Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical fitness with burnout and mental health among female sports teachers in Gorgan and in this regard, four hypotheses were proposed. This research is applied in terms of purpose and based on descriptive-survey data collection method and in terms of data analysis method is correlational and a questionnaire was used to collect information. The hypotheses presented in this study were examined using the structural equation model and show that there is a significant inverse relationship between physical fitness and mental health and burnout. There is a significant positive relationship between mental health and burnout. The results of data analysis also show that mental health has a mediating role in the relationship between physical fitness and burnout.
Keywords: Exercise; Mental Health; Burnout; Physical Health
Introduction
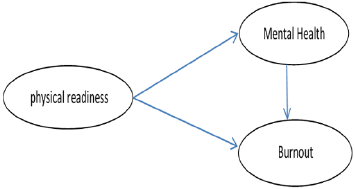
Paying attention to physical fitness and maintaining a basic physical strength is one of the methods that has been studied in recent years by sports science researchers to deal with stress and subsequently in order to be aware of people’s satisfaction [1]. Positive feeling about work is one of the important factors in organizational and job psychology and is an important feature in the quality of work life [2]. Job burnout is a type of occupational risk that is associated with a decrease in physical and mental energy in employees [3]. Exercise is known as a positive factor in increasing the feeling of wellbeing, self-esteem, mood, self-efficacy and self-confidence, high social adjustment and better cognitive function. The main purpose of this study was to identify a significant relationship between physical fitness and burnout and mental health of female sports teachers in Gorgan. According to what was said in the theoretical foundations and background of the research, the conceptual model of the research is presented as (Figure 1).
Material and Methods
The present study is an applied research in terms of purpose and a descriptive (non-experimental) research in the field of field studies in terms of data collection. In terms of the relationship between research variables, it indicates a kind of correlation. The relationship between physical fitness and job burnout and mental health of female sports teachers in Gorgan has been studied. In this study, the relationship between physical fitness and mental health and occupational burnout analysis and the relationship between mental health and occupational burnout analysis was evaluated.
Results and Discussion
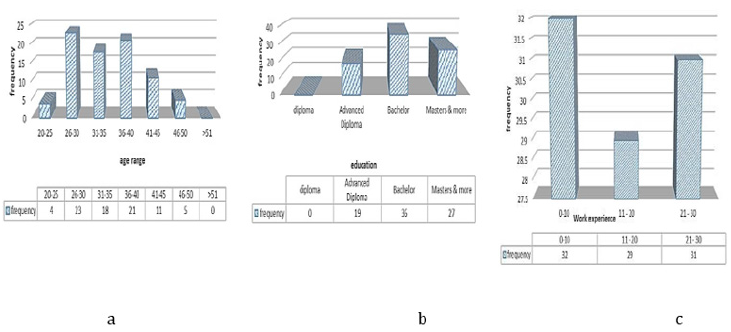
Data analysis is of particular importance for verifying the hypothesis of any type of research. Raw data are analyzed using statistical software and after processing are provided to users as information. Among the respondents to the questionnaire in terms of age, the most respondents were in the age group of 26 to 30 years and the lowest frequency was in the age group of 51 years and above. Also, in terms of education level, 23% had a master’s degree, 44% a bachelor’s degree and 33% a master’s degree or higher. Finally, 39% of the respondents to the questionnaire had 0 to 10 years of work experience, 35% had 11 to 20 years of work experience and 26% had 21 to 30 years of work experience as shown in (Figure 2). After performing the confirmatory analysis, the proposed model was tested using LISREL 8.8 software to establish the relationships between the independent and dependent variables of the research. This method of multivariate analysis is one of the most powerful methods of analysis in behavioral and social sciences research. Also, the results obtained from the study of hypotheses are in line with the research of researchers such as [4-6].
Hypothesis 1
There is a significant relationship between physical fitness and mental health. According to the model, it can be said that the path coefficient of the relationship between physical fitness and mental health is -0.77. The t-statistic for this coefficient is -6.57, which means that this relationship is negative and its value is less than the significance threshold of -1.96, which confirms the first hypothesis.
Hypothesis 2
There is a significant relationship between physical fitness and job burnout. According to the model, it can be said that the path coefficient of the relationship between physical fitness and burnout is -0.25. The t-statistic for this coefficient is -2.35, which means that this relationship is negative and its value is less than the significance threshold of -1.96, which confirms the second hypothesis.
Hypothesis 3
There is a significant relationship between mental health and job burnout. According to the model, it can be said that the path coefficient of the relationship between mental health and job burnout is 0.64. The t-statistic for this coefficient is 5.05, which means that this relationship is positive and its value is greater than the significance threshold of + 1.96, which confirms the third hypothesis.
Hypothesis 4
Mental health plays a mediating role in the relationship between physical fitness and burnout As can be seen in the model coefficients, the coefficient of significance between physical fitness and mental health is -0.77 and the coefficient of the relationship between mental health and burnout is 0.64. The product of these two path coefficients together (-0.64 0. 0.64) is equal to -0.49, which indicates the mediating role of mental health in the relationship between physical fitness and burnout. According to the obtained results, it is observed that the indirect effect (-0.49) is more than the indirect effect (-0.25); As a result, the mediating role of the mental health variable is accepted and mental health is related to physical fitness and burnout.
Conclusion
Due to the significant relationship between physical fitness and mental health and between physical fitness and burnout, it is suggested that schools use support programs to improve the physical condition of teachers. Therefore, by creating extracurricular courses and holding physical fitness classes, the grounds for improving the physical condition and physical activities of teachers should be provided. Because, as the results of the study show, teachers who scored higher on physical fitness tests had fewer symptoms of mental illness, and conversely, teachers who did not have a good physical condition had more symptoms than symptoms. They had mental illnesses. Due to the significant relationship between mental health and burnout, it is recommended to take measures to create a flexible work environment and work plan to pay attention to the physical condition, anxiety, social functioning and depression of employees. Because with the increase of these symptoms in employees, job burnout also increases and with the decrease of symptoms of mental illness, teachers’ job burnout also decreases.
offices, companies and organizations to create better conditions for employees. But it also seems that various activities are not able to completely eliminate job anxiety. For this reason, the best way to control and reduce job anxiety is to combine organizational change and anxiety management. It is also possible to pay attention to the social function of employees by creating programs and group meetings and increasing employee communication (horizontal and vertical) in the organization. Because with the increase of social actions in employees, their performance decreases and in order to improve performance, it is necessary to reduce these symptoms in teachers. And finally; The organization’s work plans should be designed in such a way that employees experience less stress in performing their job duties. Because with the increase of depression in employees, their job burnout also increases and in order to improve performance, it is necessary to reduce these symptoms in employees. The cause of frustration may be excessive fatigue or lack of confidence in the workplace and perhaps outside the workplace and may also affect working hours.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest related to this study.
References
- Elahi Tahereh, Fathi Ashtiani Ali, Bigdeli Elias (2012) The Relationship between Physical Fitness and Mental Health in the Staff of a Military University. Journal of Military Medicine 14(3): 92-99.
- Warner TH (2001) The effects of job satisfaction and organizational commitment on intent to leave among nurse anesthetists: A comparative study. Dissertation (PhD), Walden University. p. 49-66.
- Fedai, Mustafa Demir, Yeter (2010) The impacts of structural and psychological empowerment on burnout: a research on staff nurses in Turkish state hospitals. Canadian social science 6(4): 63-72.
- Farshad Commercial, Sheikh Alizadeh Mahboub, Azarbayjani Mohammad Ali, Rezaei Manesh Alireza, (2010) A Study of Physical Fitness and Feelings at Work: A Case Study in Male Employees of Post, Sports and Biomotor Sciences Company 3: 79-72.
- Short essay by Fereydoun, Sanei Saeed, Amirtash Ali Mohammad (2004) Physical fitness and its relationship with the rate of exhaustion and mental health of faculty members of military universities, Harakat 22: 19-46.
- Khorvash Majid, Alam Shahram, Idol Breaker Manijeh (2009) The relationship between physical activity and burnout in faculty members of Islamic Azad universities in four countries. Journal of Sports Management and Motor Behavior 10: 49-60.

 Short Communication
Short Communication