Abstract
Brain is three pound structure in weight, controls all the function such as emotion,
creativity, and learning. It’s protected within the skull. Learning is a process to acquire
new skills, knowledge, behaviors and values. It also synthesizes different type of
information. In learning process, the part of brain may be involved. Over a course of
time, each part of brain grows. The forebrain is the most complex and largest part of
the brain. It is responsible for human higher level of behavior as speaking and thinking.
Introduction
Brain is three pound structure in weight, controls all the function such as emotion, creativity, and learning. It’s protected within the skull. Brain receives information through five senses: hearing, sight, smell touch and taste. Since learning disabilities are the neurobiological or brain injury. So the areas of brain which are involved in this are following. The central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord .The brain consists of three main parts:
- Forebrain
- Midbrain
- Brain stem/hind brain ( medulla, pones and the cerebellum)
Fore Brain
The forebrain is the most complex and largest part of the brain. It is responsible for human higher level of behavior as speaking and thinking. It also functions as the processor and receptor of sensory information like thought, perception, memory and speech. We divide forebrain into four parts:
- Cerebrum
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
Cerebrum
Cerebrum contains the Cerebral Cortex, which has two cerebral hemi-spheres:
a) Right hemisphere
b) Left hemisphere
The right side of hemisphere control left side of body and receive left side of body impulses and left hemisphere control right side of body [1].
Cerebral Cortex
The surface of cerebrum has folded membrane which is called cortex the cortex contain 100 billion of nerve cells. The color of bodies of nerve cells is grey. Why it’s called grey matter, between the neurons long connecting a fiber, which is called grey matter [2].
Lobes of Cerebrum
a) Frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital. In the right and left hemisphere, there is very complex relationship between them [3].
Thalamus
Thalamus lies in between the telencephalon and the brain stem. Thalamus works as a relay station for ascending information from the cortex and also receives information from senses. The Third ventricle divides the thalamus into right and left [4].
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus is located in just below the thalamus, about the size of the tip finger. One of major function is to maintain the steady internal environment of the body.It also includes the limbic system, which is a sub cortical part involved in emotional responses and memory formation. The limbic system includes the amygdala, hippocampus, basal ganglia, and cingulated gyres. The Amygdala is located in the temporal lobe, just in front of the hippocampus. The Amygdala consists of cluster of neuron, which is primarily involved in the memory, learning and emotions [5].
Mid Brain
Midbrain connects the forebrain with the hindbrain. It play an important function and works as a relay station for messages coming into the brain, also plays an important role in seeing, movement and hearing [6].
Hind brain
Hindbrain is divided into three major parts:
The Medulla
a) The Pons
b) The cerebellum
Medulla
It contains fiber and nerve cells, which are important in reflex activities such as, heart rate, blood pressure etc. It also acts as a relay station. The medulla contains many tracts of fiber that are originated in the higher areas of the brain and carries command to the nerve cell in the spinal cord [7].
The Pons
It receives input from the hearing receptors and the head positioning receptors of the inner ear [8].
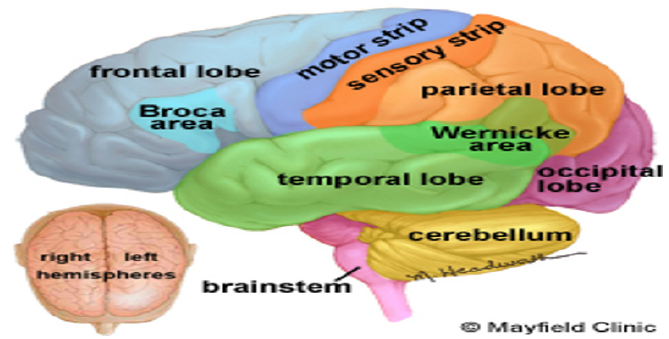
The Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a large, complex structure located to the back of the brain stem. It receives sensory information from brain stem, spinal cord and forebrain [9] (Figure 1).
How Human Brain Involve in Learning: Learning is a process to acquire new skills, knowledge, behaviors and values. It also synthesizes different type of information. In learning process, the part of brain may be involved. Over a course of time, each part of brain grows [10].
The Frontal Lobe: It is located behind the forehead and is involved in problem solving and is also involved in memory, impulse control or judgment. The damage to frontal lobe affects the problem solving or critical thinking [11].
Brain Sides: The left side of brain is more involve in language as compare to right side of brain. The right side of brain is more involve in processing [12].
The Temporal Lobe: It is involved in organizing information, memory and speech. Amygdala is the part of temporal lobes, which is involved in organization and storage of information. In case of dysfunctions its function decreases [13].
Neurotransmitters
There are specific neurotransmitters, which are involved in memory storage and learning:
- Epinephrine
- Dopamine
- Serotonin
- Glutamate
- Acetylcholine
Dopamine: It is the neurotransmitter, which is found in brain and plays a vital role in learning. It associates with reward seeking behavior. There are two types of dopaminergic neurons, one is reward neuron or another is non-reward neuron. The level of dopamine is directly proportional to mood, creativity and alertness [14].
Acetylcholine: It is involved in learning and acquisition of new memory. The hippocampus has central high level of glutamate, which plays an important role in learning, Axon send processes to pre synaptic neuron which are called buttons, the postsynaptic dendrite are constantly producing processes called spines that will receive the input from the other cell. It is the head of the spine that is most active, growing and connecting with the button. Very complex building and rebuilding of microtubule scaffolding structures determine these changing structures of the neuron membrane. [10] In pre-synaptic neuron acetylcholine is made from choline and acetyl CoA. In the synaptic cleft Ach is rapidly broken down by the enzyme.
Conclusion
Brain is three pound structure in weight, controls all the function such as emotion, creativity, and learning. It’s protected within the skull. Learning is a process to acquire new skills, knowledge, behaviors and values. It also synthesizes different type of information. In learning process, the part of brain may be involved. Over a course of time, each part of brain grows. The forebrain is the most complex and largest part of the brain. It is responsible for human higher level of behavior as speaking and thinking [15-18].
References
- Anon nd Learning Disabilities Association of America.
- Anon nd Learning Disabilities Association of America.
- Anon nd National Aphasia Association.
- Cadogon M (2010) Ach Synthesis and Release.
- Disabilities NJ Co Lnd American Speech-Language-Hearing Association.
- Eljou JG (2009) Awareness about learning disabilities among the primary school teachers. Cauvery Research Journal 3(1): 71-78.
- Goldstein NM a S nd Ldonline.org.
- Heward W (2010) Causes of Learning Disabilities.
- kanawll d (2013) Hub Pages.
- Lieff J (2013) New Type of Neuroplasticity Involving Changes in Neurotransmitters.
- Morin A nd Understood.org.
- Morin A n.d. (2017) Understood.org.
- Neena Sawhney SB (2014) Study of awarness of learning disabilities among elementary school teachers. patiala, research gate.
- Online L (2006) Timeline of Learning Disabilities.
- Poorna Shukla GA (2015) Awareness of Learning Disabilities among Teachers of Primary Schools. Online Journal of Multidiciplinary Research 1(1): 2395-4892.
- Shari MM NV (2015) knowledge of primary school teachers in identifying children with learning disabilities. Disability, CBR and Inclusive Development journal of india 26(3): 68-76.
- Swaine R nd (2017) Osla.on.ca.
- Tonya Hines CMC (2016) May Field Brain and Spine.

 Mini Review
Mini Review