Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Ron Carlson*
Received: June 05, 2018; Published: June 20, 2018
*Corresponding author: Ron Carlson, Carlson Bridge Technologies, Inc. Private Enterprise, Hawaiia, USA
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2018.05.001257
This presentation keys off the biological Principle of Cleansing- sterility or purity. As we move through this document together we’ll return to this fundamental Principle clarifying why biological systems Cleanse, maintaining correct pure form and function. A key factor in this discussion is how we as dental surgical professionals may be aiding the natural process of Cleansing, and thus total human health, or obstructing it. We begin with the physiology of sterility of compartments of the human body, the starting point for our discussion. Normally “sterile sites” are defined and known as tissues such as: blood, lymphatic system, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), pleural fluid-chest fluid; peritoneal fluid-abdominal fluid, pericardial fluid; bone-bone marrow; joint fluid-synovial fluid, temporal mandibular joint, knee, ankle, elbow, hip, wrist; internal body sites, lymph node, brain, heart, liver, spleen, vitreous fluid, kidney, pancreas, ovary, vascular tissue, and most important for our discussion. The Odonton, a single functional unit of the masticatory system. The Odonton is a sterile, pure, functional unit of the jaw until it is breached by micro- organisms [1] Like the functional unit of bone, the Osteon, micro- organisms (m- o) do not play a role in normal biological tissue metabolism and function. It is accepted that “m- o” invasion of tissues, called “infection,” do the opposite, disrupt metabolism- form and function.
For about 200 years, or more, there have been attempts to retain teeth whose sterile nutrient canals have been destroyed, compromised by putrefying m-os (micro-organisms) by placing gutta-percha, sliver points, N2 Sargenti fillers, or other concoctions within the canals hoping for a return to sterility of the Odonton [1] The continuous contentions of the pro-root canal proponents and the so-called “Extractionest,” anti-root canal contingent, came to a head in the early 20th Century, well documented in the Dental Cosmos- monthly record of dental science 1859-1936.
Case reports in the Dental Cosmos on dental causes of and systemic improvement of diseased conditions were actively re ported such as this on “Systemic Conditions Due to Oral Focal Infections” cited here: https://quod.lib.umich.edu/d/dencos/ 0527912.0062.001/113:14?rgn=full+text;view=image and, here regar ding “Focal Infections and Its Difficult Diagnosis”: https:// quod.lib.umich.edu/d/dencos/0527912.0063.001/421:168?rgn=- full+text;view=image;q1=oral+sepsis
I suggest the readers review these discussions and get a sense of the intensity of the support for the Focal Theory and its controversy. As the years moved along discussions were vast and heated regarding focal dental infections and their systemic impact until about the 1945 when the Focal Theory Of Infection was allegedly discredited, not being taught in formal dental settings from then until today. However, as of this writing we see the reemergence of the concept, well accepted by general medicine, taking on a new name as Oral Systemic Infectious Connections. Interesting to note and curious is the fact that about this time of 1945 antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers were developed that could suppress symptoms of putrefaction and its gas production within the Odonton giving the false impression of cure.
Revisiting the purity (sterility) compartments of the body, we note that of the lymphatic system, cerebrospinal fluid system, establish the blood brain barrier of the human brain compartment, which are all designed in maintaining the sterility of the human brain compartment without which this sterility, the brain is subject to sever breakdown and death. The functioning unit of the human being is the brain, analogous to the functioning unit of an Odonton or Osteon. Metabolism takes place in a sterile environment for multiple reasons. The three main purposes of metabolism are the conversion of food and fuel to building structures for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids and some carbohydrates, and elimination of nitrogenous waste products. Enzymes of metabolism catalyze essential reactions in Life without the input of foreign items such as bacteria, viruses, prions, or other foreign microorganisms (m-os) ensuring a “pure pathways to successful metabolism”-growth and development. Our human design is impeccable in its purity, functions, and outcomes avoiding foreign input from exogenous or endogenous sources not overseen by innate predetermined DNA/RNA patterns. Common truthful sense will verify this, if we’ve take chemistry.
Meningitis of the brain compartment linings is an inflammation of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord-violation of sterility. Most commonly caused by infections with various bacteria of viruses it is most terminal, if it can be treated at all. When the meninges are inflamed, the blood–brain barrier is be disrupted. This disruption may increase the penetration of various substances into the brain. Antibiotics used to treat meningitis may aggravate the inflammatory response of the central nervous system by releasing neurotoxins from the cell walls of bacteria. The rare brain abscess is caused by inflammation and collection of lymphatic cells and infected material originating from a local or remote infection. A brain abscess is a rare, life-threatening condition. Local sources may include infections of the ear, the oral cavity and teeth, the Para nasal sinuses, or an epidural abscess. Remote sources may include infections in the lung, heart or kidney. A brain abscess may also be caused by head trauma or as a complication of surgery. In children cerebral abscesses are usually linked to congenital heart disease.
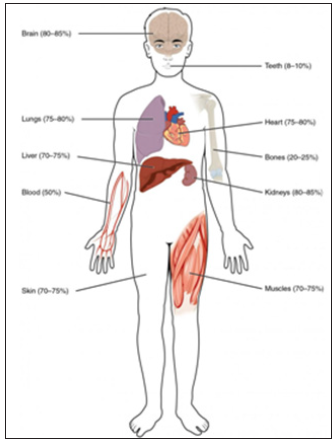
Figure 1: Human Being sterile water content varies in different body organs and tissues, from as little as 8 percent in the teeth to as much as 85 percent in the brain.
Note: Sterile Water Compartments Human Being.
The author’s position is neither pro nor con regarding modern root canal therapy but bases this presentation on the fact that “sterility” is a Principle of Health ensured by the Principle of Cleansing. Recall the fact that the functional unity of mastication, the Odonton, is a sterile space within many sterile spaces of the human body. The Odonton once dead-unsterile-now becomes a reservoir septic tank, nesting site, foci of infecting “m-os” that are pumped into the blood and lymph (sterile spaces) through masticatory action, pumping of the teeth.With proper observation of the “dead odontons” in Figures 1-4 bicuspid and Figure 5 lower molar, we see the black, yellowish brown roots with soft apical abscess materials. Upon removal of impure root canal teeth, we are struck with not only the color of the organ but also the odor often of putrefaction.
Numerous innovative mechanical techniques have been developed over the years to render the canals sterile and uninhabitable for microorganisms. Virtually all educational courses and advertisements within professional journals emphasize “mechanical obturation” and not the biological aspects of sterility of the canal system, or if the canals can be sterilized at all in the short or long term. As reported recently, overemphasis on this aspect of simply filling the empty spaces within the root canal system and its importance has misled the field of endodontology.2 What is most critical, is that root canal teeth become nesting sites, foci, for microbes and their “endotoxins” who, due to the loss of outward hydraulic pressure from within the body of the dental organ since the pulp is necrotic (no circulation or oxygen), migrate though the dentin into the peri-radicular tissues, thence into the systemic circulatory system and other tissues.
In Dental Clinics of North America, Vol. 18, No. 2, April 1974, Kaare Langeland, D.D.S., Ph.D. reviewed “Root Canal Sealants and Pastes” in which he states: “The fact that sealers and pastes will contact vital or disintegrating tissue connected with the general circulation allows for generalized distribution by blood and lymph…The restorability of sealers and pastes has been abundantly demonstrated by gross radiographic evidence. There is, therefore, no doubt that material is transported away from the site where it was originally applied.”What has been shown today as of equal or more significant importance is the “sterility”-lack thereof-of the intra- radicular-canal system [1-5] Current research shows that the significant presence of bacteria in the canal systems lead to the pathogenesis of “apical periodontitis” (AP)-now known as “endodontic disease.” This condition (AP) is a chronic/acute inflammation of the tissue about the roots of root filled teeth also designated as “apical granuloma.” [6,7].
Putrefaction, which is an essential stage in Odonton bio-film pulpal decomposition, is associated with a marked shift from aerobic bacterial species, which require oxygen to grow, to anaerobic ones, which do not. These anaerobic bacteria, called decomposers, subsist in a tenacious bio-film (plaque) attached to the various anatomical features of the root canal system feeding on the degenerating pulp tissues, dentinal lymph fluids and their organic contents, other biological fluids from the dental crown and surrounding periodontal ligaments and bone, thus fermenting the sugars in them to produce gaseous by-products such as methane, hydrogen sulphide and ammonia, and end products of impurities identified as cadaverene and putracine, which accumulate within the Odonton, inflating (or ‘bloating’) the pulp and root chambers through gas expansion-causing the “leaky root syndrome,” we call a tooth ache and pus- emission.
These decomposition products noted previously cause further discoloration of the body of the Odonton. As damaged blood cells continue to leak from disintegrating vessels, anaerobic microorganisms convert hemoglobin molecules, which once carried oxygen around the body, into sulfhaemoglobin. The presence of this molecule in settled blood within a decomposing Odonton gives a greenish- black appearance characteristic of a body undergoing active decomposition. Irrespective of the truth regarding purity or sterility of tissues spaces being rendered impure in the process of root canal therapy, it is still the only medical treatment advocating the active mummification or embalmment of human tissues, leaving it in the sterile human body. The orthopedic surgeon met with a necrotic Osteon (dead bone) in the advanced decay of the foot of a diabetic will resect the dead bone of the extremity.
We present the truthful facts that when the human tissues are irretrievable damaged, necrotic, the first charge to the surgeon is to protect the purity of the other sterile compartments of the human body. In our discussion to this point we keep in view the vast num ber of pure/sterile compartments mentioned at the start of this presentation, paragraph two. As with Osteons of the toes Odon tons of the mouth should be resected too. In Figure 6 it would be critical to the general health of the human to remove the gangrene tissue of the toes with intent to maintain purity of the lymph system, remaining bones of the foot, ligaments, muscles and blood system. The end result of not doing this would be to the jeopardy of the Life of the individual. In the oral cavity we have many instances of Odonton’s appearing as the toes in Figure 6 but not so black or dramatic until removed. Here is one in Figure 7 demonstrating a “gum boil” or a parulus extruding pus on the surface, right of crown.
Once the necrotic root canal #19 was removed we see the soft tissue below the root tips but intimately attached thereto representing the very unsterile condition of the Odonton and the bone associated. We for 35 years have submitted theses tissues to a board certified pathologist at Queens Hospital Pathology Laboratory and offer the findings in this specific individual: In over 300 reports for the past 35 years we find similar results as reported in this one, “… marked acute/chronic inflammation, necrotic bone, reactive bone, osteomyelitis, cystic granulomata, with notations in about 50% of the reports of filamentous bacteria consistent with Actinomyces.”
Periodontal Disease pre se, Apical Periodontitis (endodontic disease), Peri-Implant Mucosities, and Peri-Implantitis pathogens- all basically the same, namely Actinomyces odontolyticus et al-have been linked with increased risk of systemic illness and complications in existing disease [8,9] Many articles detailing these findings have been published emphasizing the importance of the association between oral conditions as noted above and systemic health problems. In fact, a recent meta-analysis reports that oral infections have been shown to be associated statistically with mortality. By entering the bloodstream, periodontal pathogens have been shown to increase the risk of cardiovascular and pulmonary disease, and hinder glycemic control in diabetes. Due to the fact that the “micro-gap” at the dental implant junction and the gum/ bone are NON-CLEANSABLE (Impure), dental implants may inoculate into the bone interface with the implant, by micro-movements, pumping action, deep in the gum -bone support tissue gap, so that m-os and their toxins are thrust into the sterile blood and lymph tissues spaces, increasing risks to systemic health [8,9]. In the photo of Figures 8-11 one observes a dental implant (to the right of the Gold Crown) demonstrating the lose of of bone and pus extruding from the “micro-gap.” The x-ray in Figure 12 reveals the cupping of crest bone around the implant #29 and at its apex (arrows), the radiolucent evidence of abscess. Figure 13 shows the deep abscess material about the dental implant #29 and in Figure 14 we show the histopathology of the condition that was asymptomatic other than a general systemic malaise. There was necrotic bone, Actinomyces, Granuloma, and chronic inflammation.
Biofilms harboring the anaerobic bacterial species Actinomyces are the new challenges to be overcome by “modern endodontics” in the spaces that were once pure, the sterile dental organ, Odonton [1]. I the early 1980s we began to remove infected root canal teeth and associated soft tissue and bone (Odonton) and send them for pathological inspection by a board certified histopathologist. The findings were remarkably revealing to this date. In brief all of the 349 “odontons” inspected it was found that acute-chronic inflammation- sometimes marked, reactive bone, dead bone, osteomyelitis, granuloma, cyst, abscess and other attending abnormalities were present in the jaw below the tooth in question. Having carried this root canal research on since about 1983, we have also extended this methodology to implant removal due to infections or otherwise. Background on factors causing “marked acute-chronic inflammation.” As we know the dead tooth has no circulatory system internally-in a sense this is the definition of an endodontically treated tooth. As the dead tooth degrades it gives off various chemicals such as putresciene, cadaverine, thioethers, and what we call “endo-toxins.”
This fact is no longer disputed in the scientific clinical profession, not in academia either. Another factor for inflammation is bacterial presence in tissues where they should not be-sterile compartments throughout the human body. As a habit in the early days of our research the pathologist noted what he called “star-like microorganisms” in colonies with rays in the bone and soft tissues. He noted that they were certainly colonies of actinomyces that surrounded the root canal. However, it must be understood that we had not asked for a determination of bacterial review, it was an incidental finding in his pathology reports to me. Historically, Actinomyces in know from the 1800s as the “ray fungus,” mistaken as a fungus until about 1938. It is currently identified a bacterium: Actinomyces is a genus of the Actinobacteria class of bacteria-all being gram positive. Actinomyces species are facultatively anaerobic and they grow best under anaerobic conditions. Actinomyces species may form endospores, and, while individual bacteria are rod-shaped, Actinomyces colonies form fungus- like branched networks of hyphae that may transform into other shapes and actions.
They have been implicated in decay and gum or perio disease in the oral cavity since they are normal residents. However, it is not normal to find actinomyces in bone or connective tissues deep in the other jawbone or in the blood vascular system. If found in the jaw bone it may lead to a condition known as “lumpy jaw”-an abscess from either dental or peri-dental origins, or both. Systemically it may lead to Actinomycosis a condition where abscesses occur-through circulatory migration or facial migration- into jaw, throat, lungs, abdomen, genital areas. Actinobacteria are the most common cause of infection in dental procedures and deep state oral abscesses related to apical periodontitis-root canals. Many Actinomyces species are opportunistic pathogens of humans and other mammals, particularly in the oral cavity. In rare cases, these bacteria can cause actinomycosis, a disease characterized by the formation of abscesses in the mouth, lungs, or the gastrointestinal tract. Actinomycosis is most frequently caused by A. isralli, which may also cause endocardidis, though the resulting symptoms may be similar to those resulting from infections by other bacterial species. Aggreatibacter actinomycete comitias has been identified as being of note in periodontal disease.
The genus is typically the cause oral-cervicofacial disease. Lymphadenopathy is uncommon in this form of this condition. Another form of actinomycosis is thoracic disorder, which is often misdiagnosed as a neoplasm, as it forms a mass that extends to the chest wall. It arises from aspiration of organisms from the oropharynx. Symptoms include chest pain, fever, and weight loss. Abdominal disturbances are another manifestation of actinomycosis. This can lead to a sinus tract that drains to the abdominal wall or the perianal area. Symptoms include fever, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Actinomyces species have also been shown to infect the nervous system without apparent trauma and could be related to Lyme disorder that is now the recognized malady of the day.The bacteria Actinomyces are ubiquitous and abundant in soil. They are known for the important role they play in soil ecology; they produce a number of enzymes that help degrade plant root debris and waste plant materials as do Spirochetes and Candida.
A specific Spirochete has been implicated as the source of Lyme but Actinomyces may be associated likewise. Thus their presence is important in the formation of compost, as are spirochetes and candida fungi, the later specialist in degradation of cellulose. They are also known for causing diseases in humans and livestock, usually when they get an opportunity to gain access to the body’s interior through wounds. As with other opportunistic infections, people with immunologic issues are at higher risk. In all of the preceding traits and in their branching filament formation, they bear similarities to Norcardia causing Norcardosis a similar illness as Actinomycosis. It is well established that actinomycosis is an endogenous infection. The causative Actinomyces species reside on mucosal surfaces and gain access to deeper tissues via trauma, surgical procedures, or foreign bodies, which disrupt the mucosal barrier. Inside the tissue, these bacteria form masses consisting of aggregates of branching, filamentous bacilli. Actinomycosis is defined as a hard mass-type lesion with a specific histopathological structure.
There are a large number of case reports of actinomycosis in the literature, but in most cases, diagnosis has been based solely on clinical and histopathological findings. In the majority of early reports, microbiological confirmation of diagnosis was lacking and confusing. Even when microbiological assessment was included, culture was typically the only method used. If, however, antimicrobial treatment had been started before sample collection, the results of culture may be falsely negative. The increasing introduction of molecular bacterial detection and identification methods is helping to overcome such problems. An internal abscess is more difficult to identify, but signs include pain in the affected area, a high temperature, and generally feeling unwell. Internal abscesses rarely heal themselves, so prompt medical attention is indicated if such an abscess is suspected. This is important in the resolution of infected abscessed teeth, that they be surgically removed and bone cleansing-cavitation-accomplished.
This paper discusses the sterile physiological spaces making up the human being and their relationship to THE PRINCIPLE OF HEALTH and the PRINCIPLE OF CLEANSING. If one chooses to offer “root canals,” one is locked into the pharmacological trap of combative chemistry and surgeries forestalling the inevitable- segment= tectomy. Our “Opioid Crisis” today may be directly related to optional medical procedures blocking complete remission to adverse medical treatments. See here:
https://www.democracynow.org/2018/6/1/origins_of_the_ opioid_epidemic_purdue
The methodologies in this day and age lead to the oral-systemic toxemia that very innocuously infects other pure/sterile spaces of the human body. Resurgence of the idea that the human body is a “totality” and not series of parts unconnected leading to improvement or demise is now manifesting in research literature and in the awareness of the general population. The knowledge that pure spaces are to be maintained as pure spaces is verified in my experience in the return to health in individuals choosing to remove infected matter from the oral cavity-root canals, dental implants, periodontally involved Odontons.
As noted earlier the author’s position is neither pro nor con regarding the so-called “modern root canal therapy” but bases this presentation on the truthful fact that “sterility” is a Principle of Health empowered by the Principle of Cleansing. Recall the fact that the functional unity of mastication, the Odonton, is a sterile space within many sterile spaces of the human body. The Odonton once dead-unsterile-now becomes a reservoir septic tank, nesting site, foci of infecting m -os that are pumped into the blood and lymph (sterile spaces) through masticatory action, pumping of the teeth. In the final analysis it is the choice of the attending dental surgeon and his or her patient that will make the difference in patient’s health. Choices will always be based upon “pro or con” in the context of scientific debate on the subject matter; but, if one simply looks at the “sterile/pure space” issue, that is “sterile compartments,” The Principle Of Health, the Principle Of Cleansing as fundamentals of health in the human, one could not tolerate soiling the human body, thus avoiding being an obstruction to health.


