Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Munirathnamma K1, Mamatha G*2, Dhanalakshmi N3 and Lingaraju CM4
Received: April 12, 2018; Published: April 20, 2018
*Corresponding author: Mamatha Shetty,Assistant Professors,JSS College of Nursing, Mysuru,India
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2018.04.000982
Childbirth is considered a life-changing event for most women and families all over the world, but childbirth is also associated with great risks, and in severe cases disability and even death of mother or child. Majority of maternal deaths and complications attributable to obstructed and prolonged labor could be prevented by cost-effective and affordable health interventions like the use of partograph.
Aims and Objectives: The aim of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of an educational intervention regarding partograph among student nurses in selected nursing institutions at Mysuru.
Methods: The research design selected for this study was one group pre-test post test design. Non-Probability purposive sampling technique was adopted to select 30 student nurses in selected Nursing institutions at Mysuru.A pre-test observation of the dependent variable is made before implementation of treatment to the selected group, the treatment is administered and finally post-test observation of dependent variable is carried out to assess the effect of treatment on the group.
Result: Result revealed that an educational intervention on partograph was effective in increasing the knowledge of student nurses regarding partograph as evidenced by computed paired 't' test which was statistically significant at 0.05 level of significance (t(29)= 2.05, p<0.05)
Conclusion: It was concluded that educational intervention was effective in enhancing the knowledge of student nurses regarding partograph. Study finding also emphasizes the role of educational strategies to improve the knowledge of health personnel's regarding partograph.
Keywords: Partograph;Effectiveness; Educational intervention
Childbirth is considered a life-changing event for most women and families all over the world. Childbirth is also associated with great risks and in severe cases disability and even death of mother or child. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that the main tasks for the caregivers during labor are; supporting the woman, her partner and family during labor, observing the laboring woman, detecting risk factors and problems, performing minor interventions such as amniotomy and episiotomy and referral to a higher level of care if risk factors or complications develop[1].
High rate of maternal and infant mortality in India has become a matter of concern. Majority of maternal deaths and complications attributable to obstructed and prolonged labor could be prevented by cost-effective and affordable health interventions like the use of partograph.It is very essential to train the nurses with knowledge and skill in the use of partograph which will help the nurses to provide a comprehensive intra-partum care to the laboring mothers with early identification and prevention of complications, thereby playing an important role in reducing the maternal morbidity and mortality Since today's student nurses are tomorrow's staff nurses investigator felt the need to improve skills of student nurses about recording the progress of labor and motivate them to maintain partograph for women in labor as a routine practice[2].
"A Study to evaluate the effectiveness of an educational intervention on knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses in selected nursing institutions at Mysuru"[3].
a) To assess the existing knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses.
b) To determine the effectiveness of an educational intervention regarding partograph among student nurses [4].
c) To find the association between level of knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses and their selected personal variables.
a) H1- There will be significant difference in the mean pretest and post-test knowledge scores regarding partograph among student nurses.
b) H2- There will be significant association between the level of knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses and their selected personal variables.
The conceptual framework of the study is based on the Imogene King's Goal Attainment Theory.
a) Student nurses may have some knowledge regarding partograph.
b) Educational intervention may improve their knowledge regarding partograph.
c) Improvement in knowledge may influence their practice.
Study is delimited to the student nurses who are studying in selected nursing institutions at Mysuru[5].
Evaluative approach was adopted for the present study.
One Group Pre-test-Post-test research design was adopted for present study
Schematic Representation of Research Design: The symbolic representation is O1 X O2
a) O1- Pre- test
b) X - Intervention
c) O2 - Post-test
a) Dependent variable: Knowledge regarding partograph.
b) Independent variable: Educational intervention regarding partograph.
c) Other variables: Selected personal variables viz., age, gender, educational qualification, exposure to labor room and previous exposure to educational intervention regarding partograph.
a) Setting of the Study: The present study was conducted in JSS school of Nursing at Mysuru.
b) Population: population comprised of student nurses in selected nursing institutions at Mysuru.
c) Sample and Sampling:30 student nurses were selected as samples for the present study.
d) Sampling Technique: Non- probability purposive sampling technique was used in the present study to select 30 student nurses in selected nursing institutions at Mysuru.
Inclusion Criteria:
Student nurses who are:
a) Available during the period of data collection.
b) Willing to participate in the study
Exclusion Criteria: Student nurses who were sick at the time of data collection.
Development of Tool:
The tool was developed through following steps:
a) Review of research and non-research literature related to partograph.
b) Opinion of experts from the nursing department.
The tool consistsof two sections.
a) Section A: Consists of Proforma for selected personal variables of respondents seeking information such as age, gender, educational status, exposure in labor room, previous exposure to educational programme.
b) Section B: Includes 26 items of structured knowledge questionnaire regarding partograph.
Scoring: Section B consists of 26 items (knowledge questionnaires) regarding partograph. Each question carries 4 distractors out of which one distractor will be the right answer. Answering the right distractor will carry one mark.
For the Total Score Obtained, Grades will be Assigned as Mentioned Below:
a) < 13 Poor knowledge
b) 13-20 Average knowledge
c) 20 Good knowledge
Content Validity: The tool was given to 7 experts in nursing field, 01 obstetricians to establish content validity. There was 100% agreement by all experts. However, there were few suggestions to modify some questions and they were incorporated in the final draft.
Reliability: The reliability was established through split half method by administering it to 30 student nurses in JSS College of Nursing Mysuru. Co efficient correlation for structured knowledge questionnaire was 0.76. Hence the tool was found to be reliable.
Pilot Study: The pilot study was done from 14-06-17 to 21-0617. The tool and study design were found to be feasible.
Permission for conducting the study was obtained from the Principal, J.S.S School of Nursing, and Mysuru. The data was collected from 19-06-17 to 26-06-17. To obtain the free and true response, the subjects were explained about the purpose and usefulness of the study and assurance about the confidentiality of the responses was also provided. An informed consent was obtained from each subject to indicate their willingness to participate in the study On day one pre-test was conducted by administering structured knowledge questionnaire to 30 student nurses, they took 30 minutes to complete structured knowledge questionnaire. On the same day an educational intervention was conducted for the same group for 45minutes. Further on day 8 post-test was conducted by using structured knowledge questionnaire. The data collection process was terminated after thanking each respondent for their participation and their cooperation.
a) Section 1: Description of selected personal variables of study subjects(Table 1).
Table 1: Frequency and percentage distribution of student nurses according to their selected personal variables.

b) Section 2: Effectiveness of an educational intervention on knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses(Tables 2& 3).
Table 2: Frequency and percentage distribution of student nurses according to their level of knowledge.
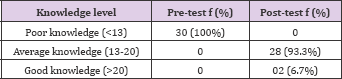
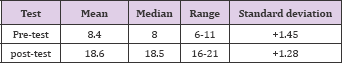
Table 3: Mean, median, standard deviation, range of pre-test and post-test knowledge scores of student nurses.
c) Significance of difference between the mean pre-test and post-test knowledge scores regarding partograph among student nurses: To determine the significance of difference between the mean pre-test and post-test knowledge scores regarding partograph among student nurses paired 't' test was computed.The null hypothesis is stated as follows
d) H01 : There will be no significant difference between the mean pre-test and post-test knowledge scores regarding partograph among the student nurses(Table 4).
Table 4: Mean, mean difference, standard deviation difference, degree of freedom and paired 't' value of pre-test and post-test knowledge scores of student nurses.

e) Section 3: Association between the level of knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses and their selected personal variables. To find out the association between the pre-test levels of knowledge regarding the partograph among student nurses and their personal variables, chi square was computed and following null hypothesis is stated.
f) H02 : There will be no significant association between the level of knowledge regarding partograph among student nurses and their selected per sonal variables.Calculated chi square value showed that there was no significant association found between the level of knowledge of student nurses regarding partograph and their selected personal variables. Hence the null hypothesis is accepted, and it is inferred that there is no significant association between level of knowledge of student nurses regarding partograph and their selected personal variable.
Implications: The findings of present study have implications for nursing practice, nursing education, nursing administration and nursing research.
Nursing practice: Student nurses will be the future staffs who will work in various areas. Those staffs who are working in labor room must have thorough knowledge and skill regarding using partograph to monitor women who is in labor. Hence it is importance for student nurses to update their knowledge regarding partograph.
Nursing education: Education is the key component to update and improve the knowledge of an individual. The nurse educator can conduct the educational programme in nursing colleges as well as in the hospital settings about partograph to improve their knowledge and skill.
Nursing administration: Nursing administrator is the key person to plan, organize and conduct educational programme. Nurse administrators can encourage the student nurses and staff to participate in educational intervention on partograph. The nurse administrator can also organize continuing nursing education which enables the learner to keep abreast of changes and development in his or her field of speciality.
Nursing research: The topic has great relevance to the present-day nursing practice. The study stresses on the need for extensive research in the subject and for more nursing implication to improve the health care delivery system. Nurse researchers have to take initiative on this topic.
a) Similar study can be carried out on a large scale to generalize the findings.
b) A Similar study can be conducted among auxiliary nurse midwives.
c) A comparative study can be conducted between staff nurses and student nurses regarding partograph.
It was concluded that educational intervention was effective in enhancing the knowledge of student nurses regarding partograph. Study finding also emphasizes the role of educational strategies to improve the knowledge of health personnel's regarding partograph.


