Abstract
In the recent years much of the scientific efforts have been shifted towards computer and its applications to assist explorations in the area of biology sciences and developed a new discipline as bioinformatics. One of the important aspect of this area of research the designing of drugs based on the in-silico methods, which ultimately are validated through wet laboratory techniques. The present efforts have been prepared to dock modified specific ligand for diabetes mellitus treatment. We have an IRAK protein which is responsible of diabetes mellitus. We have concluded from the present study that the modified acetohexamide ligand has great results from the molecular docking.
Keywords: Acetohexamide Modified Ligand; Diabetes; IRAK Protein
Introduction
In the recent years much of the scientific efforts have been shifted towards computer and its applications to assist explorations in the area of biology sciences and developed a new discipline as bioinformatics [1-3]. One of the important aspect of this area of research the designing of drugs based on the in-silico methods, which ultimately are validated through wet laboratory techniques [4]. Objective of the present study was to evaluate the docking study of modified acetohexamide and modified metformin with IRAK protein, which is involved in diabetes mellitus.
Materials and Methods
Protein sequence which is responsible for diabetes mellitus retrieved from NCBI. This IRAK protein has been used in the sequence. Briefly, acetohexamide and its modified structure; moreover metformin and its modified structure were docked with IRAK protein. The protein data bank was used to retrieve the structure of the protein. Both the protein and ligands were present in sdf files and were converted into pdb in the discovery studio, then these files were convert into pdbqt files in the auto dock software. And finally all the structures were docked with IRAK protein by using vina tool. Detailed dodifications of the parent compounds/ drugs are given here.
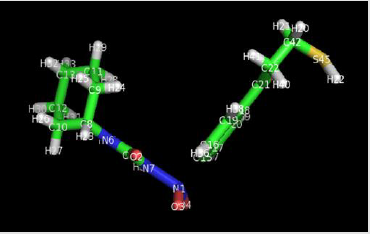
Modified Acetohaxamide
Acetohaxamide was modified as:
a) We change H45 to S45
b) Then attached O34 to N1
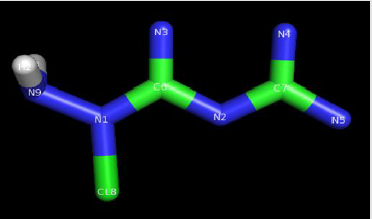
Modified Metformin
Metformin was modified as:
a) Changed H9 into N9.
b) Then H8 was changed into Cl8.
Structure of modified acetohaxamide and modified metformin
are given in Figures 1 & 2.
Results and Discussion
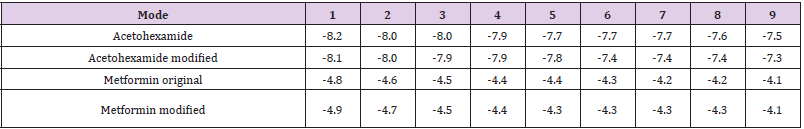
Docking results of our study are given in Table 1. There were 9 pockets in total. Modified acetohaxamide in pocket 5 gave lower bonding energy while modified metformin gave lower bonding energy in many pockets.
ADMIT Properties
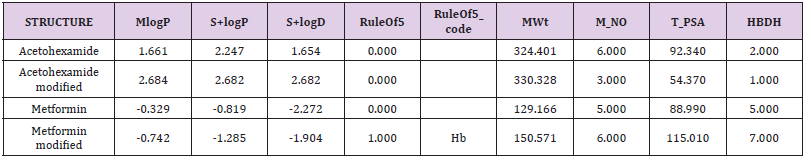
ADMIT Properties of the candidates are given in Table 2.
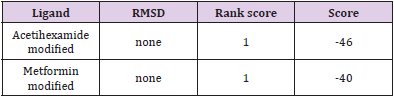
Drug Scoring by DSX-Online
Drug scoring of the modified drugs are given in Table 3 which were obtained by DSX-online. When we discuss the results of our study, we have come to know that modified metformin was a very good option to develop in real structure and go through wet laboratory validation. It showed very worthy outcome as it showed lower (-4.9) bonding energy as compared to the original compound.
Conclusion
Molecular docking study provides an opportunity to identify good drugs that may further be used for validation in actual.
References
- Ahmad FK, He Z, King GL (2005) Molecular targets of diabetic cardiovascular complications. Curr Drug Targets 6(4): 487-494.
- Bharatam PV, Patel DS, Adane L, Mittal A, Sundriyal S (2007) Modeling and informatics in designing anti-diabetic agents. Curr Pharm Des 13(34): 3518-3530.
- Bagust A, Beale S (2005) Modelling EuroQol health-related utility values for diabetic complications from CODE-2 data. Health Econ 14(3): 217-30.
- Coyle D, Lee KM, O’Brien BJ (2002) The role of models within economic analysis: focus on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacoeconomics 20(Suppl 1): 11-9.

 Short Communication
Short Communication