Abstract
Objective: The application of total quality control in the prevention and nursing of vascular crisis in patients after replantation of multiple severed fingers.
Methods: 248 patients with multiple severed fingers admitted to the hand and foot surgery department where the author work from January 2017 to December 2019 were selected as the research objects and were divided into control group and observation group by random number table method. The control group adopted traditional routine nursing and the observation group adopted the nursing method of total quality control concept. The incidence of vascular crisis, the success rate of replantation of severed fingers and the satisfaction of patients with nurses were compared between the two groups.
Results: The incidence of vascular crisis in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The success rate of replantation of severed fingers in the observation group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The nursing quality of the observation group was better than that of the control group (P < 0.05). The satisfaction of patients in the observation group to nurses was higher than that in the control group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The application of total quality control in the prevention and nursing of vascular crisis in patients after replantation of multiple severed fingers can prevent the occurrence of vascular crisis, improve the success rate of replantation of severed fingers, improve the nursing quality and improve the satisfaction of patients with nurses.
Keywords: Total quality control; Patients after replantation of multiple severed fingers; Prevention and nursing of vascular crisis
Introduction
Fingers are an important “tool” for humans to carry out production and life. Professor Chen Zhongwei of PR China completed the first case of finger replantation in 1965. With the continuous development of medicine and science and technology, the level of microsurgical treatment in China is constantly increasing. The application of replantation of severed fingers is becoming more and more widespread. Vascular crisis is a complication that occurs easily within 48 hours after replantation of severed finger. If it cannot be prevented in time, it will affect the success rate of the operation, resulting in the failure of replantation of severed finger. In our daily work, we apply the conventional nursing model, but we only care for patients in life, and we do not comprehensively sort out the patient’s nursing problems, which leads to patients’ anxiety, nervousness, low expectations for surgery, and unwillingness to cooperate with medical staff. Nursing staff use comprehensive quality control to provide patients with nursing services including illness and psychology, improve patients’ awareness of diseaserelated problems, and can make patients more cooperative during treatment [1]. Meanwhile, the quality of care is directly related to whether the treatment can be successfully completed [2].
Data and Methods
General Information
248 patients with multiple severed fingers admitted to the hand and foot surgery department where the author work from January 2017 to December 2019 were selected as the research objects and were divided into control group and observation group by random number table method.
a) Control Group: 85 males and 39 females; The age ranged from 12 to 79 years old, with an average of (42.27 ± 10. 34) years old.
b) Reasons for Medical Treatment: 53 cases of crush injury, 33 cases of chainsaw injury and 38 cases of cutting injury; The number of severed fingers was 91 cases of 2 fingers and 33 cases of 3 fingers.
c) Observation group: 83 males and 41 females; The age ranged from 11 to 71 years old, with an average of (42.43 ± 10.27) years old. The reasons for seeking medical treatment were 57 cases of crush injury, 35 cases of chainsaw injury and 32 cases of cutting injury.
d) The number of Severed Fingers: 93 cases of 2 fingers and 31 cases of 3 fingers. There is no significant difference in gender and age between the two groups of data, P > 0.05, which can be compared.
e) Inclusion: patients with multiple incompletely or completely severed fingers; 6-8 hours after injury, admitted to hospital for replantation of severed fingers. Senior professional title doctors participated in the operation; The selected subjects voluntarily participated and gave their informed consent, which has been approved by the Hospital Ethics Committee.
f) Exclusion: those who were hospitalized for less than or equal to 3 days; Complicated with serious chronic diseases; Mental disorder; Patients with cognitive impairment.
Methods
The control group adopted traditional routine nursing, and the nursing staff comprehensively observed the changes of the patient’s condition, mastered the patient’s past history and social support, and provided basic nursing services for the patient. The observation group adopted the nursing method of total quality control concept and implemented the following nursing on the basis of traditional routine nursing:
Establish Standards for Comprehensive Care Quality Control: According to the quality examination standard of hospital nursing department, formulate various standards for quality control of departments, clarify the duties of each position, standardize the management of nursing operations, let all behaviors have a system to be examined, and each quality control standard is refined into tables and set scores to achieve quantitative management, which is more operable in clinical management [3].
Three-Level Quality Control System: The nursing department, the head nurse and the key nurses in the department set up a three-level quality control system. The department set up a quality control team to track and evaluate the patients undergoing replantation of multiple severed fingers, sorted out the problems every month, found out the root causes, formulatet countermeasures, and paid long-term attention to the effect evaluation to prevent the occurrence of adverse events. According to the patient’s own characteristics, make the corresponding nursing plan for the patient [4].
Standardization of Training: Carry out nursing rounds and professional study every month to improve the nursing operation skill level of junior nursing staff, thus improving the overall nursing level of departments, following the concept of total quality management, and making better nursing plans for patients [5,6].
Regular Assessment: An assessment team was set up with the head nurse as the team leader to assess the relevant knowledge of the established quality management standards and the nursing skills after replantation of severed fingers. The work was linked to performance rewards to reward the advanced staff and encourage the those backward, so as to ensure that nursing staff carried out effective health education for patients and provide all-round services for patients after replantation of severed fingers.
Pay Attention to Perioperative Nursing
1. Psychological Nursing: Patients with finger injuries would inevitably have negative psychological emotions. Nursing staff should take the initiative to dissolve patients and tell patients successful cases of surgery so that they can gradually get out of the shadow and build up self-confidence [7].
2. Preoperative Preparation: The responsible nurse personally received the patient to the sickbed, kept the indoor temperature at 20-25℃, quiet and comfortable, and applied preoperative drugs according to the doctor’s advice.
3. Intraoperative Nursing: The nurses in the operating room should make sufficient preoperative preparations, keep the temperature in the operating room at 25 ℃, and assisted the patients to take appropriate surgical positions. During the operation, the medical staff should communicate with the patients to divert the attention of the patients [8].
4. Postoperative Nursing: Disinfect the ward before the operation is completed, ventilate at least once a day, control the temperature at 26 ℃, control the humidity at 55%, supine the patient [9], raise the limb of the severed finger to a position 13cm away from the heart, and avoid affecting the venous return of the patient [10]. Generally, 60W heating lamp was used for limb heating with a distance of 30-40cm. Anticoagulant, spasmolytic, analgesic and anti-infection drugs were used for treatment according to doctor’s advice, and the curative effect and side effects of the drugs were continuously observed. Instruct patients to quit smoking and drinking, not to eat spicy and caffeinated foods, keep high protein, high vitamin and high calcium diet, and drink at least 3000ml of water every day. Blood supply observation record sheet to observe the disease condition every hour could guide functional exercises according to the patient’s situation.
Observations
The incidence of vascular crisis was compared between the control group and the observation group; Success rate of replantation of severed fingers; The completion of nursing quality and patients’ satisfaction with nurses.
Statistics Processing
The data were recorded by Excel and processed by SPSS23.0 software. The counting data were expressed by(n), the chi-square value was tested, the measurement data were expressed by (`x ± s), and the incidence rate, success rate and satisfaction rate were used (%) by t test. The results were statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Results
Incidence of Vascular Crisis
The incidence of vascular crisis in the observation group was 2.42%, which was significantly lower than that in the control group 8.87%, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), as shown in Table 1.
Success Rate of Replantation of Severed Fingers
The success rate of replantation of severed fingers in the observation group was 95.16%, significantly higher than that in the control group (81.45%), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), as shown in Table 2.
Completion of Nursing Quality
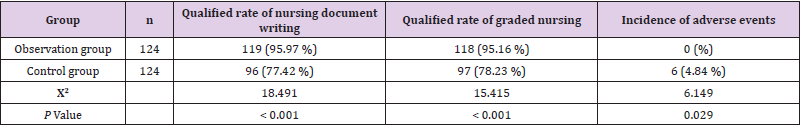
The nursing quality of the observation group was better than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), as shown in Table 3.
Patients’ Satisfaction with Nurses
The satisfaction of patients in the observation group to nurses was 95.97%, significantly higher than 82.26% in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), as shown in Table 4.
Discussion
With the continuous development of economy, patient’s demand for health in modern society is gradually improving. Expectations of patients with replantation of severed fingers are also increasing. This requires doctors to have a qualified surgery ability, and nurses also need to have an outstanding nursing ability so as to keep up with the progress and development of medical science. Comprehensive nursing quality control provides services for patients in strict accordance with the implementation standards through three-level quality control and layer-by-layer examination. All-round nursing services are implemented for patients according to the specific conditions of patients, thus improving nursing quality and further reducing the incidence of vascular crisis after replantation of severed fingers.
After replantation of severed fingers, patients will have many nursing problems. Some nursing problems will significantly increase the occurrence of vascular crisis, thus leading to necrosis of replanted fingers and affecting the survival rate of replantation of severed fingers [11-14]. The application of total quality control has improved the success rate of replantation of severed fingers. Total quality control takes the needs and satisfaction of patients as the ultimate goal, respects the personal habits of patients, and meets the psychological and physiological needs of patients through management and quality control from beginning to end, thus improving the satisfaction of patients [15]. To sum up, total quality control can solve the nursing problems of patients well, improve the nursing quality to a certain extent, improve the nursing satisfaction, and ensure the smooth and orderly development of clinical work.
References
- Tang XH, Chen YY, Liu XY (2015) Application and Experience of Total Nursing Quality Control in Continuous Improvement of Nursing Quality. PLA Journal of Nursing 28(02): 74-75.
- Feng Y (2015) Observation on the Application Effect of Nursing Quality Management in Nursing in Health Examination Center. China Health Standards Management 6(16): 224-225.
- Ling SY (2016) Application Analysis of Total Nursing Quality Control in Continuous Improvement of Nursing Quality. Contemporary Medicine16(08): 125-126.
- Yu B (2018) Role of Total Quality Management Concept in Nursing Quality Management in Orthopaedic Ward. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine Management 26(19): 145-146.
- Liu MK, Liu RH (2018) Value Evaluation of Integrating Total Quality Management Concept into Nursing Quality Management in Orthopaedic Ward. China Health Industry 15(14): 80-81.
- Guo LY (2018) Application Value of Total Quality Management Concept in Quality Management of Orthopaedic Nursing Work. Current Medicine Review 16(2): 272-273.
- Yang W, Zhao WY, Geng WX (2017) Perioperative Nursing of Replantation of Severed Fingers in microsurgery. Contemporary Medicine 23(05): 131-132.
- He HY (2017) Comparison of clinical nursing pathway and traditional nursing in perioperative period of replantation of severed fingers. Chinese Contemporary Medicine 24(27): 148-150.
- Ye HM, Hu L, He XY, Lu F, Huang YL (2014) Perioperative intervention nursing of skin defect with avulsion severed finger replantation. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 23(21): 2387-2389.
- Zeng JN, Jin RS, Yu YY (2017) Nursing experience of skin necrosis wound treatment after replantation of severed fingers. Electronic Journal of Practical Clinical Nursing 2(49): 70-71.
- Zhao PC (2017) Comparison of incidence of vascular crisis after microsurgical replantation of severed fingers by different pain management. Knowledge of Cardiovascular Prevention 6(5): 124-126.
- Liu XF (2005) Cause analysis and management of vascular crisis after replantation of severed fingers. Chinese Journal of Microsurgery 8(28): 274-276.
- Jin N (2017) Analysis of factors affecting survival rate after replantation of severed fingers and nursing care. Road to Health 9(16): 131-132.
- Dong XL, Sun JD, Chang CQ (2018) Analysis of related factors of survival rate after replantation of severed fingers and corresponding clinical countermeasures. Journal of Practical Hand Surgery 32(2): 263-264.
- Sun LM, An WJ, Gao JL (2017) Application effect of path-based quality management in continuous improvement of nursing quality in weak links. China Journal of Coal Industry Medicine 20(8): 968-971.

 Research Article
Research Article