Abstract
The aim of our study was the screening of blood cells on the basis of morphology for different diseased with Morphogenetic characters I e. ear lobe attachment, clinodactyly and tongue rolling. For this purpose, 318 blood samples were collected randomly. Samples were examined under the compound microscopic by using 100x with standard method. The results show 63 samples were found normal while in 255 samples, different types of morphological changes were observed which was 68.5%, in which Bite cell 36%, Elliptocyte 34%, Tear drop cell 30%, Schistocyte 26%, Hypochromic cell 22.5%, Irregular contracted cell 16%, Echinocytes 15.5%, Roleaux 8%, Boat shape 6.5%, Sickle cell 5%, Keratocyte 4% and Acanthocytes 1.5%. During the screening of slides, bite cell, elliptocyte, tear drop cell, schistocytes, hypochromic cell, irregular contracted cells were found frequently while echinocytes, boat shape cell, acanthocytes, sickle cells and keratocytes were found rarely. The result showed that individuals in which morphological changes were observed as 54% were able to tongue rolling, 31.8% were clinodactyly (curved little finger) and 22.2% were attach ear lobe.
Keywords: Human blood; Diseases; Morphological; Acanthocytes; Keratocyte
Abbreviations: WBC: White Blood Cells; RBC: Red Blood Cells; G6PD: Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Introduction
Blood is survival sustaining fluid that flow through the whole circulatory system .blood carries nourishment, electrolytes, vitamins, hormones, oxygen, heat, antibodies and immune cells to the body tissue, and also carrying away waste product and carbon dioxide from the body tissue [1]. The normal total blood volume is about 8% of the body weight. In adults the quantity of blood is 4-6 quarts, it is highly specialized tissue, their composition is from more than 4000 kinds of components [2]. Blood is composed of three types of blood cell, Red Blood Cell or erythrocytes (RBC), White Blood Cell or leucocytes (WBC), Platelets or thrombocytes and Plasma. The science or study of blood, blood disease and bloodforming organ is hematology. It is the branch of internal medicine, deals with the pathology, etiology, treatment, prognosis and prevention of blood related disorders. Erythrocytes are microscopic cells have no nuclei. Normally 40 to 50% of blood is made up of red blood cells. Blood remove carbon dioxide and convey oxygen from lungs to all tissue of the living body. The erythrocytes are continuously manufacture from stem cells in the bone marrow per second at the rate of about 2-3 million cells. Erythrocytes is composed of about 95 % of hemoglobin. It is a gas transporting molecule and containing about 270,000,000 iron rich hemoglobin molecules [2]. Red blood cell are described as a biconcave disc with survival time of 120 days. The average diameter of red blood cell is from 7-8um and an average volume of 90 FL [3].
Two types of terms used to describe the normal morphology of red blood cell, Normocytic cell and Normochromic cell. Normocytic cells that have normal size while Normochromic cell have the normal concentration of hemoglobin. Different type of abnormalities in the membrane of cell also change the shape of cell. A generic term poikilocyte represent red blood cell with irregular shape, it can be classified by definite shape changes some are diagnostically significant and while some others are non-specific. The red blood cell shape is recognized specifically e.g. echinocyte, acanthocyte, keratocyte [4]. Hematological malignancies comprise a group of malignant disorders including myelomas, leukemia and lymphomas [5].
White blood cell also called Leucocytes which is the part of the immune system and perform function in immune responses. They make up less than 1% of the cells in blood and involved in recognizing and neutralizing invaders such as virus and bacteria. The leucocyte contains normal nucleus and mitochondria. Under the microscope they come in five major types and divided into two groups named for their appearance [6]. White blood cell are divided into two categories on the base of chemical characteristics and structure, the granulocytes that contain the granules which are bounded by cytoplasmic membrane and the agranulocytes, that lack obvious granules. Granulocytes include neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils. Neutrophils form the 50-70% of white blood cell population and are most numerous of White blood cell.
Two types of chemicals are released by basophils, histamine and heparin. In allergic reactions histamine is involve and heparin is involved in anticoagulant. While to fight with parasitic worm eosinophil is responsible. Eosinophil release toxin that involved in inflammatory response and kill the worms. Agranulocytes include monocytes and lymphocytes, their cytoplasm is without granules [6]. The morphological features of white blood cells are less specie dependent then erythrocytes [4]. Platelets was discovered by Giulio Bizzozero in 1882 [7]. Thrombocytes are small blood cells 1.5- 3μm in diameter and play an important role in hemostasis and in coagulation mechanism. Morphological abnormalities in platelets are found in hematological diseases such as myeloproliferative syndromes and acute mega karyoblast leukemia.
But for many decades the multifunctional and dynamic nature of platelets remain a field of interest for biologist. Hemostasis or blood coagulation is not the only function of platelets. Platelets are highly sensitive to different types of disease states assigned it to be one of the most affordable markers [8]. The mature platelets are 2-3μm in diameter and for 5-9 days remain alive. Approximately 1/3 of platelets is stored in spleen and 2/3 circulates in blood. The normal count of platelet is (150-400) multiply 10 to the power 3 per microliter of blood. Plasma membrane of thrombocytes contain phospholipid bilayer which is the site of expression of surface receptor and lipid rafts which are helpful in intracellular trafficking and signaling [9].
Platelets have two storage granules alpha and dense granules which perform the function of storage of biologically active molecules involved in the recrution of other cells during inflammation and initiation of coagulation [10]. Platelets play an important role in defending viral pathogens. Platelets secrete chemokines after activation, that attract the immune cells which help in the finishing of virus platelets has antimicrobial function, secret antimicrobial molecules including platelet microbicidal peptides and kinocidins. These anti-microbial molecules kill pathogens. Another defending role of platelets is finishing of virus by phagocytosis [11]. Platelets are the smallest cells and in thrombus formation one of the main players. They undergo a series of biochemical and morphological changes. Platelets have the ability to bind to non-endothelial surface, bind to other platelets, secrete substance store in internal granules.
Platelet indicating differential dysfunction, aggregation, hyperactivation, and are capable of expressing the character of disease. Platelet biomarker is an important impact on the global scene of clinical application and development [12]. Blood is composed of about 55% of plasma. It is a light-yellow liquid and carries water, salt and enzymes. Plasma primary purpose is the transport of protein, hormones and nutrients to body parts. Blood cells deposit their waste products to plasma and it helps in removing it from the body [13]. When all types of blood cell such as erythrocytes, leukocyte and platelets are separated from the blood, plasma is derived. They have 90-92 % water, plasma including constituents have electrolytes i.e. sodium, chloride, potassium, magnesium, bicarbonate and calcium. The blood wastes collected from blood cells are transported to kidney for excretion. Plasma containing 6-8% fibrinogen. Fibrinogen is circulating in the blood is transformed to fibrin when blood clotting is started which in turn helps to form constant blood clot [14].
Plasma origin is interesting because no organ produces it. It forms from water and salts absorbed through digestive tract [15]. A condition in which lack of mineral iron in the body commonly caused a disorder known as anemia. Body needs iron for protein hemoglobin. Iron helps erythrocytes in the transport of oxygen to different parts of the body. Thalassemia is an inherited disorder caused by genetic mutation that prevent the normal production of hemoglobin [16].
Method and Material
Study Area
The current study was carried out in district Swat with population of 2.31 million. District Swat is surrounded by, from east by Kohistan and Shangla District, from north by Chitral and Ghizer District of Northern region whereas at the south by Buner and Malakand District (Figure 1 & Table 1).
Materials
The materials that are used in our study include
a) For cleaning of fingertip and for the fixation of slides, ethanol is used.
b) Cotton
c) For pricking of finger, disposable lancet is used.
d) Both thick and thin smears are prepared on, clean slides.
e) For the coloration of blood cells, Gimesa stain are used.
f) For cleaning of microscope, Xylene is used.
g) For better detection, Oil emersion is used.
h) For screening of blood, 100 X microscope is used.
Method
Collection of Blood Samples: The duration of our collection is from October 2019 to November 2019, the blood samples from students of different departments are collected for the screening of blood morphology. Informed consent was taken from individuals. A total of 318 individuals comprised of 105 females and 213 males of different age groups were included in the study. During our study, a questionnaire was designed to collect information that contain name, age, gender, locality and also about some external features. This questionnaire was given to the students before the collection of blood samples. During the collection of blood samples first we used ethanol to clean tip of ring finger and used the cotton to dry the finger from ethanol, then used the disposable lancet for pricking of finger. The lancet that once used for pricking were discarded to avoid its reuse.
Preparation of Blood Smears: The first drop of blood that comes after pricking the fingertip are discarded. The other drops of blood that comes from the prickled area were placed on the slide for the preparation of both thick and thin smear. Both the smears were prepared on one slide. Two clean slides were used, one for the preparation of smear and second were used for blood film. Fixation of Blood Smear: The prepared smears were then dried in air for a small time. After this ethanol were used for the fixation of blood smears and allowed it in air for few minutes to dry. When it became dry then dip it in water for removing of ethanol from slide.
Staining of Slides: The fixed smears are then kept in gimesa stain approximately for 15 minutes. After 15 minutes the stain slides are removed from the gimesa stain and allowed in air to become dry.
Microscopy of Slides: When slides were fully dried then present it for microscopy. The microscopy of slides was performed on 100X of a microscope of a microscope. When the slide was observed under 100X of microscope, an oil emersion was used on the site of slide. For better detection oil emersion is used. During the microscopy of slides, different morphological changes were identified.
Results
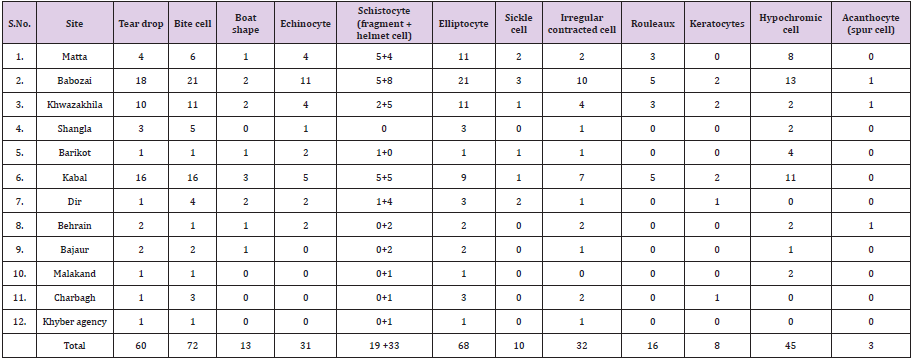
During the current study screening of human blood was carried out for different disease on morphological base. For this purpose, a total of 318 samples were collected from the students of different department in the university of swat belonging to different area of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. During the screening and microscopic study of the samples 118 were unclear for study while remaining 200 samples were studied in detail with the help of compound microscope by using 100x standard method. It was concluded that human blood cells have different shapes and size (Figure 2). During the current study 12 different types of morphological shapes of the blood cells were identified (Figure 3).
a) Tear drop (Dacryocyte)
b) Bite cell
c) Boat shape cell
d) Echinocyte (burr cell)
e) Schistocyte (helmet cell, fragment cells)
f) Elliptocyte (pencil cell)
g) Sickle cell
h) Irregular contracted cell
i) Rouleaux
j) Keratocytes
k) Hypochromic cell
l) Acanthocyte (spur cell)
Tear Drop (Dacryocyte)
Tear drop cell have slightly rounded or blunted ends. It is a kind of poikilocytosis (variability in RBC shapes). They can be seen in patients with splenic abnormalities, vitamin B 12 deficiency and some other types of anemia. Tear drop cells in the blood stream are most generally associated with iron deficiency anemia. In current study in 60 individuals tear drop were observed (Figure 3).
Elliptocyte (ovalocytes)
Elliptocytes are elongated blood cells, vary in shape from egg shaped to rod or pencil shape. In normal blood very rare elliptocytes may be found. Elliptocytes increased in iron deficiency anemia. In current study elliptocytes were observed in 68 individuals (Figure 4).
Hypochromic cell
In this type of erythrocyte have low hemoglobin level than normal. Due to Less levels of hemoglobin red blood cells appear paler in shade. Most microcytic anemias are hypochromic. This frequently happen when there is less no of hemoglobin that transport oxygen in the erythrocytes. In current study hypochromic cells were observed in 45 individuals (Figure 5).
Bite cell
The bites are usually shaped like a semicircle but may also be irregular. Abnormal shaped erythrocyte with one or more semicircular portions detached from the cell periphery. The “bites” result from the deletion of hemoglobin with a distorted structure by specific cells “macrophages” in the spleen. Bite cell formation occur due to deficiency of GP6D (Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase) and unstable hemoglobin. Hemolytic anemia associated with severe liver disease is another caused where bite cells are formed. In current study bite cells were found in 72 individuals (Figure 6).
Schistocytes
Schistocyte are fragmented erythrocytes that can take different shapes. They can be seen as helmet shaped, triangular, or comma shaped with sharp ends. They are smaller than normal red blood cells. They usually stain severely but rarely pale as the result of loss of hemoglobin at the period of fragmentation. They are frequently seen in patients having hemolytic anemia. In current study schistocytes were observed in 52 individuals in which 33 are helmet cells and 19 are fragments cells (Figure 7).
Keratocytes
They are fragmented erythrocytes. They come in a range of shapes instead of the pale-centered biconcave shape. They resemble a red cell with two horn like structure therefore also called ‘horn’ cell. It usually indicates an infection of the blood vessel walls, causes the membrane of some red blood cells to burst such as hemolytic syndromes. In current study keratocyte were observed in 8 individuals (Figure 8).
Sickle cell (Drepanocytes)
They are elongated red blood cells with pointed ends. It is formed by an inherited irregular form of hemoglobin. These hemoglobin tend to collect after unloading oxygen. In sickle cell anemia, the erythrocytes become rigid and have rod like structure. Due to irregular cell blood vessel may blocked causing tissue and organ damage. They are seen in sickle cell anemia, hemoglobin S/ beta-thalassemia. In current study sickle cells were observed in 10individuals (Figure 9).
Echinocytes (Burr cell)
Echinocytes are spiculated RBCs. They have multiple short, crusty projection evenly spaced over the cell surface. the central pallor is retained. Echinocyte can be seen in uremic patients. The projections of the cell membrane are typically numerous, sharp and be likely to be equally spaced around the edge. Spicules are usually of uniform size. In current study in 31 individuals’ echinocytes were observed (Figure 10).
Irregular Contracted Cells
They lack central pallor, the hemoglobin is distributed irregularly and condensed in the red blood cells. Irregularly contracted cells resemble spherocytes in that they are hyperchromatic and lack central pallor. They have an irregular outline and sometimes there are also small protrusions that can be shown to represent Heinz bodies. Common causes of irregularly contracted cells are hemolysis in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase shortage and he moglobinopathies, such as hemoglobin C and unstable hemoglobin’s. In current study irregular contracted cell were observed in 32 individuals (Figure 11).
Boat Shape Cell
The cell body may be dense or normal but retains central pallor. These cells have sharpened ends. In some cells it may also be slit like. these cells are formed in the presence of abnormal hemoglobin and also associated with sickle diseased. In current study boat shape cell were observed in 13 individuals (Figure 12).
Rouleaux
It is a bunch of red blood cells. Rouleaux formation may occur due to the presence of large amount of plasma protein in blood such as fibrinogen or immunoglobulins. condition that caused rouleaux formation include infections, inflammatory and connective tissue disorders and cancer. In current study rouleaux were observed in 16 individuals (Figure 13).
Acanthocyte (spur cell)
They are spiculated cells with irregular, pointed or club like projections that are unequally distributed on the cell surface. Central polar is absent. It has spiked cell membrane, due to abnormal thorny projections. It forms as a result of membrane lipid abnormalities. During current study acanthocytes were observed in 3 individuals (Figure 14).
Discussion
During the current study the results represents 12 different type of human blood cells based on morphological size variation yielding tear drop, bite cell, boat shape cell, echinocytes, schistocytes, elliptocytes, sickle cell, irregular contracted cell, rouleaux cells, keratocytes, hypochromic cells and acanthocytes. Mortimer [16] reported that in the marginal blood smear of two patients with Heinz bodies hemolytic anemia morphological abnormal red blood cells were observed, that abnormal cell were termed as bite cell because of their appearance of a piece bitten out. in each case these cells was demonstrated that led to the doubt of oxidative hemolysis. In our current study bite cell were observed in 72 individual which are caused by the GP6D deficiency and unstable hemoglobin. Steffen & Svetina [17] reported that red blood cells form aggregates in the form of rouleaux and this aggregation process is reversible. by the activation of platelets aggregation mechanism is caused in case of wound healing aggregation lead to clot formation which is lifesaving but in case of thrombus induce strock it cause death. During our current study rouleaux cells were observed in 16 individual androuleaux formation is caused by the presence of high concentration of plasma protein such as fibrinogen or immunoglobulin in the blood.
Qurashi et al. [18] worked on the prevalence and regional distribution of sickle cell disease in Saudi child. In 108 of 45,682 children’s sickle cell disease was detected .the ratio of sickle cell disease is high in eastern region. In our study we observed sickle cell in 10 adult individuals which is the risking factor for anemia and thalassemia. Alvar et al. [19] worked on erythrocyte life span in iron deficiency anemia. The study were performed on six patients having hypochromic red cell with iron deficiency and in the circulation of two patients having normal red cells, The life span of hypochromic cells were decreased, while in patients with iron deficiency anemia normal cells survive normally . They conclude that hypochromic cells have short life span. The current results of our study showed 45 adult individuals have hypochromic cells in their blood smears which is the risking factor for microcytic anemia. Shochienin [20] worked on echinocytes stomatocyte transformation and shape control of human erythrocyte.
They conclude that the erythrocyte has an energy needy shape, y-globulin was found to induce echinocytic transformation. During our current study we observed 31 echinocyte cells in the blood smear of adult individuals which is the risking factor for high level of urea in blood. Farolino DL et al. and Hematol [21] worked on tear drop shape red cell in autoimmune hemolytic anemia. The presence of tear drop shape cell in peripheral blood has alter myelofibrosis. They access two patients with the splenomegaly having hemolytic anemia, on the examination of their blood tear drop shape red cell was observed. During our study we observed tear drop shape cells in the blood smear of 60 adult individual out of 200 samples. In a distinct group of inherited and acquired diseased state acanthocytosis is encountered which represent uncommon ethological variant of erythrocyte morphology. Due to difference in the membrane protein, acanthocytes is associated with the McLeod phenotype probably. acanthocyte have a decreased survival in the circulation owing to splenic destruction. We observed acanthocytes in the blood smear of 3 adult individuals.
Neubauer and Robier [22] Study erythrocyte morphology in patients with B-thalassamia minor. They examined blood smear of 33 patients by using light microscope. Results show that ovalocytes in 32 subjects, dacrocytes (81%), elliptocytes (75.8%) and irregular contracted cells (63.6%) were commonly found. Schistocytes (15.2%), bite cell (65%) and pencil cell (3%) were rarely found. They observed elliptocytes, ovalocytes, dacryocytes and irregular contracted cells in large number in the analyzed slides. In our current study the blood smear of 200 patients were examined in which ovalocytes are in 68 , dacrocytes in 60 , schistocytes in 52 , irregular contracted cell 32 , bite in 72 individuals. We observed bite cells and dacrocytes cells in the majority of analyzes slides. Rodgers et al. worked on the elliptocytes and tailed piokilocytes correlate with the severity .in this study they examined abnormal red blood cell morphology. They count thousand red blood cells from each of the 22 patients and correlation were determined between parameters. They observed with increased in the number of elliptocytes, level of hemoglobin is decreased and with increase in the number of tailed piokilocytes, level of hemoglobin. In their result they point out that microscopic assessment of red blood cells morphology remains an important tool for the pathologist to estimate the severity of anemia in patient with iron deficiency. In our current study we observed elliptocytes in the blood smear of 68 individuals [23-31].
Conclusion
The aim of our study was the screening of human blood for different diseased on the base of morphology. For this purpose, we collected 318 blood samples from asymptomatic population of university of swat whose belongs to different localities of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. During the study 118 samples was unclear for screening and the remaining 200 was clear for the screening through microscopy. In 200 clear slides 63 were normal and in remaining 137 slides different morphological changes in the shape of cells was observed. The total percentage of morphological changes in clear slides were 68.5%, in which Bite cells are 36 %, Elliptocytes 34%, Tear drop cells 30 %, Schistocytes 26% ( helmet cells 16.5 % and fragment cells 9.5%), Hypochromic cell 22.5%, Irregular contracted cells 16%, echinocytes 15.5%, rouleaux 8%, Boat shape 6.5%, Sickle cell 5%, Keratocyte4% and Acanthocytes are 1.5%.
In the analyzed slides the ratio of bite and teardrop cells is higher. The characteristic of tear drop is myelofibrosis which is also seen in severe iron deficiency, megaloblastic anemia and thalassemia. Bite cell is produced due to the deficiency of glucose s6- phosphate dehydrogenase and risking factor for hemolytic anemia. Morphogenetic character is physical character of an individual. In the present study different morphogenetic characters i.e. ear lobe attachment, clinodactyly (curved little finger) and tongue rolling were also observed. The result showed that individuals in which morphological changes were observed in the shape of cells, prevalence of these morphogenetic characters was observed as; 54% were able to tongue rolling, 31.8% were clinodactyly (curved little finger) and 22.2% were attach ear lobe [31-42].
References
- (2019) Overview of Blood and Blood Components. URMC.
- O Neil D (1999) Blood Components.
- Westerman M P, Bacus J W (1983) Relationship Red Blood Cell Morphology in Sickle Cell Anemia as Determined by Image Processing Analysis: The to Painful Crises. American journal of clinical pathology 79(6): 667-672.
- (2013) Report on white blood cells. cornell university college of veterinary medicine eClinpath
- Hassan M, Abedi Valugerdi M (2014) Hematologic malignancies in elderly patients. Haematologica 99(7): 1124.
- (2019) Components of blood Khan Academy.
- Ribatti D, Enrico Crivellato (2007) Crivellato E Giulio Bizzozero and the discovery of platelets. Leuk Res 31(10): 1339-1341.
- Cerletti C, Tamburrelli C, Izzi B, Gianfagna F, De Gaetano G (2012) Platelet leukocyte interactions in thrombosis. Thrombosis research 129(3): 263-266.
- Blair P, Flaumenhaft R (2009) Platelet α-granules: basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood reviews, 23(4): 177-189.
- Flaumenhaft R (2003) Molecular basis of platelet granule secretion. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 23(7): 1152-1160.
- Seyoum M, Enawgaw B, Melku M (2018) Human blood platelets and viruses: defense mechanism and role in the removal of viral pathogens. Thrombosis journal, 16(1): 16.
- Ghoshal K, Bhattacharyya M (2014) Overview of platelet physiology: its hemostatic and no hemostatic role in disease pathogenesis. The Scientific World Journal 2014.
- (2019) What Is Plasma. Stanford Children Health.
- David H Yawn (2019) Plasma. Britannica.
- Mathew J, Bhimji S S (2018) Physiology, Blood Plasma. In Stat Pearls.
- Greenberg M S (1976) Heinz Body Hemolytic Anemia: Bite Cells A Clue to Diagnosis. Archives of internal medicine 136(2): 153-155.
- Wagner C, Steffen P, Svetina S (2013) Aggregation of red blood cells: from rouleaux to clot formation. Comptes Rendus Physique 14(6): 459-469.
- Al Qurashi, M M El Mouzan, M I Al Herbish, A S Al Salloum A A, Al Omar A A (2008) The prevalence of sickle cell disease in Saudi children and adolescents Saudi Med J 29(10): 1480-1483.
- Loría A, Sánchez Medal, L Lisker R, Rodríguez E D (1967) Red cell life span in iron deficiency anaemia. British journal of haematology 13(3): 294-302.
- Reinhart W H, Chien S (1987) Echinocyte‐stomatocyte transformation and shape control of human red blood cells: Morphological aspects. American journal of hematology 24(1): 1-14.
- Farolino D L, Pradip K Rustagi, Mark S Currie, Thomas D Doeblin, Gerald L Logue (1986) Tear drop shape red cell in auto immune hemolytic anemia. American journal of hematology 21(4): 415-418.
- Körber C, Wölfler A, Neubauer M, Robier C (2017) Red blood cell morphology in patients with β-thalassemia minor. Journal of Laboratory Medicine 41(1): 49-52.
- (2019) What is hematology.
- Bessis M (1973) Red cell shapes. An illustrated classification and its rationale. In Red cell shape Springer Berlin Heidelberg 1-25.
- Blasi B, D Alessandro A, Ramundo N, Zolla L (2012) Red blood cell storage and cell morphology. Transfusion medicine 22(2): 90-96.
- Bosman G J (2018) Disturbed red blood cell structure and function: An exploration of the role of red blood cells in neurodegeneration. Frontiers in Medicine 5: 198.
- Carmel R (1996) Prevalence of undiagnosed pernicious anemia in the elderly. Archives of Internal Medicine 156(10): 1097-1100.
- Diez Silva, M Dao, M Han, J Lim C, T Suresh S (2010) Shape and biomechanical characteristics of human red blood cells in health and disease. MRS bulletin, 35(5): 382-388.
- Duke W W (2019) The relation of blood platelets to hemorrhagic disease: description of a method for determining the bleeding time and coagulation time and report of three cases of hemorrhagic disease relieved by transfusion. Journal of the American Medical Association 55(14): 1185-1192.
- Ford J (2013) Red blood cell morphology. International journal of laboratory hematology 35(3): 351-357.
- Hebbel R P, Yamada O, Moldow C F, Jacob H S, White J G, (1980) Abnormal adherence of sickle erythrocytes to cultured vascular endothelium: possible mechanism for microvascular occlusion in sickle cell disease. The Journal of clinical investigation 65(1): 154-160.
- Ifeanyi O E, Chinwe A A O, Chinedum O K, Abum S C (2018) A Review on Platelets and Coagulation. Int J Curr Res Med Sci 4(7): 17-24.
- Lee H, Chen Y P P (2014) Cell morphology-based classification for red cells in blood smear images. Pattern Recognition Letters 49(1): 155-161.
- Madhloom H T, Kareem S A, Ariffin H, Zaidan A A, Alanazi, et al. (2010) An automated white blood cell nucleus localization and segmentation using image arithmetic and automatic threshold. Journal of Applied Sciences, 10(11): 959-966.
- Mark S Rodgers, Chang (1999) Elliptocytes and tailed poikilocytes correlates with severity of iron deficiency anemia. American Society of clinical pathologist. 111(5): 672-675.
- Teresa Scordino (2016) Teardrop cells or Dacrocytes. ASH.
- Patidar E (2018) Red blood cell morphology: still an important tool for anemia typing. International journal of Research Grathaalayah 6(3).
- Piuri V, Scotti F (2004). Morphological classification of blood leucocytes by microscope images. IEEE International Conference CIMSA 103-108.
- Rakshit P, Bhowmik K (2013) Detection of abnormal findings in human RBC in diagnosing sickle cell anaemia using image processing. Procedia Technology 10: 28-36.
- S Skalak, Branemark P I (1969) Deformation of red blood cells in capillaries. Science 164(3880): 717-719.
- Soltanzadeh R, Rabbani H (2010) Classification of three types of red blood cells in peripheral blood smear based on morphology. In IEEE 10th international conference on signal processing proceedings 707-710.
- Barshtein G, Bergelson L, Gratton E, Yedgar S (1996) Human red blood cell shape and volume are changed by physiological levels of hydrostatic pressure. J Basic clin physiological pharmacy 7(4): 321-329.

 Research Article
Research Article