Abstract
The article is devoted to the topical problem of modern medicine - the pathogenesis of diverticular disease, which affects only the colon. The importance of age and nature of nutrition in its development is assessed. But, according to the author, the leading role in the formation of this pathological symptom complex still belongs to the violation of the innernery of the colon, which usually occurs as early as childhood. In the correction of this pathology, special importance is attached to a set of medical and preventive measures aimed at maintaining normal peristalsis of the colon until the old age. The article has a certain interest not only for doctors of different specialties, but also for the population of all countries of the world, as now there is an increase in life expectancy, and therefore increases the risk of disease of this pathological Process. Active correction of motor activity of the colon will contribute to healthy life expectancy of people.
The Aim of the Study
To assess the importance of preventive and therapeutic measures in correcting disorders of colon inertia in the development of diverticular disease.
Introduction
Diverticular Disease (DD) is a disease, the essence of which is the appearance in the wall of the colon of local mucosa squeezing, in the form of rounded hernia-like formations. This is done in the area of weakened areas of its wall (in the course of blood vessels). In the lumen of these bulges often accumulate swallowed with food sharp foreign bodies (for example, fish bones), causing bedsores and perforation of the wall. The leading pathogenetic factor in the development of this disease is considered to be a disorder of colon peristalsis with the appearance of high blood pressure in its lumen [1-3]. Of particular importance is attached to the violation of the consistent motor segmentation of this gut, which ensures the advancement of feces to the opening. The incidence of DD population in different countries reaches 30% of the total population, and in economically developed countries this pathological process is more common, due to an increase in life expectancy in humans. For example, 40% of patients are over 70 years of age [4-6]. As you know, by this age many people develop a thick-intestinal stasi (constipation). It is even considered to be the most common pathological process of mankind. Often it is observed from the first days of a person’s life, and then, gradually speeding up and lengthening, he goes into a permanent (sometimes excruciating) cryostasis [3,6,7]. This is usually observed after 45-55 years and in women 10-15 years earlier. It is classified as a major factor in the body’s aging and is associated with the consumption of predominantly protein and fatty foods - without plant fiber and with a limited amount of water [7,8].
As a result, there is an suppression of motor activity of the colon. Fecal masses turn into stone-like formations and linger in it for 2-3 days or more. The act of defecation turns into a problem - a person is very tense to free him from the feces masses, and this is accompanied by an excessive increase in pressure in the lumen of the colon. There is a real threat of the development of diverticulitis of this gut, as well as various inflammatory-destructive processes and malignancies. However, there is another cause of this disease, and it is associated with the violation of the innernery of the thick and straight intestines - mainly rec-sigmoidal department. In this process, there is a violation of the normal structure of the Auerbach and Meissner plexus, which is accompanied by the fallout of peristalsis in the area of ganglionitis [4,6,7]. If the newborn (in the presence of an anus) stool does not have from the first days of his life, it is a congenital pathology - acute disease Hirschsprung, which requires urgent manipulation of the cut drainage of the lumen of the colon, and even the imposition of colostomy.
In the sub-acute form of this disease, the child from birth has problems with the act of defecation, and parents are forced to resort to the staging of enemas and giving laxatives up to 1-3 years. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by a slower development of cryostasis, which is observed already in adolescence [1,2,7]. If we compare both versions of the causes of constipation, it is clear that only an acute form of Hirschsprung disease properly puzzles adults (parents and doctors) immediately after the birth of the child, as the lack of a chair makes him accept effective measures to save his life. In all other cases, adults show startling frivolity. They think that the child everything will normalize over time and the delay of the chair 2-3 days is considered even a physiological norm. Adult sick people gradually get on with this pathology of the colon and “courageously” tolerate all direct intestinal discomfort. In fact, they do not treat them, and the whole fight against constipation is limited to the correction of the food regime [2,5,7]. At the All-Union Symposium (1979) the following classification of diverticular disease was adopted:
a) Diverticulitis without clinical manifestations (the disease is diagnosed by accident or during preventive examinations, or during examination by about other diseases of the abdominal cavity),
b) Diverticulitis with clinical manifestations (there is pain in the course of the colon and various disorders of the colon),
c) Diverticulitis with a complicated current (inflammatory infiltration, perforation, intestinal obstruction, fistulas) [2,3].
In the second stage of the disease in 80% of patients during colon examination reveal a lot of bulges, going in two rows on both sides of the colon. Most often they are localized in sigma (60-65%), then in the descending intestine (20-25%), transverse (7-8%), ascending (2-3%), blind (2-3%). inflammatory process occurs in 3-5 years, and episodic abdominal pain bothers 30-40%. In their re-x-ray examination, 30% of them have an increase in the number of diverticula and the spread of the pathological process to other parts of the colon. Pneumonia-inflammatory complications are observed in 40-60% of patients, and bleeding - in 7-38%. In 5-10% of patients, the bleeding is profuse. Blind gut diverticulitis is sometimes complicated by the development of dense inflammatory infiltrations that are difficult to distinguish from cancer. In diverticulitis, mortality reaches 5% [3,9]. Thus, on the social, economic and humanitarian aspects, the disease deserves close attention.
Materials and Methods
79 patients with DB, whose age was between 64 and 87 years old, were observed in the BSMP Krasnodar. Men 42 (51.9%), women - 37 (48.1%). the left half of the colon was affected, and 5 (6.3%) were affected. left and right. All patients from childhood suffered constipation. The clinical picture of the disease depended on the nature of the course of DD. For example, 60 (75.9%) have a case in the uk. patients before admission to the hospital for several years observed constant constipation, alternating with snorts, and moderate pain during the colon, flatulence and the release of mucus with feces, which was associated with the exacerbation of chronic colitis. 8 (10.1%) had an acute onset - severe abdominal pain, stool and gas retention, vomiting, increased body temperature, tachycardia and leukocytosis. This symptom was initially regarded as acute pancreatitis. 5 (6.3%) patients began the disease resembled acute appendicitis. To recognize the cause of the above symptoms, used an abdominal X-ray, baria passage on the intestines, ultra-sound, laparoscopy and other diagnostics, but the leading importance was the irrigation, which revealed a clear The db-evidence test is the detection of a barium suspension depot that extends beyond the gut wall.
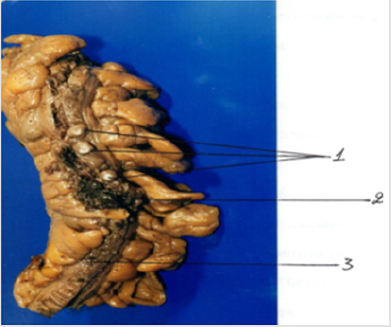
Even more diagnostic value was the double contrast of the colon, that is, the staging of barium enemas and the introduction of gas into the abdominal cavity. Intermural diverticula were characterized by a small irregular shape of the contours of the colon (a symptom of crumpled gutters). Irrigation was applied in all 73 (92.3%) Patients. It allowed to identify DD, either in the clinic (in 42 patients), or a few days after admission of patients to the hospital (in 31 patients). In 60 patients who clinically observed only dysfunction of the colon, immediately developed measures aimed at preventing complications of the disease and normalization of the stool. They included: rational diet therapy with a lot of plant fiber and vegetable oil, as well as a direct and indirect massage of the abdominal cavity for 5-7 minutes. Patients were informed of the nature of their illness and the need to follow the recommended regimen day in and day out throughout their lives. In 13 patients with diverticulitis (first they had suspected, or acute pancreatitis, or appendicitis) initially used drug therapy - antibiotics, vitamins B and C, immunostimulatory, diuretics and other signaling drugs, and after slinging out inflammation, switched to dietary therapy and massage. Operations were performed in 6 (7.7%) patients, including: 2 - for acute intestinal obstruction, 2 - intestinal bleeding, 2 - colon perforation. The cause of acute surgical pathology - DD, was determined only during the operation. Before that, they suffered from persistent chronic constipation. All 6 patients underwent Hartman surgery (Figure 1). The picture shows the macro drug of the affected part of the sigmoid gut,
a) Carrying a lot of diverticular,
b) Bleeding diverticular,
c) Inflammatory infiltration.
Results
All 73 patients who received conservative treatment tested positive - the stool became daily, abdominal pain either stopped or decreased significantly. It took 5 to 7 days. We consider it necessary to indicate that 17 (23.3%) of the patients after 2-3 weeks began to neglect the recommendations that gave them on dietary therapy and abdominal massage and switched to the previous diet - intake of dairy products, fatty meat food with a small amount of plant fiber and so on. After 3-4 days it led to a recurrence of symptoms of DD. We had to start the correction measures described by pathological symptoms again. There were no complications. Of the 6 patients who underwent Hartman surgery, 1 (16.6%) died after surgery patient for sepsis.
Discussion
DD refers to severe colon diseases. It often develops in childhood and this is associated with the disorder of the innernery of the colon, which is accompanied by a disorder of its motor function. Constipation is accompanied by flatulence, which dramatically and unevenly increases the pressure inside that gut. The mucous of its shell is squeezed through the weak spots of the wall. The disease initially proceeds asymptomatically and only with the addition of inflammatory, necrotised and ulcerative processes, there are various terrible complications. The development of the disease can be slowed down by diet, stool normalization, active lifestyle and massage of the anterior abdominal wall. This disease is most appropriate to detect during inspections. Timely conservative treatment is usually effective. Operations are performed in lifethreatening states.
Conclusion
Diverticular colon disease has now become global social, economic and demographic. This is due to an increase in life expectancy, which is accompanied by impaired innervations of the colon with a disorder of its motor function. The severity of this pathological process necessitates the development of effective prevention methods for the disease on a human scale. Observations have shown that this can be done only with the help of a rational diet containing plant fiber and abdominal massage, which contributes to the arousal of bowel peristalsis in the usual rhythm. With DD, the developed mode must be observed constantly. Neglecting it leads to a recurrence of the pathological symptoms of the disease. Diverticular colon disease has now become global social, economic and demographic. This is due to an increase in life expectancy, which is accompanied by impaired innervations of the colon with a disorder of its motor function. The severity of this pathological process necessitates the development of effective prevention methods for the disease on a human scale. Observations have shown that this can be done only with the help of a rational diet containing plant fiber and abdominal massage, which contributes to the arousal of bowel peristalsis in the usual rhythm. With DD, the developed mode must be observed constantly. Neglecting it leads to a recurrence of the pathological symptoms of the disease.
References
- Abdullayev AG (2013) Hospital Surgery. Syndrome. GEOTAR-MEDIA. 414s.
- Timerbulatov VM, Mehdiyev DI, Menshikov AM, Verzakova IV, Mikheyev Et, et al. (2000) Therapeutic tactics in diverticular disease of the colon/surgery. 9: 48-51.
- Fedorov VD, Dultsev JV (2007) Proctology M: Medicine.
- Bryn VB (2016) Normal Physiology Edited by BI Tkachenko (Ed.), 3rd (edn.). Spanish. And dop. M: GEOTAR - Media, pp. 688s.
- Kirienko AI (2012) Surgical diseases. Textbook Geotar – Media.
- Tupikova AP, Podmarenkova LF (1990) Features of motor function of the large intestine in patients divirtikuljozom. Abstracts of the regional scientific-practical Conference. -Kuibyshev, pp. 40-41.
- Stepanov EA (1988) Malformations and diseases of the abdominal wall and abdominal organs Childhood surgery Clinical surgery. A reference guide for doctors edited by YM. Pantsyrev M (Ed.), Medicine. pp. 600-614.
- De Siqueira J, Tawfiq O, Garner J (2014) Managing the open abdomen in a district general hospital. Ann R Coil Surg Engl 96(3): 194-198.
- Phillips Robin CS (2009) Colorectal Surgery. English translation GEOTAR-Media, No. S. 3065.

 Research Article
Research Article