the natural resistance to pathological agents from the external environment, establishing a psychophysical balance between the body and the environment. In view of the above, we have developed a methodology for the physical development of pre-school children. The experimental methodology has involved the use of rhythmic gymnastics methods. The lessons were conducted three times a week for 60 minutes and it contained three basic parts. The preparatory part of the lesson (15-20 minutes) includes the total warm-up of the body, of all the muscles. Particular objectives involve the formation of the right posture and the beautiful walking. This time period of the lesson includes different variations of walking, running; light acrobatic elements; choreographic jumps. The particularity of the jumps includes the combination of the work of the legs and arms, which involves tightening some muscles and relaxing others.
The basic part of the lesson lasts 35-40 minutes and starts with educating the sense of balance. For this are used different forms of choreographic balances (vertical, horizontal) with different positions of the arms. Next it is learned two-leg and one-leg turns with different free-leg positions. The next half of the basic part is for work with the objects of rhythmic gymnastics: rope, hoop and ball. This is divided into semesters: the first semester, September – December, working with the rope; second semester, January – May, working with hoop and ball. Based on the non-object and object elements, the technical elements, which have an appropriate structure, were processed, and then combinations on parts and a complete composition were performed during the training, which were presented under the musical accompaniment with all types of tempo. The final part lasts 10-15 minutes and is represented by the strength exercises for the large muscles (abdominal and back) and the deep stretches.
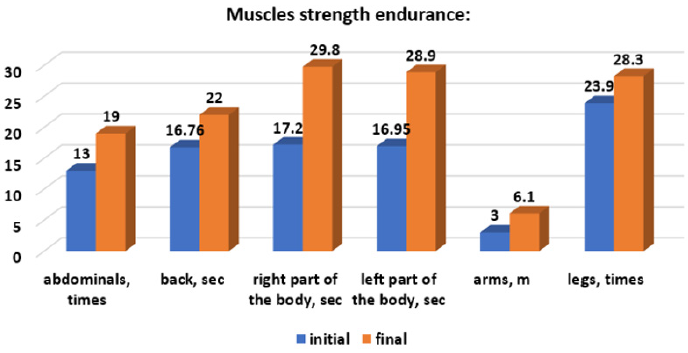
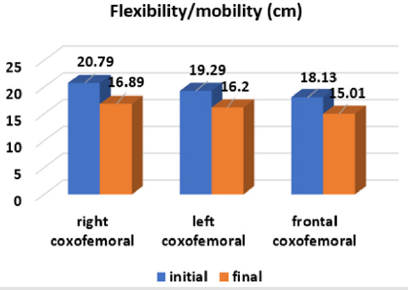
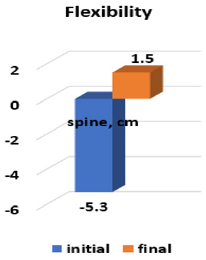
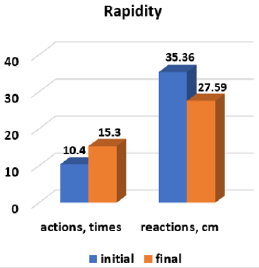
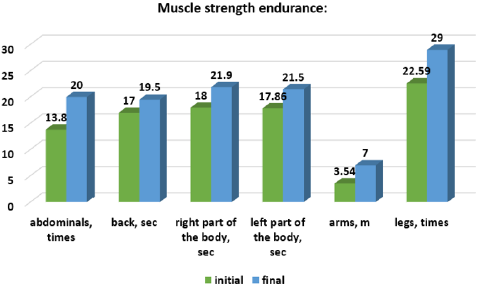
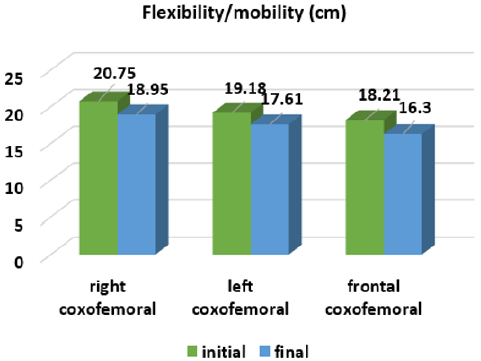
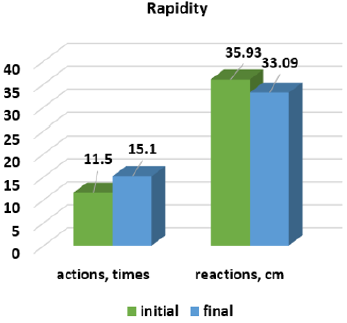
At the end of the part, the dynamic rhythmic-musical games took place [7]. In order to assess the effectiveness of the experimental method, the physical qualities of the children from the experimental group were carried out. In Figures 1-4 are presented the results of the dynamics of physical qualities development. The results from the strength endurance group category explain that from 6 parameters: two, the muscles of the right and left parts of the body are significant at the threshold ρ < 0.001; the four parameters – at the threshold ρ < 0.01: the strength endurance of the abdominal muscles, back, arms and legs. The results obtained demonstrate the quite high potential of the means of rhythmic gymnastics, oriented to the development of strength abilities. To confirm the flexibility/mobility parameters we have investigated the dynamics of the development of the coxofemoral joints and the spine. From 4 parameters the three: coxofemoral flexibility/mobility of the right, frontal, and of spine are significant at the threshold ρ < 0.001; one parameter, left coxofemoral flexibility/mobility – at the threshold ρ < 0.01. These data confirm the specificity of the rhythmic gymnastics’ sports sample, in which the elasticity capacities are preferred. In the group of the parameters of the rapidity of both: the rapidity of the actions and the rapidity of the reaction are significant at the threshold ρ < 0.01. Working with rhythmic gymnastics objects contributes to the development of these physical abilities. In another case we see in the control group (Figures 5-8).
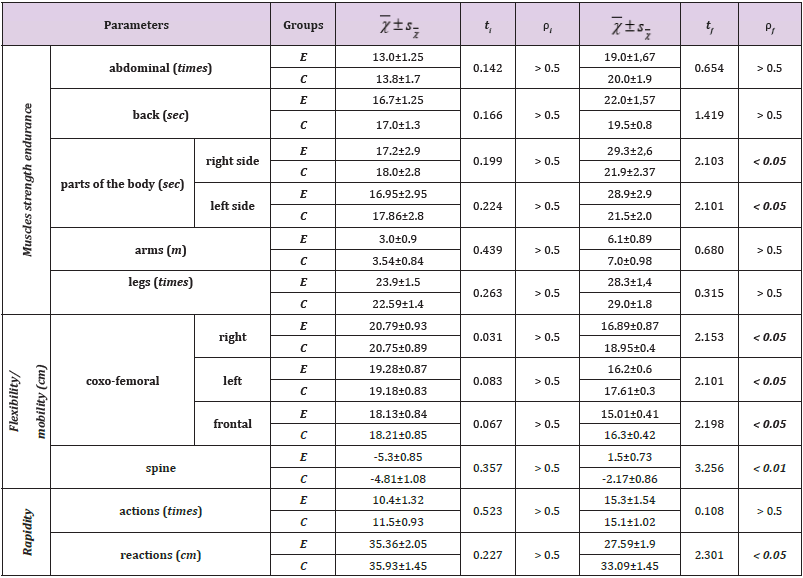
No parameter presented the statistical significance on the threshold ρ < 0.001. Of the 12 parameters, four: the strength endurance of the back muscles, the flexibility/mobility of the right and frontal coxofemoral, of the spine, are significant at the threshold ρ < 0.05. Three parameters: the strength endurance of abdominal muscles, arms, legs and the rapidity of actions showed statistical significance on the threshold ρ < 0.01. And the data of four parameters are not significant (ρ > 0.5): muscles strength endurance of the right part of the body and the left part of the body, the flexibility/ mobility of the left coxofemoral and the rapidity of the reaction. The results obtained imply that the development of physical abilities in pre-schoolers requires the development of physical education lessons with special orientation to the prevention of muscular imbalance. The effectiveness of the experimental method can be looked at through the data in Table 1, where the comparative analysis of the average group indexes of the examined children is presented.
Table 1: Comparative analysis of the average group indices of physical development in the experimental (E) and control (C) groups.
As can be seen, out of 12 parameters more than half (7) showed the statistical significance, of which one (spine flexibility) – on the threshold ρ < 0.01, other six – on the threshold ρ < 0.05. It should be noted that all the parameters in the flexibility group are significant in favour of the experiment group, thereby determining the specificity of rhythmic gymnastics lessons. Noteworthy is the fact that two parameters: the muscles strength endurance of the parts of the body, are also significant (ρ < 0.05), which argues in the lessons the sense of balance and correct attitude, where more skeletal muscles participate. The parameter “rapidity of reaction” (ρ < 0.05) which confirms the work with objects (circle and ball) in rhythmic gymnastics arouses interest.
Conclusion
Thus, the results of the research have demonstrated the effectiveness of the experimental method with the use of the rhythmic gymnastics means oriented to the physical development in the preschool children. The methodology developed can be used in different physical culture activities, carried out not only with preschoolers, school-age children, but also with mature people. The use of music in the lessons of physical culture of fortification can help to enrich the teachers, both in the plan of its cultural elevation and of the practitioners, as well as in the aspect of the creative approach to his profession.
References
- Kim DJ, Cho ML, Park YH, Yang YA (2015) Effect of an exercise program for posture correction on musculoskeletal pain. Journal Physical Therapy Science 27(6): 1791-1794.
- Dadaev OA, Sklyarenko RT, Travnikova NG (2003) Clinical and psychological characteristics of children and adolescents with scoliosis. In: Medical and Social Expertise and Rehabilitation, Russia 3: 10-14.
- Cailliet R (2004) The Illustrated Guide to Functional Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System. USA, Amer Medical Association.
- Dvorakova H (1989) Forming the correct body position. În: Învăţământul preş Bucureşti: Didactică şi Pedagogică, Romania 3: 15-19.
- Marishchuk VL, Bludov YuM, Plakhtienko VA, Serova LK (1990) Methods of psychodiagnostics in sports: Textbook. Education, Мoscow, Russia.
- Lyah VI (1998) Tests in physical education of pupils: Teacher Manual. Vlados, Moscow, Russia.
- Aftimiciuc O, Faur ML (2000) Jocuri ritmico-muzicale. Facla, Timişoara, Romania.

 Research Article
Research Article