Abstract
Background and Objective: The main theme of this article is to discuss and
compare the workplace organization method 5S with the 7 wastes (Muda) in waste and
failure management tool, in the health care quality management.
Methods: The Author of this article has chosen literature review methodology of 18
random research articles and quality management websites. By reviewing the literature,
we have chosen 10 different points in 18 articles discussing or agreeing on where 5S and
7 Muda are beneficial. Most of the chosen articles discusses the quality management in
the health sector and their benefits.
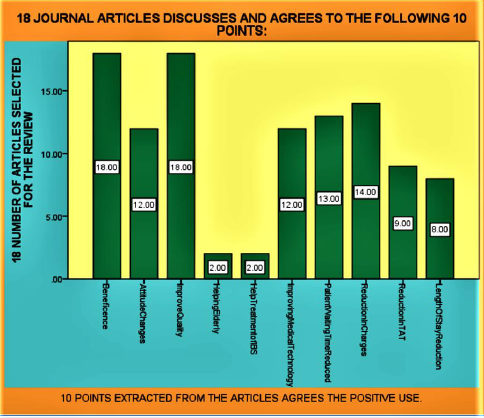
Results: There is a table and SPSS diagram representing the literature review
regarding 18 articles including quality management website. Table title is (18 journal
articles discusses and agrees to the following 10 points). SPSS diagram clearly shows the
number of times each article discusses the chosen 10 points. The 10 points includes the
agreement of points beneficial for health sector by using 5S and 7 Muda methodology.
Conclusion: To conclude the article, 18 of the articles including the quality
management websites agrees on the use of 5S and 7 Muda methodology. Different
organization around the globe are using 5S and 7 Muda methodology to get benefits for
improvement of their health care system. The step-by-step process of 5S and 7 Muda
methodology is smart way to start, monitor, finish and follow up the broken health
system in several countries.
Keywords: 5S Methodology; 5S Examples; 7 Wastes; 7 Muda; Overproduction; Overprocessing; Inventory; Waste Motion; Information Management; Lean; Medical Records; Process Improvement; Teamwork
Introduction
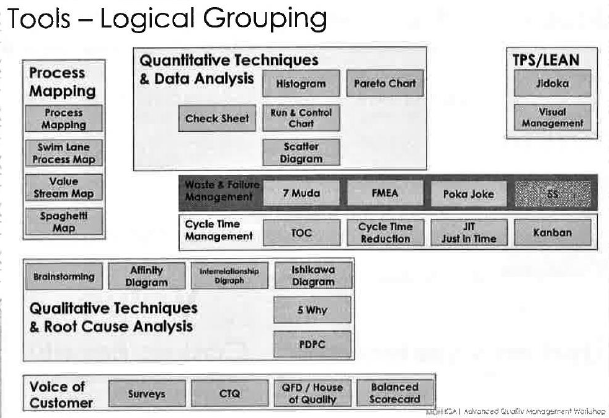
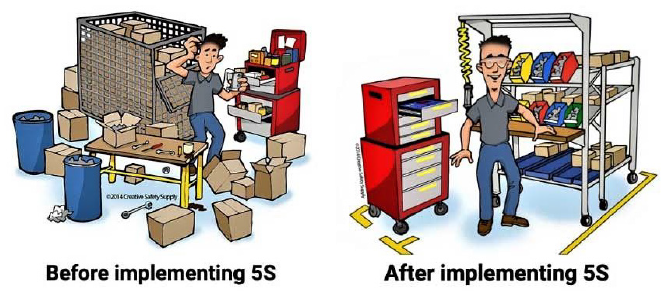
The 5S is a workplace organization system [1] designed to help build a quality work environment, both physically and mentally. The 5S condition of a work area is critical to the morale of employees and the basis of customers first impressions. Management’s attitude regarding employees is often reflected in the 5S condition of the work area. The 5S are: (Redesighningcare, 2017) [1] Seiri (sorting or “SORT”), Seiton (set in order or “STREIGTEN”), Seiso (Systematic cleaning or “SHINE”), Seiketsu (Standardizing or “STANDERDIZE”), Shitsuke (Sustaining or “SUSTAIN”) (Figures 1& 2).
5S – Step 1 – Sort: Eliminate Items
(Marc Karschies, 2017) “When in doubt, move it out” [2].
Inventories can hold significant values of overstocked, expired
and/or useless items. Sort items by logical grouping and get rid of
unnecessary or expired items to make space for everything else. If
you are not sure about something, put it aside for a few days and see
if anyone needs it. Sorting Categories includes: [2]
1. Expired stock (Discard),
2. Replaced by different item/ Never used/ Obsolete items
(Discard),
3. Does not belong/ To be returned (Returned to correct dept)
4. Stored elsewhere (Move to correct storage)
5. Overstock to be used (Block reorder until used – Kanban),
6. Mystery items (Investigate and then recategorize),
7. Rarely used (Move to less prominent storage location),
8. Patient specific (Move to special storage) (Figure 3).
5S – Step 2 – Set in Order, Arrange Items
“A place for everything and everything in its place” [2]. Use containers that hold exactly the right quantity to prevent overstock. Use to bin system – time to restock + buffer = bin size; empty bin = reorder. Label items (with pictures) so everyone can find them or put them away (Figure 4).
5S – Step 3 – Shine. Neat & Clean
Spot problems quickly by keeping the area spotless [2]. Shine regularly. If something is always in the wrong spot, maybe it needs a new home.
5S – Step 4 – Standardize. Consistent Approach
Make sure everyone is doing things the same way [2]. All drawers organized the same way.
5S – Step 5 – Sustain. Maintain Correct Procedures
When clean in the normal, it is time to see what else you can improve [2]. Perform 5S Audits (e.g with laminated preprinted test scripts like “find XYZ”. Is everything in the right place? Is everything in the right quantity? Perform team huddles to identify further improvement opportunities.
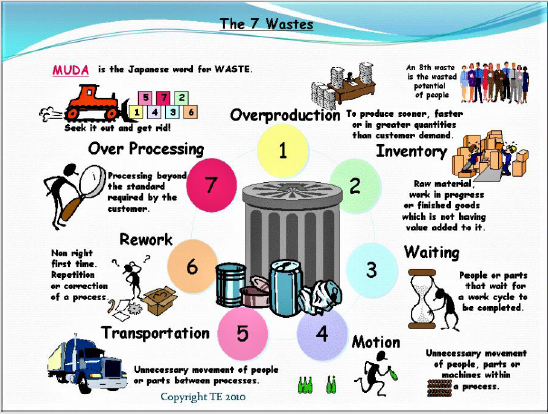
Toyota’s (Ohno’s) Seven Forms of Waste [3]
Taiichi Ohno “father” of the Toyota Production System originally identified seven forms of Muda or waste [3].
Transportation
Every time a product is touched or moved unnecessarily there is a risk that it could be damaged, lost, delayed, etc. as well as being a cost for no added value.
Inventory
Whether in the form of raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), or finished goods, represents a capital outlay that cannot yet produce an income [3].
Motion
Motion refers to the damage and costs inflicted on what creates the product. This can include wear and tear for equipment, repetitive strain injuries for workers or unnecessary downtime.
Waiting
Whenever the product is not in transportation or being processed, it is waiting (typically in a queue).
Overproduction
Making more of a product than is required results in several forms of waste, typically caused by production in large batches.
Over processing
Doing more to a product than is required by the end-customer results in it taking longer and costing more to produce [3].
Defects
Having to discard or rework a product due to earlier defective work [3] (Figure 5).
Methods
The Author of this article has chosen literature review methodology of 18 random research articles and quality management websites. By reviewing the literature, we have chosen 10 different points in 18 articles discussing or agreeing on where 5S and 7 Muda are beneficial. Most of the chosen articles discusses the quality management in the health sector and their benefits. The 5S management method [4] (where 5S stands for sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain) was originally implemented by manufacturing enterprises in Japan. It was then introduced to the manufacturing sector in the West and eventually applied to the health sector for organizing and standardizing the workplace. 5S has recently received attention as a potential solution for [4] improving government health-care services in low- and middleincome countries. The 5S has the potential to improve [5] client satisfaction at resource-poor health facilities and could therefore be recommended as a strategic option for improving the quality of healthcare service in low- and middle-income countries. To explore more effective intervention modalities, further studies need to address [5] the mechanisms by which 5S leads to attitude changes in healthcare staff.
The pilot intervention of the 5S management method [6] was perceived to have improved the quality of healthcare services and staff motivation in a resource-poor healthcare facility with a disorderly work environment in Senegal. Quantitative and qualitative research based on a larger-scale intervention would be needed to elaborate and validate these findings and to identify the [6] cost-effectiveness of such intervention in low- and middleincome countries. Dental caries and periodontal disease [7] are common in elderly with AD. These dental problems are ambulatory care-sensitive conditions, where effective community dental care can help to prevent the need for hospital admission. 5S is a problem-solving approach to helping elderly with AD [7] build and sustain effective oral hygiene practices for improving their oral health. Irritable Bowel syndrome IBS specialists [8] from around the world established by consensus two best practice charters: the 5S Principles and the 5C Concept. The 5S Principles were conceived to provide health care providers with key guidance for improving clinical practice based on best management approaches. They comprise the following categories: Stage the disease; Stratify patients; Set treatment goals; Select appropriate treatment; and Supervise therapy. Optimized management of patients with IBD based on the 5S Principles can be [8] achieved most effectively within an optimized clinical care environment.
Measure and Statistical Analysis (Table 1 & Figure 6)
Results
There is a table and SPSS diagram representing the literature review regarding 18 articles including quality management website. Table title is (18 JOURNAL ARTICLES DISCUSSES AND AGREES TO THE FOLLOWING 10 POINTS). SPSS diagram clearly shows the number of times each article discusses the chosen 10 points. The 10 points includes the agreement of points beneficial for health sector by using 5S and 7 Muda methodology. The healthcare organization is the place [9] where defects and mistakes cannot be tolerated. A simple mistake can cost a human life so defects or mistakes must be eliminated in healthcare service processes. The LSS methodology optimizes the average reduction of a desired process. The expected results can be reductions in several aspects of healthcare such as patient waiting time in emergency departments, lost charges for billing in patient financial services, delinquent medical records, diagnostic result turnaround [9] times, accounts receivable days, patients’ length of stay, or medication errors. Findings lean six sigma LSS is a powerful process improvement [10] methodology that could be applied by health-care sectors to reduce medication errors, increase patient safety and reduce operational costs. Common Lean and Six Sigma tools play a significant role in improving and sustaining the medication process. Practical implications It is necessary for the project team to select the most appropriate LSS tools to address medication process problems. Adoption of a LSS [10] roadmap could help health-care organizations in the successful implementation of LSS. Lean and Six Sigma can be considered [11] valuable process optimization approaches in acute health care settings. The success of their implementation requires significant participation of clinical personnel from the frontline as well as clinical leaders and managers. More research is needed to better understand the factors of success and the barriers to their [11] implementation, as well as their long-term impact.
Discussion
The Medical record department (MRD) [12] is the critical department for the hospital information system and, therefore, the continuous improvement of its services and processes, through scientific methods such as Lean management, are essential. The benefits of Lean for healthcare organizations are that first, the quality of the outcomes in terms of mistakes and errors improves. The second is [12] that the amount of time taken through the whole process significantly improves. Lean and Six Sigma are (Janet H Sanders and Tedd Karr, 2015) continuous improvement methodologies that have garnered international fame for improving manufacturing and service processes. Six Sigma’s Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control methodology is very similar to good medical practice: first, relevant information is obtained and assembled; second, a careful and thorough diagnosis is completed; third, a treatment is proposed and implemented; and fourth, checks are [13] made to determine if the treatment was effective. The role of Six Sigma philosophy in improvement [14] of the quality of healthcare services is recognized both by researchers and by quality practitioners; discrete-event simulation models are commonly used to improve the key performance measures of patient care delivery. The two approaches are seldom referenced and implemented together however, they [14] could be successfully integrated to carry out quality improvement programs. Six Sigma’s data measurement and process [15] improvement methodology is the impetus for health care organizations to rethink their workflow and reduce malpractice. It involves measuring, recording and reporting data on a regular basis. This enables the administration to monitor workflow continuously. Implementation of the design, measure, analyse, improve and control (DMAIC) improvement cycle, workflow chart, fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts [15] were employed, together with rigorous data collection in the department [16-18].
Conclusion
To conclude the article, 18 of the articles including the quality management websites agrees on the use of 5S and 7 Muda methodology. Different organization around the globe are using 5S and 7 Muda methodology to get benefits for improvement of their health care system. The step-by-step process of 5S and 7 Muda methodology is smart way to start, monitor, finish and follow up the broken health system in several countries.
Conflicts of Interest
None.
References
- (2021) Redesighningcare. 5S in health care.
- Marc Karschies (2017) Advance quality management workshop for healthcare sector.
- (2021) Wikipedia Muda. Muda (無駄, on'yomi reading, ateji) is a Japanese word meaning "futility”.
- Shogo K, Akira S, Masamine J (2016) Applicability of the 5S management method for quality improvement in health-care facilities: a review. Trop Med Health 44: 21.
- Shogo K, Marcia C, Seydou S, Rui M, Alioune Cissokho, et al. (2016) Impact of the Japanese 5S management method on patients’ and caretakers’ satisfaction: a quasi-experimental study in Senegal. Glob Health Action 9: 10.
- Shogo Kanamori, Seydou Sow, Marcia C Castro, Rui Matsuno, Akiko Tsuru, et al. (2015) Implementation of 5S management method for lean healthcare at a health center in Senegal: a qualitative study of staff perception. Glob Health Action 8: 27256.
- Sherry G, Chun HC, Fanny FY (2020) Integrating 5S Methodology into Oral Hygiene Practice for Elderly with Alzheimer’s Disease. Dent J (Basel) 8(2): 29.
- Toshifumi Hibi, Remo Panaccione, Miiko Katafuchi, Kaoru Yokoyama, Kenji Watanabe, et al. (2017) The 5C Concept and 5S Principles in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management. J Crohns Colitis 11(11): 1302-1308.
- Selim A, Noor A M, Rafikul I (2013) Effects of Lean Six Sigma application in healthcare services: a literature review. Rev Environ Health 28(4): 189-194.
- Yaifa Trakulsunti, Jiju Antony (2018) Can Lean Six Sigma be used to reduce medication errors in the health-care sector? Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl) 31(4): 426-433.
- Simon Deblois, Luigi Lepanto (2016) Lean and Six Sigma in acute care: a systematic review of reviews. Int J Health Care Qual Assur 29(2): 192-208.
- Sima A, Saeedeh K, Akram S, Sakine S (2015) Improving the medical records department processes by lean management. J Educ Health Promot 4: 48.
- Janet H Sanders, Tedd Karr (2015) Improving ED specimen TAT using Lean Six Sigma. Int J Health Care Qual Assur 28(5): 428-440.
- Giovanni C, Antonio C, Sergio F, Giuseppe T (2012) Linking Six Sigma to simulation: a new roadmap to improve the quality of patient care. Int J Health Care Qual Assur 25(4): 254-273.
- Mehmet T, Bulent S, Kamal A (2012) Application of Six Sigma methodology to a diagnostic imaging process. Int J Health Care Qual Assur 25(4): 274-290.
- (2021) 5S Today. What is 5S?
- (2021) Lean manufacturing tools.
- (2021) Google images. 5s before and after.

 Mini Review
Mini Review