Abstract
In December 2019 a pandemic of acute respiratory distress syndromes occurs in Wuhan, china, the early evidence suggests this may be due to exposure to local sea foods in china. The pathogen was isolated from Chinese patients and designated as severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-COV-2). COVID-19 mainly affects lungs by producing respiratory predominant symptoms like fever, cough, flu and dyspnea. As SARS-Cov-2 firstly find a mechanism to escape the immune system of humans and animals followed by a huge release of cytokines named as cytokine storms and the hyper activation of the other immune system responses. To avoid these conditions in any type of viral infections such as in SARS-Cov-2 infections and influenza virus induce lung injury vitamin D is now is recently considered as proposed therapy. Vitamin C acts as strong antioxidant and help to scavenge all the damaged species that is why vitamin C is regarded helpful in SARS-Cov-2 and other viral infections. Many findings from different clinical studies show that vitamin C when administrated orally can reduce SAR-Cov-2 and other viral infection. Taking vitamin C intravenously has also profound effect on the reduction of viral infections. As health care workers and professional are risk community for COVID-19 so vitamin C should be included in prevention and treatment of COVID-19 in this community. As vitamin C is also a prooxidant so smaller pharmacological concentration of vitamin C milli-molar is beneficial. But in case of COVID-19 high intravenous dose of vitamin C would be the right choice.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-Cov-2; Viral Infections; Vitamin C; Immune Modulation; Vitamin D; Influenza Virus
Introduction
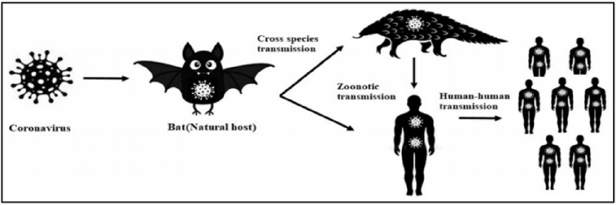
In December 2019 a pandemic of acute respiratory distress syndromes occurs in Wuhan, china, the early evidence suggests this may be due to exposure to local sea foods in china [1]. The pathogen was isolated from Chinese patients and designated as severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-COV-2). WHO announces this as global pandemic on March 11; 2020. COVID-19 mainly affects lungs by producing respiratory predominant symptoms like fever, cough, flu and dyspnea [2]. The virus primarily attacks the angiotensin converting enzyme-2 receptor (Ace2) of the lung [3]. Corona virus are enveloped, positive stranded RNA virus, genome size ranges between 26kb to 32 kb, resembles a solar corona, have four sub families i.e. alpha, beta, gamma and delta Coronaviruses and was first described by Tyrell and Bynoe in 1996 [4-7]. Most accepted model at first was animal to human transmission from Wuhan sea food market but after sometimes person to person transmission model was the most acceptable mode of transmission i.e. by aerosol, air droplets and fecal oral transmission has also clarified [8-15].
As till now there is no specific pharmacological treatment against COVID-19 [16,17]. By advising people to adapt healthy lifestyle and to consume more healthy food would be more helpful to combat with this pandemic of COVID-19. People should strictly follow WHO recommendations regarding nutritional supplements [18-20]. Immune system has a major role in fighting against different types of infection but for proper immune cells functioning there is need of some supplements like vitamin C [21-23]. This vitamin has a major role in maintaining proper immune cell functions [24]. Lake of vitamin C makes one more susceptible to scurvy and pneumonia [25- 28]. Taking vitamin C less than or equal to 1g/day reduces the risk of mortality up to 35% from common colds [29]. Using early large dose of vitamin C intravenously can reduce risk of COVID-19 [30]. This review is an effort to highlight the immune modulatory function of vitamin especially vitamin C and role of these vitamins in prevention and treatment of COVID-19.
Etiology, Epidemiology and Mortality Rate of COVID-19
On the basis of previous reports, it was confirmed that SARSCov- 2 has up to 96% genome resemblance with that of SARS Coronaviruses derived from bats [31]. Therefore, this virus is named as 2019 novel corona virus. The virus contains enveloped RNA and resembles solar corona [32]. The genome of coronavirus is enclosed in an envelope on the surface of that envelope there are spike protein which are four in number and these spikes help the virus for attachment to the human ACE2 receptor for entering into host cell [33,34]. At early time the transmission of the outbreak was attributed to sea animals but later on human to human transmission was also confirmed [35]. At the end of January WHO reported approximately 10,000 known cases. But at the middle of February about 13332 cases was reported [31]. Approximately 74,280 overall cases in china and 924 cases is reported in other countries by February 19, 2020 [36-38]. After some time, virus spreads in nearly 210 countries on April 26, 2020. And over all 2.4 million confirmed cases was reported in the month of April mainly on 26 to 30 April. 15 % mortality rate was observed in Algeria, 13.95% in Belgium, 13% in Italy and United Kingdom, and Netherland (11.35%). Lower mortality rate was found in countries Qatar 0.17%, Singapore 0.2%, United Arab Emirate 0.6%, and Australia 0.97The WHO keeps on updating and sharing these figures on daily basis and till April 28th it had issued ninety seven reports giving country wise details of number of cases [39] (Figure 1).
Role of Vitamins as Adjuvant Therapy Against SARSCov- 2 and Other Viral Infections
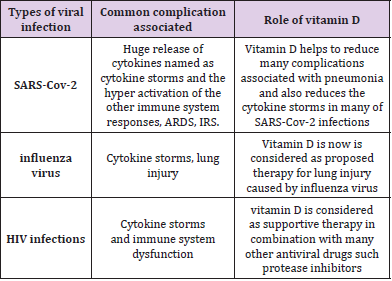
As SARS-Cov-2 firstly find a mechanism to escape the immune system of humans and animals followed by a huge release of cytokines named as cytokine storms and the hyper activation of the other immune system responses. As these are also common mechanisms in the acute respiratory syndrome and inflammatory response syndrome. To avoid these conditions in any type of viral infections such as in SARS-Cov-2 infections and influenza virus induce lung injury vitamin D is now is recently considered as proposed therapy [39-41]. Vitamin D helps to reduce many complications associated with pneumonia and also reduces the cytokine storms in many of SARS-Cov-2 infections [42,43]. In case of HIV infections vitamin D is considered as supportive therapy in combination with many other antiviral drugs such protease inhibitors and many more [44]. Patients with ARDS can get recovered if he was pre-treated with vitamin D. vitamin D helps to modulate the rennin- angiotensin system which in turn regulate the normal expression of ACE2 receptor a common binding site for SARS-Cov-2.
The beneficial role of vitamin D get more clearer because of the presence of vitamin D receptor genes so if proper amount of the vitamin D is not present the body the receptor genes will make one more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections [45-48]. As COVID-19 is now declared as pandemic and the finding of effective therapy against this pandemic would take a lot of time, so the world is seeking to find an alternative to protect themselves from this pandemic. Vitamin C is also considered as one of the possible therapy for COVID-19 because vitamin C has a promising role in maintaining proper body functions and also helps in removing damaged ROS and protect cell from oxidative damage. Vitamin C is needed in larger amount for proper immune function. The beneficial role of vitamin C in SARS-Cov-2 and other viral infections is clear from the fact the level of vitamin C decreases during infection and body needs more of it to fight [49]. Table 1 shows the common complications associated with SARS-Cov-2 and other viral infections and role of vitamin D [39-48].
Table 1: Shows the common complications associated with SARS-Cov-2 and other viral infections and role of vitamin D.
Vitamin C as A Proposed Therapy for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19
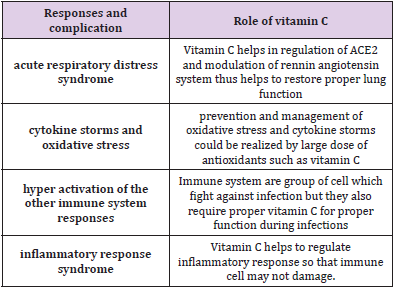
As acute respiratory distress syndrome, multi organs failure, cytokine storms, cellular injury are all the outcomes of SARS-Cov-2 and other viral infections. Vitamin C found to be helpful in these complications. Vitamin C acts as strong antioxidant and help to scavenge all the damaged species that is why vitamin C is regarded helpful in SARS-Cov-2 and other viral infections. Many findings from different clinical studies show that vitamin C when administrated orally can reduce SAR-Cov-2 and other viral infection. Taking vitamin C intravenously has also profound effect on the reduction of viral infections. There are two possible route of administration for vitamin C one is orally and other is intravenously studies have revealed that both administration routes of vitamin C has no side effects. As health care workers and professional are risk community for COVID-19 so vitamin C should be included in prevention and treatment of COVID-19 in this community. As vitamin C is also a prooxidant so smaller pharmacological concentration of vitamin C milli-molar is beneficial. But in case of COVID-19 high intravenous dose of vitamin C would be the right choice [50-53] (Table 2).
Table 2: Shows list adverse responses of body against viral mechanism of infections and role of vitamin C in modulation of the responses.
Why Vitamin C as Therapy Against SARS-COV-2?
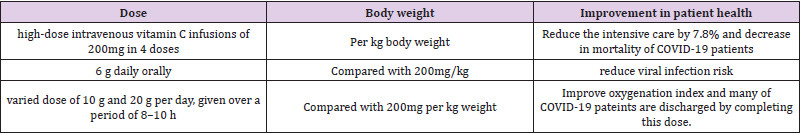
For reduction of ARDS, cytokine storms, neutrophils damage, oxidative stress, alveolar damage, acute respiratory failure, and mortality caused due to SARS-Cov-2 vitamin C is a proposed drug [54-57]. In a report of 29 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, 27 (93%) showed increased hsCRP, a marker of inflammation and oxidative stress. Transcription factor, nuclear factor erythroid 2 (nfe2)-related factor 2 (nrf2), is a major regulator of antioxidant response element (ARE)-driven cytoprotective protein expression. Activation of Nrf2 signaling plays an essential role in preventing cells and tissues from injury induced by oxidative stress. Vitamin C is important part of cellular antioxidant system” [58,59]. Vitamin C is very effective in intensive care management [60]. Vitamin C is a suggested therapy in COVID-19 because it minimizes the effect of oxidative stress and cytokine and this promising role was also observed in 146 COVID-19 patients [61]. It has been reported that administrating high intravenous dose of 200mg/kg body weight can reduce clinical symptoms in viral infected [62]. And this reduction was also observed in patients infect with influenza virus [63,64]. Using antioxidants in nutrients decrease inflammatory response syndrome cause by SARS-Cov-2 [65]. Oral dosage vitamin C up to 6g per day can reduce the risk of many viral infections [66] and helps to improve health conditions [67]. In China upto 50 COVID-19 patients were treated using vitamin C by giving 10g to 20g dose per day [68]. For several decades high intaravenous dosage of vitamin C is used in treating viral infection [69] (Table 3).
Table 3: Suggested doses of vitamin C for COVID-19 patients and health improvement related with dose.
Vitamin C Involvement in Immune Modulation and Proper Immune Function
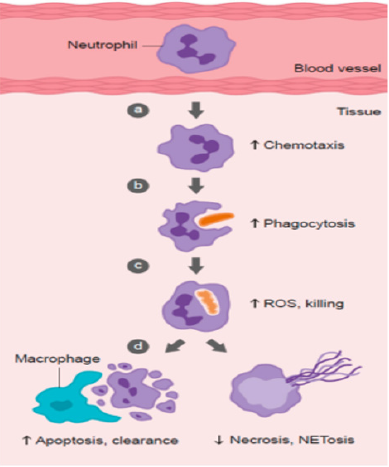
Mainly vitamin C is accumulated in larger quantity by 50 to 100 folds in leukocytes which contribute to its normal functioning [70,71]. For normal immune cell function a person needs to take 100mg per day vitamin C [72,73]. As compared to immune cells another cell requires high vitamin C [70]. Neutrophils the first cell to travel at the site of infection accumulate vitamin C at 1mM concentration inside the cell [74,75]. Neutrophils can also take oxidized form of vitamin when it is needed in high concentration [76,77]. Dehydroascorbate known as DHA is oxidized form of vitamin C which is then converted to ascorbate the reduced form to raise intracellular level of vitamin C up to 10Mm [77]. It is believed than milli molar concentration of vitamin C contributes to normal functioning of vitamin C [77]. vitamin C is very beneficial in scavenging activity of dead cell, normal neutrophils function, regeneration of vitamin E, activation of pro-inflammatory transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NFκB), modulation of signaling pathways, activation of signaling cascade , regulation of inflammatory mediators, phagocytosis, gene regulation and signaling pathways in T-cells, activation of κB (NFκB) in dendritic cells and neutrophils, increases neutrophils motility so that it may reach to the site of infection, vitamin c has also a promising role in immune modulation and proper immune functions [78-87] (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Highlights the role of vitamin C in immune cell function vitamin C is involved in following different function
a) Shows enhance neutrophils migration in response to chemo attractants (chemo taxis),
b) Enhance engulfment (phagocytosis) of microbes, and
c) Stimulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and killing of microbes.
d) Vitamin C supports caspase-dependent apoptosis, enhancing uptake and clearance by macrophages, and inhibits necrosis, including NETosis, thus supporting resolution of the inflammatory response and tissue damage” [87].
Vitamin C Deficiency and Onsets of Infections
Scurvy one of the outcomes of vitamin C deficiency makes on susceptible to respiratory infection [88]. Pulmonary infections are also associated with low vitamin C level [89]. And many of the lungs infections can be cleared by using intravenous vitamin C [90]. Decrease in intracellular concentration of vitamin C is observed in common colds [91-96]. Patients admitted with respiratory complication shows improvement by administration of vitamin C [89].
Conclusion
Vitamins especially vitamin C has a lot of positive impacts on immune system functions. Vitamin C is also a strong antioxidants helps in scavenging of oxidative species , normal neutrophils function, regeneration of vitamin E, activation of pro-inflammatory transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NFκB),modulation of signaling pathways, activation of signaling cascade , regulation of inflammatory mediators, phagocytosis, gene regulation and signaling pathways in T-cells, activation of κB (NFκB) in dendritic cells and neutrophils, increases neutrophils motility so that it may reach to the site of infection,vitamin c has also a promising role in immune modulation and proper immune functions. As health care workers and professional are risk community for COVID-19 so vitamin C should be included in prevention and treatment of COVID-19 in this community. As vitamin C is also a prooxidant so smaller pharmacological concentration of vitamin C milli-molar is beneficial. But in case of COVID-19 high intravenous dose of vitamin C would be the right choice. More ever vitamin C should be used as preventive therapy against COVID-19 and other viral infections.
References
- CI Paules, HD Marston, AS Fauci (2020) Coronavirus infections – more than just the common cold, JAMA Epub ahead of print.
- J Yang, Y Zheng, X Gou (2020) Prevalence of comorbidities in the novel Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect 94: 91-95.
- D Wang, B Hu, C Hu (2020) Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Epub ahead of print. 323(11):1061-1069.
- Update on the prevalence and control of novel coronavirus-induced pneumonia as of 24:00 on February 21. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202002/543cc50897 8a48d2b9322bdc83daa6fd.shtml (accessed February 23, 2020). (in Chinese).
- Huang CL (2020) Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet 395: 497-506.
- Tyrrell DA, Bynoe ML (1966) Cultivation of viruses from a high proportion of patients with colds. Lancet 1(7428): 76-77.
- GISAID Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data. Phylogeny of SARS-like beta corona viruses including novel coronavirus (nCoV). (Available from: https://nextstrain. org/groups/blab/sars-like-cov).
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG (2020) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579(7798): 270-273.
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R (2020) Clinical course, and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Published correction appears in Lancet. 395(10229):1038.
- Zhang T, Wu Q, Zhang Z (2020) Probable Pangolin origin of SARS-CoV-2 associated with the COVID-19 outbreak. Curr Biol 30(7): 1346-1351.
- Rothan HA, Byrareddy SN (2020) The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J Autoimmun 109: 102433.
- Van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH (2020) Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med 2020. 382:1564-1567.
- Yeo C, Kaushal S, Yeo D (2020) Enteric involvement of coronaviruses: is faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2 possible? Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(4): 335-337.
- Zhang H, Kang Z, Gong H (2020) The digestive system is a potential route of 2019- nCov infection: a bioinformatics analysis based on single-cell transcriptomes. bioRxiv. 2020.
- Chen Y, Peng H, Wang L (2020) Infants born to mothers with a new coronavirus (COVID-19). Front Pediatr 8: 104.
- Chen H, Guo J, Wang C (2020) Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records [published correction appears in Lancet. 395 (10229):809-815.
- Schwartz DA (2020) An analysis of 38 pregnant women with COVID-19, their newborn infants, and maternal-fetal transmission of SARS-CoV-2: maternal coronavirus infections and pregnancy outcomes. Arch Pathol Lab Med 10.
- Savarino A, Boelaert JR, Cassone A, Majori G, Cauda R (2003) Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: an old drug against today’s diseases? Lancet Infect Dis 3(11): 722-727.
- Colson P, Rolain JM, Raoult D (2020) Chloroquine for the 2019 novel coronavirus SARSCoV-2. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55(3): 105923.
- World Health Organisation. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public, 2020. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/ diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public
- UK Government. Coronavirus (COVID-19): guidance, 2020. Available: https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/coronavirus-covid-19- list-of-guidance
- Irish Government. COVID-19 (Coronavirus), 2020. Available: https:// www.gov.ie/en/campaigns/c36c85-covid-19-coronavirus/
- Parkin J, Cohen B (2001) An overview of the immune system. Lancet 357(9270): 1777-1789.
- Maggini S, Wintergerst ES, Beveridge S, Hornig DH (2007) Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses. Br. J Nutr 98(Suppl 1): S29-S35.
- Webb AL, Villamor E (2007) Update: Effects of antioxidant and non-antioxidant vitamin supplementation on immune function. Nutr Rev 65(5): 181.
- Burns JJ (1957) Missing step in man, monkey and guinea pig required for the biosynthesis of L-ascorbic acid. Nature 180(4585): 553.
- Nishikimi M, Fukuyama R, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Yagi K (1994) Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human nonfunctional gene for L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the enzyme for L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in man. J Biol Chem 269(18): 13685-13688.
- Sauberlich HE (1997) A history of scurvy and vitamin C. In Vitamin C in Health and Disease Packer, L Fuchs J(Eds.), Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA pp. 1-24.
- Hemila H (2017) Vitamin C and Infections. Nutrients 9(4): 339.
- Hemila H (1994) Does vitamin C alleviate the symptoms of the common cold? A review of current evidence. Scand. J Infect Dis 26(1): 1-6.
- Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X (2020) Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 323(11): 1061-1069.
- Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B (2020) Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. The Lancet 395(10224): 565-574.
- Zu ZY, Jiang MD, Xu PP, Chen W, Ni QQ (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a perspective from China. Radiology 21: 200490.
- Kirchdoerfer RN, Cottrell CA, Wang N, Pallesen J, Yassine HM, et al. (2016) Pre-fusion structure of a human coronavirus spike protein. Nature 531(7592): 118-121.
- Xu X, Chen P, Wang J, Feng J, Zhou H, et al. (2020) Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission. Science China Life Sciences 63(3): 457-460.
- Lam TTY, Shum MHH, Zhu HC, Tong YG, Ni XB, et al. (2020) Identification of 2019-nCoV related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins in southern China. BioRxiv
- Chan JFW, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KKW, Chu H, et al. (2020) A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-toperson transmission: a study of a family cluster. The Lancet 395(10223): 514-523.
- Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, et al. (2020) Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. New England Journal of Medicine 382(13):1199-1207.
- Winter G (2020) COVID-19 and emergency planning. British Journal of Healthcare Management 2020: 1-3.
- Guo YR, Cao QD, Hong ZS, Tan YY, Chen SD (2020) The origin, transmission, and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak - an update on the status. Mil Med Res 7(1): 11.
- Hong M, Xiong T, Huang J, Wu Y, Lin L(2020) Association of vitamin D supplementation with respiratory tract infection in infants. Matern Child Nutr 16(3): e12987.
- Huang F, Zhang C, Liu Q, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2020) Identification of amitriptyline HCl, flavin adenine dinucleotide, azacitidine and calcitriol as repurposing drugs for influenza A H5N1 virus-induced lung injury. PLoS Pathog 16(3): e100834.
- Jiménez Sousa MA, Jiménez JL, Fernández Rodríguez A, Brochado Kith O, Bellón JM (2019) VDR rs2228570 polymorphism is related to non-progression to AIDS in antiretroviral therapy naïve HIVinfected patients. J Clin Med 8(3): E311.
- Jiménez Sousa MÁ, Martínez I, Medrano LM, Fernández Rodríguez A, Resino S (2018) Vitamin D in human immunodeficiency virus infection: influence on immunity and disease. Front Immunol 9: 458.
- Jolliffe DA, Greiller CL, Mein CA, Hoti M, Bakhsoliani E (2018) Vitamin D receptor genotype influences risk of upper respiratory infection. Br J Nutr 120(8): 891-900.
- Teymoori Rad M, Shokri F, Salimi V, Marashi SM (2019) The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections. Rev Med Virol 29(2): e2032.
- Tsujino I, Ushikoshi Nakayama R, Yamazaki T, Matsumoto N, Saito I (2019) Pulmonary activation of vitamin D3 and preventive effect against interstitial pneumonia. J Clin Biochem Nutr 65(3): 245-251.
- Xu J, Yang J, Chen J, Luo Q, Zhang Q (2017) Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the reninangiotensin system. Mol Med Rep 16(5): 7432-7438.
- Zhou YF, Luo BA, Qin LL (2019) The association between vitamin D deficiency and community-acquired pneumonia: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(38): e17252.
- Carr AC, Rosengrave PC, Bayer S, Chambers S, Mehrtens J (2017) Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes. Crit Care 21(1): 300.
- Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 323: 1061-1069.
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, et al. (2020) Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 395(10223):507-513.
- Fowler III AA, Kim C, Lepler L, Malhotra R, Debesa O, et al. (2017) Intravenous vitamin C as adjunctive therapy for enterovirus/rhinovirus induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. World J Crit Care Med 6(1): 85-90.
- MG Kashiouris, ML Heureux, CA Cable, BJ Fisher, SW Leichtle (2020) The Emerging Role of Vitamin C as a Treatment for Sepsis Nutrients 12(2): 292.
- Meng L, Zhao X, Zhang H (2019) HIPK1 interference attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress of acute lung injury via autophagy. Med Sci Monit 25: 827-835.
- Yan X, Fu X, Jia Y, Ma X, Tao J, et al. (2019) Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling mediated an antioxidative protection of human placental mesenchymal stem cells of fetal origin in alveolar epithelial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019: 2654910.
- Hecker L (2018) Mechanisms and consequences of oxidative stress in lung disease: therapeutic implications for an aging populace. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 314(4): L642-653.
- Chen L, Liu HG, Liu W, Liu J, Liu K, et al. (2020) Analysis of clinical features of 29 patients with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia. Zhonghua Jie He Hu Xi Za Zhi 43(0): E005.
- Liu Q, Gao Y, Ci X (2019) Role of Nrf2 and its activators in respiratory diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019: 7090534.
- Nabzdyk CS, Bittner EA (2018) Vitamin C in the critically ill-indications and controversies. World J Crit Care Med 7(5): 52-61.
- Li J (2018) Evidence is stronger than you think: a meta-analysis of vitamin C use in patients with sepsis. Crit Care. 22(1): 258.
- Hemilä H, Chalker E (2019) Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: a metaanalysis. Nutrients 11(4): 708.
- Marik PE, Khangoora V, Rivera R, Hooper MH, Catravas J (2017) Hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock: a retrospective before-after study. Chest. 151(6): 1229-1238.
- High dose vitamin C and influenza: a case report. ISOM, cited on Feb 9, 2020 (. https:// isom.ca/article/high-dose-vitamin-c-influenza-case-report/?from=groupmessage&isappinstalled=0).
- Levy T. Primal Panacea. MedFox Publishing; 350 p. (Kindle Edition).
- Patel V, Dial K, Wu J, Gauthier AG, Wu W, et al. (2020) Dietary antioxidants significantly attenuate hyperoxia-induced acute inflammatory lung injury by enhancing macrophage function via reducing the accumulation of airway HMGB1. Int J Mol Sci 21(3): 977.
- Kim TK, Lim HR, Byun JS (2020) Vitamin C supplementation reduces the odds of developing a common cold in Republic of Korea Army recruits: randomised controlled trial. BMJ Mil Health.
- Gorton HC, Jarvis K (1999) The effectiveness of vitamin C in preventing and relieving the symptoms of virus-induced respiratory infections. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 22(8): 530-533.
- Shanghai Expert Panel, cited on Mar 23. . http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz= MzA3Nzk5Mzc5MQ==&mid=2653620168&idx=1&sn=2352823b79a3cc42e48229a0c38f65e0&chksm=84962598b3e1ac8effb763e3ddb4858435dc7aa947a8f41790e 8df2bca34c20e6ffea64cd191#rd; 2020.
- High-dose vitamin C (PDQ®)–Health professional version. National Cancer Institute, cited on Feb 9, 2020 (. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/hp/ vitamin-c-pdq)
- Washko P, Rotrosen D, Levine M (1989) Ascorbic acid transport and accumulation in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 264(32): 18996-19002.
- Bergsten P, Amitai G, Kehrl J, Dhariwal KR, Klein HG (1990) Millimolar concentrations of ascorbic acid in purified human mononuclear leukocytes. Depletion and reaccumulation. J Biol Chem 265(5): 2584-2587.
- Evans RM, Currie L, Campbell A (1982) The distribution of ascorbic acid between various cellular components of blood, in normal individuals, and its relation to the plasma concentration. Br J Nutr 47(3): 473-482.
- Levine M, Conry Cantilena C, Wang Y, Welch RW, Washko PW, et al. (1996) Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: Evidence for a recommended dietary allowance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(8): 3704-3709.
- Levine M, Wang Y, Padayatty SJ, Morrow J (2001) A new recommended dietary allowance of vitamin C for healthy young women. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(17): 9842-9846.
- Carr AC, Bozonet SM, Pullar JM, Simcock JW, Vissers MC (2013) Human skeletal muscle ascorbate is highly responsive to changes in vitamin C intake and plasma concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr 97(4): 800-807.
- Vissers MC, Bozonet SM, Pearson JF, Braithwaite LJ (2011) Dietary ascorbate intake affects steady state tissue concentrations in vitamin C-deficient mice: Tissue deficiency after suboptimal intake and superior bioavailability from a food source (kiwifruit). Am J Clin Nutr 93(2): 292-301.
- Corpe CP, Lee JH, Kwon O, Eck P, Narayanan J (2005) 6-Bromo-6-deoxy-l-ascorbic acid: An ascorbate analog specific for Na+ -dependent vitamin C transporter but not glucose transporter pathways. J Biol Chem 280: 5211-5220.
- Washko PW, Wang Y, Levine M (1993) Ascorbic acid recycling in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 268(21): 15531-15535.
- Buettner GR (1993) The pecking order of free radicals and antioxidants: Lipid peroxidation, alpha-tocopherol, and ascorbate. Arch Biochem Biophys 300(2): 535-543.
- Sen CK, Packer L (1996) Antioxidant and redox regulation of gene transcription. FASEB J 10(7): 709-720.
- Li N, Karin M (1999) Is NF-kappaB the sensor of oxidative stress? Faseb J 13(10): 1137–1143.
- Macdonald J, Galley HF, Webster NR (2003) Oxidative stress and gene expression in sepsis. Br J Anaesth 90(2): 221-232.
- Tan PH, Sagoo P, Chan C, Yates JB, Campbell J (2005) Inhibition of NF-kappa B and oxidative pathways in human dendritic cells by antioxidative vitamins generates regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 174(12): 7633-7644.
- Winterbourn CC, Hampton MB (2008) Thiol chemistry and specificity in redox signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 45(5): 549-561.
- Griffiths HR, Willetts RS, Grant MM, Mistry N, Lunec J (2009) In vivo vitamin C supplementation increases phosphoinositol transfer protein expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy individuals. Br J Nutr 101(10): 1432-1439.
- Grant MM, Mistry N, Lunec J, Griffiths HR (2007) Dose-dependent modulation of the T cell proteome by ascorbic acid. Br J Nutr 97(1): 19-26.
- Carr AC, Maggini S (2017) Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients 9(11): 1211.
- Hemila H (2017) Vitamin C and Infections. Nutrients 9(4): 339.
- Bakaev VV, Duntau AP (2004) Ascorbic acid in blood serum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and pneumonia. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis 8(2): 263-266.
- Hunt C, Chakravorty NK, Annan G, Habibzadeh N, Schorah CJ (1994) The clinical effects of vitamin C supplementation in elderly hospitalised patients with acute respiratory infections. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 64(3): 212-219.
- Hume R, Weyers E (1973) Changes in leucocyte ascorbic acid during the common cold. Scott Med J 18(1): 3-7.
- Wilson CW (1975) Ascorbic acid function and metabolism during colds. Ann NY Acad Sci 258: 529-539.
- Schwartz AR, Togo Y, Hornick RB, Tominaga S, Gleckman RA (1973) Evaluation of the efficacy of ascorbic acid in prophylaxis of induced rhinovirus 44 infection in man. J Infect Dis 128(4): 500-505.
- Davies JE, Hughes RE, Jones E, Reed SE, Craig JW (1979) Metabolism of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in subjects infected with common cold viruses. Biochem. Med 21(1): 78-85.
- Anderson RM, Heesterbeek H, Klinkenberg D, Hollingsworth TD (2020) How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic? Lancet 395(10228): 931-934.
- Noor AU, Maqbool F, Bhatti ZA, Khan AU (2020) Epidemiology of CoViD-19 Pandemic: Recovery and mortality ratio around the globe. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 36(COVID19-S4).

 Review Article
Review Article