Abstract
Aim: Particularly trace elements play an essential role in assessing the medicinal value of plants, health, and disease treatment. For most organisms, such as plants, animals, and humans, these elements are essential for all biochemical and physiological processes.
Methodology: The review explored the influence of trace metals in medicinal plants. This research area has received little attention and a thorough understanding of trace metals’ roles in medicinal plants.
Result & Conclusion: This review summarizes the survey on evaluating these elements’ status in medicinal plants. Hence, a thorough study was considered necessary to determine these two toxicity levels of plants. Also, in-vitro and in-vivo studies must be conducted to demonstrate its safety and effectiveness. Besides, harvest season is another climatic factor related to changes in element concentration in medicinal plants.
Keywords: Trace Elements; Medicinal Plants; Essential; Non-Essential; Review
Introduction
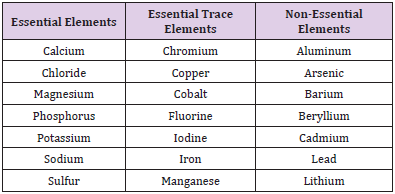
A medicinal plant contains the necessary nutrients, carbohydrates, fats, and primitive proteins required for the human body and is considered the best energy source. In addition to these biomolecules, some plants are also crucial for human health. Micro and Macro-elements, as well as heavy metals, are considered as a potential health risk [1,2]. plants are also primary sources of food, minerals, vitamins, and essential antioxidants for many communities facing economic difficulties. However, some researchers have found similar anti-nutrients in many conventional and traditional plants [3-5]. Although knowledge of plant materials is generally limited, there is little data on nutrients and proximity elements [6]. This article will enrich the literature to provide worth full information on trace minerals of medicinal plants. Fresh plant material contains 80-90% of water, and the remainder over 90% consists of C, H, and O. Organic material is removed by the dried plant samples by ashing. The remaining 1.5% of the plants, the fresh weight represents its mineral content [7,8]. Elements such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, boron, manganese, copper, zinc, chlorine, sodium, and silicon are present in various medicinal plants [9]. The herbs also naturally produce trace metals such as zinc, cadmium, copper, manganese, aluminum, iron, and lead. Usually, the herbs contain Zn (666 ppm), Cu (118 ppm), Pb (44 ppm), Ni (33 ppm), V (24 ppm), Mo (19 ppm), Cr (10 ppm), and Co (11 ppm) [10-12].
Most of the research focuses on the role of metabolic function of trace elements throughout the world. There is a need to analyze these medicinal plants’ elements to detect their components, essential for normal human body function. In the case of an abnormal quantity of these elements, the human body faces different disorders. Moreover, even a small amount of toxic elements can harm the average human body. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the appropriate amount of these elements in the human body [13-15]. The plants produce several essential chemicals [16,17]. The deviation of the plant element content is mainly due to the difference in a plant structure (botanical) and availability of minerals in the soil where the plants are implanted. Other factors include the climate conditions, irrigation water, use of fertilizers, and absorptive capacity of the plant [18-20]. Metals are categorized with macro (primary) or micro (trace) elements. The 3rd class is the ultra-trace elements. Macro-minerals contain Calcium, Phosphorus, Sodium, and Chloride, whereas the micro-elements include Iron, Copper, Cobalt, Potassium, Magnesium, Iodine, Zinc, Manganese, Molybdenum, Fluoride, Chromium, Selenium, and Sulphur [21]. The macro minerals are required in amounts greater than 100 mg/dl, and the micro-minerals are required in amounts less than 100 mg/dl. [22].
The level of elements permitted by the WHO should not endanger the health of consumers [23,24]. Trace elements are inorganic substances that exist in trace elements at low concentrations. The essential elements at trace levels play a role in the human body and can cause some diseases beyond the limit of average concentration. The recommended daily trace elements mineral intake (about 1.5 grams) is considered adequate for healthy people [24]. Trace elements are present in all body tissues and fluids, and their presence is necessary. Although they do not produce energy, they play an essential role in many activities in the body [25]. Trace elements comprise only a fraction of the total body weight Table 1. These are crucial for many body functions. These include transporting oxygen, normalizing the central nervous system (CNS), and stimulating the growth, maintenance, and repair of tissues and bones [26]. It has been reported in the literature that most of the trace elements found in the tissues and body fluids are also present in the blood [27]. Nevertheless, plants’ composition depends on several factors, such as the industrial use of components of human activities and climatic conditions Table 2. These components are essential to ensure the quality of plant raw materials and pollutants’ presence if human consumption is core [28-30].
Conclusion
This review summarizes research regarding the trace elements of commonly used medicinal plants. Many plants contain a large number of trace elements, which even cross the limit permitted by WHO. In the case of overuse of such plants, it can be toxic. Hence, a thorough study was considered necessary to determine these two toxicity levels of plants. Also, in-vitro and in-vivo studies must be conducted to demonstrate its safety and effectiveness. Besides, harvest season is another climatic factor related to changes in element concentration in medicinal plants.
Acknowledgement
The author is thankful to the West China School of Public Health, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, for support and cooperation.
References
- Basgel S, Erdemog˘lu SB (2006) Determination of mineral and trace elements in some medicinal herbs and their infusions consumed in Turkey. Science of the Total Environment 359(1-3): 82-89.
- Baye H, Hymete A (2010) Lead and cadmium accumulation in medicinal plants collected from environmentally different sites. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 84(2): 197-201.
- Kalny P, Fijałek Z, Daszczuk A, Ostapczuk P (2007) Determination of selected microelements in polish herbs and their infusions. Science of the Total Environment 381(1-3): 99-104.
- Kara D (2009) Evaluation of trace metal concentrations in some herbs and herbal teas by principal component analysis. Food Chemistry 114(1): 347-354.
- Varghese CP, Ambrose C, Jin SC, Lim YJ, Keisaban T, et al. (2013) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of Eurycoma longifolia Jack, a traditional medicinal plant in Malaysia. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology 5(4): 1875-1878.
- Hosseinzadeh S, Jafarikukhdan A, Hosseini A, Armand R (2015) The application of medicinal plants in traditional and modern medicine: A review of thymus vulgaris. International Journal of Clinical Medicine 6: 635-642.
- Siriwatanametanon N, Fiebich BL, Efferth T, Prieto JM, Heinrich M (2010) Traditionally used Thai medicinal plants: In vitro anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antioxidant activities. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 130(2): 196-207.
- Malik J, Szakova J, Drabek O, Balik J, Kokoska L, et al. (2008) Determination of certain micro and macroelements in plant stimulants and their infusions. Food Chemistry 111(2): 520-525.
- Matsuura H, Hokura A, Katsuki F, Itoh A, Haraguchi H, et al. (2001) Multielement determination and speciation of major-to-trace elements in black tea leaves by ICP-AES and ICP-MS with the aid of size exclusion Chromatography. Analytical Sciences 17(3): 391-398.
- Nookabkaew S, Rangkadilok N, Satayavivad J (2006) Determination of trace elements in herbal tea products and their infusions consumed in Thailand. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 54(18): 6939-6944.
- Raman P, Patino LC, Nair MG (2004) Evaluation of metal and microbial contamination in botanical supplements. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 52(26): 7822-7827.
- Łozak A, Sołtyk K, Ostapczuk P, Fijałek Z (2002) Determination of selected trace elements in herbs and their infusions. Science of the Total Environment 289(1-3): 33-40.
- Maiga A, Diablo D, Bye R, Paulsen BS (2005) Determination of some toxic and essential metal ions in medicinal and edible plants from Mali. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 53(6): 2316-2321.
- Gallaher RN, Gallaher K, Marshall AJ, Marshall AC (2006) Mineral analysis of ten types of commercially available tea. J Food Compos Anal 19: S53-S57.
- Yalcin Gorgulu T, Kipcak AS, Dere Ozdemir O, Moroydor E, Piskin S, et al. (2014) Examination of the lemon effect on risk elements concentrations in herbaland fruit teas. Czech J Food Sci 32(6): 555-562.
- Ozcan MM, Unver A, Ucar T, Arslan D (2008) Mineral content of some herbs andherbal teas by infusion and decoction. Food Chem 106(3): 1120-1127.
- Malik J, Frankova A, Drabek O, Szakova J, Ash C, et al. (2013) Aluminium andother elements in selected herbal tea plant species and their infusions. Food Chem 139(1-4): 728-734.
- Novotnik B, Zuliani T, Scancar J, Milacic R (2015) Content of trace elements andchromium speciation in Neem powder and tea infusions. J Trace Elem Med Biol 31: 98-106.
- Konieczynski P, Wesołowski M Phytate (2014) inorganic and total phosphorus andtheir relations to selected trace and major elements in herbal teas. Acta Pol. Pharm 71(1): 85-93.
- Lozak A, Soltyk K, Kiljan M, Fijalek Z, Ostapczuk P, et al. (2012) Determination of selected elements in dietary supplements containing plant materials. Pol J Nutr Sci 62(2): 97-102.
- Murray RK, Granner DK, Mayes PA, Rodwell VW (2000) Harper’s Biochemistry, 25th Edition, McGraw-Hill, Health Profession Division, USA 8(2).
- Aletor VA, Omodara OA (1994) Studies on some leguminous browse plants, with particular reference to their proximate, mineral and some endogenous antinutritional constituents. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol 46(3-4): 343-348.
- (2011) WHO (World Health Organization) The world traditional medicines situation. in Traditional Medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland 3: 1-14.
- (2007) WHO? WHO guidelines for assessing quality of herbal medicines with reference to contaminants and residues. Geneva 2007.
- Thor M, Harnack L, King D, Jasthi B, Pettit J, et al. (2011) Critical review: Evaluation of the comprehensiveness and reliability of the chromium composition of foods in the literature. J Food Comp Anal 24(8): 1147-1152.
- Feinendegen LE, Kasperek K (1980) Trace elements in medicine. In: International Workshop on Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, P Braetter and P Schramel (Eds.), pp. 1 de Gruyter Berlin 1980.
- Shenkin (1997) In: Ronbeau JL, Rolandelli RH, Saunders WB. (Eds.), Micronutrients in Clinical Nutrition. Enteral and Tube feeding (3rd) 96.
- Naila Masood, Imran Ali Shaikh, Ali Raza Memon, Saira Baloch (2013) Evaluation of Antioxidant Level and Trace Metals in Anemia. IJCRR 05(2): 135-139.
- Kumar A, Nair AGC, Reddy AVR, Garg AN (2005) Availability of essential elements in Indian and US tea brands. Food Chemistry 89(3): 441-448.
- Street R, Szakova J, Drabek O, Mladkova L (2006) The status of micronutrients (Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn) in tea and tea infusions in selected samples imported to the Czech Republic. Czech Journal of Food Sciences 24(2): 62-71.

 Mini Review
Mini Review