Abstract
Purpose: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a common gynecological malignancy with complex pathogenesis. The purpose of this study is to find out the important genes of poor prognosis and its potential mechanism.
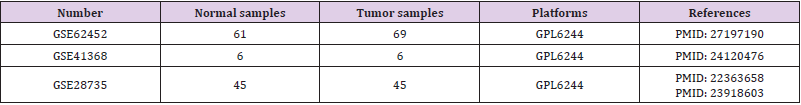
Materials and Methods: The gene expression profiles of GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735 can be obtained from the GEO database. There are 120 PDAC and 112 normal samples in the three profile data sets. GEO2R as well as Venn diagram software were used to screen the differentially expressed genes between PDAC and normal samples. Secondly, use database for visualization, annotation and integrated discovery, and analyze KEGG path and gene ontology. Then we use Cytoscape with search tools to search for interaction genes to visualize the protein-to-protein interaction of these DEGs.
Results: A total of 19 genes were consistently expressed in three datasets, of which 3 up-regulated genes and 16 down-regulated genes were rich in biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions. Through the analysis of PPI network by molecular complex detection plug-in, 10 down regulated genes were screened. In addition, in order to analyze the overall survival rate of these genes, Kaplan Meier analysis was conducted, and the prognosis of one gene was significantly poor. In order to verify the effectiveness of gene expression profile analysis, it was found that the expression of ALB gene in PDAC was lower than that in normal tissues. The high expression of ALB gene was related to the lower overall survival rate of patients with PDAC.
Conclusion: On the basis of the comprehensive bioinformatics method, ALB is the down regulated DEG in PDAC, with poor prognosis, which may become an important target for diagnosis and treatment of PDAC.
Keywords: Bioinformatic; Differentially Expressed Gene(Degs); Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma(PDAC); Prognosis; ALB
Abbreviations: PC: Pancreatic Cancer ; PDAC: Pancreatic Duct Adenocarcinoma; GEO: Gene Expression Omnibus; DESs: Differential Expression Genes; DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery; BP: Biological Process; CC: Cell Composition; MF: Molecular Function; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
Introduction
Pancreatic Cancer (PC) is one of the most lethal tumors, which is considered to be a fatal disease [1]. The 5-year relative survival rate is less than 10% (about 3% of metastatic cancer) [2]. Pancreatic Duct Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common pancreatic tumor, accounting for 90% of all PCs [3]. PDAC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths and is expected to become the second leading cause of cancer deaths by 2030 [4]. In the past few decades, the progress of PDAC treatment has been very slow. In 2006-2012, the 5-year survival rate of PDAC was 9% [5]. Therefore, it is important to find new biomarkers to predict the prognosis and improve the survival rate of patients with PDAC. Gene chip can detect differentially expressed genes quickly, which has been proved to be a reliable technology for more than ten years [6]. In addition, microarray can generate and store many slice data in a common database. Hence, on the basis of these data, a wealth of valuable clues can be unearthed for new research [7]. In recent years, some bioinformatics research have been carried out on PDAC [8,9], which prove that integrated bioinformatics method is helpful for further study and exploration of the potential mechanism of PDAC.
In this study, GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735 were firstly selected from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Secondly, GEO2R searching tool and Venn graph software were used to obtain the common Differential Expression Genes (DEGs) in the above three datasets. Thirdly, the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) was used to analyze these DEGs, including Biological Process (BP), Cell Composition (CC), Molecular Function (MF), and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway. Fourthly, a Protein Interaction (PPI) network was established to analyze DEGs and identify some core genes by using cellular MCODE (molecular complex detection). In addition, the core DEG was imported into Kaplan-Meier plotter online database to obtain significant prognostic information (P < 0.05). Moreover, the expression of DEGs between PDAC and normal samples was confirmed by Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) (P < 0.05). As the result, only 10 DEGs were qualified. Then, we carried out the enrichment analysis of KEGG pathway for these 10 DEGs. Finally, 6 DEGs and 6 genes (CELA3A, CEL, PNLIPRP1, CELA2B, CELA2A and CTRL) were produced, which significantly enriched the pancreatic secretion pathway. In conclusion, our bioinformatics research shows that ALB may be a useful biomarker, which can be used as an effective target and a better prognosis for patients with PDAC. The low expression of ALB indicates that the prognosis of PDAC is better.
Materials and Methods
Microarray Data Information
NCBI-GEO is considered as a free microarray/gene profile public database. We obtained gene expression profiles of GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735 in PDAC and normal samples. The microarray datas of GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735 were all based on GPL6244 platform ([HuGene-1_0-st] Affymetrix Human Gene 1.0 ST Array [transcript (gene) version]). Details about these datasets are shown in Table 1.
Data Processing of DEGs
Identify the DEGs between the PDAC sample and the normal sample by GEO2R online tools with |logFC| > 2 and adjust P value < 0.05 [10]. Then, the original data in TXT format is checked online in Venn software to detect the common DEGs in three data sets. DEGs with logFC < 0 are considered as down-regulated genes, and those with logFC > 0 are considered as up-regulated genes.
Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
Gene Ontology Analysis (GO) is a commonly used method to define genes and their RNAs or protein products to identify the unique biological characteristics of high-throughput transcriptome or genome data [11]. KEGG is a collection of databases, involving genomes, diseases, biological pathways, drugs and chemical materials [12]. DAVID is an online bioinformatics tool designed to recognize the functions of a large number of genes or proteins [13]. We used DAVID to observe the DEGs enrichment of Biogenic Process (BP), GO Cell Components (CC), Molecular Function (MF) and KEGG pathway (P < 0.05).
Protein–Protein Interaction Network and Module Analysis
Protein-Protein Interaction Network (PPI) information can be evaluated by an online tool, STRING (search tool for searching interaction genes) [14]. Then, the STRING app in Cytoscape is applied to check the potential correlation between these DEGs (maximum number of interactions = 0 and confidence score ≥ 0.4) [15]. In addition, the MCODE app in Cytoscape is used to check the modules of the PPI network (degree cutoff = 2, max. depth = 100, k-core = 2, node score cutoff = 0.2).
Survival Analysis and RNA Sequencing Expression of Core Genes
Kaplan Meier-plotter is a common website tool used to evaluate the impact of a large number of genes based on EGA, TCGA database and GEO (only limited to Affymetrix microarray) on the Overall Survival rate (OS) [16]. The log rank P value and Hazard Ratio (HR) of 95% confidence interval are calculated and shown on the graph. In order to verify these DEGs, we use GEPIA website to analyze the RNA sequence expression data of thousands of samples from the GTEx projects and TCGA [17].
Results
Identification of DEGs in PDAC
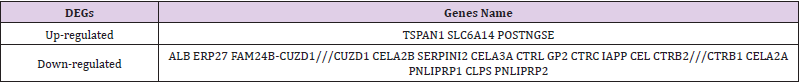
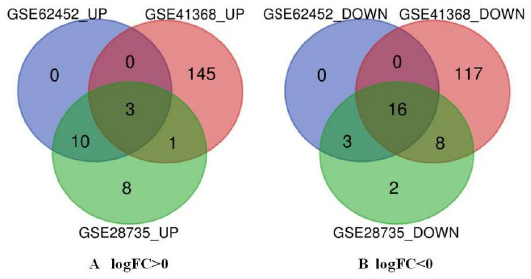
There were 120 PDAC and 112 normal pancreas specimens in this study. Through GEO2R online tool, we extracted 33, 591 and 57 DEG from GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735, respectively. Then, we used Venn diagram online tool to identify the common DEGs in these three datasets. The results showed that 19 DEGs were detected in PDAC, including 3 up-regulated genes (logFC > 0) and 16 down regulated genes (logFC < 0) (Table 2 and Figure 1).
Table 2: All 19 commonly differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected from three profile datasets, including 3 up-regulated genes and 16 down-regulated genes in the PDAC samples compared to normal pancreatic samples.
Figure 1: Authentication of 19 common DEGs in the three datasets (GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735) through Venn diagrams software (available online: http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/). Different color meant different datasets.
a) 3 DEGs were up-regulated in the three datasets (logFC> 0).
b) 16 DEGs were down-regulated in three datasets (logFC < 0).
DEGs Gene Ontology and KEGG Pathway Analysis in PDAC
All 19 DEGs were analyzed by DAVID software, and the results of GO analysis showed that:
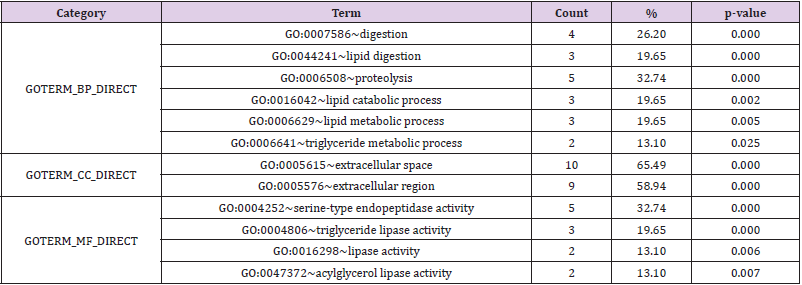
a) For Biological Process (BP), the regulation of down regulated DEGs in digestion, lipid digestion, protein decomposition, lipid catabolism, lipid metabolism and triglyceride metabolism were particularly rich
b) For GO Cell Composition (CC), down regulated DEGs were significantly enriched in extracellular space and region
c) For Molecular Function (MF), the content of down regulated DEGs were higher in serine-type endopeptidase activity, triglyceride lipase activity, lipase activity and acylglycerol lipase activity (Table 3).
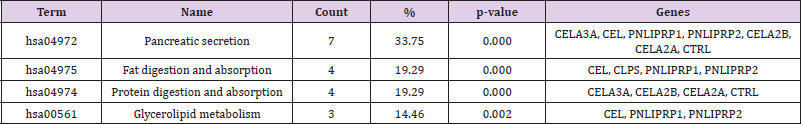
The results of KEGG analysis were shown in Table 4. The downregulated DEGs were particularly enriched in pancreatic secretion, fat digestion and absorption, protein digestion and absorption, and glycolipid metabolism (P < 0.05), while the up-regulated DEGs has no obvious signal transduction pathway.
PPI and Modular Analysis
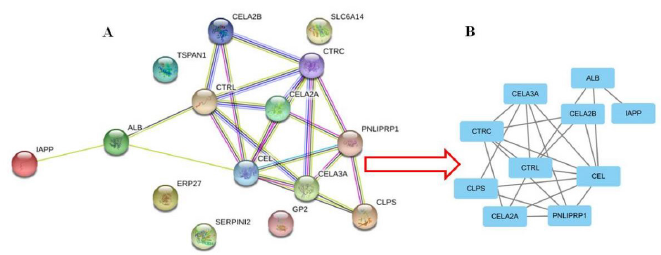
A total of 15 DEGs were introduced into the DEGs PPI network complex, including 13 down-regulated genes and 2 up-regulated genes (Figure 2A). 4 of the 19 DEG’s were not included in the DEG PPI network (Figure 2A). Then we used Cytotype MCODE for further analysis, and the results showed that 10 core genes were found in 15 DEGs, all of which were down regulated genes (Figure 2B).
Figure 2: Common DEGs PPI network constructed by STRING online database and Module analysis.
a) There were a total of 107 DEGs in the DEGs PPI network complex.
b) Module analysis via Cytoscape software (degree cutoff = 2, node score cutoff = 0.2, k-core = 2, and max. Depth = 100).
Analysis of Core Genes by the Kaplan Meier Plotter and GEPIA
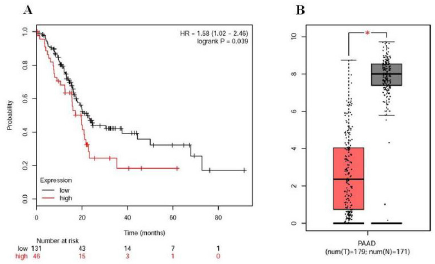
Kaplan Meier plotter was used to identify the survival data of 10 core genes. The results showed that the survival rate of one gene was significantly higher than that of the other nine genes (P < 0.05, Table 5). Then, GEPIA method was used to detect the expression of ALB gene in cancerous and normal people. Our results showed that ALB overexpression in PDAC patients was associated with more severe OS (P < 0.05, Figure 3A). In addition, the expression of ALB in PDAC samples was lower than that in normal pancreas samples (P < 0.05, Table 5 and Figure 3B).
Figure 3: Prognostic value of ALB and expression level of ALB gene in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
a) The prognostic information of ALB. Kaplan meier plotter online tools were used to identify the prognostic information of the 10 core genes and 1 of 10 genes had a worse significantly OS rate (P < 0.05).
b) ALB was significantly expressed in PDAC cancer patients compared to healthy people. GEPIA website was used to further identify the ALB expression level between PDAC and normal people. The result showed there was significant expression level in PDAC specimen compared to normal specimen (*P < 0.05). Red color means tumor tissues and grey color means normal tissues.
Re-Analysis of 15 Selected Genes via KEGG Pathway Enrichment
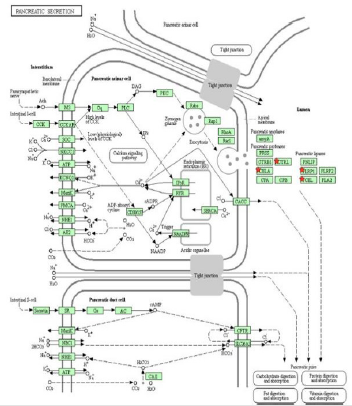
In order to understand the possible pathways of the 10 selected DEGs, the enrichment of KEGG pathway was re-analyzed by DAVID. The results showed that 6 genes (CELA3A, CEL, PNLIPRP1, CELA2B, CELA2A and CTRL) were significantly enriched in the pancreatic secretion pathway (P < 0.05, Table 6 and Figure 4). 4 genes (CELA3A, CELA2B, CELA2A and CTRL) were significantly enriched in fat digestion and absorption pathway, and 3 genes (CEL, CLPS and PNLIPRP1) were significantly enriched in protein digestion and absorption pathway (P < 0.05, Table 6).
Figure 4: Re-analysis of 10 selected genes by KEGG pathway enrichment. CELA (CELA3A, CELA2A, CELA2B), CTRL, PNLIPRP1 and CEL were significantly enriched in the pancreatic secretion pathway. CELA included CELA3A, CELA2A, CELA2B. PLRP1 means PNLIPRP1.
Discussion
In this study, we used the bioinformatics method to determine the more useful prognostic biomarkers in PDAC based on three profile data sets (GSE62452, GSE41368 and GSE28735). 120 PDAC samples and 112 normal samples were included in the study. Via GEO2R and Venn software, we found that there are 19 common DEGs in PDAC, among which 3 genes were up-regulated and 16 genes were down regulated. Then, the analysis of gene ontology and pathway enrichment using DAVID online website showed that:
a) For BP, the regulation of down regulated DEGs in digestion, lipid digestion, protein decomposition, lipid catabolism, lipid metabolism and triglyceride metabolism were particularly rich.
b) For GO CC, down regulated DEGs were significantly enriched in extracellular space and region.
c) For MF, the content of down regulated DEGs were higher in serine-type endopeptidase activity, triglyceride lipase activity, lipase activity and acylglycerol lipase activity.
In addition, the DEGs PPI network complex was constructed by using STRING online database and Cytoscape software. Then, 10 down regulated genes were screened from PPI network complex by Cytotype MCODE analysis. After that, we used Kaplan Meier plotter to analyze and found that 1 of 10 genes had a significant better survival. Then we used GEPIA analysis and proved that the expression of the gene in PDAC samples was lower than that in normal samples (P < 0.05). ALB is the main protein in human plasma, which is also considered as an important indicator of nutritional status and a powerful predictor of poor prognosis in patients undergoing major surgery [18]. ALB has been considered as an endogenous antioxidant, which plays a role in many physiological and pathological processes as well as exerting anti-carcinogenic effects [19]. The lower serum ALB level in cancer patients may be due to the persistent systemic inflammatory response of aggressive metabolically active tumors. A population-based prospective study showed that a higher level of ALB was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer [20]. Previous studies [21-23] reported that low ALB level was a reliable risk factor for poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer. It might emphasize the importance of metabolic changes in the natural history of pancreatic cancer [24]. In addition, some studies have identified clinic pathological prognostic factors associated with serum ALB levels in PDAC patients, including C-Reactive Protein (CRP)-to-albumin ratio [25] and Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS) [26].
However, no study has reported that ALB gene in tumor tissue predicts survival in patients with PDAC. In this study, ALB gene was down regulated in PDAC compared with normal pancreas. This might be the reason that only hepatocytes and HCC express ALB mRNA under normal conditions [24,25]. It is worth noting that our study shows that in patients with PDAC, the high expression of ALB and poor prognosis are statistically significant. Whether this is related to the progress of PDAC is uncertain. More research is needed in this area. Taken above, bioinformatics analysis of three sets of PDAC microarray data showed that the high expression of ALB in PDAC tissue was related to unsatisfactory survival effect. It may provide useful information for the study of potential biomarkers and biological mechanism of PDAC. However, the study of molecular mechanism and biological function of ALB gene, and whether ALB gene can be used as a new potential biomarker or therapeutic target for PC patients need further study.
Acknowledgement
This work was partly supported by the National Nature Science Foundation (81804153), Scientific Research Project of Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (20191090), Basic and Applied basic research Foundation of Guangdong Province (2019A1515110161) and Fundamental Research for the Central Universities (21619344).
References
- Ashburner M (2000) Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genetics 25: 25-29.
- Davis S, Meltzer PS (2007) GEO query: a bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and Bio Conductor Bioinformatics 23(14): 1846-1847.
- Feng H, Gu ZY, Li Q, Liu QH, Yang XY (2019) Identification of significant genes with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer via bioinformatical analysis. Journal of Ovarian Research 12(1).
- Feng L, Gu S, Wang P, Chen H, Chen Z (2018) Pretreatment values of bilirubin and albumin are not prognostic predictors in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med 7: 5943-5951.
- Haruki K, Shiba H, Shirai Y, Horiuchi T, Iwase R, et al. (2016) The C-reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio Predicts Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer After Pancreatic Resection. World Journal of Surgery 40(9): 2254-2260.
- Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nature Protocols 4: 44-57.
- Imaoka H (2016) Evaluation of Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score for Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pancreas 45(2): 211-217.
- Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Research 27(1): 29-34.
- Kar S, Carr BI (1995) Detection of liver cells in peripheral blood of patients with advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 21(2): 403-407.
- Kuhn T, Sookthai D, Graf ME, Schubel R, Freisling H (2017) Albumin, bilirubin, uric acid and cancer risk: results from a prospective population-based study. British Journal of Cancer 117: 1572-1579.
- Long J, Liu Z, Wu X, Xu Y, Ge C (2016) Screening for genes and subnetworks associated with pancreatic cancer based on the gene expression profile. Mol Med Rep 13: 3779-3786.
- Niwa Y, Matsumura M, Shiratori Y, Imamura M, Kato N (1996) Quantitation of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin messenger RNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 23: 1384-1392.
- Roche M, Rondeau P, Singh NR, Tarnus E, Bourdon E (2008) The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. Febs Letters 582(13): 1783-1787.
- Ruiz Tovar J, Martin Perez E, Fernandez Contreras ME, Reguero Callejas ME, Gamallo Amat C (2010) Impact of preoperative levels of hemoglobin and albumin on the survival of pancreatic carcinoma. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 102(11): 631-636.
- Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT (2003) Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Research 13: 2498-2504.
- Siddiqui A, Heinzerling J, Livingston EH, Huerta S (2007) Predictors of early mortality in veteran patients with pancreatic cancer. Am J Surg 194: 362-366.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer Statistics, 2017. Ca-a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 67(1): 7-30.
- Rebecca L Siegel, Kimberly Miller, Ahmedin Jemal (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. Ca-a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 69(1): 7-34.
- Szasz AM, Lanczky A, Nagy A, Forster S, Hark K (2016) Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget 7(31): 49322-49333.
- Szklarczyk D (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Research 43: D447-D452.
- Tang ZF, Li CW, Kang BX, Gao G, Li C (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Research 45: W98-W102.
- Tesfaye AA, Kamgar M, Azmi A, Philip PA (2018) The evolution into personalized therapies in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: challenges and opportunities. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy 18(2): 131-148.
- Vigano A, Bruera E, Jhangri GS, Newman SC, Fields AL (2000) Clinical survival predictors in patients with advanced cancer. Arch Intern Med 160: 861-868.
- Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou SB, Diaz LA (2013) Cancer Genome Landscapes. Science 339: 1546-1558.
- Zhang Z, Qin W, Sun Y (2018) Contribution of biomarkers for pancreatic cancer-associated new-onset diabetes to pancreatic cancer screening. Pathol Res Pract 214: 1923-1928.
- Zhou J, Hui XL, Mao Y, Fang LY (2019) Identification of novel genes associated with a poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via a bioinformatics analysis. Bioscience Reports 39(8): 0625.

 Research Article
Research Article