Abstract
Antares Placido topographer CSO had been used to measure 50 eyes corneas at Ophthalmological Clinic of the Greek Red Cross hospital «Korgialeneio - Benakeio in collaboration with University of West Attica and their refractive maps were taken. The refractive power map was taken before cataract surgery with the method of phacoemulsification. The keratometric measurements for 3 & 5mm were recorded before and one month after surgery. The correlation of the K1, K2 readings before and one month after the phacoemulsification procedure, do not cause changes in the refractive power of the two main meridians of the cornea of patients, in order to alter the final astigmatism refractive post-operative effect, to a statistically significant degree.
Keywords: Cornea; Main Meridians; Astigmatism; With the Rule; Against the Rule; Surgical Incisions; Phacoemulsification; Topography; Correlation
Purpose
The study of the effect – impact of surgical incisions that are performed during the phacoemulsification surgery, through the topographic imaging of refractive forces, of the corneal under examination, both preoperative and postoperatively. The study concerns evaluating the changes induced in corneal topography at 3mm and 5mm central diameter after phacoemulsification due to corneal incisions. In cataract surgery Phacoemulsification is the latest preferred technique due to the minimization of postoperative astigmatism and the rapid visual rehabilitation.
Introduction
The lens is surrounded by an elastic, transparent membrane, the periphery, that allows the molecules to pass both inside and outside the lens [1-5]. It consists of epithelial cells, type IV collagen fibers, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), laminin, pelican, fibronectin and type XVIII [6-10] collagen. The interactions of the molecules with water make the membrane viscoelastic enough to withstand and transmit the forces of adaptation. Thus, it can change shape during the adaptation process. The thickness of the periphery varies, ranging from 2 to 28 μm [11-13]. It is thicker near the equator and thinner at the rear. This is because its first surface is secreted by the epithelium as opposed to the posterior from the superficial laccase fibers. With age, the periphery increases in thickness and loses its elasticity, resulting in reduced adaptability and the appearance of presbyopia. So, according to researchers, the capacity of the subframe extends to 60% initially, without rupturing, which gradually decreases with time. Local differences in the thickness of the periphery are significant surgically, especially due to the risk of cracks or thinning of the posterior membrane during cataract surgery [13-14].
Materials and Method
A synchronous study was carried out in the corneal department of the Ophthalmological Clinic of the Greek Red Cross hospital «Korgialeneio - Benakeio», from May 2018 to September 2018, in 50 eyes – patients who met the admission criteria and had been scheduled to have a surgical removal of their cascade lens, with the method of phaco-emulsification. A topography was taken, of the eye surgery, with the topographer Antares of the company CSO and then the examination was repeated one or more calendar months after the surgery [14-16]. Statistical analysis of corneal refractive forces was performed before and after, followed by a statistical study of the surgical induced astigmatism. The study involved 24 female patients and 26 male patients. The minimum age of participants was 56 years and the maximum age was 88 years. The Arithmetic mean of Age was = 75.18±1.23 years.
Results
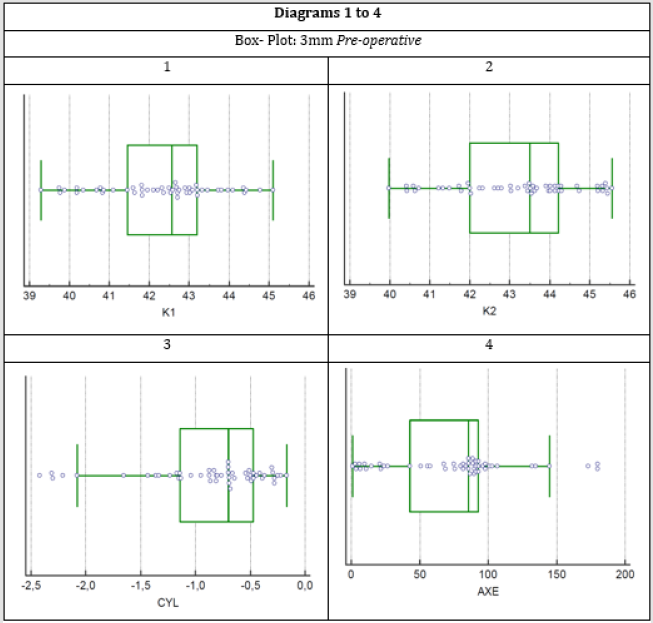
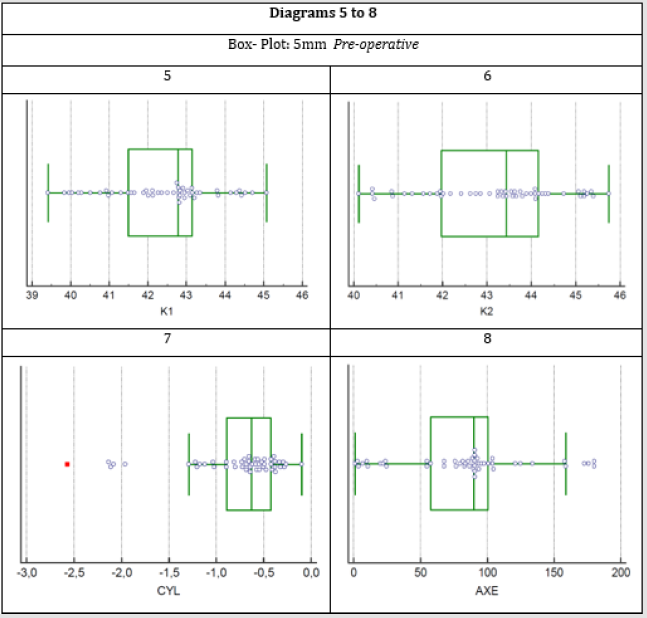
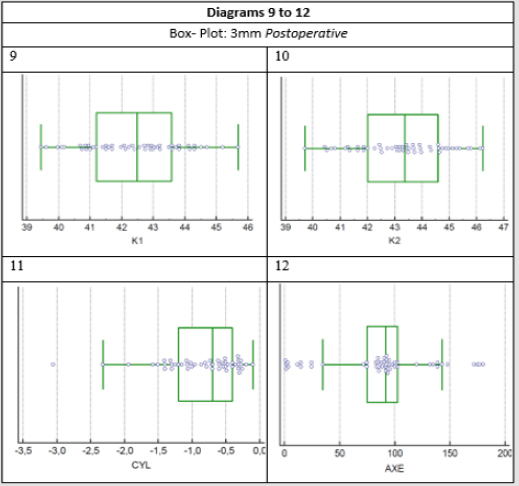
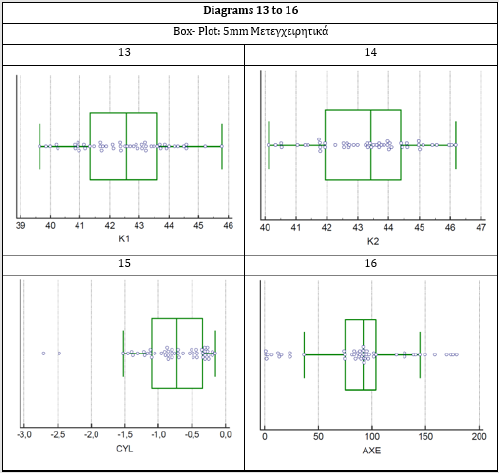
The mean power values of the two vertical meridians in the optical zone of 3mm found in diopters were pre-operatively K1 (D) 42.3212±0.2012 and K2 (D) 43,2032±02196 while postoperatively were K1 (D) 42,4198±0.2117 and K2 (D) 43,2698±0.2263 respectively. In the 5 mm optical zone the respective pre-operatively values were K1 (D) 42,4002±0.1964 and K2 (D) 43,1838±0.2136 while postoperatively were K1 (D) 42,5034±0.2072 and K2 (D) 43,2836±0.2187. The corneal astigmatism as it emerged from the measured eyes were pre-operatively in the zones of 3mm and 5mm in diopters -0,8774± 0.08189 and -0,7842±0.0767 respectively, while postoperatively in the respective zones received values -0,8552±0.08197 and -0,7854±0.07548. From the statistical processing of the results through two paired samples t-test for each pair of variables was found that for the meridian K1 P-value was 0.1765>0.05, for the meridian K2 the p-value was 0.4244>0.05 and for the astigmatism (Cyl) the value of p-value was 0.7470>0.05 in the optical zone of 3mm. The above values show that the three studied variables and mainly astigmatism do not present a statistically significant difference before and after the surgery of phacoemulsification (Tables 1 & 2) and The results of the measurements, are presented with the box plot scatter diagrams for each variable separately (Figures 1-4).
Table 1: The standard deviation value shows how close to the mean the sample values are for each variable.
Table 2: The standard deviations for each variable before and after surgery for the 3 mm and 5 mm are shown.
Conclusions
From this study it was demonstrated that the surgical incisions during the operation of the phacoemulsification procedure, do not cause such changes in the refractive power of the two main meridians of the cornea of patients, in order to alter the final astigmatism refractive post-operative effect, to a statistically significant degree.
Discussion
According to the bibliography, it has been found that the surgical incisions affect the final astigmatism refractive effect, in cases of high preoperative astigmatism as these incisions have a decreasing effect when they occur at the most stipe meridian and increasing effect when performed at the flattest meridian. Therefore, the surgical technique is modified accordingly, in order to achieve the most desirable result. In this study, preoperative values of corneal astigmatism were mostly low while on the other hand, most patients presented pre-operative astigmatism with the rule.
References
- Danysh, Brian P, Melinda K Duncan (2009) The Lens Capsule Experimental Eye Research. Experimental Eye Research 88(2): 151-164.
- Augusteyn, Robert C (2008) Growth of the Lens: in Vitro Observations. Clinical and Experimental Optometry 91(3): 226-239.
- Lou MF (2003) Redox Regulation in the Lens. Prog Retin Eye Res 22(5): 657-82.
- Michael R, Bron AJ (2011) The Ageing Lens and Cataract: A Model of Normal and Pathological Ageing. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 366(1568): 1278-1292.
- Takemoto L, Boyle D (1998) The possible role of alpha-crystallins in human senile cataractogenesis. Int J Biol Macromol. 22: 331-337.
- (2012) American Academy of Ophthalmology. BCSC. Section 11: Lens and Cataract. Pages 19-21.
- Fincham EF (1925) The changes in the form of the crystalline lens in accommodation. Transactions of the Optical Society 26(5): 239.
- Glasser, Adrian, Paul L Kaufman (1999) The mechanism of accommodation in primates. Ophthalmology 106(5): 863-872.
- Kuszak JR, RK Zoltoski, C Sivertson (2004) Fibre cell organization in crystalline lenses. Experimental eye research 78(3): 673-687.
- Wiederholt M (1980) Physiology of epithelial transport in the human eye. Klinische Wochenschrift 58(19): 975-984.
- Kirkwood, Bradley J, Rodney A Kirkwood (2013) Accommodation and presbyopia. Insight 38(3): 5-8.
- Heron, Gordon, WN Charman, Lyle S Gray (2002) Accommodation dynamics as a function of age. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 22(5): 389-396.
- Asbell, Penny A (2005) Age-related cataract. The Lancet 365(9459): 599-609.
- Hoffmann PC, Hütz WW (2010) Analysis of biometry and prevalence data for corneal astigmatism in 23239 eyes. J Cataract Refract. Surg. 36(9): 1479-1485.
- Nichamin LD (2006) Astigmatism control. Opthalmol Clin North Am 19: 485-493.
- Gross RH, Miller KM (1996) Corneal astigmatism after phacoemulsification and lens implantation through unsutured scleral and corneal tunnel incisions. Am J Ophthalmol 121(1): 57-64.

 Research Article
Research Article