Abstract
Objective: To first describe the treatment of type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fractures with a newly proposed technique, through supra-patellar approach utilizing intramedullary nailing and hollow screws.
Clinical Presentation and Intervention: We report a case of a 46-year-old male who sustained a closed fracture of the left tibial plateau and proximal fibula. The patient underwent an intramedullary nailing and hollow screws surgery. The long leg brace was fixed for two weeks after the operation. Two weeks later, functional exercise was conducted under the guidance of the rehabilitation physician. The patient improved muscle strength and obtained high scores for HSS and AKSS in a relatively short time.
Conclusion: In this case, a type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fracture treated with an intramedullary nailing and hollow screws provided satisfactory radiologic and clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Intramedullary Nailing ; Schatzker Type VI; Tibial Plateau Fracture
Abbreviations: ER: Emergency Room; CSEA: Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia; ROM: Range of Motion; HSS: Hospital for Special Surgery; AKSS: American Knee Society Score
Introduction
Type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fractures are very complex intra-articular fractures that often occur after high-energy trauma, as the fracture pattern involves joint and metaphyseal-diaphyseal region [1,2]. It is common sense that the more complex the fracture type, the more difficult the choice of treatment about the ideal type of fixation. The common standard treatment is dual-plate fixation through two incisions; however, the skin complication and infection rate are relatively high [3-6]. The aim of the present study was to report the treatment of type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fractures with a newly proposed technique, through supra-patellar approach utilizing intramedullary nailing and hollow screws.
Case Report
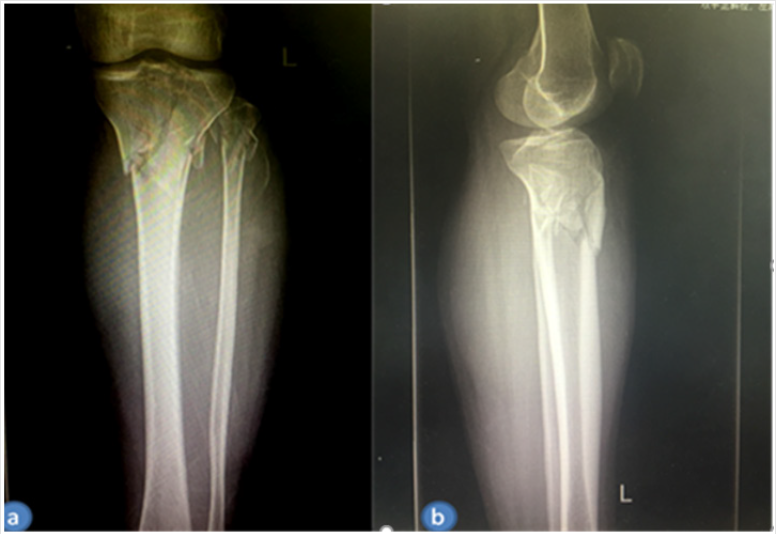
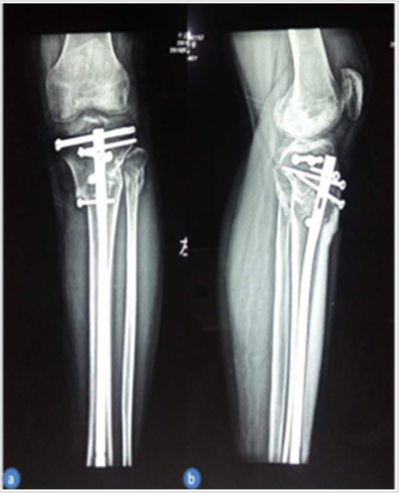
A previously healthy 46-year-old man who was walking experienced a traffic accident was sent to our emergency room(ER) with a comminuted fracture of the proximal fibula and left tibial plateau diagnosed by X-rays and confirmed by CT scan (Figures 1A & 1B). No peripheral nerve and vascular damage were found, and a brace was immediately applied in the ER. The patient was affected by a C1 fracture according to the AO classification and a typical type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fracture according to the Schatzker classification. The patient agreed that his case would be submitted for publication. The time from injury to operation was 1 day (Figures 1A & 1B).
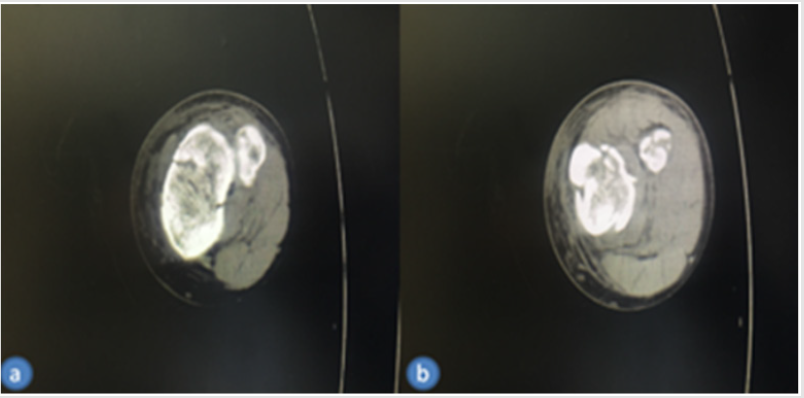
Figure 1(b): Preoperative CT scan of the tibial plateau.
(a) Proximal axial and
(b) Distal axial views.
Surgical Technique
The patient was placed in the supine position and combined spinal-epidural anesthesia (CSEA) induced. The surgery procedure was performed in two steps: firstly, the articular surface was stabilized and fixed with two 6.5 mm diameter/75 mm length hollow screws. The screw was positioned 0.5-1.5 cm below the articular surface and just medial to the lateral line of the tibial metaphysis. Secondly, after the placement of the screws, typical intramedullary nailing would follow from supra tendons approach (Figure 2). The Tibia nail of 11 mm diameter and 340 mm length was used along with four 5.0 mm fully threaded locking screws for proximal locking and two 5.0 mm fully threaded locking Screws for distal locking. The supra-patellar approach technique was described by previous literatures [7,8]. Postoperative sensation, movement and blood supply of distal limb were normal. After operation, the treatment protocol is identical to established protocols of tibial nailing, and early range of motion (ROM) exercises of the knee and ankle are encouraged. After immobilization with a long-leg brace for 2 weeks without knee movement, an early rehabilitation exercises were done in order to reduce swelling and improve knee function (Figure 2).
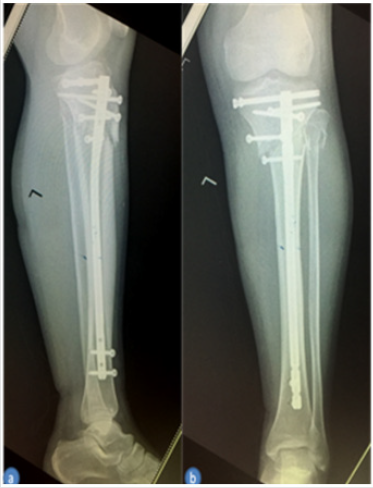
Figure 3: X-rays of tibial plateau obtained 3 day after operation.
(a) Frontal view and
(b) Lateral view.
Figure 4: X-rays of tibial plateau obtained 1 year after operation.
(a) Frontal view and
(b) Lateral view.
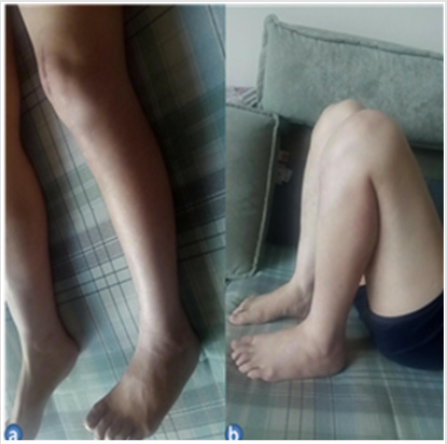
The loss of blood was 50ml and the operation lasted only 150 minutes. An x-ray obtained 1 day postoperatively demonstrated the knee joint plane and the alignment of the lower limb were in satisfactory condition (Figure 3). On x-ray followed up 1 year, the joint space and articular surface were satisfactory (Figure 4). ROM of the left knee joint was 5° to 125° (Figure 5). The Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) Knee Score at 12 months after surgery was 89 (pain, 30; function, 22; range of motion, 14; muscle strength, 10; flexion deformity, 5; and stability, 8). The American Knee Society Score (AKSS) [9] was Clinical AKSS 91 (pain, 50; range of motion, 23; Anteroposterior stability, 10; Mediolateral stability, 15; Flexion contracture, -2; Extension deficit, -5; Alignment 0) and Function AKSS 100(disabled walked, 50; stairs, 50; Use of walking aids, 0) (Figures 3-5).
Discussion
A revision of international clinical records performed by surgeons [10] shows a lack of general agreement about the best treatment in type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fractures, while a warning to avoid wide skin incisions seems to be generally recommended. In this case report, we describe an alternative technique for the treatment of type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fractures with a newly proposed technique, utilizing supra-patella portal intramedullary nailing and hollow screws. Firstly, two percutaneous mediolateral hollow screws were applied to fix the articular surface, then the proximal locking screws were used to support the articular surface and the distal locking screws enhanced the stability. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study utilizing intramedullary nailing and hollow screws through suprapatellar approach for type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fracture.
The technique of intramedullary nailing offers some advantages. Type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fracture is high-energy injury and early serious swelling, which have a higher risk of traditional methods of two-incision double-plating technique. Besides, Double incisions of the tibia may further compromise soft tissue and revascularize bone fragments, leading to serious complications such as oozing and wound infection. In contrast, intramedullary nail fixation employed in the present case can provide the advantage of minimal surgical dissection with preservation of the extraosseous blood supply to the fracture [11,12]. The indications for intramedullary nailing are more suitable for fractures involving the proximal and distal metaphysis. But a recently biomechanical study shows that intramedullary nailing and compression bolts can also maintain a rigid intra-articular stability similar to the stiff dual buttressing plating [13]. In this case, tibial intramedullary nailing through a supra-patellar approach has a number of potential advantages.
Firstly, tibial plateau fractures seem to be at risk for apex anterior deformities utilizing infra-patella intramedullary nailing because of the hyperflexion of the knee [12,14], whereas the Semiextended position through a suprapatellar portal can greatly eliminate the apex anterior deformities[15,16]. Secondly, tibial plateau fractures associated with serious soft tissue injuries involving the infrapatellar area may make it inappropriate to place a surgical incision in this area; the suprapatellar approach may provide a reasonable alternative in these situations [7]. Besides, the cost burden is lower than that of the traditional double plates. However, this technique is difficult to restore serious joint surface subsidence of type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fracture, so it is not recommended for patients with articular surface collapse.
Conclusion
On the basis of the findings obtained from this study, we propose that supra-patellar approach utilizing intramedullary nailing and hollow screws technique is an effective minimal invasive method for the treatment of type VI Schatzker tibial plateau fractures. It can provide satisfactory radiologic and clinical outcomes, with no obvious complications. The patient improved muscle strength and obtained high scores for HSS and AKSS in a relatively short time.
References
- Li YS, Dong J, Yue X, Cai ZY, Kuang GX, et al. (2015) [Treatment and analysis of the early postoperative complications of tibial plateau fractures]. Zhongguo Gu Shang 28(9): 846-849.
- Keightley AJ, Nawaz SZ, Jacob JT, Unnithan A, Elliott DS, et al. (2015) Ilizarov management of Schatzker IV to VI fractures of the tibial plateau: 105 fractures at a mean follow-up of 7.8 years. Bone Joint J 97(12): 1693-1697.
- Kavin Khatri, Vijay Sharma, Darsh Goyal, Kamran Farooque (2016) Complications in the management of closed high-energy proximal tibial plateau fractures. Chin J Traumatol 19(6): 342-347.
- Rohra N, Suri HS, Gangrade K (2016) Functional and Radiological Outcome of Schatzker type V and VI Tibial Plateau Fracture Treatment with Dual Plates with Minimum 3 years follow-up: A Prospective Study. J Clin Diagn Res 10(5): RC05-10.
- Chang H, Zhu Y, Zheng Z, Chen W, Zhao S, et al. (2016) Meta-analysis shows that highly comminuted bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated by single lateral locking plate give similar outcomes as dual plate fixation. Int Orthop 40(10): 2129-2141.
- Bertrand ML, Pascual López FJ, Guerado E (2017) Guerado, Severe tibial plateau fractures (Schatzker V-VI): open reduction and internal fixation versus hybrid external fixation. Injury 48(Suppl6): 81-85.
- Zelle BA, Boni G, Hak DJ, Stahel PF (2015) Advances in Intramedullary Nailing: Suprapatellar Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fractures in the Semiextended Position. Orthopedics 38(12): 751-755.
- Zelle BA, Boni G, Hak DJ, Stahel PF (2015) Advances in Intramedullary Nailing: Suprapatellar Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fractures in the Semiextended Position. Orthopedics 38(12): 751-755.
- Martimbianco AL, Fernanda Rizzo Calabrese, Luiz Alberto Nakao Iha, Marcelo Petrilli, Ozório Lira Neto, et al. (2012) Reliability of the "American Knee Society Score" (AKSS). Acta Ortop Bras 20(1): 34-38.
- Wu K, Huang J, Lin J, Wang Q (2017) Diagnosis and Treatment of Anterior Tibial Plateau Fracture-Dislocation: A Case Series and Literature Review. J Knee Surg 30(2): 114-120.
- Morandi M, Banka T, Gaiarsa GP, Guthrie ST, Khalil J, et al. (2010) Intramedullary nailing of tibial fractures: review of surgical techniques and description of a percutaneous lateral suprapatellar approach. Orthopedics 33(3): 172-179.
- Garnavos C, Lasanianos NG (2011) The management of complex fractures of the proximal tibia with minimal intra-articular impaction in fragility patients using intramedullary nailing and compression bolts. Injury 42(10): 1066-1072.
- Lasanianos NG, Garnavos C, Magnisalis E, Kourkoulis S, Babis GC (2013) A comparative biomechanical study for complex tibial plateau fractures: nailing and compression bolts versus modern and traditional plating. Injury 44(10): 1333-1339.
- Hiesterman TG, Shafiq BX, Cole PA (2011) Intramedullary nailing of extra-articular proximal tibia fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 19(11): 690-700.
- Chan DS, Serrano-Riera R, Griffing R, Steverson B, Infante A, et al. (2016) Suprapatellar Versus Infrapatellar Tibial Nail Insertion: A Prospective Randomized Control Pilot Study. J Orthop Trauma 30(3): 130-134.
- Sun Q, Nie X, Gong J, Wu J, Li R, et al. (2016) The outcome comparison of the suprapatellar approach and infrapatellar approach for tibia intramedullary nailing. Int Orthop 40(12): 2611-2617.

 Case Report
Case Report