Abstract
The main theme of this short report is to discuss the magnitude of Disaster because of Earthquake 2005 in Kashmir Pakistan and implementation of disaster management lifecycle. The author has done the literature review of 14 articles and websites to collect and analyze the disaster data and information of Kashmir 2005 earthquake. Author has presented the used disaster management plan, Disaster preparedness, mitigation, response, and recovery used by helping organizations and government of Pakistan. The crux of the discussion is that till date there is significant progress in relocating people building schools hospitals houses and roads in affected areas after the 2005 Kashmir earthquake.
Disaster Management Plan [1]
Organizations involved:
1. Earthquake Reconstruction & Rehabilitation Authority
Pakistan (ERRA since 2005)
2. NDMA (National Disaster management authority Pakistan
(Since 2010)
3. US Marine and Army helicopters from Afghanistan, Pakistan
Army and retired.
4. UN, WHO, EU, OIC, UNDP, UNESCO, UNICEF, Oxfam, ICRC-red
crescent, JEN-Japan Others.
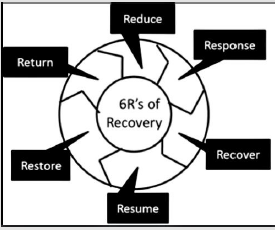
Management Cycle
(Figures 1 & 2) [2].
Kashmir Earthquake 2005 [3]
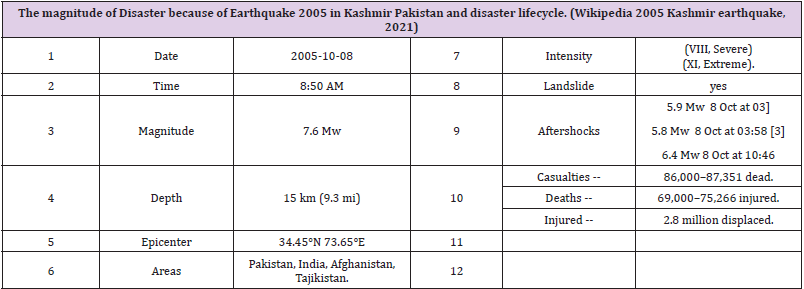
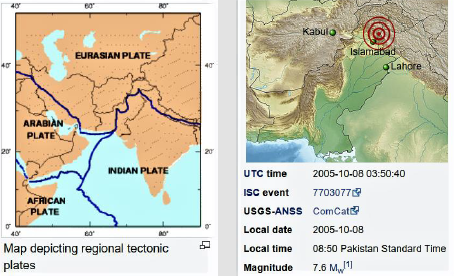
The 2005 Kashmir earthquake occurred at 08:50 am Pakistan Standard (Wikipedia, 2021) Time on 8 October in Pakistani Azad Kashmir. It registered a moment magnitude of 7.6 and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe) or XI (Extreme). The earthquake also affected countries in the surrounding region where tremors were felt in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, India and the China Xinjiang region. The severity of the damage caused by the earthquake is attributed to severe upthrust. Over 86,000 people died a similar 100,000 number were injured and millions were displaced. It is considered the deadliest earthquake to hit South Asia (Table 1).
Table 1: The magnitude of Disaster because of Earthquake 2005 in Kashmir Pakistan and disaster lifecycle.
Preparation [4]
Disaster preparedness: 5 key components to effective
emergency [4] management were used in the 2005 Kashmir
earthquake.
1. Clear communication.
2. Comprehensive training.
3. Knowledge of assets.
4. Technology fail-safes and protocol.
5. Healthcare leadership involvement. Disaster response in
the early phase of [5] earthquake relief is complex with local
facilities often overwhelmed and damaged. Coordinated effort
is required for success with lessons learnt to improve future
disaster management.
Financial Assistance and Aid [6]
In late 2006 a staggering $20 billion USD development scheme was mooted [6] by Pakistan for reconstruction and rehabilitation of the earthquake hit zones in Azad Kashmir. A land use plan for Muzaffarabad city had been prepared by Japan International Cooperation Agency. Countries of Asia, Africa, EU, Americas, Oceana, Multinational organizations, NGOS - On November 19, 2005, it was estimated that the international community as a whole pledged about US$5.8 billion. (Wikipedia 2005 Kashmir earthquake, 2021) [7] (Figures 3-5).
Mitigation [8]
Risk mitigation refers to the process of planning and
developing [8] methods and options to reduce threats or risks to
project objectives. The following five strategies can be used in risk
mitigation planning and monitoring.
1. Assume and accept risk.
2. Avoidance of risk.
3. Controlling risk.
4. Transference of risk.
5. Watch and monitor risk.
Although susceptibility zoning maps represent [9] a powerful
tool in natural hazard management caution is needed when
developing and using such maps. The October 2005 earthquake
triggered several thousand landslides in the Lesser Himalaya of
Kashmir in northern Pakistan and India. Preliminary results from
repeat photographs from 2005 and 2006 after the snowmelt
season reveal that much of the ongoing land sliding occurred along
rivers and roads, and the extensive earthquake-induced fissuring.
Although the susceptibility zoning success rate for 2001 was low
many of the co post seismic land sliding in 2005 occurred in areas
that had been defined as being potentially dangerous on the 2001
map [9]. Within a designated study area of 2250 km2 the number
of landslides increased from 369 in 2001 to 2252 in October 2005.
Response [10]
Disaster response is the assistance and intervention [10] during or immediately after an emergency or disaster. Focus is on saving lives and protecting community assets (buildings, roads, animals, crops, infrastructure). Usually measured in hours, days or weeks. Immediately after the earthquake occurred the largest rescue and relief [11] operation was launched in the history of Pakistan. The Pakistani Army was directed to extend help to the civilian population in the quake affected areas and all civilian and military hospitals were directed to deal with the situation on an emergency basis. Many countries international organizations, and nongovernmental organizations offered relief aid to the region in the form of donations as well as relief supplies including food, medical supplies, tents, and blankets. International rescue and relief workers brought rescue equipment including helicopters and rescue dogs.
Recovery [12]
During the recovery period, restoration efforts occur concurrently with regular operations and activities. Preventing or reducing stress related illnesses and excessive financial burdens. Rebuilding damaged structures and reducing vulnerability to future disasters. It posed unique challenges and efforts on a massive scale for [13] reconstruction. For residential buildings the Pakistan government adopted a house owner driven approach. The reconstruction policy stated that the government and other agencies would provide equal technical assistance and subsidy to each family without differentiating between who lost what. To increase capacity in earthquake resistant construction large scale training of artisan’s technicians, engineers, and community mobilisers has been conducted. Campaigns to “build back better” have raised awareness in the communities. Local Housing Reconstruction Centers have been established for training advice and [13] dissemination of earthquake resistant technology. This decentralized approach has helped in achieving reconstruction smoothly [14].
Conclusion
To conclude, the importance of disaster medicine and disaster management is well recognized in last decades. The role of disaster management cycle with steps, preparation, mitigation, response and recovery with detail efforts enables the EMS of the countries to help during disaster prevention and recovery.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest with any institution/organization.
References
- (2021) ERRA. Earthquake Reconstruction & Rehabilitation Authority Pakistan, Earthquake 2005 reconstruction sector.
- (2021) Google Disaster life cycle. Google Disaster life cycle images.
- (2021) Wikipedia. 2005 Kashmir earthquake.
- (2021) Healthcare dive. Disaster preparedness: 5 key components to effective emergency management.
- Mulvey J, Awan S, Qadri A, Maqsood M (2008) Profile of injuries arising from the 2005 Kashmir Earthquake: The first 72 h. 39(5): 554-560.
- (2021) Wikipedia International response. International response to the 2005 Kashmir earthquake.
- (2021) Wikipedia 2005 Kashmir earthquake. The 2005 Kashmir earthquake occurred at 08:50:39 Pakistan Standard Time on 8 October in Pakistani Kashmir.
- (2020) Indeed, risk mitigation (2020) Five Key Risk Mitigation Strategies (With Examples).
- Kamp U, Owen A, Growley J, Ghazanfar A Khattak. (2009) Back analysis of landslide susceptibility zonation mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake: an assessment of the reliability of susceptibility zoning maps. Nat Hazards 54: 1-25.
- (2021) Resilient community organization. Emergency Management: Prevention, Preparedness, Response & Recovery summary.
- Sabri AA, Qayyum MA (2006) Why Medical Students Should Be Trained in Disaster Management: Our Experience of the Kashmir Earthquake. PLOS Medicine 3(9): e382.
- (2021) Training.fema.gov. Unit four. Emergency Management in the United States.
- Mumtaz H, Mughal H, Stephenson M, Bothara K (2008) The challenges of reconstruction after the October 2005 Kashmir earthquake. Bulletin of the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering 41(2): 68-82.
- (2021) United Nations oceans and law of sea. United Nations System Links.

 Mini Review
Mini Review