Abstract
The studies have demonstrated that several polymorphisms in the apolipoprotein CIII (ApoCIII) gene are associated with hypertriglyceridemia, but the link with coronary artery disease (CAD) among different ethnicities is still controversial. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between the polymorphisms of ApoCIII with plasma lipid levels, lipoprotein subfractions and risk of CAD in Chinese Han population. Four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of ApoCIII gene, including rs5128, rs2542051, rs11216153 and rs2849174 were detected by TaqMan Genotyping Assays in 268 subjects with CAD who had angiographically documented coronary atherosclerosis, and 108 controls without CAD. Genotype-specific odds ratios (OR) were estimated by logistic regression. The levels of serum lipid profiles were also detected by biochemical methods. Three polymorphisms (rs2542051, rs11216153 and rs2849174) were first studied. The rs11216153 in 5’-near regions of ApoCIII gene showed evidences associated with increased risk of CAD (per minor allele OR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.08-2.26; P= 0.017). Compared with the most common rs11216153 genotype, variant genotypes (TT) increased an individual’s susceptibility to CAD (OR, 3.2; 95%CI, 1.15-7.05; P=0.004). However, carriers of the minor allele of rs2542051 had lower risk of CAD (per minor allele OR, 0.67; 95%CI, 0.46-0.97; P=0.035). We also showed that rs2542051 CC genotypes predicted lower risk of CAD than TT genotypes (OR, 0.344; 95% CI, 0.154-0.767; P=0.009). The other ApoCIII gene polymorphisms (rs5128, rs2849174) in this study were not associated with the risk of CAD. In addition, we also found that rs2849174 carriers of the ApoCIII T allele had higher ApoA plasma levels compared with C allele carriers (t=-2.445, P =0.020) in this study population. Our data supported a relationship between the two polymorphisms of ApoCIII gene (rs11216153, rs2542051) and the risk of CAD. SNP rs2849174 was associated with ApoA plasma levels.
Keywords: Coronary Artery Disease; Polymorphism; Apolipoprotein C III
Abbreviations: SNPs: Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms; tagSNPs: Tagging SNPs; MALDI-TOF: Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/ Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry; HWE: Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium; MAF: Minor Allele Frequency; 3’UTR: 3’Untranslated Region; 5’NEAR: 5’- near regions; 3’NEAR: 3’-near regions; AD: coronary artery disease; TG: triglyceride; CHOL: cholesterol; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; VLDL: very-low-Density Lipoprotein; LDL: Low-Density Lipoprotein; ApoA: Apolipoprotein A; ApoAIV: Apolipoprotein A IV; ApoB: Apolipoprotein B; ApoCⅢ: Apolipoprotein C; ApoE: Apolipoprotein E; OR: Odds Ratios; CI: Confidence Interval; M: Median; SD: Standard Deviation
Introduction
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) remains a significant health concern worldwide. Dyslipidemia has been identified as one of the principal risk factors for the development of CAD [1]. ApoCIII is implicated in the adjustment of the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and it is a principal constituent of chylomicrons and VLDL. Apo CIII inhibits the hydrolyzing effect of lipoprotein lipase for TG-rich particles and the hepatic absorption mediated by ApoE [2,3], and also is detrimental to the elimination of ApoB lipoproteins from plasma by interrupting their capacity to bind to hepatic lipoprotein receptors [4]. A high ApoCIII levels not only correlates with hypertriglyceridemia but also may directly contribute to the development of atherosclerosis [5]. Immense clinical studies have shown that ApoCIII level is a better way to predict the risk for evolution and progression of CAD than the traditional way by measuring TG levels [6-11]. Although the risk burden is mainly constituted by traditional risk factors, the heritable factors are critical for the development of CAD [12].
The human ApoAI and ApoCIII genes are tightly linked and form a gene complex together with the ApoAIV gene on the long arm of the chromosome11. Within and around the ApoC III gene, some polymorphie sites have been determined. ApoC-III gene polymorphisms correlated with coronary atherosclerosis could be a link of label for an atherogenic gene in the ApoAI-CIII-AIV gene complex. Numerous studies show a connection between the appearance of the polyporphie SstI(rs5128) site located in the untranslated region of the ApoCIII gene and the raised risk of CAD. In addition, polymorphisms in T-455C (rs2854116), and C-482T (rs2854117) have been found to be associated with CAD risk [13- 20]. The T2854G polymorphism located in the intergenic region was reported to be associated with elevated fasting or postprandial TAG concentrations in Caucasians [21]. To find a linkage marker for the putative atherogenic gene in ApoCIII gene of Chinese Han population, four qualified tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (tagSNPs) of ApoCIII gene were selected from the Genbank dbSNP database and we utilize these to appraise the linkage and association between these polymorphisms with plasma lipid levels, lipoprotein subfractions and risk of CAD in Chinese Han population.
Materials and Methods
Study Population
Approval was obtained from the Hebei Medical University Clinical Research Ethics Committee. After informed consent had been given, samples of venous blood were drawn from each subject after an overnight fast. All subjects in the study were ethnically homogenous Han Chinese derived from the Northern Chinese population. Patients who documented by coronary angiography at least a 70% stenosis in a major epicardial artery were eligible. Subjects with congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy, valvular disease, and renal or hepatic disease were excluded from the study. Age-matched control subjects were judged to be free of CAD by history, clinical examination, electrocardiography, and Rose questionnaire. A set of questionnaires was completed that included details of medical history, family history of CAD, drug intake, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption. Blood pressure, weight, height, and the body mass index were calculated.
TagSNPs Selection
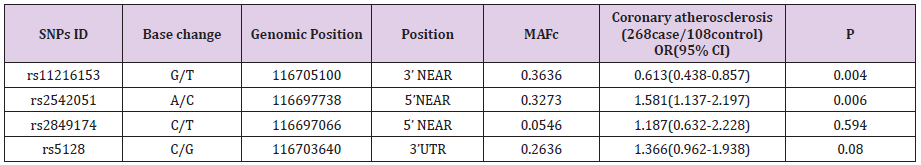
Bioinformatics analysis with Haploview software 4.2(Mark Daly’s lab of Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, Britain) was performed to analyze the haplotype block based on the CHB (Chinese Han Beijing) population data of HapMap (HapMap Data Rel 27 PhaseII +III, Feb09, on NCBI B36 assembly, dbSNP b126 (International HapMap Project). Four tagSNPs were found to cover all the potential functional common SNPs in the ApoCⅢ gene, including rs5128 in the 3’UTR, rs2542051 and rs2849174 in the 5’ near regions, and rs11216153 in the 3’ near regions.
Genotyping Analysis
Genomic DNA was isolated from the peripheral blood of the study subjects. MassArray (Seque-nom, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for genotyping all markers using allele-specific MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry [22]. Primers and multiplex reactions were designed using the RealSNP.com Website.
Statistical Analysis
The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) was tested by a goodness-of-fit chi-square test to compare the expected genotype frequencies with observed genotype frequencies (p2+2pq+q2=1) in CAD-free controls. The association between case-control status and each SNP was measured by the Odds Ratio (OR), and its corresponding 95% Confidence Interval (CI) was estimated using an unconditional logistic regression model. Logistic regression modeling was used for the trend test. Homogeneity among stratum variable related ORs was tested. Baseline characteristics were shown as mean ± SD. Due to plasma lipid concentrations had a skewed distribution, the median and interquartile ranges (Q: difference of Q25 and Q75) were presented: M ± Q. The difference of lipid levels in different genotypes in CAD and controls was evaluated by one-way ANOVA after rank transformation when necessary. All calculations were computed with the aid of SPSS statistical software (version 16.0). P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
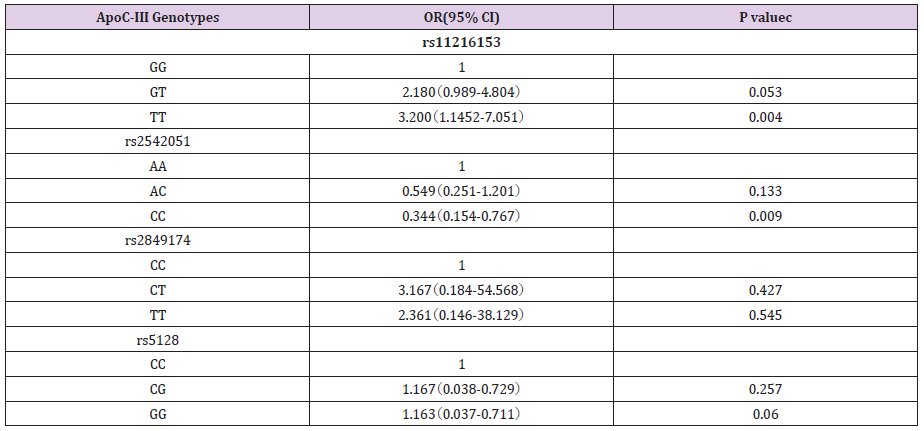
A total of 376 individuals were in the analysis. Among individuals in the study, 268 (191 men and 77 women) with CAD were confirmed. CAD was described exactly as stenosis (>70%) of no less than 1 major epicardial coronary artery proved by angiography. The non-CAD group include 108 subjects (78 men and 30 women) who were in hospital for cardiac examinations and showed no clinical, electrocardiographic, or angiographic the presence of disease symptom of CAD. The mean age of CAD patients and non-CAD subjects was 59.5±9.8 years and 58.5±9.0 years, respectively (P>0.05), and there was no significant difference in the BMI, diabetes, smoking, blood pressure between the two groups (P> 0.05). We genotyped four SNPs in CAD case-control studies. All polymorphisms were in the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in both groups. To estimate the CAD risk related to ApoCⅢ genotypes, we performed logistic regression analysis. Genotyping results showed that rs2542051 and rs11216153 was significantly associated with CAD in Chinese population (Table 1).
Compared with the most common rs11216153 genotype, variant genotypes (TT) increased an individual’s susceptibility to CAD (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.15-7.05; P=0.004). The result revealed that homozygotes for rs11216153 T had higher risk of CAD than wild-type individuals. Conversely, the adjusted OR of carrying the rs2542051 CC genotype was 0.344, compared with the AA genotype (P=0.009). The result showed that CC homozygotes had lower risk of CAD than those who carried the AA genotype. The previous reports showed evidences of increased CAD risk associated with ApoCⅢ gene polymorphisms. However, our result suggested that rs2542051 C variation decreased probability of the disease. No associations were found between rs5128, rs2849174 and CAD. In addition, we also evaluated the association between alleles and CAD risk (Table 2). Carriers of the minor allele of rs11216153 had increased risk of CAD (per minor allele OR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.08- 2.26; P=0.017). Conversely, SNP rs2542051 was associated with decreased risk of CAD (per minor allele OR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.97; P=0.035). Patients who carried the C allele tended to have a lower rate of CAD than those who carried the A allele. Thus, minor allele of rs2542051 was associated with reduced risk of CAD in Chinese. Our data also indicated that S2 alleles were common and not associated with coronary atherosclerosis (OR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.51- 1.12; P=0.166). Meanwhile, the C allele of rs2849174 that was first measured in the present study, was not related to CAD (P>0.05).
Table 2: Associations between ApoCIII genotypes and CAD risk.
Note: *The most common allele in controls is given first.
cMAF: minor allele frequency in CAD controls.
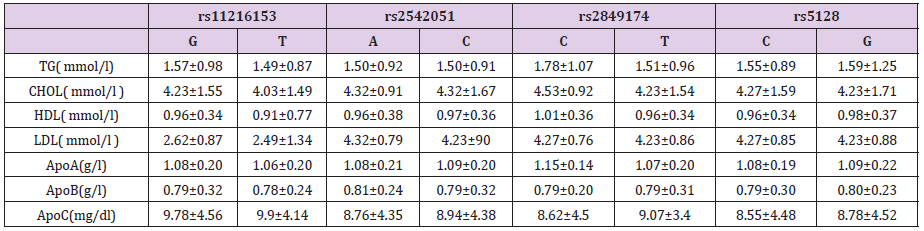
To estimate whether the abnormal lipid metabolism in subject carriers to the mutation contributed to the risk for CAD concerning the emergence of the ApoCIII variant, further analyses were performed. A total of 268 patients were analyzed, and the results were showed in Table 3. Although SNP rs2849174 was not associated with risk of CAD, the carriers of the T allele had higher ApoA plasma levels compared with C allele carriers (t=- 2.445, P=0.020). However, we did not find any statistically relevant differences between lipid variables levels and ApoCIII genotypes.
Table 3: Plasma levels of lipids, lipoproteins and apoproteins related parameters according to ApoC-III genotypes.
Note: Data was shown as mean ± SD; skewed variables were M ± Q. M: median, Q: inter-quartile range, difference of Q25 and Q75.
Discussion
ApoCIII plays an obligatory role in the determination of the levels of possibly atherogenic VLDL and small dense LDL in the circulation. The results of large-scale clinical studies have demonstrated that it is more preferable to use plasma ApoCIII concentrations as a predictor of risk for the development and progression of CAD compared with the traditionally measured TG levels [23]. However, the correlation between ApoCIII and CAD was provoking strong disapproval, for some studies indicating a likely association with genetic variability at the locus [24] and others not proving those associations. In present study, we genotyped four SNPs. To estimate the risk of disease related to ApoCIII genotypes, logistic regression analysis was performed. One of them is S1/S2 polymorphism (rs5128) in the 3’untranslated region. Although the previous studies demonstrated that there were the associations between S2 allele, lipids, glucose and insulin concentrations and risk of CAD, our results couldn’t provide any evidence to support the association between increased CAD risk and the S2 allele. Furthermore, no relationship between the rs5128 and plasma or serum lipid levels was observed.
The other three polymorphisms (rs2542051, rs11216153 and rs2849174) were first evaluated whether these were associated with an increased risk of CAD. We found the minor allele of rs11216153 was associated with an increased risk of CAD. The result revealed that homozygotes for rs11216153 T had higher relative risk of CAD than those observed in wild-type individuals. SNP rs11216153 seems to be unique in being strongly associated with CAD risk. Previous studies concerning ApoCIII polymorphisms and CAD risk have brought in debatable results, probably relevant to differences in methodological aspects such as the selection of cases and controls, their ethnical composition, and the sample size of this case study [11,16,25-28]. However, no study has reported ApoCIII polymorphisms were associated with reduced risk of CAD. Our result suggested that rs2542051 C variation decreased probability of disease. The minor allele of rs2542051 was associated with a reduced risk of CAD. Although SNP rs2849174 which was first studied was not associated with risk of CAD, we found that carriers of the T allele had higher ApoA plasma levels compared with C allele carriers. In this study, we were confident that we maximized the opportunity of precise results in the analysis of the connection with ApoCIII genotypes.
Conclusion
The present study genotyped four SNPs of ApoCIII. We found some evidences for association of SNP rs11216153 with increased risk of CAD and SNP rs2542051 with reduced risk of CAD. SNP rs5128 was not major risk factors of CAD in Han Population in China. Only rs2849174 was significantly associated with ApoA plasma levels.
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank the patients, their families and the control volunteers for participating in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 31071003 and 31271222, the Program of International S&T Cooperation of China 2011DFA32700.
Author Contributions
The study was conceived and designed by WC. The clinical data of all subjects were obtained by HH and SG. Data analyses were performed by MH and MG. The paper was written by HH and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The experimental protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hebei Medical University (Shijiazhuang, China). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Sharrett AR, CM Ballantyne, SA Coady, G Heiss, PD Sorlie (2001) Coronary heart disease prediction from lipoprotein cholesterol levels, triglycerides, lipoprotein(a), apolipoproteins A-I and B, and HDL density subfractions: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation 104(10): 1108-1113.
- Caron S, B Staels (2008) Apolipoprotein CIII: a link between hypertriglyceridemia and vascular dysfunction? Circ Res 103(12): 1348-1350.
- Mc Conathy WJ, JC Gesquiere, H Bass, A Tartar, JC Fruchart (1992) Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase activity by synthetic peptides of apolipoprotein C-III. J Lipid Res 33(7): 995-1003.
- Ginsberg HN, NA Le, IJ Goldberg, JC Gibson, A Rubinstein (1986) Apolipoprotein B metabolism in subjects with deficiency of apolipoproteins CIII and AI. Evidence that apolipoprotein CIII inhibits catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Clin Invest 78(5): 1287-1295.
- Clavey V, S Lestavel Delattre, C Copin, JM Bard, JC Fruchart (1995) Modulation of lipoprotein B binding to the LDL receptor by exogenous lipids and apolipoproteins CI, CII, CIII, and E. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 15(7): 963-971.
- Kawakami A, M Yoshida (2009) Apolipoprotein CIII links dyslipidemia with atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 16(1): 6-11.
- Hodis HN, WJ Mack, SP Azen, P Alaupovic, JM Pogoda, et al. (1994) Triglyceride- and cholesterol-rich lipoproteins have a differential effect on mild/moderate and severe lesion progression as assessed by quantitative coronary angiography in a controlled trial of lovastatin. Circulation 90(1): 42-49.
- Mack WJ, RM Krauss, HN Hodis (1996) Lipoprotein subclasses in the Monitored Atherosclerosis Regression Study (MARS). Treatment effects and relation to coronary angiographic progression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16(5): 697-704.
- Luc G, C Fievet, D Arveiler, AE Evans, JM Bard, et al. (1996) Apolipoproteins C-III and E in apoB- and non-apoB-containing lipoproteins in two populations at contrasting risk for myocardial infarction: the ECTIM study. Etude Cas Temoins sur 'Infarctus du Myocarde. J Lipid Res 37(3): 508-517.
- Thompson GR (1998) Angiographic evidence for the role of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in progression of coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J 19(H): H31-36.
- Sacks FM, P Alaupovic, LA Moye, TG Cole, B Sussex, et al. (2000) VLDL, apolipoproteins B, CIII, and E, and risk of recurrent coronary events in the Cholesterol and Recurrent Events (CARE) trial. Circulation 102(16): 1886-1892.
- Damani SB, EJ Topol (2007) Future use of genomics in coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(20): 1933-1940.
- Shanker J, G Perumal, VS Rao, NB Khadrinarasimhiah, S John, et al. (2008) Genetic studies on the APOA1-C3-A5 gene cluster in Asian Indians with premature coronary artery disease. Lipids Health Dis 7: 33.
- Chhabra S, R Narang, R Lakshmy, S Vasisht, DP Agarwal, et al. (2004) Apolipoprotein C3 SstI polymorphism in the risk assessment of CAD. Mol Cell Biochem 259(1-2): 59-66.
- Olivieri O, C Stranieri, A Bassi, B Zaia, D Girelli, et al. (2002) ApoC-III gene polymorphisms and risk of coronary artery disease. J Lipid Res 43(9): 1450-1457.
- Russo GT, JB Meigs, LA Cupples, S Demissie, JD Otvos, et al. (2001) Association of the Sst-I polymorphism at the APOC3 gene locus with variations in lipid levels, lipoprotein subclass profiles and coronary heart disease risk: the Framingham offspring study. Atherosclerosis 158(1): 173-181.
- Parzianello L, G Oliveira, JC Coelho (2008) Apolipoprotein CIII polymorphism and triglyceride levels of a Japanese population living in Southern Brazil. Braz J Med Biol Res 41(6): 462-467.
- Kawakami A, M Osaka, M Tani, H Azuma, FM Sacks (2008) Apolipoprotein CIII links hyperlipidemia with vascular endothelial cell dysfunction. Circulation 118(7): 731-742.
- Yiyang L, Y Ruixing, L Meng, L Kela, L Xingjiang (2010) Apolipoprotein C-III gene polymorphism and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Hei Yi Zhuang and Han populations. J Investig Med 58(6): 777-785.
- Tsai MY, JM Ordovas (2009) APOC3 mutation, serum triglyceride concentrations, and coronary heart disease. Clin Chem 55(7): 1274-1276.
- Woo SK, HS Kang (2003) The apolipoprotein CIII T2854G variants are associated with postprandial triacylglycerol concentrations in normolipidemic Korean men. J Hum Genet 48(11): 551-555.
- Jurinke C, P Oeth, D van den Boom (2004) MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: a versatile tool for high-performance DNA analysis. Mol Biotechnol 26(2): 147-164.
- Scheffer PG, T Teerlink, JM Dekker, G Bos, G Nijpels, et al. (2008) Increased plasma apolipoprotein C-III concentration independently predicts cardiovascular mortality: the Hoorn Study. Clin Chem 54(8): 1325-1330.
- Lee HY, AL Birkenfeld, FR Jornayvaz, MJ Jurczak, S Kanda (2011) Apolipoprotein CIII overexpressing mice are predisposed to diet-induced hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin resistance. Hepatology 54(5): 1650-1660.
- Dallongeville J, D Cottel, M Montaye, V Codron, P Amouyel (2006) Impact of APOA5/A4/C3 genetic polymorphisms on lipid variables and cardiovascular disease risk in French men. Int J Cardiol 106(2): 152-156.
- Ordovas JM, F Civeira, J Genest, S Craig, AH Robbins, et al. (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms of the apolipoprotein A-I, C-III, A-IV gene locus. Relationships with lipids, apolipoproteins, and premature coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 87(1): 75-86.
- Surguchov AP, GP Page, L Smith, W Patsch, E Boerwinkle (1996) Polymorphic markers in apolipoprotein C-III gene flanking regions and hypertriglyceridemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16(8): 941-947.
- Miettinen HE, K Korpela, L Hamalainen, K Kontula (1994) Polymorphisms of the apolipoprotein and angiotensin converting enzyme genes in young North Karelian patients with coronary heart disease. Hum Genet 94(2): 189-192.

 Research Article
Research Article