Abstract
Health care is one of the basic needs of each community. Since considering to healthcare and investing in this sector increases labor productivity and service production, therefore, optimal resource allocation and use of resources is very important. It was found during the study that majority of the patients were more than 60 years of age (47.4%), evening hours (45.0%) were peak time when most of the patients reported. Majority of the Admissions were Direct and significant number of cases were Medico legal (16.0%).
Keywords: Emergency Department; Profile; Utilization
Introduction
Health care is one of the basic needs of each community. Since considering to healthcare and investing in this sector increases labor productivity and service production, therefore, optimal resource allocation and use of resources is very important [1]. Evaluation of health care programs can determine their quality and progress of implementation and failure or success rate [2]. Hospital services absorb almost half of health sector costs, so efficiency promotion of these services through cost reduction and use of potential capacity of health care organizations is necessary [3]. Diverse economic incentives have been used for cost reduction in hospitals. However, in the field of patient access to hospital services and the quality of services have not yielded to positive results. For preserving quality and accessibility, it is necessary to focus on cost containment indexes by attention to the appropriateness or inappropriateness of health care services [4]. Some cost containment strategies such as reduction in hospital beds have increased hospital waiting time. To overcome this problem, we should use hospital beds at highest efficiency and the best way for efficient use of hospital beds is to avoid or to minimize inappropriate patient hospitalization and not to decrease the quality [5]. The study of profile of patients attending emergency department will allow appropriate utilization of resources and hence this study was carried out.
Aims and Objectives
To study the profile of the patients attending the Emergency Medicine Department.
Material and Methods
Study Design and Duration
A retrospective study for a period of six months from 31st October 2018 to Ist May 2018 was carried out to know the sociodemographic profile of patients admitted in the Emergency Medicine Department from inpatient records from Medical Record Department.
Sampling
All the admissions (10,581) in the Emergency Medicine Department during the study period were included.
Study Tool
A pretested and predesigned Proforma was used to record information from the patient’s records about each case admitted to study demographic data, specialty of admission, length of stay and medico legal cases.
Statistical Analysis
The data was entered in MS excel. Descriptive analysis was done to calculate proportions.
Results and Observations
A total of 10581 patients admitted in the Emergency Medicine Department were studied for the profile.
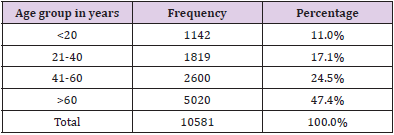
Age- Wise Distribution of Patients
A total of 10581 patients were studied, out of which 47.4% (n=5020) of the patients belonged to the age group of >60 followed by 24.5% (n=2600) of the patients in 41-60 age group. Only 11.0 % (n=1142) belonged to the age group of <20 (Table 1).
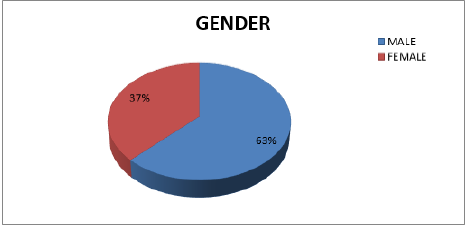
Gender-Wise Distribution of Patients
Out of 10581 cases studied during the study period, 63.0% (n=6616) were males and 37.0% (n=3965) were females (Figure 1).
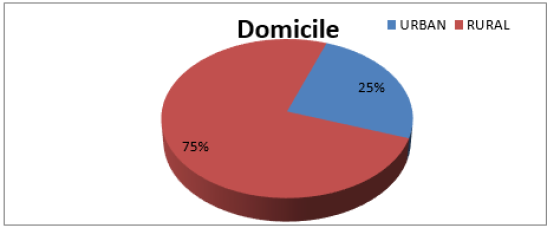
Geographical Distribution of Patients
In our study, majority of the patients 75.0 % (n=7956) patients were from rural area and only 25.0% (n=2625) from urban area (Figure 2).
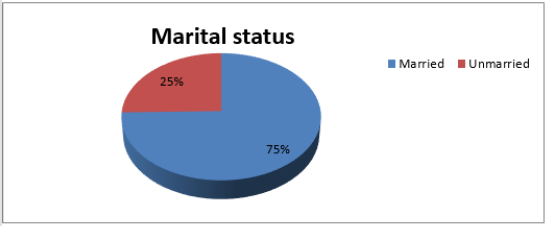
Marital Status
In our study, 75.0% (n=7900) of the study population were married and 25.0% (n=2681) were unmarried (Figure 3).
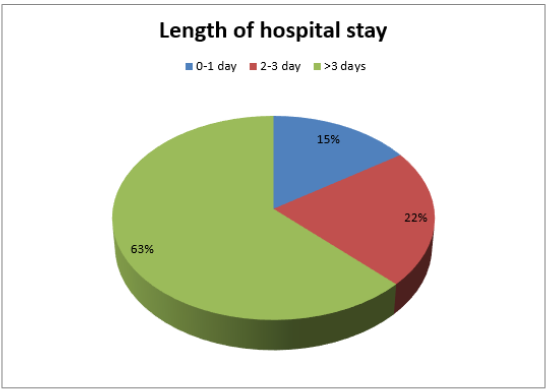
Length of Hospital Stay
In our study, out of 10581 patients, majority of the patients 63.0% (n=6634) had length of stay >3 days followed by 22.0% (n= 2300) had length of stay 2-3 days, only 15.0% (n=1647) of the patients had length of stay 0-1 day (Figure 4).
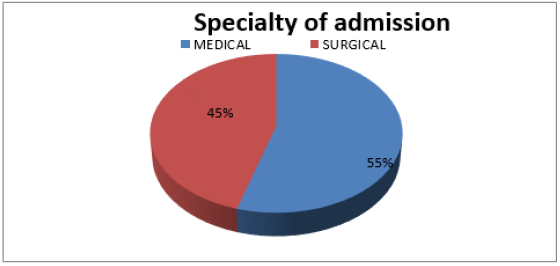
Specialty of Admission
Out of 10581 admissions studied during the study period, 55.0% (n=5779) admissions were from Medical side and 45.0% (n=4802) admissions were from Surgical side (Figure 5).
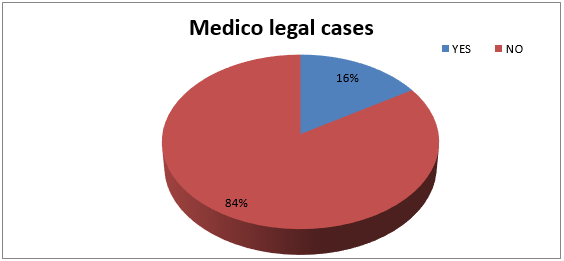
Medico-Legal Cases
Only 16.0% (n=1700) of the cases were Medicolegal out of 10581 cases studied (Figure 6).
Discussion
A 10581 patients were followed retrospectively for studying the profile.
Age-Wise Distribution
Apolone G et al. [6] observed that 57.0% of the patients were in the age group of > 60 years. In our study, majority of the patients (47.0%) belonged to the age group of more than 60 years. It could be because of the fact that majority of admissions in Emergency were of older people who either had new conditions or acute exacerbation of old conditions.
Gender-Wise Distribution
Apolone G et al. [6] observed that 58.0% of the patients were males observed. In our study, majority of the admissions were of the males (63.0%). These findings are consistent with our study.
Geographical Distribution
Hwang JI et al. [7] conducted a study on hospital stay and observed that 53.5% of the patients were from rural areas. In our study, majority of the patients were from rural areas (75.0%).
Marital Status
Tawakoli N et al. [8] conducted a study on hospital stay and observed that 54.5% patients were married. In our study, maximum of the study population was married (75.0%).
Day of Admission
Hwang JI et al. [7] observed that 84.8% patients were admitted on weekdays. In our study, 72.0% of the admissions were done during weekdays. These findings are consistent with our study.
Length of Stay
In line with the finding of our study, Apolone G et al. [6] showed that 90.0% of the patients had length of stay > 3days while as Tawakoli N et al. [8] showed that 60.0% of cases had length of stay > 3days. In our retrospective part, out of 10581 patients, majority of the patients (63.0%) had length of stay > 3days.
Specialty of Admission
Victor SE et al. [9] observed that 70.7% of the admissions were from Medical Side. In our study, majority of admissions were from Medical Side (55.0%).
Conclusion
It was found during the study that majority of the patients were more than 60 years of age (47.4%), evening hours (45.0%) were peak time when most of the patients reported. Significant number of cases were Medico legal (15.0% in prospective and 16.0%).
References
- Arab M, Zarei A, Rahimi A (2010) Analysis of Factors Affecting Length of stay in Public Hospitals in Lorestan Province, Iran. Hakim Health Sys Res 12(4): 27-32.
- Yaghoobifar M, Maskani K, Akaberi A (2011) The Rate of Inappropriate Admissions and Staying of Patients in Hospitals of Sabzevar, Iran. J of Sabzevar Uni Med Sci 18(3): 224-232.
- Mc Donagh MS, Smith DH, Goddard M (2000) Measuring appropriate use of acute beds: A systematic review of methods and results. Health Policy 53(3): 157-184.
- Chopard P, Perneger TV, Gaspoz J (1998) Predictors of inappropriate hospital days in a department of internal medicine. Int J Epidemiol 27(3): 513-519.
- Panis LJ, Gooskens M, Verheggen FW (2003) Predictors of inappropriate hospital stay: a clinical study. Int J Qual Health Care 15(1): 57-65.
- Apolone G, Alfleri V, Braga A (1991) A survey on the necessity of the hospitalization day in an Italian teaching hospital. Qual Assur Hlth Care 3(1): 1-9.
- Hwang JI (2011) Inappropriate hospitalization days in Korean Oriental Medicine hospitals. International J for quality in health care 23(4): 437-444.
- Tavakoli N, Hoseini KM, Yasinzadeh MR (2015) Evaluation of appropriate and inappropriate admission and hospitalization days according to appropriateness evaluation protocol (AEP). Arch Iran Med 18(7): 430-434.
- Soria AV, Carrillo AA, Campill SA (2009) Associated factors and cost of inappropriate hospital admissions and stays in a second-level hospital. Am J Med Qual 24(4): 321-332.

 Research Article
Research Article