Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
*Rita Karmakar
Received: June 29, 2017; Published: July 03, 2017
Corresponding author: Rita Karmakar, Assistant Professor, Amity University, 139, Rajkumar Mukherjee Road, Kolkata, West Bengal- 700035, India
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2017.01.000170
Personality generally refers to the way of responding to the external demands. This study tries to explore the Big Five Factor traits among students of different disciplines. Implications have been raised by giving propositions for future researchers to validate these propositions.
The term personality comes from the Latin word persona, meaning “mask.” Personality generally refers to the way of responding to the external demands. According to Allport [1], personality is the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his characteristic behavior and thought. Psychologists distinguish between type and trait approaches to personality. The type approaches attempts to comprehend human personality by examining certain broad patterns in the observed behavioural characteristics of individuals. In contrast, trait approach focuses on the specific psychological attributes along which individuals tend to differ in consistent and stable ways. The personality trait refers to enduring personal characteristics that are revealed in a particular pattern of behaviour in a variety of situations. Personality trait is a characteristic that is specific and consistent in individual’s behavior. The trait approach is very popular and much advancement in this respect have already been taken place. Alloprt [2] described differents trait like central, secondary, common and cardinal traits while Cattell’s [3] research explored 16 primary and five secondary factors and Hysenck expressed that only three traits of extraversion, neuroticism and psychoticism are enough to explain the personality of individuals [4]. However, relatively recent trend in assessing personality trait is Big Five Model of Goldberg [5]. Big Five Model is mostly accepted for the personality trait constructs which contain five core dimensions of personality. The Big five includes openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness and neuroticism [6]. The descriptions of these five personality traits are given below:
Openness to experience is the degree of intellectual curiosity, creativity and novelty. People high on this trait are imaginative, independent minded, have a variety of interests, think divergently, likes complex and unusual situations, enjoys adventure and are broad minded. People low on this trait is practical, close minded, and conservative and tends to avoid new experiences.
Conscientiousness: Highly conscientious individuals are rigid, efficient, striking for achievement, thorough and disciplined. People scoring low on this trait are flexible and voluntary, but are also recognized as being clumsy and irresponsible.
It implies an energetic approach to the social and objective world and includes traits such as sociability, action oriented, positive emotionality, adaptive, active and the tendency o seek energy from social situations, and talkativeness. People high on extraversion are often regarded as seeking attention, excited, dominating, jolly adventurous and cheerful in the social situations. People low on this trait are found to be reserved, quiet, remaining aloof from the social situations and less involved in the social world.
It involves a pro-social behaviour across different situations towards others. It also includes traits such as kindness, tendermindedness, cooperative, simplicity, warm, being compassionate, helpful, generous, trusting and are willing to accommodate their interests with others. Agreeable individuals also have a bright view of human nature. People scoring high on this trait are often seen as innocent and accommodating, while people scoring low on this are often competitive and like arguing with people.
People scoring high on this trait are found to be reactive, vulnerable to stress, worries a lot by interpreting ordinary situations as threatening, excitable, unstable and insecure. People scoring low on this trait are stable, calm and free from persistent negative feelings. The Big Five Factor Inventory can be used to measure personality traits of college students to assess their career trends and evaluate the pattern of career choices and inclination of college students towards a career choice based on their Personality traits. The present study aims to assess personality trait of college students and thereby giving some directions of career choices based on the Big Five Personality traits. Vedel [7] searched numerous academic databases of North American and European students aged between 18 to 26 years and found that psychology students tended to score higher on neuroticism and openness to experience economics, politics and medicine students score higher on extraversion. Arts and humanities scored lower on conscientiousness than most.
The objective of the study is to explore the personality traits of undergraduate college students using the Neo Personality Inventory (NEO- FFI). The present study deals with medical students and students pursuing Honours’ in Applied Psychology.
Sample includes 70 college students (boys and girls) drawn randomly from different colleges of Kolkata among which 40 students from the field of Psychology and 30 students from the field of medical sciences. The age range of students was 18- 22 years with a mean age 19.34 years (standard deviation 2.01 years). Most of the students belong to middle socio-economic status.
The short form of Neo Personality Inventory (NEO- FFI), a well validated measure of the five factor model of personality [8] was administered on students. Students rated their response on 60 items with five point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree [1] to strongly agree [5]. For negatively coded items, scoring will be reverse.
The study is based on primary data which was collected from undergraduate college students of different colleges in Kolkata. Consent form was requested from each individual with the permission granted by college authorities only after the NEO- FFI questionnaire was asked to be filled in.
The study is based on primary data. Descriptive statistics such as mean and standard deviation (SD) and inferential statistics such as t –test for independent groups have been calculated and presented in the (Table 1). Reveals that psychology students score significantly higher on openness to experience and extraversion than medical science students. The reverse trend is evident in case of neuroticism trait.
Table 1: Mean, SD and t value of Big Five Factors by different stream of education.
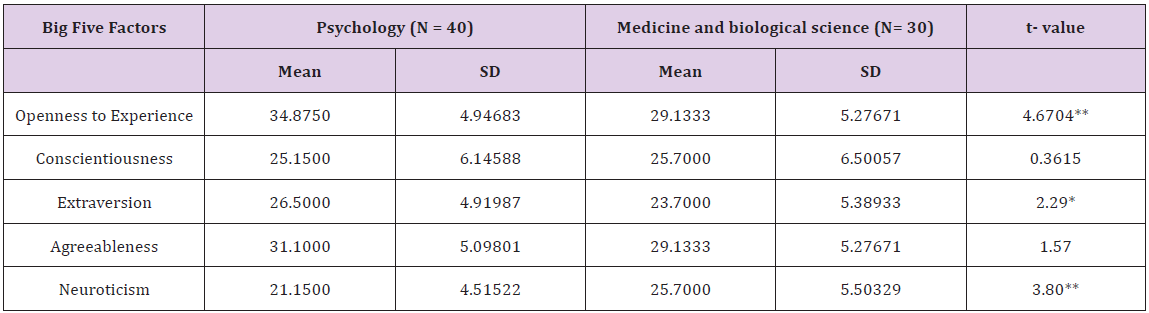
** Significant at 0.01 level, * Significant at 0.05 level.
The present study aims to determine the personality traits of undergraduate college students using the Neo Personality Inventory (NEO- FFI). Students in field of medical sciences scored significantly higher on neuroticism than students pursuing psychology honours’. This may be due to the fact that medical students deal with severe illness and diseases in their everyday lives which make them exposed to stress evoking environment. Heightened responsibility of human lives also evokes sense of guilt and helplessness in the field of medicines. Psychology honours’ students are on openness to experience and extraversion than medical students. The probable reason is that psychology students need to build up rapport with people to better understand their problems.
It may be concluded from the findings of the present study that medical science students are significantly higher on neuroticism trait whereas psychology honours’ students are higher on openness to experience and extraversion trait of Big Five Factor.
Despite the intriguing finding done, there are few limitations to the study. The results found through self-reports must be replicated using other methodologies in order to measure its ability of generalization to a large population.
In spite of having limitations, the results of the present study have significant implications. The study implies that the fields of Medicines are significantly lower in the dimension of Openness to Experience as compared to psychology. It also shows that the field of Medicine ranging the highest in the dimension of Neuroticism. The results imply the need to create stress free environment for the medical field and allow flexibility in their approach.


