Mini Review
General Information
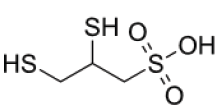
DMPS: SODIUM 2.3 DIMERCAPTOPROPANE-L-SULPHONATE (Figure 1): DMPS was developed in the former Soviet Union in 1958. It became available to the Western world in 1978 and is since synthesized and produced by the German pharmaceutical company Heyl, Berlin. This chelating agent is registered in Germany under the name of Dimaval®. DMPS is an analogue of BAL (British Anti- Lewisite) and belongs to the group of dithiols along with DMSA. DMPS is approved in its oral form and as an injectable by the German authorities for the treatment of acute metal intoxication. DMPS is included in the FDA list of Bulk Chemicals That May Be Used In Pharmacy Compounding, meaning it is available to physicians on request. Final approval of the list is still pending [1]. As of March 21, 2019, DMPS has been placed on FDAs list 503A Category 1- Bulk Drug Substances Under Evaluation, i.e. it has been nominated for pharmacy compounding use in the USA. In Europe (and on a limited basis in North America), DMPS has been used extensively as a treatment for mercury, arsenic or lead intoxication. When compared with D-penicillamine and N-acetyl-DL-penicillamine, DMPS was most effective to clear mercury from the blood of victims of the Iraqi mercury disaster in the 1960s.
DMPS Bioavailability
The metabolism of DMPS, being hydrophilic in nature, has been thoroughly studied. DMPS undergoes both renal and biliary excretion and is excreted largely through the urine. DMPS is distributed in both an intracellular and extracellular manner. DMPS does not cross the blood brain barrier and does not re-distribute arsenic, lead or inorganic mercury to the brain [2-4]. Adverse reactions are known but are relatively rare. About 90% of DMPS is eliminated via the kidneys. After 24h about 80% of the dose received has been excreted. DMPS does not accumulate in tissue even after repeated use. Since the kidneys are the main organs of excretion for DMPS and its complexes, patients with a limited kidney function should not be chelated with this antidote if serum creatinine values exceed 2.5mg/dl. Animal studies on the acute and chronic toxicity of DMPS have been carried out and results illustrate the safety of this agent and its wide therapeutic window. DMPS is not mutagenic and seems to have no teratogenic effects. It is not carcinogenic.
Scope of Application
DMPS is widely recognized as an antidote for a range of metal intoxications. In Germany, it is widely used as an effective diagnostic and antidote in the treatment of chronic metal exposure [5]. There is widespread medical acknowledgement that ‘DMPS is effective in accelerating metal excretion without severe adverse effects in acute and chronic intoxication by inorganic and organic mercury, bismuth, arsenic, and chronic lead poisoning [6]. Because DMPS is not easily available in the US and other countries, Dimercaprol or BAL are still used as an alternative. In Sweden, Hong Kong or the USA for instance, DMPS is available as an emergency medication. Officially, the oral administration should be considered before parenteral use (intravenous or intramuscular). Heyl does not recommend that DMPS is used in combination with other chelating agents.
Side Effects
Numerous human studies have failed to uncover any significant adverse impacts of DMPS upon human renal function. Minor effects such as local irritation at the site of parenteral infusion or hypotension with overly rapid infusion of the agent have been reported [7]. Adverse reactions during treatment with DMPS include gastrointestinal discomfort, skin reactions, mild neutropenia and elevated liver enzymes. Some patients, especially those with allergic asthma symptoms, may develop hypersensitivity to DMPS. If this occurs, DMPS treatment must be discontinued [8]. Does DMPS treatment affect existing amalgam fillings or be contraindicated in a patient with amalgam fillings? Dr. J. Ruprecht, previous research scientist at Heyl, Berlin stated that this is ‘highly unlikely. DMPS does not come in contact with fillings and even if it would, the level found in blood would not be sufficient to affect the amalgam’. DMPS may be given to patients with fillings.
Oral VS Intravenous Use
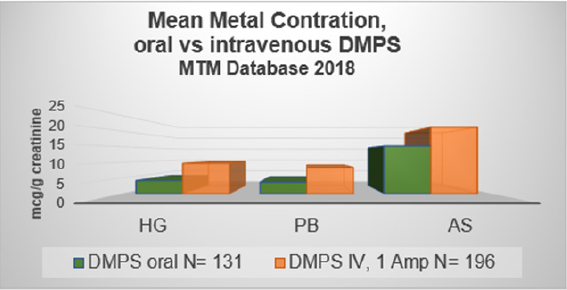
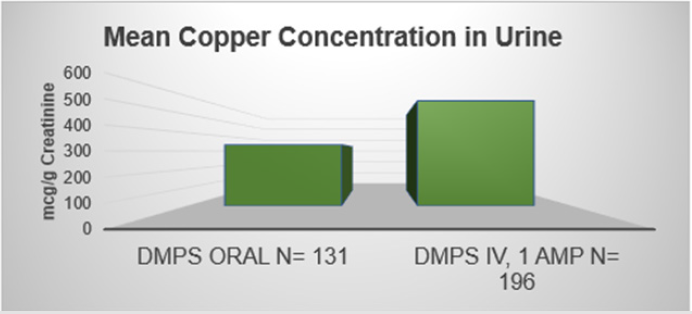
The bioavailability of oral DMPS is about 50%. Table 1 indicates that oral administration of arsenic (As) binding exceeds the estimated 50%. For mercury (Hg) and lead (Pb), the 50% estimate seems right. (Source: Micro Trace Minerals Laboratory, Germany, 2018) (Figures 2). As has been pointed out before, DMPS is a strong binder of copper. Figure 3 demonstrates this [9].
DMPS Protocol for Intravenous Administration
Important Notes
1. Opened ampules cannot be stored for reuse as the solution is oxygen-sensitive
2. Expired DMPS ampules are not to be used.
3. Metals such as zinc, copper or any other metal cannot be added to the injectable or to carrier solutions containing DMPS
4. A challenge test is performed in symptomatic patients or in patients with a suspected past or present metal intoxication.
5. Dose and treatment schedule depend on the individual case. For adults. 1 ampule is injected or 3 mg DMPS/kg Body Weight (BW)[10].
6. DMPS should not be administered to patients with serum creatinine values >2.5mg/dl.
7. The peak excretion time of DMPS is between 1-2 hours after the injection has been completed. During that time, the patient should wait in the office and drink at most 300ml water.
If possible, the patient should hold off urination for maximal 2 hours, after which some urine is taken into a normal urine cup.
8. Paravenous infiltration of DMPS is harmless but creates discomfort and an itching sensation at the injection site for half an hour approximately.
9. Occasionally, side effects are observed such as allergic reactions, and skin rashes.
10. If DMPS is injected or infused too quickly, blood pressure may drop. Observe patient.
11. DMPS easily binds with zinc. Skin problems can develop if the patient is borderline zinc deficient before treatment start.
12. Check the patient’s zinc status before DMPS treatment is started. Hair mineral analysis provides information about how much zinc has been stored in tissue over time; blood zinc levels are an indication of the present status.
13. Repeated DMPS treatments reduce zinc blood and tissue levels. Repeated administration of DMPS without proper supplementation may create a zinc deficiency state. Supplementation should not be provided on the day of chelation.
14. If the patient’s zinc status indicates a need for supplementation, zinc and vitamin B6 should be given daily for one to two weeks prior to treatment. Stop supplementation at least 24hrs before the DMPS treatment and resume 24hrs later.
Material for Urine Metal Testing
Baseline Urine: This urine shows the metal excretion before chelation and is used to rule out immediate exposure through food, water, medication etc.
Acute Toxicity: 24hr urine collection is recommended. Of that the laboratory needs 5-7ml . The total volume of the 24hr urine collection must be recorded and provided to the laboratory.
Chronic Exposure: DMPS Challenge or Provocation Test: Urine should be collected for 1-2 hour after DMPS injection has been completed. The laboratory needs 5-7ml of urine for testing. The total volume is not needed if results are based on creatinine. For the 24hr urine test, results are reported in mg or mcg/total volume. Provision of exact amount of total volume is a must.
DMPS IV Administration
1. Check and write down blood pressure.
2. The content of the DMPS ampule (5ml or 3 mg/kg body weight) is drawn up into a 5cc syringe and slowly injected into the vein with a 25gauge butterfly, 1ml per 1minute. A slower injection rate of 1cc/2min is recommended for sensitive patients[11].
3. During the time of administration, some patients notice a sulfuric taste in the mouth. Occasionally, a blood pressure drop may be observed. If the patient complains about dizziness, ask the patient to lie down[12]. If this does not alleviate the problem, discontinue the treatment.
4. Urine collection: 1 to 2 hours.
DMPS Infusion
1. Check and write down blood pressure.
2. The content of the DMPS ampule (5ml or 3 mg/kg body weight) is added to 100ml sodium chloride (0.9%). Infusion time: 15minutes, not longer.
DMPS-Protocol for Oral Use
The Challenge or Provocation Test
1 capsule of Dimaval (Heyl) contains 100 mg DMPS for oral use.
Application for Adults: 10 mg DMPS/kg BW on an empty stomach. Generally, 200 mg to 400 mg oral DMPS/day are recommended for chronically exposed adults, and are usually given in a single dose, at most once weekly. The urine challenge test requires a 3h collection time [13].
According to Heyl the 200-400mg daily dose may also be divided into three single doses. In such a case, the urine collection for the challenge test would have to be taken over 24hrs [13].
Transdermal DMPS (TD-DMPS)
The concept of administering DMPS as a transdermal treatment has received attention, largely because this concept appeals to parents of autistic children. Dr. Buttar who promoted this type of application argued that TD-DMPS circulates in the lymphatic system and acts as a potential transfer system. There is a problem with this theory. DMPS is a water-soluble chemical [14]. To function within the lymphatic system, it would have to be fat-soluble. Dr. Ruprecht, former head of Heyl’s pharmaceutical research confirmed that DMPS is not lipophilic and therefore cannot be active within the lymphatic system. Furthermore, DMPS is highly oxygen reactive. If added to a lotion, the reaction with oxygen would render DMPS inactive. Cohen after in-depth evaluation of plasma and urine concentrations before and after TD-DMPS concluded: ‘Our results argue that TD-DMPS is an ineffective metal chelator‘ (Cohen 2012). Dr. Van der Schaar, founder of IBCMT, applied the TD-DMPS to patients with a known mercury burden. MTM analyzed the patients’ blood samples, even repeated blood tests, but could not detect any amount of mercury or any other toxic metal in the blood stream, nor could we detect an increase in urinary metal excretion after TDDMPS treatment. Dr. Ruprecht. research scientist and author of the Dimaval monograph. published 2008 by Heyl, Berlin stated that ‘I cannot imagine that adequate blood levels of DMPS are achieved by sniffing, transdermal or homeopathic administration in order to mobilize and excrete deposits of heavy metals in the body. Furthermore, the sensitivity of the active substance to oxidation must be taken into account with these methods of administration. DMPS should be administered only via the oral or parenteral (i.m. or i.v.) route.
Summary
TD-DMPS is ineffective.
References
- Ruprecht J (2008) Dimaval Wissenschaftliche Produktmonographie. Heyl, Berlin.
- Andersen O (1999) Principles and recent developments in chelation treatment of metal intoxication. Chem Rev 99: 2683-2710.
- Aposhian MM, Maiorino RM, Xu Z (1996) Sodium 2.3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonate (DMPS) treatment does not redistribute lead or mercury to the brain of rats. Toxicology 109: 49-55.
- Flora SJS, Pachauri V (2010) Chelation in Metal Intoxication. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7: 2745-2788.
- Clarkson TW, Magos L, Cox C, Greenwood MR, Amin-Zaki L, et al. (1981) Tests of efficacy of antidotes for removal of methyl mercury in human poisoning during the Iraq outbreak. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 218: 74-83.
- Gonzalez-Ramirez D, Zuniga-Charles M, Narro-Juarez A, Molina-Recio Y, Hurlbut KM, et al. (1998) DMPS (2.3-Dimercaptopropane-1-sulfonate. Dimaval) Decreases the Body Burden of Mercury in Humans Exposed to Mercurous Chloride. J Pharmacology 287(1): 8-12.
- Kazantzis G (1994) Diagnosis and treatment of metal poisoning – general aspects; IN: Nordberg GF. Fowler BA. Nordberg. McNeill Consumer Products Co. Chemet Product Information; McNeill Consumer Products Co. Fort Washington. PA. USA.
- Cohen JP, Ruha AM, Curry SC, Biswas K, Westenberger B, et al. (2013) Plasma and Urine Dimercaptopropanesulfonate Concentrations after Dermal Application of Transdermal DMPS (TD-DMPS). J Med Toxicol 9: 9-15.
- Campbell JR, Clarkson TW, Omar MD (1986) The therapeutic use of 2.3-dimercaptopropane-1-sulfonate in two cases of inorganic mercury poisoning. J Am Med Assoc 256: 3127-3130.
- Gerhard I, Waldbrenner P, Thruo H, Runnebaum B (1992) Diagnosis of heavy metal loading by the oral DMPS and chewing-gum tests. Klin Lab 38: 404-411.
- Aposhian HV (1983) DMSA and DMPS - water soluble antidotes for heavy metal poisoning. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 23: 193-215.
- Schiele R, Schaller KH, Weltle D (1998) Mobilization of mercury reserves in the organism by means of DMPS (Dimaval). Med Soc Med Prevent Med 24: 249-251.
- Chisolm JJ Jr, Thomas DJ (1985) Use of 2.3-dimercaptopropane-1-sulfonate in treatment of lead poisoning in children. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235: 665-669.
- Hrdina R, Gersl V, Vávrová J, Holeckova M, Palicka V, et al. (1998) Myocardial elements content and cardiac function after repeated i.v. administration of DMPS in rabbits. Hum Exp Toxicol 17(4): 221-224.

 Mini Review
Mini Review