Abstract
Purpose of the Article: The purpose of the article is to present a paper about to compared research which has dealt with musculoskeletal disorders in physiotherapists and other health professionals at work and to record ergonomic problems.
Materials and Methods: In March and April 2019 were searched various biomedical databases such as PubMed, ResearchGate and Academia.edu using the keywords “Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders”, “Musculoskeletal Injuries”, “Work Injuries”, “Physiotherapists”, “Occupational health”, on the basis of which the presentation of the data obtained in the found research was done.
Results: We have selected four studies that we have included in this scientific review of the literature based on the purpose and objectives of the paper. The studies are from India, Greece and Iran.
Conclusion: Based on the reviewed studies, the conclusions are: the main ergonomic risks for physiotherapists are: bending the torso forward, flexion of the neck and prolonged standing; education, awareness-raising and training programs on prevention and strategies for dealing with musculoskeletal disorders related to work oblige health professionals, especially high-risk groups such as nurses, dentists and physiotherapists, to reduce the occurrence of these disorders; work-related musculoskeletal disorders can be prevented with three affordable things, i.e. designing an ergonomic work environment, postural education, and regular exercise.
Keywords: Ergonomic Problems; Musculoskeletal Disorders; Physiotherapists; Review
Introduction
Ergonomics is a scientific discipline that deals with improving working conditions and products, reducing the risk of injuries, reducing the risk of work-related diseases and promoting healthy attitudes towards the environment and the work environment. Musculoskeletal disorders related to work are responsible for morbidity in many working populations and are known to be an important work problem that leads to increased health costs, reduced productivity, and lower quality of life [1]. There are more and more lost working days due to back pain, which also affects health care itself [2]. Nonspecific lower back pain is an uncomfortable medical condition that can make work impossible and is a common reason for absenteeism. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), human health hazard assessment is “a procedure that assesses the nature and likelihood of adverse effects on human health due to exposure to one or more factors of physical or mental stress” (WHO 1981). Health hazards are classified as biological, chemical, organizational, or psychosocial that include work-related violence. Health and social work activities have a higher rate of work-related disorders than other activities. These are mainly musculoskeletal disorders, stress, depression and anxiety. Nurses, nurses and other staff are among the 10 occupations with the highest risk of muscle and joint sprains. The assessment of health hazards related to physical activities is the subject of a number of guidelines [3]. It is very important to educate healthcare professionals about all the dangers of their job in time, as well as to enable work with devices that help prevent the occurrence of diseases. Unfortunately, nurses and physiotherapists today do most of the work manually. Every healthcare professional needs to be warned about the risks they are exposed to every day [4]. The main problems of traditional ergonomics were how to reduce muscle work and movements, and today the problems are related to static and repetitive work.
Objectives of the Work
The purpose of the article is to present a paper about to compared research which has dealt with musculoskeletal disorders in physiotherapists and other health professionals at work and to record ergonomic problems.
Materials and Methods of Work
In March and April 2019 were searched various biomedical databases such as PubMed, ResearchGate and Academia.edu using the keywords “Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders”, “Musculoskeletal Injuries”, “Work Injuries”, “Physiotherapists”, “Occupational health”, on the basis of which the presentation of the data obtained in the found research was done. The research is limited to articles published in English. The research of ergonomic problems among physiotherapists is a non-experimental qualitative research, ie a scientific review of the literature.
Results and Discussion
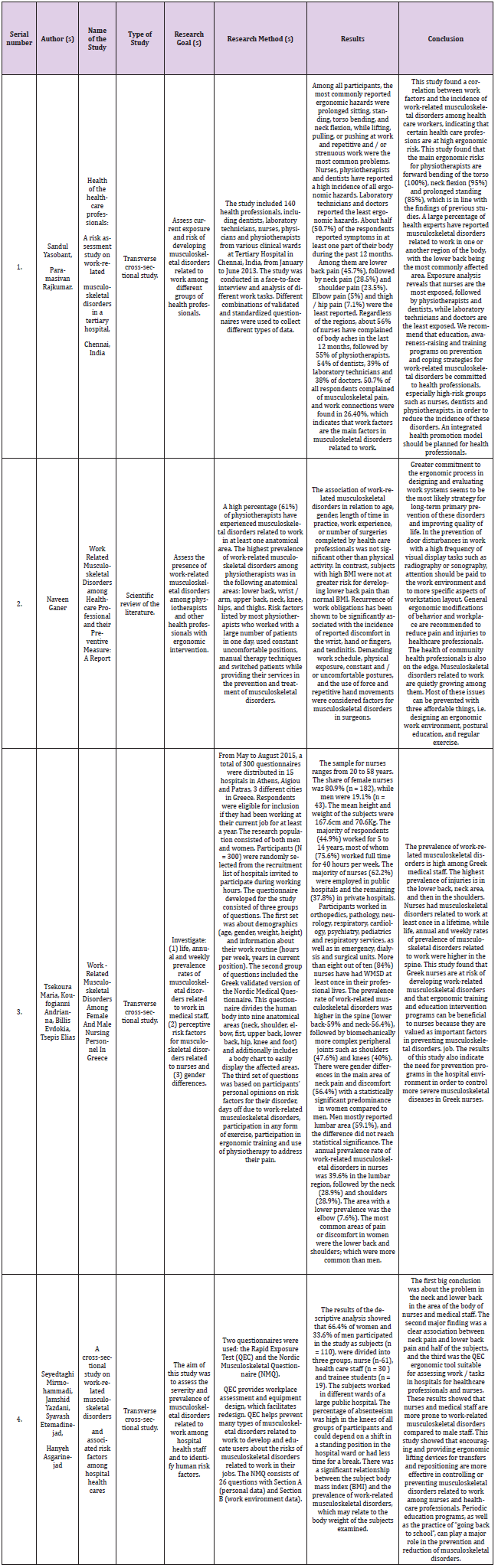
We have selected four studies that we have included in this scientific review of the literature based on the purpose and objectives of the paper. The studies are from India, Greece and Iran. The studies are presented in Table 1.
Conclusion
1) The main ergonomic risks for physiotherapists are:
bending the torso forward, flexion of the neck and prolonged
standing;
2) Education, awareness-raising and training programs
on prevention and strategies for dealing with musculoskeletal
disorders related to work oblige health professionals, especially
high-risk groups such as nurses, dentists and physiotherapists, to
reduce the occurrence of these disorders;
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders can be prevented
with three affordable things, i.e. designing an ergonomic work
environment, postural education, and regular exercise.
References
- Sandul Y, Paramasivan Rajkumar (2015) Health of the healthcare professionals: A risk assessment study on work-related musculoskeletal disorders in a tertiary hospital, Chennai, India. International Journal of Medicine and Public Health 5(2): 189-195.
- Waters T, JD Lloyd, Edward Hernandez, Audrey Nelson (2011) AORN ergonomic tool 7: pushing, pulling, and moving equipment on wheels. AORN J 94(3): 254-260.
- Osha (2011) Procjena rizika u zdravstvu.
- Berguer R (1999) Surgery and ergonomics. Arch Surg 134(9): 1011-1016.

 Mini Review
Mini Review