Abstract
In this work, we investigated the work of a neural network for recognizing speech in the Mongolian language and the emotional state in it. For the experiment, we used four commonly used words, which are composed of frequently used consonants and vowels. Emotional states in the speech were selected taking into account further research on changes in human mental disorders. For the analysis, we used a database of speeches of 12 men and women with eight types of emotions. Neural eat recognizes words by syllables with an efficiency of up to 96 percent, and emotions - up to 80 percent. These results show that for further analysis of human mental disorders, it remains only to collect a database from the speeches of patients of the relevant medical institutions.
Keywords: Speech Recognition; Mental Disorders; Word; Syllable; Neural Network
Introduction
Speech recognition as one of the methods of automatic speech analysis allows analyzing a person’s mental state, such as loneliness [1], depression [2] and predicts the development of psychosis that accompanies many mental disorders, including, for example, schizophrenia and bipolar disorder [3,4]. A change in the psychological and mental state of a person is found in the violation of both semantic and syntactic components: for example, poverty (using simple constructions and understanding only closed types of questions) and confusion (impaired speech coherence) of speech [5]. For the analysis of human speech, the choice of parameters by which we determine the mental state of a person also depends on whether it is written or oral. If audio recordings are examined, then the spatial and temporal parameters of speech should be taken into account: pauses, voice pitch, and the average time spent on pronouncing one word. Also, to increase the reliability of the result, the most frequent words and phrases used by people with different diagnoses should be calculated. Based on these parameters, using them to distinguish features, the neural network issues a “diagnosis” about the mental state of a person [2]. Therefore, to master the methods of automatic analysis of a person’s mental state based on oral speech in Mongolian, we needed to develop a neural network that recognizes not only words, but also syllables in a word, and also distinguishes such parameters of a speech signal as pauses, voice pitch and average time spent pronouncing one word.
Materials and Methods
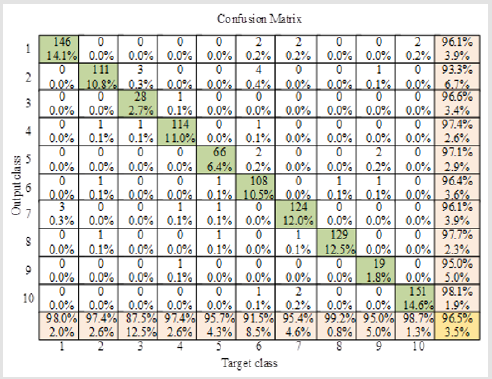
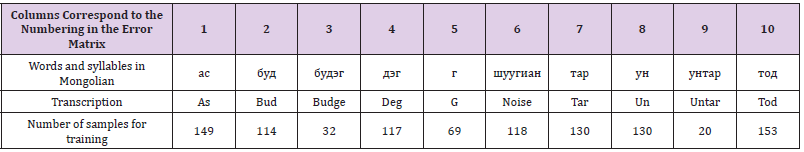
To recognize words and a syllable in a word, we used a neural network based on the Levenberg-Marquardt method [6]; after training, the neural network recognizes short words or speech syllables in Mongolian with an accuracy of 96.5 percent. (Table 1) shows the words and syllables used, and the numbering of the columns in the table corresponds to the numbering on the error matrix [7] used to assess the accuracy (Figure 1). The error matrix allows you to evaluate the efficiency of the algorithm used by comparing the prediction and the real value. These words were chosen for the reason that they are often used in colloquial speech and they contain the basic sounds of speech in the Mongolian language. Besides, noise is recognized to better highlight nonvoiced vowels and consonants when splitting words into syllables. In addition to recognizing words and syllables, for the analysis of a person’s mental state, such parameters of a speech signal as pauses, voice pitch, and the average time spent on pronouncing one word are distinguished. Calculating such parameters of a speech signal as speech rate, speech signal energy, pitch frequency, I, II, and III formants, as well as I, II, and III coefficients of the chalk filter bank [8,9], we recognized eight types of emotions in speech human [10,11]:
a. Neutral speech
b. Calm speech
c. Joyful speech
d. Sad speech
e. Angry speech
f. Frightened speech
g. Speech with disgust
h. Surprised speech
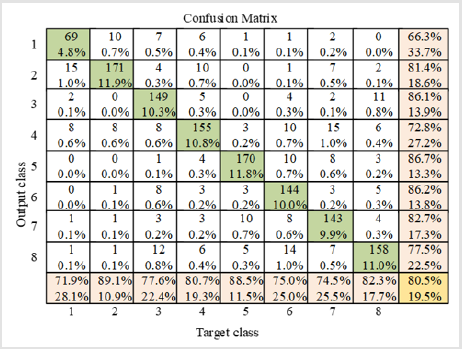
To analyze the emotional state of a person with the help of speech signals and train the neural network, a database consisting of the speech of 12 men and 12 women was used. And the result of training and recognition of the emotional state of a person from his speech is also shown in the form of error matrices in (Figure 2). The error matrix in (Figure 2) shows that the neural network recognizes emotion in human speech with a probability of 80.5 percent. The results obtained enable us to conclude that we correctly calculate the speech parameters we need to analyze and determine the mental state of a person. Speech recognition using a neural network not only allows you to analyze the mental state of a person but also allows you to detect and classify speech pathologies [12], helps in the detection of Parkinson’s disease [13], and to identify loneliness, which becomes a factor in the development of type II diabetes [14] and ischemic heart disease [15].
Figure 2: Confusion matrix in recognizing emotions in a person’s oral speech: the numbering corresponds to emotions in a person’s speech.
Conclusion and Further Work
It is obvious that the introduction and development of modern artificial intelligence technology in various fields of medicine is a very important task, but most of the research and experiments were carried out in a native speaker of English or another popular language. Therefore, we began our research on a neural network for speech recognition in the Mongolian language and highlighting the parameters necessary for analyzing the speech signal. The neural networks that we trained for the Mongolian language are good at recognizing both words and emotions with efficiency up to 96 and 80 percent, respectively. In the future, we plan to contact medical centers in the country and work with patients who need one or another support, both mental and pathological treatment.
References
- Varsha D Badal, Sarah A Graham, Colin A Depp, Kaoru Shinkawa, Yasunori Yamada, et al. (2020) Prediction of Loneliness in Older Adults Using Natural Language Processing: Exploring Sex Differences in Speech. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
- Al Hanai T, Ghassemi M, Glass J (2018) Detecting Depression with Audio/Text Sequence Modeling of Interviews. Proc Interspeech, pp. 1716-1720.
- Corcoran CM, Carrillo F, Fernández Slezak D, Bedi G, Klim C, et al. (2018) Prediction of psychosis across protocols and risk cohorts using automated language analysis. World Psychiatry 17(1): 67-75.
- Rezaii N, Walker E, Wolff P (2019) A machine learning approach to predicting psychosis using semantic density and latent content analysis. npj Schizophr 5: 9.
- Andreasen NC, Grove WM (1986) Thought, language, and communication in schizophrenia: diagnosis and prognosis. Schizophr Bull 12(3): 348-359.
- M Sanaullah, MH Chowdhury (2014) Neural network based classification of stressed speech using nonlinear spectral and cepstral features. 2014 IEEE 12th International New Circuits and Systems Conference (NEWCAS): 33-36.
- Ting KM (2011) Confusion Matrix. In: Sammut C, Webb GI (Eds.)., Encyclopedia of Machine Learning. Springer, Boston, MA.
- Akash Shaw, Rohan Kumar Vardhan, Siddharth Saxena (2016) Emotion Recognition and Classification in Speech using Artificial Neural Networks. International Journal of Computer Applications 145(8): 5-9.
- Gharavian D, Sheikhan M (2010) Emotion Recognition and Emotion Spotting Improvement Using Formant-Related Features. Majlesi Journal of Electrical Engineering 4(4).
- Banse R, Scherer KR (1996) Acoustic profiles in vocal emotion expression. J Pers Soc Psychol 70(3): 614-636.
- Javidi MM, Roshan Ebrahim (2013) Speech Emotion Recognition by Using Combinations of C5.0, Neural Network (NN), and Support Vector Machines (SVM) Classification Methods. Journal of mathematics and computer Science 6: 191-200.
- S Santhana Megala, R Padmapriya, B Jayanthi, M Suganya (2019) Detection and Classification Of Speech Pathology Using Deep Learning, International Journal Of Scientific & Technology Research 8(12): 3045-3051.
- Noor Afza, Manoj Challa, Jitendranath Mungara (2013) Speech Processing Algorithm for Detection Of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) 2(4): 1798-1803.
- Hackett RA, Hudson JL, Chilcot J (2020) Loneliness and type 2 diabetes incidence: findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Diabetologia 63(11): 2329-2338.
- Valtorta NK, Kanaan M, Gilbody S, Sara Ronzi, Barbara Hanratty (2016) Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for coronary heart disease and stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal observational studies. Heart 102: 1009-1016.

 Mini Review
Mini Review