Abstract
Old age is a process of gradual disappearance of tissue’s ability to repair itself or replace itself and maintain its normal structure and function. Degenerative diseases in the elderly for example were hypertension, arthrosclerosis, diabetes mellitus and cancer. This study aims to find out the effectiveness of deep breathing against decreased blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension. This research uses one group preposttest method. The sample used as many as 13 people. This research uses Purposive Sampling technique and the tool used to obtain data is observation. This study used paired sample t-test with significance α = 0.05. The results of this study showed that there is an influence of deep breathing on the decrease in blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension on the 1st day pre and 3rd day post with a value of p = 0.000<α = 0.05. There is an effect of deep breathing on the decrease in blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension on the 4th day pre and day 6 post with a value of p = 0.000<α = 0.05. And there is an effect of deep breathing on the decrease in blood pressure in the elderly who have hypertension on the 7th day pre and the 9th day post with a value of p = 0.000<α = 0.05. It was concluded that there is an effect of deep breathing on the decrease in blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension on days 1, 4, 7 pre and day 3, 6, 9 post. The conclusion of the study is that there is an effect of deep breathing effectiveness on the decrease in blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension
Keywords: Deep Breathing; Blood Pressure; Hypertension; Elderly
Introduction
Elderly or aging (getting old) is a process of gradual disappearance of tissues to repair themselves or replace themselves and maintain their normal structure and function so that it cannot be gradual to scart (including infections) and repair the damage that causes degenerative diseases e.g., hypertension, arteriosclerosis, diabetes mellitus and cancer [1,2]. According to Jubaidi (2008) In Sulastri [2] there are some physical changes in the elderly that can become an elderly condition affected by diseases, such as cardiovascular changes that are decreased elasticity of blood vessels, changes in respiration that is decreased strength of respiratory muscles, as well as changes in hearing and changes in vision. There are several kinds of diseases that commonly afflict the elderly, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary diseases, stroke, cataracts, and so on. These kinds of health problems that often afflict the elderly are hypertension that can be the complication of various other cardiovascular problems that are more serious. Nowadays, the increase in equality, especially in the field of health, is an important highlight. The onset of various diseases in the community has a huge impact on their lives. One type of disease that continues to develop and increase is hypertension or known by lay people as High Blood. Changes in lifestyle and the needs of the community are considered to have a great influence on the occurrence of hypertension. Hypertension itself can be monitored through blood pressure measurement.
Hypertension is persistent high blood pressure where the systolic pressure is above 140mmHg and the diastolic pressure is above 90mmHg [3]. Nearly 1 billion or a quarter of the population of adults and the elderly has high blood pressure, and this number is likely to increase. In the elderly population, the number of people with high blood pressure is even higher, experienced by more than half of the population of people over the age of 60. In 2025 it is estimated that people with high blood pressure reach almost 1.6 billion people in the world [4]. Blood pressure is one of the things that affect the human body system. An increase or decrease in blood pressure will affect homeostasis in the body. Many factors that can increase the risk or anxiety of a person suffering from hypertension, including individual characteristics such as age, weight, sex and ethnicity, genetic factors as well as environmental factors that include obesity, stress, salt consumption, smoking, consuming alcohol, and so on (Ryadi, 2002). The incidence of hypertension worldwide is about 972 million people or 26.4% of the earth’s inhabitants have hypertension with a ratio of 26.6% of men and 26.1% of women. This figure is likely to increase to 29.2% in 2025 from 972 million hypertension sufferers, 333 million are in developed countries and the remaining 639 million are in developing countries, including Indonesia (WHO, 2012).
Hypertension is found with several risk factors that can cause the occurrence of high blood pressure, namely old age and the presence of a history of high blood pressure in the family. In addition there are also so many causes of hypertension that it causes hypertension is a disease with many sufferers even referred to as the silent disease (Cold-blooded Killer) (Palmer, 2007) [4]. Sugiharto et al (2003) mentioned the incidence of hypertension is directly proportional to the increase in age. Arterial blood vessels lose elasticity or flexibility with age, most people have increased blood pressure when age 50-60 years and above. In the concept of nursing, decreased blood pressure in hypertension can use management with the application of non-pharmacologists, one of which is deep breath relaxation techniques. Deep breath relaxation techniques are one form of stress management in an effort to make lifestyle modifications. The right relaxation techniques (non-pharmacology) are progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic exercise, breathing and visualization. Deep breath relaxation technique is one of the relaxation therapies that can make the body more calm and harmonious, and able to empower his body to overcome the disorders that attack him (Schwickert, 2006).
Based on previous research by Elrita Tawang, 2013 [5] on the effect of deep breath relaxation techniques on changes in blood pressure in people with moderate-severe hypertension, shows that deep breath relaxation techniques can lower blood pressure in people with moderate-severe hypertension (Tawang E, 2013). This research was supported by Heryanto (2004) that Diaphragm breathing until now has been an easy method of relaxation in its implementation. Relaxation therapy diaphragm breathing technique is very good to be done every day by people with high blood pressure, in order to help relax the muscles of the body, especially the muscles of the blood vessels so as to maintain the elasticity of arterial blood vessels so that it can help lower blood pressure (Evelyn,2011). According to Audah (2011) breathing in a good way and control is able to provide relaxation as well as reduce stress. Deep breath training is a form of non-pharmacological therapy, in which the nurse teaches the client how to do deep breaths, slow breaths (holding the maximum inspiration) and how to exhale slowly, in addition to lowering the intensity of pain can also improve pulmonary ventilation and increase blood oxygenation (Niken, 2010 in Putra 2013). Non-pharmacological management of deep breath relaxation therapy to lower blood pressure in hypertension patients was chosen because deep breath relaxation therapy can be done independently, relatively easy to do than other non-pharmacological therapies, does not take long for therapy and is able to reduce the adverse effects of pharmacological therapy for hypertension patients (Suwardianto, 2011).
Based on data obtained from the Tresna Werdha Gau Mabaji social home in Gowa Regency in 2016, there were 97 elderly people, namely the number of men 34 people or (35%) and women 63 people or (65%), who suffer from hypertension is 24 people or (25%). According to nurses at the orphanage said that never before did Deep Breathing or deep breath relaxation techniques in the elderly specifically for hypertensive diseases. Therefore, the researchers felt need to conduct research on the Effectiveness of Deep Breathing Against Decreased Blood Pressure in Elderly People with Hypertension.
Method of Research
This research uses One-Group Pretest-Posttest Design research design. This design is a Preexperimental study in which researchers give treatment to the measured study group orin the next pretest after the treatment of the study group is measured or in the retest (Posttest) (Table 1). This research will be conducted in Panti Trisna Werdha Gau Mabaji Gowa Regency. This research conducted in May – September 2019. Population is a subject or data with certain characteristics to be studied (Nursalam, 2013). The populations in this study were all elderly people who had hypertension in Panti Trisna Werdha Gau Mabaji Gowa Regency. The sample is part of the population to be studied (Nursalam, 2013). The samples used in this study were elderly people who had hypertension degree 1 in Panti Trisna Werdha Gau Mabaji Gowa Regency. Elderly who are sampled must have criteria that correspond to the study. Using purposive sampling is a sample taken from elderly respondents who meet the criteria that have been determined by researchers with inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria. Data collection instruments can be questionnaires (questionnaires), observation forms and other forms related to data recording (Dharma, 2011). The data feeder instrument used in this study is an observation form sheet. The data used in this study are primary data and secondary data. Before data analysis, data processing is carried out using computerized SPSS (Statistical Product and Service Solution). Data Analysis is done using univariate analysis and bivariate analysis. The consent sheet is given to respondents who will be examined and meet the inclusion criteria. To the respondents explained about the benefits and risks of research that may arise. If the subject refuses then the researcher will not impose the will and respect the rights of the subject.
Result
Univariate Analysis
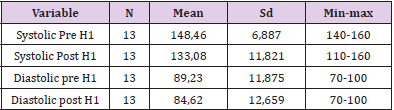
Day 1: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 148.46mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 160mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 89.23mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 100mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 133.08mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 110mmHg and the highest is 160mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 84.62mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 100mmHg (Table 2).
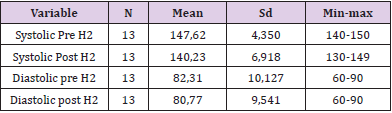
Day 2: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 147.62mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 82.31mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 60mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 140.23mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 130mmHg and the highest is 149mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 80.77mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 60mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Table 3).
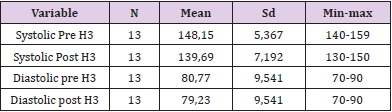
Day 3: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 148.15mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 159mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 80.77mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 139.69mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 130mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 79.23mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Table 4).
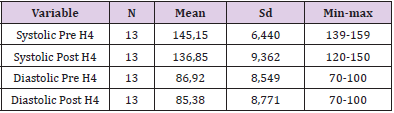
Day 4: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 147.62mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 86.92mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 100mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention is 136.85mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 120mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 85.35mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 100mmHg (Table 5).
Day 5: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 148.23mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 84.62mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 138.23mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 120mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 81.54mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Table 6).
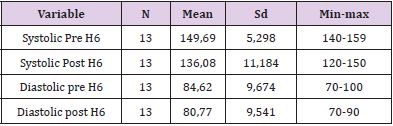
Day 6: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 149.69mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 159mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 84.62mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 136.08mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 120mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 80.77mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Table 7).
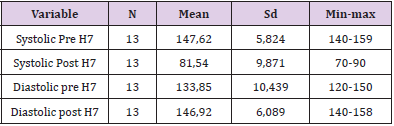
Day 7: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 147.62mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 159mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 81.54mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 133.85mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 120mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 80.77mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Table 8).
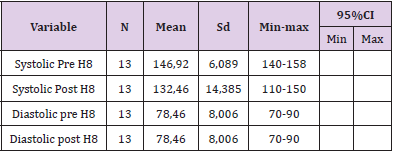
Day 8:The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 146.92mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 158mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 78.46mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 132.46mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 110mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 78.46mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Table 9).
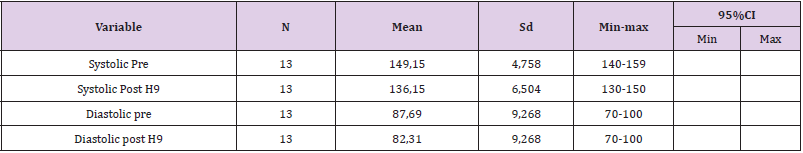
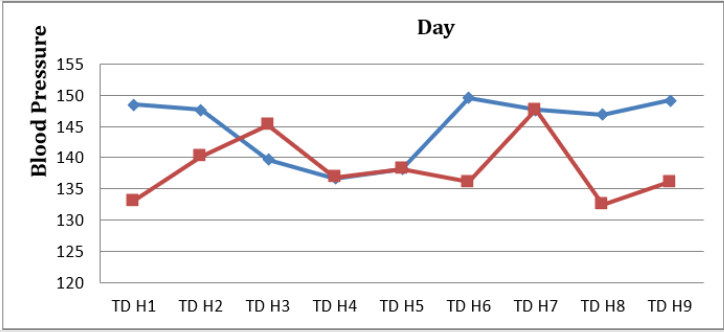
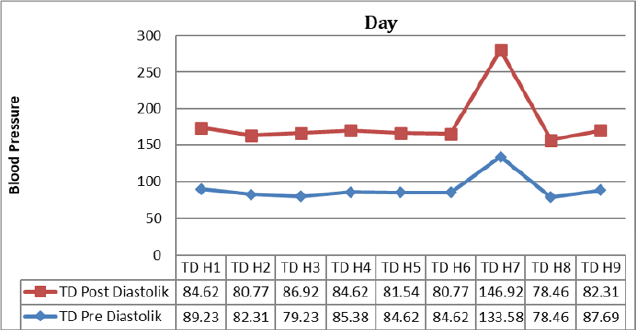
Day 9: The result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data before intervention was found that the average systolic blood pressure of respondents before intervention was 149.15mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 140mmHg and the highest is 159mmHg. The result of diastolic blood pressure analysis before intervention was 87.69mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 100mmHg. While the result of analysis of systolic blood pressure data after intervention was 136.15mmHg. The lowest systolic blood pressure is 130mmHg and the highest is 150mmHg. The result of analysis of diastolic blood pressure data after intervention was 82.31mmHg. The lowest diastolic blood pressure is 70mmHg and the highest is 90mmHg (Graphs 1 & 2). Based on (Table 10) The result of data analysis obtained the average value of systolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 148.46 with a standard deviation of 6,887. The average post-day blood pressure of 9 is 136.15 with a standard deviation of 6,504. After the statistical test obtained p value = 0.000 < α = 0.05 which means there is an effect of giving Deep Breathing to decrease blood pressure. The average diastolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 89.23 with a standard deviation of 11,875. The average diastolic blood pressure post day 9 is 82.31 with a standard deviation of 9,268. After the statistical test obtained p value = 0.108 > α = 0.05 which means there is no effect of giving Deep Breathing to decrease blood pressure (Table 10).
Discussion
In this discussion, researchers will discuss about the effectiveness of Deep Breathing against decreased blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension.
1. Effect of decreased blood pressure day 1 psystolic re with day 9 post systolic and pre day 1 diastolic with diastolic 9th day. The result of data analysis obtained the average value of systolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 148.46 with a standard deviation of 6,887. The average post-day blood pressure of 9 is 136.15 with a standard deviation of 6,504. After the statistical test obtained p value = 0.000 < α = 0.05 which means there is an effect of giving Deep Breathing to decrease blood pressure. The average diastolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 89.23 with a standard deviation of 11,875. The average diastolic blood pressure post day 9 is 82.31 with a standard deviation of 9,268. After the statistical test obtained p value = 0.108 > α = 0.05 which means there is no effect of giving Deep Breathing to decrease blood pressure. Ardiansyah (2012) that hypertension is generally abnormally high blood pressure and a person is considered to have hypertension if his blood pressure exceeds 140/90mmHg. Brunner & Suddarth (2002) states that pathophysiology of hypertension occurs at the same time that the sympathetic nervous system stimulates the blood vessels as an emotional excitatory response, the adrenal glands are also aroused, resulting in additional vasoconstriction activity. Medulla adrenal secretes epinephrine, which causes vasoconstriction. The adrenal context secretes cortisol and other steroids, which can strengthen vasoconstrictor responses of blood vessels. Vasoconstrictor stimulates the formation of angiotensin I which is then transformed into angiotensin II, a powerful vasoconstrictor, which in turn stimulates the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex. This hormone causes retention of sodium and water by the renal tubules, causing an increase in intravascular volume. All these factors tend to trigger hypertension.
In line with Joseph’s research, et al. (2005) conducted in 20 respondents with hypertension (age 56.4 ± 1.9 years and above) intervened with normal breathing and slow breathing (6x/min) and fast (15x/min). From the results of the study obtained slow deep breathing can lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure in hypertensive patients (from 147.7 ± 3.7 mmHg to 141 ± 4 mmHg, p< 0.05 and from 82.7 ± 3 mmHg to 77.8 ± 3.7 mmHg, p< 0.01). Joseph, et al. (2005) stated that Deep breathing affects the modulation of the cardiovascular system. Deep breathing has the effect of increasing fluctuations of RR intervals (rate of respiration). Fluctuations in RR intervals (relative to changes in blood pressure) have an impact on increased bar reflex effectiveness and may contribute to a decrease in blood pressure. Deep breathing also decreases sympathetic activity by increasing central inhibitory rhythms which eventually lead to a decrease in blood pressure when bar reflex is activated. Deep breathing also affects tidal volume increase, activating Hering-Breuer reflex which has an impact on decreasing chemo reflex activity and ultimately increasing bar reflex sensitivity. This mechanism can decrease sympathetic activity and blood pressure. Based on the theory and research above, as a researcher agreed that the provision of deep breathing techniques in hypertension patients, especially in accordance with the research in the elderly is very effective to decrease blood pressure.
According to Sunanto (2009) Hypertension is a condition in which a person experiences a blood pressure increase above normal for a long period of time.
When measured the results of blood pressure measurements showed 140/80mmHg. According to WHO (2012) in Porwanto (2012) hypertension is a public health problem in the world and closely related to the pattern of people’s behavior. Until now hypertension still remains a problem because of several things, including the increasing prevalence of hypertension, there are still many hypertensive patients who have not received treatment or who have been treated but whose blood pressure has not reached the target, as well as the presence of participating diseases and complications in the form of damage to the target organs, especially in the heart and blood vessels that worsen the prognosis of hypertensive patients. Ramdhani (2014) stated that deep breath relaxation is one of the techniques of self-management based on the workings of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Relaxation techniques are increasingly common because they are proven to be effective in reducing tension and anxiety, and can lower blood pressure in hypertension sufferers. Diaphragm breathing until now has been an easy method of relaxation in its implementation. Therapy techniques relaxation deep breath is very good to be done every day by hypertension sufferers, in order to help the body, especially the blood vessels so as to maintain elasticity of elastic blood vessels
The results of research from Hastuti and Insiyah (2015) showed that. Blood pressure in hypertensive patients at The Bendosari Health Center in Sukoharjo Regency before deep breathing therapy is an average systole blood pressure of 177.33mm hg and an average diastole of 95.87mm hg. Blood pressure in hypertensive patients in Bendosari Health Center, Sukoharjo Regency after deep breathing therapy, namely systole blood pressure averaged 173.20mm hg and diastole averaged 90.5 mm hg. There is an effect of deep breathing therapy on blood pressure reduction in hypertensive patients at Bendosari Health Center in Sukoharjo Regency. The advice in this study is for health workers, especially nurses, to intervene in nursing, namely deep breathing therapy for decreased blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Based on the research and theories above as a researcher I agree that deep breathing techniques given to elderly people who have hypertension will be very effective to lower blood pressure. And also deep breath relaxation techniques include one of the non-pharmacological treatments that are good for the elderly as well as not difficult to do even the elderly who are already unable to walk or get out of bed.
2. Hypothesis Proofing: Based on the results of the data analysis obtained the average value of systolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 148.46 with a standard deviation of 6,887. The average post-day blood pressure of 9 is 136.15 with a standard deviation of 6,504. After the statistical test obtained the value of p value = 0.000 < α = 0.05 which means there is an effect of giving Deep Breathing to the decrease in blood pressure. The average diastolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 89.23 with a standard deviation of 11,875. The average diastolic blood pressure post day 9 is 82.31 with a standard deviation of 9,268. After the statistical test obtained p value = 0.108 > α = 0.05 which means there is no effect of giving Deep Breathing to the decrease in blood pressure. The results of this study are in line with research conducted by Werdyastri et al (2014) that the decrease in blood pressure before and after the administration of deep breathing therapy in hypertensive patients at Tugurejo Hospital Semarang in March-April 2014 obtained blood pressure results before the administration of deep breathing (Deep Breathing) 170mmHg, after deep breathing was obtained blood pressure 161mmHg , while in diastolic blood pressure is also obtained before the administration of deep breathing 96mmHg, after the relaxation of deep breathing is obtained blood pressure 89mmHg.
Researchers assumed that after the action of giving deep breathing techniques in the 1st to 9th day can be known the effectiveness of deep breathing against decreased blood pressure in elderly people who have hypertension. This can be seen in the provision of deep breathing techniques on the first to the 9th day. Thus it is known that deep breath relaxation techniques are effective to lower blood pressure in the elderly. According to the assumptions of researchers with relaxation techniques that are easy to do and without any side effects for the elderly, it is very important to be applied in everyday life and can be done alone by respondents to lower blood pressure because with this relaxation technique helps the body to stay relaxed, can supply oxycalyan with the necessary levels of the body and help relieve the work of the heart, as well as maintain the depletion of blood vessels [6-15].
Research Limitation
The limitations in this study are:
1. Difficulty in communicating with the elderly.
2. The time used by researchers is in the morning but some respondents are still sleeping, so they have to wait until the elderly wake up with different hours.
Summary
After the research conducted under the title “Effectiveness of Deep Breathing Against Decreased Blood Pressure in Elderly People Who Have Hypertension” it can be concluded that:
1. It can be known that the average pre-day systolic blood pressure is 148.46 with a standard deviation of 6,887. The average post-day blood pressure of 9 is 136.15 with a standard deviation of 6,504. After the statistical test obtained the value of p value = 0.000 < α = 0.05 which means there is an effect of giving Deep Breathing to the decrease in blood pressure.
2. It can be known the average diastolic blood pressure pre day 1 is 89.23 with a standard deviation of 11,875. The average diastolic blood pressure post day 9 is 82.31 with a standard deviation of 9,268. After the statistical test obtained p value = 0.108 > α = 0.05 which means there is no effect of giving Deep Breathing to the decrease in blood pressure.
Suggestion
The results of this study can be used for the development of nursing science on the Effectiveness of Deep Breathing against Decreased Blood Pressure in Elderly People Who Have Hypertension.
References
- Nuraini B (2015) Risk Factors of Hypertension. Universitas Lampung 4(5).
- Sulastri Dwi (2015) Pengaruh Senam Lansia Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Lansia Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kalijambe Srage. Stikes Kusuma Husada Surakarta 8(2).
- Kurniawan, P Andi (2014) Pemberian Teknik Relaksasi Napas Dalam Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah pada Asuhan Keperawatan Tn.S dengan Hipertensi Diruang Melati 1 Rumah SakitDr Moewardi. Stikes Kusuma Husada Surakarta 4(2): 91-98.
- Palmer A Williams B (2007) Tekanan Darah Tinggi Diterjemahkan. In. Astikawati R, Safitri A Penerbit (eds.) Erlangga Jakarta, Indonesia.
- Erlita Dkk, Mulyadi, Henry Palandeng (2013) Pengaruh Teknik Relaksasi Napas Dalam Terhadap penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Lansia Hipertensi Sedang Hingga Berat Di Ruang Irina C Blu Prof Dr DR D Kandou Manado & Bitung 1(1).
- Azizah M Lilik (2011) Keperawatan Lanjut Usia. Graha Ilmu Yogyakarta: 175-176.
- Bandiyah Siti (2009) Lanjut Usia dan Keperawtan Gerontik. In Yogyakarta : Nuha Medika Medical Book (eds.), Indonesia.
- Hart TJ Dkk (2010) Tanya Jawab Seputar Tekanan Darah Tinggi. Edisi 2. ARCAN. Jakarta.
- Kluwer W, Wilkins Williams Lippincott (2012) (2nd) Kapita Selekta Penyakit Dengan Implikasi Keperawatan. In EGC Jakarta (eds.). Diterjemahkan Widiarti Dwi Dkk Penerbit Buku Kedokteran.
- Mayer, Welas, Kowalak (2012) Buku Ajar Patofisiologi. Penerbit Buku Kedokteran. EGC Jakarta, Indonesia.
- Hidayat Alimul Aziz A (2007) Riset Keperawatan Dan Teknik Penulisan Ilmiah. Penerbit Salemba Medika, (2nd). Jakarta, Indonesia.
- Maryam S Fatma, Mia Dkk (2010) Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Lansia. CV Trans Info Media Jak-Tim.
- Wisnu D Wardani (2015) Pengaruh Teknik Relaksasi Napas Dalam Sebagai Terapi Tambahan Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien Hipertensi Tingkat 1. Univeritas Negeri Semarang.
- Ervan K Putra (2013) Pengaruh Latihan Napas Dalam Terhadap Penuruna Tekanan DarahPada Penderita Hipertensi Diwilayah Kecamatan Karas Kabupaten Magetan. Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta: 1-18.
- Anggriani AD, A Waren, E Situmorang, SS Siahaan (2009) Faktor-faktor yang berhubungan dengan kejadian Hipertensi Pada Pasien yang Berobat di Poloklinik Dewasa Puskesmas Banginang Periode Januari sampai juni.

 Research Article
Research Article