Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Richard M Fleming*1, Matthew R Fleming2, William C Dooley3, Arif Sheikh4, Andrew McKusick5 and Tapan Chaudhuri6
Received: May 16, 2018; Published: May 25, 2018
*Corresponding author: Richard M Fleming, 707 E. Grand Avenue, #8 El Segundo, CA 90245, USA
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2018.04.001116
Keywords: FMTVDM, FHRWW, The B.E.S.T. Protocol, Enhanced MPI, True Quantified MPI, True Quantified Nuclear Cardiac MPI, True Quantified Nuclear Medicine, Sestamibi Redistribution, Myoview Redistribution, The Fleming Method (TFM) for Quantitative Standardization
The Fleming Method for Tissue and Vascular Differentiation and Metabolism (FMTVDM©℗) using same state single or sequential quantification comparisons [1-15] “True Quantification” of Cardiac Disease using Myocardial Perfusion Imaging following Single Injection of Tc99m Isotope (Sestamibi) and “True Quantification” Measurement of Isotope Redistribution.
Enhancement & “True Quantification” using FMTVDM-FHRWW ©℗: A 44-year old African American male presented to the Emergency Room with retrosternal chest discomfort after working in his garage. He had no prior history of heart disease and was being treated only for hypertension with a loop diuretic. His blood pressure left arm sitting was 142/90 mmHg and 146/88 mmHg in his right arm sitting with a regular heart rate of 78 bpm. No other cardiovascular risk factors were identified. His cardiac exam was remarkable for an S4. His lungs were clear to auscultation and percussion with peripheral pulses of 2/2 in both upper and lower extremities. His Myocardial Perfusion Image (MPI) study included pharmacologic stress and Sestamibi, using FMTVDM©℗ to de termine 5-minute and 60-minute redistribution measurements. Following image acquisition the nuclear technologist generated the regions-of-interest (ROIs) as shown in Figure 1, using FMTVDM- FHRWW (Cardiac protocol) ©℗ [16-20].
a) What clinical conclusion can be drawn from the FMTVDM- FHRWW©℗ MPI study?
Answer: Measurement of myocardial ischemia using “True Quantification” of isotope redistribution using planar, SPECT or PET imaging “wash-in” and “washout” assessment is only possible using FMTVDM-FHRWW(Cardiac) ©℗, which can differentiate between vulnerable inflammatory plaques (VIPs) and coronary lumen narrowing. Figure 1 revealed ischemia in all three epicardial arteries.
b) Teaching Point
Standard MPI provides a qualitative comparison between two sets of images, which are time sensitive in their ability to find coronary artery disease. The qualitative appearance of the patient’s images reveals no perfusion abnormalities in either the 5-minute acquisition (left panels) or the 60-minute acquisition (right panels) images. This qualitative visual appearance is misleading and incorrect. Technetium-99m compounds redistribution including Sestamibi, Myoview and Teboroxime can all be accurately measured by “True Quantification” of the 5 and 60-minute images acquired using planar and SPECT. Similar application of FMTVDM©℗ can be applied to PET camera acquisition using applicable isotopes. Using these acquired images, “actual (TRUE v Virtual) quantification” of isotope redistribution using FMTVDM©℗ can be made and a calculation of “wash-in”, “washout” or “normal” isotope redistribution can be determined. From this “quantification” the type and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) can be made for each coronary artery vascular territory, enhancing both diagnosis and treatment management. FMTVDM©℗ can be used with hand-held probes, planar, SPECT or PET imaging depending upon the isotope employed [21].
Figure 1: FMTVDM-FHRWW (Cardiac protocol)©℗. Application of TRUE QUANTIFICATION following isotope redistribution. Image displays in horizontal (top) and vertical (bottom) long axis views show TRUE QUANTIFICATION using measurement of Sestamibi redistribution using FMTVDM©℗. While each reconstructed image revealed “qualitatively” normal appearing MPI, the TRUE QUANTIFICATION measurement showed lower Sestamibi counts in each myocardial region at 5-minutes (left panels) compared with the 60-minute acquisitions demonstrating “wash-in” seen with vulnerable inflammatory plaques and critically narrowed arteries. This TRUE (not virtual) QUANTIFICATION demonstrated triple vessel coronary artery disease in this individual.

FMTVDM©℗ “True Quantification” of Breast Cancer. “The B.E.S.T. Protocol for Early Breast Cancer Detection and Treatment Response”3-5, 16-25.
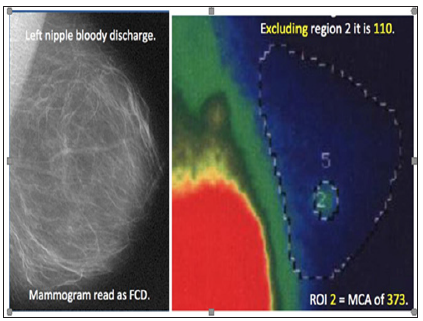
Enhancement & Quantification using FMTVDM-BEST©℗: A 38-year old woman with dense breasts and normal mammogram was referred for TRUE QUANTIFICATION Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI) using FMTVDM-BEST©℗ Protocol for enhancement and measurement of possible breast cancer. This mother of twins had previously had two normal mammograms. Following this third “normal” mammogram and bloody left nipple discharge she was referred for FMTVDM-BEST©℗. Following FMTVDM-BEST©℗ employing pharmacologic enhancement following regional shifts in delivery and uptake of isotope based upon differences in regional blood flow and metabolism, nuclear image acquisition was obtained and TRUE QUANTIFICATION Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI) measurements were made as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: FMTVDM-B.E.S.T. (Breast Cancer protocol)©℗ Protocol. Application of TRUE QUANTIFICATION following isotope Enhancement. Mammography (left) interpretation reported fibrocystic disease. Following FMTVDM-The B.E.S.T. ©℗ Protocol, TRUE QUANTIFICATION following isotope Enhancement, revealed normal breast tissue in the majority of the breast with maximum count activity (MCA) values of 110. Region 2 revealed a MCA of 373 revealing breast cancer. Surgical biopsy confirmed.
a) What clinical conclusion can be drawn from this FMTVDM- BEST©℗ Protocol?
Answer: “TRUE QUANTIFICATION” of nuclear images can only be obtained allowing for tissue and vascular differentiation, using FMTVDM©℗. This can be accomplished using any pharmacologic or physiologic enhancement method, any isotope and any nuclear imaging device, including hand-held probes, planar, SPECT and PET depending upon the isotope being used. In this instance the study was performed using a planar camera and Sestamibi following dipyridamole enhancement to analyze breast tissue (FMTVDM- BEST©℗) [22-24].
b) Teaching point
Prior nuclear medicine methods have employed “qualitative” image analysis and have not Enhanced the physiologic properties of regional blood flow and metabolism differences to distinguish between tissue type using “TRUE QUANTIFICATION” FMTVDM- BEST©℗. Using FMTVDM-BEST©℗, machine learning (aka Artificial Intelligence) and patient derived “TRUE QUANTIFICATION” can differentiate breast cancer from pre-cancerous tissue from inflammatory changes, normal breast tissue and calcium deposits. “TRUE QUANTIFICATION” FMTVDM-BEST©℗ can also be used to direct patient treatment, using pre and post treatment “Quantification” to assess treatment response, saving time, money and lives [25].


