Abstract
The significance of horticulture to every single human culture is portrayed as never before, with the expanding total populace. Nanotechnology has been characterized as identifying with materials, frameworks, and procedures which work on a size of 100 nanometers or less. Nanotechnology has numerous applications in all phases of creation, handling, putting away, bundling and transport of agrarian items. The phytotoxic conduct of the nanoparticles should be tended to logically before using them for agribusiness rehearses. It will be trusted that the controlled arrival of dynamic plant development stimulators and different chemicals typified in Nano composites made of layered twofold hydroxides could be an achievable alternative to natural farming. Take-up of nanoparticles by plants, their translocation, and impact on plants will be accounted for. In this study, the impact of ZnO nanoparticles on seed germination and root development of the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) will be researched and the treated gatherings will be contrasted with control bunches all together with screen positive or toxic impact. The leaf physical parameters like root length, shoot length and its external territory will be noted.
Keywords: Solanum Lycopersicum; ZnO Nanoparticles; Seed Germination; Root Development
Introduction
Food techniques were basically progressed in the forms
of smart distribution of minerals, bio-separation of proteins,
quick examining of ecological and chemical pollutants,
nanoencapsulation of Nutraceuticals, solubilization, distribution,
and color in feeding methods; these being few of the developing
texts of nanotechnology in meal and farming [1]. Meanwhile, food
nanotechnology as a recent technology was needing surveys of
potential of the many positive results also has the negative results.
In this view, we designed to cover a few of the developments in
nanotechnology and their application to food and Nutraceutical’s mechanisms. It presents a few of the Nanoscale-sized structures
that are particularly related to the food products, the various food
production methods that were assisting from nanotechnology,
and nanotechnologies used for the preparation and keeping of
food, collected by recognizing the great challenge [2-4]. Zinc is the
required proteins for plant generation. It is also the major structure
of ribosome and is ecessary for their growth.
Zinc is the dynamic component in biochemical methods and
have a chemical and a biological interface with several more
components [5]. Phosphorus is the one of the main components
which disturbs on zinc absorb by plants. Phosphorus is the main
components that disturbs with zinc absorb, as zinc absorb by plants
decreases by rising phosphorus in loam. High levels of phosphorus
may decrease the availability of zinc or the onset of zinc deficiency
associated with phosphorus fertilization may be due to plant
physiological factors. More strengths of copper in the mud results,
apply to zinc, be able to shrink the accessibility of zinc to a plant in
view of rival for the similar places of interest in the plant stem. It
would take place once the use of a copper as fertilizer. Zinc scarcity
is due to iron (Fe) insufficiency, due to inhibit of a move to iron from
root to shoot at the zinc insufficient situation. Acceptable quantity
of zinc in the plant recovers the injurious causes of boron (B)
scarcity. Zinc scarcity reduces plant growth by raising the strength
of boron in the tips and the fresh leaves of the parts [6,7].
The study and progress in the area of nanotechnology are
increasing quickly everywhere on the earth. The main part of that
field is the improvement of newly substances on the nanoscale. In
the area of nanotechnology, the particles can be measured at zero
dimension, i.e., in quantum dots and in one dimension the particles
are approximately less than 100 nanometers (nm). The several
physical and chemical techniques are applied for the nanoparticle’s
synthesis. The elements generally used are poisonous, flammable,
not simply disposed towards the ecological problems, having
low products rate, and so on by applying these kinds of harmful
methods. The rate of reducing metal ions using plants is formed
to be much quicker as compared with the microorganisms and the
stable forming of metal nanoparticles [8,9]. These particles are
applied in several consumer products, and it is predicted that these
NPs will enter into different ecosystems, where their actions are
not recognized.
As a result, the organisms which are interactive with NPs are
supposed to, that’s an advantage or negative issue. The relations
between microorganisms and the metals are well known and the
ability of micro-organisms to extricate and/or assemble metals is
once applied in biotechnological techniques such as bioleaching
and bioremediation [10]. With the sudden increase in the using
of engineered nanoparticles (NPs) that can be applied in many
fields like pharmaceuticals, cosmetic products, energy industry
and in machines [11-15]. At present observation nano toxicity is
accepting increased, it is considered that engineered nanoparticles
can be discharged to the atmosphere, mistakenly or indifferently.
Regardless of the detail that more and more investigators are
briefed the nanotoxicity in plants, the studies require at the rest of
the rising phase and information on the results of nanoparticles in
plant structures require for more analysis, especially in crop plants,
given that the engineered nanoparticles may be a risk to people’s
condition for the group of food. These nanoparticles are distributed
into four classes as carbon-based materials, metal-based materials,
and complexes.
The metal oxide nanoparticles and all the metal-based materials
playing an important role that is generally applied in monitor to
atmospheric viruses, self-cleaning and catalysis [16-19]. Different
types of metal oxide NPs are useful in farming, particularly used for
the protection plant and germinate. Silicon dioxide nanoparticles
can be applied for the happening of control release transported in
narcotic method and as a mobile component in opposition to worms’
pests, zinc oxide nanoparticles are used as pesticides. Absolutely,
several metal oxide NPs are described to include positive causes
on crop vegetation. For the case sprayed of TiO2 can considerably
enhance the production of spinach, stem height of green peas
considered by ZnO on soil is roughly two stages higher than the
limitation. However, many of the investigators are describing the
phytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in crop vegetative stage.
In that situation, it can be observed that differing conclusions
(positive responses or negative responses) can be drawn about a
similar metal oxide nanoparticle in various plants. By adding, the
toxicity in crop plants is normally evaluated by applying one or two
types of metal oxide NPs. Thus, it is vital to thoroughly examine
the phytotoxicity of a wide group of metal oxide NPs in crop plants
[8,9]. Dye Sensitized Solar Cells on its basis for various explicit
band-gap semiconductors will be produced as well as designed
though obtaining preferred outputs but growing conveyer cycles
had great effects. By comparison with normal chips, a quadruped
figure for zinc oxide will establish the important interest into the
Dye Sensitized Solar Cells whereas their background structure of
an interlinked quadruped structure gives better tracks through its
transporters which move once that rearrange therefore controlling
for the development conveyer cycles.
Other research group manufactured the Dye Sensitized
Solar Cells on the basis of 30mm broad layer upon its interlinked
zinc oxide quadruped structure from a conducted surface and
considered their routine. These dimensions established like the
zinc oxide quadruped structure bases of Dye Sensitized Solar Cells
will attain its performance that should be moreover upon this
Dye Sensitized Solar Cells bases on zinc oxide nanowire displays
or circular zinc oxide nanoparticles attain [6,20]. This thought is the portion of the evolved discipline of accuracy in farming, in
which farmers build the use of technical to regularly use irrigate,
nourishment, and other benefits. Chemical substances are applied
to the growth of plant and fruit with the help of fertilizers. Spinach
(Spinacia oleracea L.) is one commonly used green leafy vegetable
eaten up in Pakistan. Spinach consists of a high nutritional
rate of other vitamins i.e., vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K, iron,
folate, magnesium and manganese and it is the best resource of
the nutrient fiber, potassium, calcium, vitamin B, vitamin E and
riboflavin. The main purpose of this present analysis is to yield a
nanoparticles fertilizer supply on the nutrient use in productivity
of spinach plant [21-24].
Materials and Methods
Solanum lycopersicum seeds in this experiment will be taken from the Ayub research centre, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. ZnO nanoparticle will be used in sowing of these seeds in pots. The synthesized nanoparticles (ZnO) were used for treating fresh Solanum lycopersicum seeds in different concentrations [25]. Equal quantity of soil and equal amount of water will be added in pots. Treatment group will be compared with the control group. The plant parameters like root length, shoot length, shoot dry and fresh weight will be monitored. The number of treated samples and controlled sample will be monitored daily. The different growth parameter will be monitored and calculated in order to examine any positive or toxic effect of nanoparticles for the Solanum lycopersicum plant.
Results and Discussion
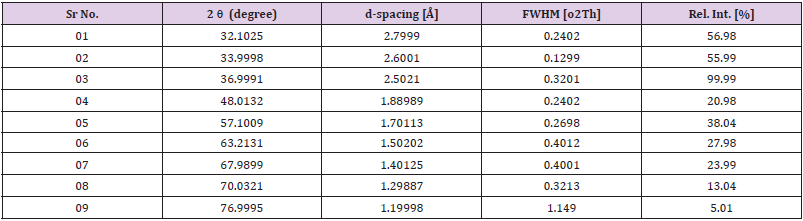
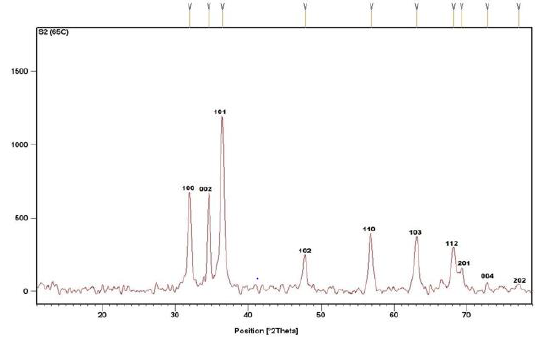
The pure zinc oxide powder was manufactured by chemical process named co-precipitation method by using Zinc Nitrate. Sodium hydroxide was used to maintain the pH of the solution, it was maintained at value 11. Throughout the process of adding mixture, composites of zinc were prepared, and zinc ions totally dissolved in the solution. X-ray powder diffractometer patterns of zinc oxide samples were recorded using Cu-Ka radiation (=1.540598A) with 2 theta range from 20 to 80 To identify the peaks and phase transformations, the XRD pattern of zinc oxide sample is described in (Figure 1), together along with their appropriate XRD data (d-spacing, 2θ values, half maximum intensity, and relative intensity) Table 1. Debye Scherer’s formula has been used to measure the crystalline size of all the specimens, and miller indices were also used to estimate the lattice parameters [26].
Lattice Parameter
The following equation help out to measure the lattice parameter and miller indices (hkl).
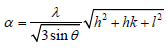
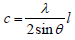
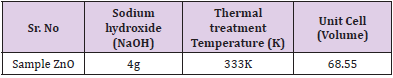
In this equation λ, explained wavelength of x-rays while its values are 1.540598Å on the other hand and c shows the lattice parameter and its value of sample in the (Table 2).
Volume of Unit Cell
Using the formula, calculate the volume of hexagonal wurtzite unit cells of ZnO
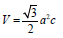
The lattice parameters are ‘a’ and ‘c.’ (Table 3)
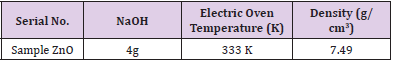
Density of Unit Cell
The density of a unit cell is defined as ratio of own mass to its own volume. The formula is used to determine it.
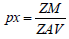
Where Z is the number of molecules per unit cell, M is the sample’s molar mass, NA is Avogadro’s number, and V is the unit cell’s volume. The density of a unit cell is determined by measuring the amount of the unit cell and the sample’s molar mass (Table 4).
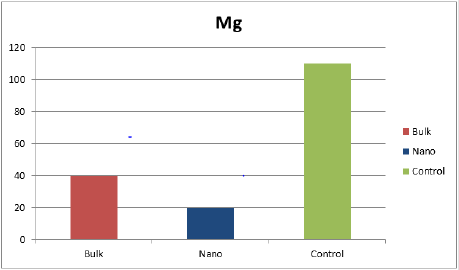
Concentration Level of Magnesium in Solanum lycopersicum
This graph shows the effect of Bulk, Nano and Control groups of the spinach leaves as using ZnO nanoparticles (Figures 1 & 2). By adding ZnO the concentration level of magnesium in control group gradually increased as compared to other groups [27] (Figure 3).
Concentration Level of Iron in Solanum Lycopersicum
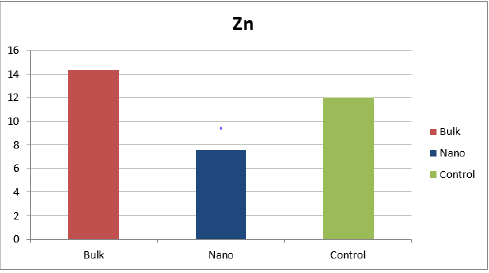
This graph shows the effect of Bulk, Nano and Control groups of the tomato leaves as using ZnO nanoparticles. By adding ZnO the concentration level of iron in control group gradually increased as compared to other groups [28] (Figure 4).
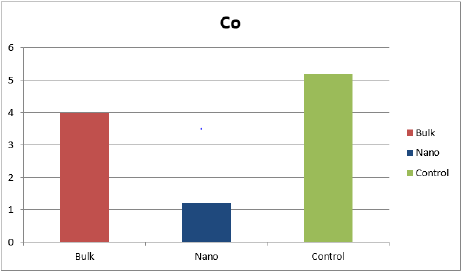
Concentration Level of Cobalt in Solanum Lycopersicum
This graph shows the effect of Bulk, Nano and Control groups of the tomato leaves as using ZnO nanoparticles. By adding ZnO the concentration level of cobalt in control group gradually increased as compared to other groups [29-31].
Conclusion
The co-precipitation method was used to obtain the ZnO nanoparticle. Zinc oxide specimens have prepared by using the solution, Zinc Nitrate and sodium hydroxide solution having different ratios. The pH was maintained to the value 11. For further process furnace treatment 400 oC for two hours is given to that powder to make comparison between the obtained nanoparticles from the oven. Scherrer’s formula was used to calculate the crystal size of the material. All of the specimens’ x-ray diffraction patterns were very comparable to the new patterns. The size of the produced particles was determined using Scherrer’s formula. The Debye’s formula was used for the lattice constants zinc oxide showed precisely same peaks as of the pure zinc oxide. Peak thickness and concentrations were varied. Their lattice constants varied significantly, but their ratio remained stagnant.
References
- Bilal M, Mehmood S, Iqbal HM (2019) Immobilized enzyme-based biocatalytic cues: an effective approach to tackle industrial effluent waste. In Microbes for Sustainable Development and Bioremediation, pp. 287-311.
- Al Tayyar NA, Youssef AM (2020) Antimicrobial packaging efficiency of ZnO-SiO2 nanocomposites infused into PVA/CS film for enhancing the shelf life of food products. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 25: 100523.
- Kim I, Viswanathan K, Kasi G, Thanakkasaranee S, Sadeghi K, et al. (2020) ZnO nanostructures in active antibacterial food packaging: Preparation methods, antimicrobial mechanisms, safety issues, future prospects, and challenges. FOOD REVIEWS INTERNATIONAL, p. 1-29.
- Sun J, Jiang H, Wu H, Tong C, Pang J, et al. (2020) Multifunctional bionanocomposite films based on konjac glucomannan/chitosan with nano-ZnO and mulberry anthocyanin extract for active food packaging. PubAg 107: 105942.
- Bilal M, Mehmood S, Rasheed T, Iqbal H (2019) Bio-catalysis and biomedical perspectives of magnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers. Magnetochemistry 5(3): 42.
- Khan M, Sabir M, Mustafa GM, Fatima M, Mahmood A, et al. (2020) 300 keV cobalt ions irradiations effect on the structural, morphological, optical and photovolatic properties of Zn doped TiO2 thin films-based dye sensitized solar cells 46(10): 16813-16819.
- Rehman WU, Wang H, Manj RZA, Luo W, Yang JJS (2021) When Silicon Materials Meet Natural Sources: Opportunities and Challenges for Low‐Cost Lithium Storage 17(9): 1904508.
- Bian F, Zhong Z, Zhang X, Yang C, Gai X (2020) Bamboo–An untapped plant resource for the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Bioremediation 246: 125750.
- Chen H, Yang X, Wang H, Sarkar B, Shaheen SM, et al. (2020) Animal carcass-and wood-derived biochars improved nutrient bioavailability, enzyme activity, and plant growth in metal-phthalic acid ester co-contaminated soils: A trial for reclamation and improvement of degraded soils. J Environ Manage 261: 110246.
- Bilal M, Rasheed T, Mehmood S, Tang H, Ferreira L, et al. (2020) Mitigation of environmentally-related hazardous pollutants from water matrices using nanostructured materials–A review. Chemosphere 253: 126770.
- Hussain A, Usman M, Manj RZA, Liu F, Li D, et al. (2021) Rational Design of Graphene-based Sorbents for Water Purification. In Nanostructured Catalysts for Environmental Applications, pp. 309-329.
- Manj RZA, Chen X, Rehman WU, Zhu G, Luo W, et al. (2018) Big potential from silicon-based porous nanomaterials: in field of energy storage and sensors. Front Chem 6: 539.
- Manj RZA, Zhang F, Rehman WU, Luo W (2020) Toward understanding the interaction within Silicon-based anodes for stable lithium storage 385: 123821.
- Rehman WU, Zhang F, Manj RZA, Ma Y, Yang JJ (2021) Corncob derived porous carbon anode for long-term cycling in low-cost lithium storage. J o E E C& Storage 19(1): 010909.
- Yang W, Cheng P, Adams CA, Zhang S, Sun Y, et al. (2021) Effects of microplastics on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in a soil spiked with ZnO nanoparticles. Biochemistry 155: 108179.
- Hassan N, Lu S, Xu W, Ge H, Naseer MA, et al. (2021) Fabrication of Pd nanoparticles on Al substrate with excellent superhydrophobicity and photocatalytic activity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 148: 109704.
- Hassan N, Lu S, Xu W, Ge H, Sultana A, et al. (2021) Fabrication of stable superhydrophobic bismuth material on the aluminum substrate with high photocatalytic activity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 23(4): 1-15.
- Hassan N, Lu S, Xu W, He G, Faheem M, et al. (2019) Fabrication of a Pt nanoparticle surface on an aluminum substrate to achieve excellent superhydrophobicity and catalytic activity. New Journal of Chemistry 43(15): 6069-6079.
- Hassan N, Lu S, Xu W, Yu T, He G, et al. (2018) Fabrication of Ag-Fe3O4/Fe superhydrophobic surface on galvanic sheet for its application. Journal of Solid-State Chemistry 266: 121-132.
- Ezhov AV, Aleksandrov AE, Zhdanova KA, Zhdanov AP, Klyukin IN, et al. (2020) Synthesis of Zn (II) porphyrin dyes and revealing an influence of their alkyl substituents on performance of dye-sensitized solar cells 269: 116567.
- Adetola OY, Onabanjo OO (2020) The search for sustainable solutions: Producing a sweet potato based complementary food rich in vitamin A, Zinc and Iron for infants in developing countries. Stark AHJSA 8: e00363.
- Alexander J, Tinkov A, Strand TA, Alehagen U, Skalny A, et al. (2020) Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19. Nutrients 12(8): 2358.
- De Grande A, Ducatelle R, Delezie E, Rapp C, De Smet, et al. (2021) Effect of vitamin E level and dietary zinc source on performance and intestinal health parameters in male broilers exposed to a temperature challenge in the finisher period. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 105(4): 777-786.
- Sharif Y, Sadeghi O, Dorosty A, Siassi F, Jalali M, et al. (2020) Association of vitamin D, retinol and zinc deficiencies with stunting in toddlers: findings from a national study in Iran. Public Health 181: 1-7.
- Sheoran P, Grewal S, Kumari S, Goel S (2021) Enhancement of growth and yield, leaching reduction in Triticum aestivum using biogenic synthesized zinc oxide nanofertilizer. J B & Biotechnology A 32: 101938.
- Holzwarth U, Gibson N (2011) The Scherrer equation versus the'Debye-Scherrer equation. Nature Nanotechnology 6(9): 534-534.
- Koch M, Winkelmann MK, Hasler M, Pawelzik E, Naumann M (2020) Root growth in light of changing magnesium distribution and transport between source and sink tissues in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). 10(1): 1-14.
- Ghidan AY, Kahlel AM (2020) Effect of nanotechnology liquid fertilizers on yield and nitrogenous compounds of broad bean (Vicia faba l.). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 29(6): 41244128.
- Reta D (2020) Biosynthesis of Co3O4-Zno Nanocomposite Material Using Waste Extract of Potato And Banana Fruits Peel For Antibacterial Application. ASTU.
- Mahmood S, Ashfaq UA (2015) Dengue NS5 global consensus sequence development to find conserved region for antiviral drug development. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.
- Sabir S, Zahoor MA, Waseem M, Siddique MH, Shafique M, et al. (2020) Biosynthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Bacillus Subtilis: Characterization and Nutritive Significance for Promoting Plant Growth in Zea mays L 18(3): 1559325820958911.

 Research Article
Research Article