Abstract
Background: DRPs are one of the major challenges to health care providers as this may affect morbidity, mortality and patients’ quality of life.
Objective: This study aimed to compare the prevalence of uncontrolled blood pressure and drug therapy problems in two Nigerian tertiary institutions.
Methods: This was a retrospective cross sectional study carried out in the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital (UNTH), Ituku/Ozalla, Enugu state and Federal Medical Centre Lokoja (FMCL), Kogi State, over a period of two months (June1, 2019- July 31, 2019). Ethical clearance for the study was obtained from the Health and Research ethics committee of both hospital. A well designed proforma adopted from similar studies was used to collect patients’ socio-demographic and clinical variables from their folders. Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe (PCNE) Classification tool Version8.02 (PCNE, 2010) was used to document the types and causes of Drug therapy problems. The data cleaning was conducted in Microsoft excel after which information were exported and analysed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS for windows, Version 16.0. SPSS Inc. 2007.Chicago, USA) software. Continuous data were presented as mean ± standard deviation while categorical data were presented as percentages and frequencies.
Results: The ratio of male to female patients was 1.03: 1 with a greater number of the patients being above 55 years of age. the ratio of controlled blood pressure to uncontrolled blood pressure was 1:1.02 for UNTH and 1:0.601 for FMCL. FMCL recorded a percentage of patients with uncontrolled blood pressure. Older patients had more DTPs than the younger ones and this was statistically significant. Blood pressure control was associated with age in both study centres as increase in age decreased blood pressure control and this was statistically significant.
Conclusion: Blood pressure control in both centres were below average while prevalence of DRPs was high in both centres too. An educational interventional programmes is recommended to enlighten patients on the need adopt lifestyle modifications to control their blood pressure and the dangers of uncontrolled blood pressure.
Keywords: Hypertension; Blood Pressure Control; Drug Related Problems
Abbreviations: UNTH: University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital; FMCL: Federal Medical Centre Lokoja; PCNE: Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe; SPSS: Statistical Package for Social Sciences
Introduction
DRPs are one of the major challenges to health care providers as this may affect morbidity, mortality and patients’ quality of life [1]. DRPs have been found to lead to reduced quality of life, increased hospital stay, increased overall health care cost with an increase in morbidity and mortality [2]. Also, inappropriate use of drugs are harmful and can possibly evoke side effects [3]. Clinical pharmacists in coordination with other health care providers can identify DRPs through medication reconciliation [4]. Although there are several classifications of DRPs, there is no single standardized classification in the world [5]. However, the PCNE classification system has been commonly practiced because it has better usability and internal consistency as it is being updated and revised periodically. It is also being employed in pharmaceutical care process for documenting DRPs [6].
In a recent study, it was observed that the occurrence of DRPs per patient increased linearly with the number of drugs used, where one unit increase in the number of drugs yielded 8.6% increase in the number of DRPs [7]. In addition, a prospective study conducted in Jordan reported that 98.3% of all the patients who attended the hospital had DRPs and on an average, 9.35% of DRPs occurred per patient [1]. Although there are no documented figure for Nigeria, it has been documented that the economic burden arising from DRPs was $177.4 billion and £100707 annually in the United states of America [8] and Australia [9] respectively. Therefore, improving drug therapy by minimizing DRPs can help reduce treatment related costs [10].
Objective
This study aimed to compare the prevalence of uncontrolled blood pressure and drug therapy problems in two Nigerian tertiary institutions.
Methods
Study Design
This was a retrospective cross sectional study carried out in the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital (UNTH), Ituku/Ozalla, Enugu state and Federal Medical Centre Lokoja (FMCL), Kogi State, over a period of two months (June1, 2019- July 31, 2019) to evaluate the prescription pattern, determine the rate of control of blood pressure, identify Drug related problems in the management of Hypertension.
Ethical Clearance
Ethical clearance for the study was obtained from the Health and Research ethics committee of University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Ituku-Ozalla and the Federal medical centre (FMC) Lokoja, Kogi State.
Eligibility Criteria
The inclusion criteria were:
a) Hypertensive patients who received care from January 1, 2018 - December 31, 2018.
b) Availability of patient demographic data on the patient folder.
c) Patient folder having prescriber’s information (signature and/or name).
d) Patient folders with ages > 18 years.
e) All patient folders having at least a single antihypertensive medication.
Sample size and selection: The entire patient folders that met the eligibility criteria were included in the study.
Data Collection
A well designed proforma adopted from similar studies was used to collect patients’ socio-demographic and clinical variables from their folders. Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe (PCNE) Classification tool Version8.02 (PCNE, 2010) was used to document the types and causes of Drug therapy problems.
Data Analysis
The data cleaning was conducted in Microsoft excel after which information were exported and analysed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS for windows, Version 16.0. SPSS Inc. 2007. Chicago, USA) software. Continuous data were presented as mean ± standard deviation while categorical data were presented as percentages and frequencies. Chi square and correlation test was also used to examine association between the variables in the data collected.
Results
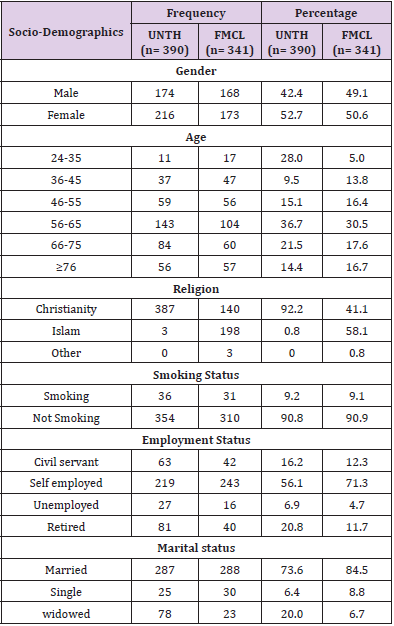
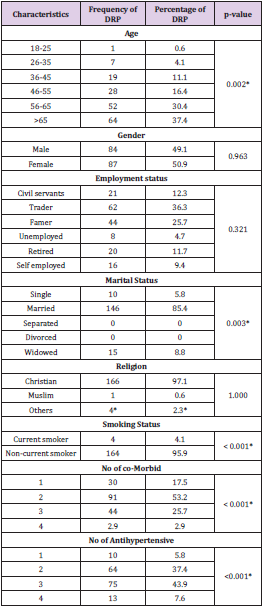
From Table 1, majority of the hypertensive patients were females 216(52.7) and 173(50.6) at UNTH and FMCL respectively. Also, a majority of the patients were aged 56-65 years 143 (36.7) and 104 (30.5) at UNTH and FMCL respectively. Majority of the hypertensive patients that visited UNTH within the study period were Christians by religion 387 (92.2) while 198 (58.1) who visited the FMCL within the study period were Muslims by religion. Almost all the patients that visited the study centres were not smokers with 354 (90.8) and 310 (90.9) for UNTH and FMCL respectively. Also, a majority of the patients at both study centres were married and had a source of income (Table 1).
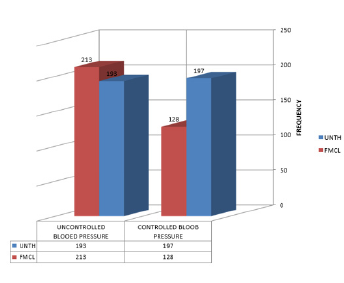
From Figure 1, UNTH had an almost equal distribution of patients with controlled and uncontrolled blood pressure, while FMCL had a majority of patients with uncontrolled blood pressure (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Distribution of blood pressure control between the two centres.
Note: Controlled blood pressure= SBP< 140 mm Hg; DBP <90 mm Hg.
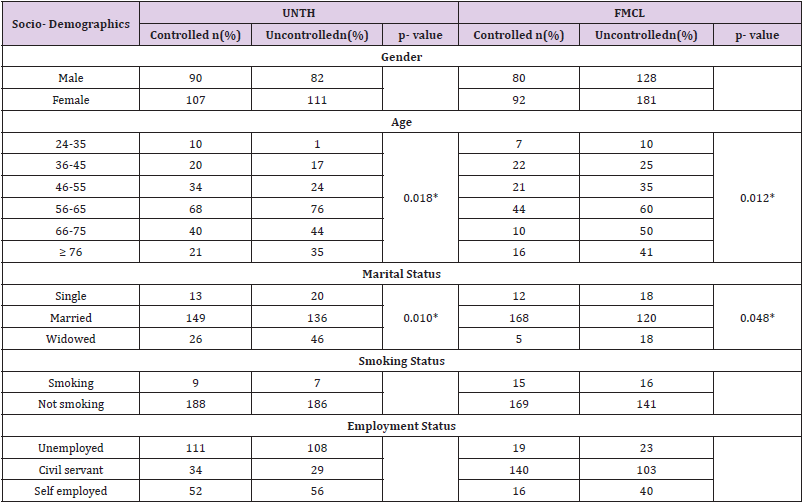
From Table 2, A majority of the patients who were aged 56- 65 years had their blood pressure uncontrolled in b UNTH and FMCL and this was statistically significant (p= 0.018 and 0.012 respectively). Also, singles and widowed who had uncontrolled blood pressure were more than those that had controlled blood pressure in both UNTH and FMCL and this was statistically significant (p= 0.010 and 0.048 respectively) (Table 2).
Table 2: Relationship between blood pressure control and patients socio-demographics and clinical characteristics.
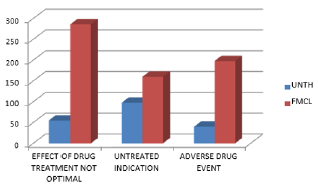
From Figure 2, the most common type of drug related problem encountered in UNTH was untreated indication while the least type of DRP was adverse drug event. Whereas the most common type of DRP encountered in FMCL was effect of drug not optimal while the least type of DRP was untreated indication (Figure 2).
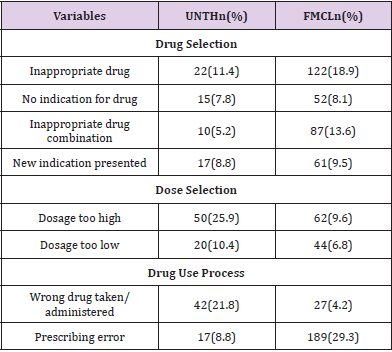
From Table 3, dosage too high 50 (25.9) was the major cause of DRP encountered in UNTH while prescribing error 189 (29.3) was the major cause of DRP encountered in FMCL. Inappropriate drug combination 10 (5.2) was the least reported cause of DRP in UNTH while wrong drug taken/ administered 27 (4.2) was the least reported cause of DRP in FMCL (Table 3).
From Table 4, majority of the DRPs were found among patients who were 65 years and older and this was statistically significant (p = 0.002). Most of the DRPs were found in the females 87 (50.9) and traders 62 (36.3). Also, 146 (85.4) of the DRPs reported were found among those who were married and this was also statistically significant. Also increase in DRP was seen in increased number of co-morbid states and in patients receiving more than one antihypertensive medication (P <0.001) (Table 4).
Discussion
The ratio of male to female patients was 1.03: 1 with a greater number of the patients being above 55 years of age. This finding is comparable to similar studies among hypertensive patients in a Nigerian Hospital [11]. Increase in arterial and arteriole wall stiffness, decreased baroreceptor sensitivity, increased responsiveness to sympathetic nervous stimuli, altered renal and sodium metabolism which are associated with aging could be a reason why hypertension is more prevalent in older adults [12]. Also, the ratio of controlled blood pressure to uncontrolled blood pressure was 1:1.02 for UNTH and 1:0.601 for FMCL. FMCL recorded a percentage of patients with uncontrolled blood pressure. The BP cut off of 140/90 mmHg was used in this study to define good BP control as recommended by JNC 8. Studies that used the same BP cut off also reported similar proportion of patients with controlled BP [13]. Blood pressure control was associated with age in both study centres as increase in age decreased blood pressure control and this was statistically significant.
This could be because older patients are more likely to have more co-morbid conditions which could affect hypertension management. Also, it is possible that older patients must have had hypertension for longer years which could lead to high disease burden as they may get tired of being on daily medications. Both centres recorded that married patients had a better BP control than the singles and widowed and this was statistically significant too. This could be because married patients could be more emotionally stable than unmarried ones. Also, it is possible that married people can have someone supporting them both financially and emotionally too. Methyldopa and frusemide were majorly involved in DTPs. This could be because they were more commonly prescribed that other antihypertensive. A combination of methyldopa and frusemide can lead to an enhanced hypotensive effect.
The most common type of DTP found in UNTH was untreated indication while the most common type of DTPs found in FMCL was drug treatment not optimal. This could be the reason why FMCL reported a higher proportion of patients with uncontrolled BP than UNTH. Older patients had more DTPs than the younger ones and this was statistically significant. This could be because older patients have a likelihood of having more co-morbid conditions and this will invariably expose them to more number of drugs. Increase in the number of drugs has been found to lead to an increase in DTPs. Although the female patients had more DTPs than the male, it was not statistically significant. Unsurprisingly, smokers had more DTPs than non- smokers. This could be explained by the fact than smoking could predispose one to more ailments which can lead to increased number of medications. Also, patients who were on more than one antihypertensive medication encountered more DTPs. This is because increased number of drugs can lead to an increase in drug-drug interactions.
References
- Aburuz SM, Bulatova NR, Yousef AM, Al Ghazawi MA, Alawwa IA, et al. (2011) Comprehensive assessment of treatment related problems in hospitalised medicine patients in Jordan. Int J Clin Pharm 33(3): 501-511.
- Adibe MO, Igboeli NU, Ukwe CV (2017) Evaluation of drug therapy problems among renal patients receiving care in some tertiary hospitals in Nigeria. Trop J Pharm Research 16(3): 697-704.
- Chiatti C, Bustacchini S, Furneri G, Mantovani L, Cristiani M, et al. (2012) The economic burden of inappropriate drug prescribing, lack of adherence and compliance, adverse drug events in older people: A systematic review. Drug Saf 35(Suppl 1): 73-87.
- Khan MU, Ahmad A (2014) The impact of clinical pharmacist’ intervention on drug related problems in a teaching hospital. Int J Pharm Clin Res 6(3): 276-280.
- Basger BJ, Moles RJ, Chen TF (2015) Development of an aggregated system for classifying causes of drug-related problems. Ann Pharmacother 49(4): 405-418.
- Van Mill JF, Westerlund LT, Hersberger KE, Schaefer MA (2004) Drug-related problem classification systems. Ann Pharmacother 38(5): 859-867.
- Viktil KK, Blix HS, Moger TA, Reikvam A (2007) Polypharmacy as commonly defined is an indicator of limited value in the assessment of drug-related problems. Br J Clin Pharmacol 63(2): 187-195.
- Easton KL, Chapman CB, Brien JA (2004) Frequency and characteristics of hospital admissions associated with dru-related problems in paediatrics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 57(5): 611-615.
- Ernst FR, Grizzle AJ (2001) Drug-related morbidity and mortality: Updating the cost-of- illness model. J American Pharm Association 41(2): 192-199.
- Roughead EE, Barratt JD, Gilbert AL (2004) Medication-related problems commonly occuring in an Australian community setting. Pharmacoepidemiology 13(2): 83-87.
- Busari OA, Oluyombo R, Fasae AJ, Gabriel EO, Ayodele LM, et al. (2014) Prescribing pattern and utilization of antihypertensive drugs and blood pressure control in adults patients with systemic hypertension in a rural tertiary hospital in Nigeria. Am J Intern Med 2(6): 144-149.
- Weber MA, Neutel JM, Cheung DG (1989) Hypertension in the aged: A pathophysiologic basis for treatment. Am J Cardiol 63(16): 25H-32H.
- Olanrewaju TO, Aderibigbe A, Chijioke A, Sanya EO, Busari OA, et al. (2011) Descriptive analysis of blood pressure control among treated hypertensive patients in a tertiary hospital in Nigeria. Afrrican J Med 40(3): 207-212.

 Research Article
Research Article