Abstract
Introduction: Globally, studies have shown conflicting results regarding the
association of blood groups with SARS CoV-2 infection. The novel coronavirus SARSCoV-
2 is causing COVID-19 severe cases leading to hospitalization of some people while
others experience moderate to mild symptoms. The aim of this study is to investigate
the role of ABO blood group in COVID-19 disease susceptibility and severity in Nigeria.
Methods: This study is a case series that includes patients that are evaluated
between June and August 30, 2020, and diagnosed with COVID-19. ABO blood grouping
was done on the COVID-19 samples to known the blood type associated with mild to
severe cases of COVID-19. Hospitalization and death were evaluated for association
with blood type.
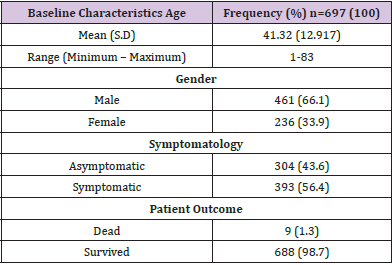
Results: The total number of COVID-19 patients enrolled was 697, 66.1% male and
the mean age 41.3 ±12.9 years. Most were symptomatic [56.4%] and mortality rate
was 1.3%. The most common symptoms were dry cough [27.5%], fever [26.5%] and
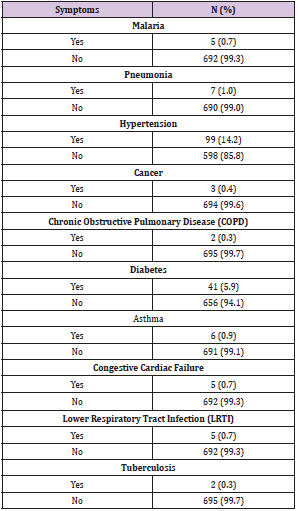
breathing difficulty [18.5%]. Co-morbidities were also present in [24.0%] of the study
participants. Blood group profile shows group O [59.25%] to be more prevalent than
group A [22.2%], and B [15.10%] and AB [3.44%] being the least. The blood group that
showed association with severe covid-19 diseases were: B, A and O [10.5%, 9.0%] and
8.5%]. There seem to be no significant difference between the severity of SARS-CoV- 2
and the blood group profiles.
Conclusion: There is no statistical significance between the blood group profiles
in association with SARS CoV-2 severity from this preliminary report. However, the
patients having blood group B may have a higher risk of persistent positivity having
the highest prevalence among those who had moderate SARS-CoV-2 disease [41.9%].
Further studies on the individuals with confirmed exposure to COVID-19 infection
may reveal better association.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; ABO Blood Group Profile; Nigeria
Introduction
COVID-19 caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Coronavirus-2 [SARS-CoV-2] was first described as a serious
infection leading to significant morbidity and mortality in Wuhan,
China in January 2020 Zhou, et al. [1]. The number of deaths was
increasing due to the catastrophic effect of the emerging new
strains. Research has shown that there are predicting factors of
COVID-19 severity such as demographic, clinical, immunologic,
haematological, biochemical, and radiographic factors Benjamin,
et al. [2]. According to Samra, et al. [3] ABO groups can play a role
in COVID-19 severity and susceptibility. The rapid global spread of
the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has strained existing healthcare
and testing resources, and it is causing COVID-19 severe cases in
some people than in others. While some people experience only
mild symptoms, others are being hospitalized Samra, et al. [3]. The
pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 and the associated respiratory
failure are still unclear, but the higher mortality rate is consistently
associated with older age and being male Samra, et al. [3]. Many
studies have shown that the ABO blood type is a potential risk for
various diseases such as cancer, myocardial infarction, acute kidney
injury, and venous thromboembolism Dentali, et al. [4,5]
Apart from comorbidities and other predicting factors,
findings have shown that the ABO blood group has a correlation
with COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. Biological factors that
determine susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 and severity of COVID-19
are yet to be fully understood Samra, et al. [3]. The ABO blood
grouping may influence the susceptibility of COVID-19 and severity
of the disease Zhao, et al. [6]. As reported by Nagla, et al [7], patients
from three hospitals in Wuhan, Shenzhen, and China showed the
likelihood of association between ABO blood groups and the
susceptibility to COVID-19 exposure after the outbreak of the
COVID-19 infection. The study results showed that individuals with
blood group A had a markedly greater risk of COVID-19 exposure,
while those with blood group O had a significantly reduced risk of
COVID-19 infection. In a meta-analysis of two different case-control
cohorts, blood group A was reported to confer a greater risk of
aggravated COVID-19, while blood group O offer protection against
COVID-19 infection WU, et al. [8].
However, A, B and O blood group are antigenic complex
oligosaccharide molecules located on the extracellular surface
of the red blood cell membrane Storry JR, et al. [9]. ABO blood
group are also expressed on the surface of other human cells and
tissues, including the epithelium, sensory neurons, platelets, and
the vascular endothelium Eastlund [10]. The ABO blood group
have been reported to play a key role in various human diseases
such as diabetes, cardiovascular, neoplastic, carcinoma and other
infectious disorders Cheng et al. [11-13]. ABO and Rh blood
groups polymorphism are valuable and indispensable tools in
contemporary medicine, population genetics and anthropology. The
distribution of these two blood groups has been reported different
populations of the world and they showed considerable variation
in different geographic locations, reflecting the underlying genetic
and ethnic diversity of human populations Garratty ,et al. [14,15]
reported the distribution and gene frequencies of ABO and Rh
[D] blood group systems in six geopolitical zones of Nigeria. Their
data revealed that the ABO blood group frequencies were found
in the order O [52.93%] A [22.77%] B [20.64%] and AB [3.66%]
respectively among Nigeria population. This was in agreement with
other studies from other parts of the world from different race and
ethnic groups in USA having [O; 46.6%, A; 37.1%, B; 12.2% and
AB; 4.1%] Garratty, et al [14]. Another report from a study done
in Mauritania, Morocco, Cameroun, Tunisia, Ethiopia and Iran is
also consistent with the Nigerian study showing [O > A > B > AB]
Hamed, et al. [16-21]. The report from Madagascar and Guinea
showed slightly different result [O > B > A > AB]. However, Nigerian
ABO blood group results are slightly different from the study in
Madagascar and Guinea that reported this trend [O > B > A > AB]
Randriamanantany, et al. [22,23]. Reports from studies in India
and Bangladesh showed blood group B having highest prevalence
followed by O and the least was AB [B > O > A > AB] Dewan, et al.
[24,25]. In Nigeria, there is a limited information of association
between ABO blood groups and the susceptibility to COVID-19
in Nigeria. This study therefore, evaluated the role of ABO blood
group in SARS-CoV- 2 infection susceptibility and disease severity
in Lagos, Nigeria.
Methods
Study Design and Participants
This study is a case series that includes patients that are
evaluated between June and August 30, 2020, and diagnosed with
COVID-19.With ethical approval obtained from the Institutional
Review Board [IRB] at the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research
[NIMR], Yaba, Lagos, Nigeria, patient data were obtained and
reviewed at the Mainland Infectious Disease Hospital and the
Nigerian Institute of Medical Research, Yaba. Informed consent
was also obtained from the study participants before their health
records were obtained. They were confirmed to have been infected
with SARS-CoV-2 by a positive reverse transcriptase polymerase
chain reaction test [Qpcr] of nasopharyngeal, throat and blood
samples. Clinical outcomes were also monitored and recorded.
Data Collection and Statistical Analysis: Clinicians and
trained research assistants retrospectively reviewed and copied
patients’ health records out to a standardized data collection
form. Health records copied out include demographic information,
signs and symptoms presented with, co-morbidities, and patient
outcome. A formal sample size was not calculated for this study
because the objective of the study was to describe the clinical
characteristics of the patients and their Blood group profile of
participants who had enough information in their health records
for analysis. Records were double entered into the forms before
merging to reduce errors during data entry. Descriptive analyses
were performed using Statistical Package for the Social Science
[SPSS] version 25 [IBM, USA].
Results
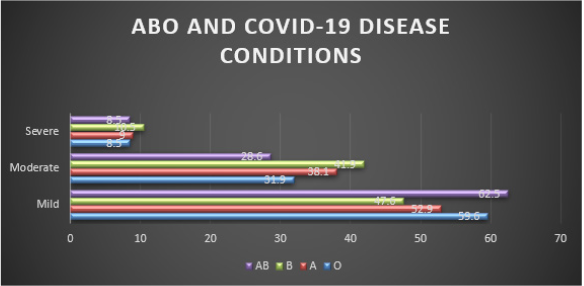
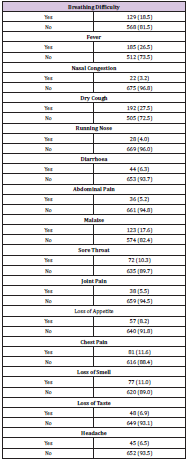
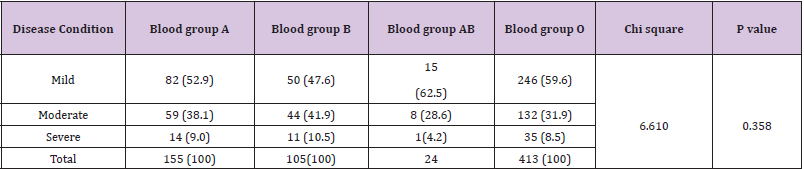
A total of 697 COVID-19 patients were included in this study. The mean age [S.D] of the study participants is 41.32 [12.917]. COVID-19 was common in males [66.1%] than in females [33.9%]. Out of the 697 participants, 43.6% were asymptomatic while 56.4% were symptomatic showing symptoms like breathing difficulty, fever, dry cough, running nose, sore throat and others as shown on Tables 1 & 2. The most frequently detected blood group in the population was O accounting for [59.2%], followed by A 155[22.2%], B 105[15.10%] and the least is AB 24[3.4%]. Figure 1 showed the blood groups that accounted for COVID-19 severity: blood group B 11 [10.5%] followed by A 14 [9.0%], O 35 [8.5%] and AB 1 [4.2%]. There was no significant statistical difference between the blood groups in relation to COVID-19 severity [p=0.358].
Table 2: Symptomatic patients (56.4%). The most common symptoms were: dry cough (27.5%), Fever 185 (26.5) and breathing difficulty (18.5%).
Tables 3 & 4 showed five [5] persons having blood group O were among the deceased [55.6%]. Four out of the 5 deceased had severe COVID-19 and were males. Their age, ranged from 53 to 65 years. The youngest being 53years was a woman who had a mild symptom of COVID-19. Three [3] women having blood group A were among the deceased [33.3%]. Aged ranged 66-75 years. Two out of these three women had mild cases and one severe COVID-19 case. This is a proof to show that old age and co morbidities are risk factors to COVID-19 disease complications and death. Five [5/ 55.6%] persons having blood group O were among the deceased four out of the 5 deceased had severe COVID-19 and were males and aged 53 to 65 years. The youngest being 53 years was a woman who had a mild symptom of COVID-19. Three [3/ 33.3%] women having blood group A were among the deceased. Their age ranged from 66 to 75.
Discussion
A person’s blood group [A, B, AB and O] is determined by
the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells
which trigger an immune response. Reports from some recent
studies, suggests that ABO blood group may play a role in the
immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 disease with group A conferring
a higher susceptibility to infection and or severe disease and group
O individuals less likely to test positive (Geol, et al. [26]) and Fan,
et al. [27]. However, reports are in contrast to our current study
which shows no statistical ssignificant evidence [p = 0.358] that
individuals with the blood group profile A were associated with
increased risk to severe cases of COVID-19. Furthermore, in
moderate cases of Covid-19 infection, group B [41.9%] individuals
were more represented and may have increased risk to COVID
-19 susceptibility when compared to other blood groups. We also
observed that most of the deceased persons [5/ 55.6%] had blood
group O, were males and age 53 to 65 years. Three [3/ 33.3%]
women having blood group A were equally among the deceased
aged 66 to 75 years with co-morbidities which include Pneumonia,
Diabetes, LRTI , Hypertension in both severe and mild cases
confirming that both age and comorbidities can lead to death with
COVID-19 disease.
A recent study that supported our data reported that a
significantly increased risk was associated with blood group B
Almadhi, et al. [28], which is also comparable to findings by Latz,
et al. [29] and meta-analysis by Liu, et al. [30]. In Nigeria and other
parts of the globe, blood group O Rhesus positive has consistently
been the most common, followed by A, then B, and AB being the
least [Anifoweshe et al 2016]. According to [Geol et al 2021],
group O originated in Africa before early human migration, and
has anti‐A and/or anti‐B antibodies present in group O individuals
which binds to the corresponding antigens on the viral envelope
and contribute to viral neutralization, thereby conferring some
protection by preventing target cell infection. However, our data
proposed that group B and or O individuals may be more likely to
be infected with COVID-19 disease suggesting that COVID -19 in
Nigeria and few other studies from other parts of the world may
not be affected by the anti A or B that has been proposed to confer
protection to these that have it. Furthermore, ABO blood group is
determined by inheritance, natural selection, showing underlying
genetic and ethnic diversity which may have influenced the current
frequencies of ABO types among Nigerian populations based on
susceptibility to particular diseases or disorders. Hospitalization,
higher infection chances, and death were found among those with
blood group A and O, and ethnicity was also a factor considered to
weigh COVID-19 risks in this study.
Conclusion
The ABO blood group was not associated with the presentation and recovery period of COVID-19 disease during the period of this study. However, the patients of blood group B profile seem to have higher risk of COVID-19 disease susceptibility. To further detect the susceptibility and severity of COVID-19 infection, more samples of individuals with confirmed exposure to COVID-19 infection should be conducted.
Availability of Supporting Data
Besides those presented in the study, there are no other supporting data for this manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors report no competing (commercial/academic) interests.
Ethical Approval
Approval to conduct this study was received from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at NIMR, Yaba, Lagos.
Funding
This study was funded by the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research, NIMR (Grant Number: NMG-CIF-06-0024). The PI and co-authors financed this study.
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge the director general and CEO of the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research (NIMR) for providing enabling environment for this study.
References
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, et al. (2020) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579(7798): 270-273.
- Benjamin Gallo Marin, Ghazal Aghagoli, Katya Lavine, Lanbo Yang, Emily J Siff, et al. (2021) Predictors of COVID-19 severity. A literature review Rev Med Virol 31(1): 1-10.
- Samra S, Habeb M, Nafae R (2021) ABO groups can play a role in susceptibility and severity of COVID-19. The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology 15(1): 9.
- Dentali F, Sironi AP, Ageno W, Turato S, Bonfanti C, et al. (2012) Non-O blood type is the commonest genetic risk factor for VTE: results from a meta-analysis of the literature. Semin Thromb Hemost 38(5): 535-548.
- Sun W, Wen CP, Lin J, Wen C, Pu X, et al. (2015) ABO blood types and cancer risk - a cohort study of 339,432 subjects in Taiwan. Cancer Epidemiol 39(2): 150-156.
- Zhao J, Yang Y, Huang H, Li D, Gu D, et al. (2020) Relationship between the ABO Blood Group and the COVID-19 Susceptibility. Clin Infect Dis 73(2): 328-331.
- Nagla AES, Manal El H, Ahlam A A, Basma G Eid, Thikryat Neamatallah, et al. (2021) The Impact of ABO Blood Grouping on COVID-19 Vulnerability and Seriousness: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Controlled Study among the Arab Community. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(1): 276.
- Wu B, Gu D, Yang YJ, Jie Yang, Wang Qin Shen (2020) Association between ABO blood groups and COVID-19 infection, severity and demise A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Genet Evol 84: 104485.
- Storry JR, Olsson ML (2009) The ABO blood group system revisited A Review and Update. Immunohematology 25(2): 48-59.
- Eastlund T (1998) The histo-blood group ABO system and tissue transplantation. Transfusion 38(10): 975-988.
- Cheng Y, Cheng G, Chui CH, Lau FY, Chan PK, et al. (2005) ABO blood group and susceptibility to severe acute respiratory syndrome. JAMA 293(12): 1450-141.
- Liumbruno GM, Franchini M (2013) Beyond immunohaematology the role of the ABO blood group in human diseases. Blood Trans 11(4): 491-499.
- Gershman B, Moreira DM, Tollefson MK, Frank I, Cheville JC, et al. (2016 ) The association of ABO blood type with disease recurrence and mortality among patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder undergoing radical cystectomy. Urol Oncol 34(1): 1-9.
- Garratty G, Glynn SA, McEntire R (2004) ABO and Rh (D) phenotype frequencies of different racial/ethnic groups in the United States. Transfusion 44(5): 703-706.
- Anifowoshe AT, Owolodun OA, Akinseye KM, Iyiola OA, Oyeyemi BF (2016) Gene frequencies of ABO and Rh blood groups in Nigeria: A review. The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 18(3): 205-210.
- Hamed CT, Bollahi MA, Abdelhamid I, Mahmoud M, Ba B, et al. (2012) Frequencies and ethnic distribution of ABO and Rh (D) blood groups in Mauritania: results of first nationwide study. Int J Immunogenet 39(2): 151-154.
- Maatoghi TJ, Paridar M, Shoushtari MM, Kiani B, Nori B, et al. (2016) Distribution of ABO blood groups and rhesus factor in a Large Scale Study of different cities and ethnicities in Khuzestan province Iran. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 17(1): 105-109.
- Tesfaye K, Petros Y, Andargie M (2015) Frequency distribution of ABO and Rh (D) blood group alleles in Silte Zone Ethiopia. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 16(1): 71-76.
- Ndoula ST, Noubiap JJN, Nansseu JRN, Wonkam (2014) A Phenotypic and allelic Distribution of the ABO and Rhesus (D) blood groups in the Cameroonian Population. Int J Immunogenet 41(3): 206-210.
- Boulahdid S, Adouani B, Laouina A, Mokhtari A, Abdelmajid Soulaymani, et al. (2013) Distribution of ABO and Rhesus D blood antigens in Morocco. Int J Biol Anthropol 6(1).
- Said N, Ben Ahmed F, Doghri A, Ghazouani E, Layouni S, et al. (2003) The ABO system polymorphism in Tunisian blood. Transfus Clin Biol 10(5): 331-334.
- Randriamanantany ZA, Rajaonatahina DH, Razafimanantsoa FE, Rasamindrakotroka MT, Andriamahenina R, et al. (2012) Phenotypic and allelic profile of ABO and Rhésus D blood group system among blood donor in Antananarivo. Int J Immunogenet 39(6): 477-479.
- Loua A, Lamah MR, Haba NY, Camara M (2007) Frequency of blood groups ABO and Rhesus D in the Guinean population. Transfus Clin Biol 14(5): 435-439.
- Dewan G (2015) Comparative frequency and allelic distribution of ABO and Rh (D) blood groups of major tribal communities of southern Bangladesh with General population and their determinants. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 16(2): 141-147.
- Chandra T, Gupta A (2012) Frequency of ABO and rhesus blood groups in blood donors. Asian J Trans Sci 6(1): 52-53.
- Goel R, Bloch EM, Pirenne F, Arwa Z Al Riyami, Elizabeth Crowe, et al. (2021) ABO blood group and COVID-19: a review on behalf of the ISBT COVID-19 working group. Vox Sang 116(8): 849-861.
- Fan Q, Zhang W, Li B, Li DJ, Zhang J, et al. (2020) Association Between ABO Blood Group System and COVID-19 Susceptibility in Wuhan. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10: 404.
- Almadhi M, A Abdulrahman, A Alawadhi, Ali A Rabaan, Stephen Atkin, et al. (2021) The effect of ABO blood group and antibody class on the risk of COVID-19 infection and severity of clinical outcomes. Sci Rep 11(1): 5745.
- Latz CA, DeCarlo C, Boitano L, Png CYM, Patell R, et al. (2020) Blood type and outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Ann Hematol 99(9): 2113-2118.
- Nanyang Liu, Tingting Zhang, Lina Ma, Huiqing Zhang, Huichan Wang, et al. (2020) The impact of ABO blood group on COVID-19 infection risk and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Reviews 48.

 Research Article
Research Article