Abstract
Purpose: This paper provides a bibliometric study of the research performance of Tamil Nadu, India, over the 10-year period between 2009 and 2018. Tamil Nadu has published 1,87,817 articles over a period of 10 years, of which they have been published in authoritative journals indexed by SCOPUS.
Methods: On November 9, 2019, data were collected from the Scopus. We carried out a qualitative and quantitative study using bibliometric methods of publishing inputs, papers, writers, organizations, countries, keywords and terms. Using bibliometric analysis, the data are analyzed using the excel. The analysis also aims to analyze yearly wise circulation, author wise distribution, origin wise distribution of research papers, keyword distribution, organization partnership, subject area and geographic distribution.
Results: From 2009 to 2018, we found 18,7817 publications in Tamil Nadu. I found an improvement in the annual publishing rate over time. Over the past decades, 2018 has the largest number of publications. Mr. Mohan, Viswanathan Krishna, who works at the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Chennai has the largest number of research findings over the periods of analysis. Research India Publications ‘ International Journal of Applied Engineering Research journal is the largest number of literatures. The USA is India’s most active collaborating country with India, the Indian Institute of Technology Madras was the most active institution, keyword analysis showed that human, controlled study, nonhuman and others were the hot spots of these research studies.
Conclusion: This bibliometric study revealed that publication research output from Tamil Nadu growing well from all fields. As per the comparison of Tamil Nadu population growth [1] and publication growth, the publication growth rate is 2 % lower than population growth so we need to increase the publication growth.
Keywords: Bibliometrics Study; Tamil Nadu; Research Productivity; Research Output; h-Index, International Collaboration
Abbreviations: UGC: University Grant Commission; IITM: Indian Institute of Technology Madras; NIRF: National Institute Ranking Framework
Introduction
Tamil Nadu is one of India’s 28 states. Chennai (formerly known as Madras) is its capital and largest city. Located in the southernmost part of the Indian subcontinent, Tamil Nadu is bordered by the union territories of Puducherry and Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh, South Indian states. It is bordered on the north by the Western Ghats, the Nilgiri Mountains, the Meghamalai Hills, and on the west by Kerala, on the east by the Bay of Bengal, on the southeast by the Gulf of Mannar, and on the south by the Indian Ocean. The state shares a sea border with the Sri Lankan government. In Tamil Nadu, there are 22 state universities and 29 Deemed Universities operating, which include the disciplines of arts and science, engineering, agriculture and medicine. [2]. University Grant Commission (UGC) is the major funding sponsor in Tamil Nadu publications UGC and other statutory regulatory bodies are responsible for the organization and maintenance of standards in universities and colleges in Tamil Nadu.
Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM) got third rank and Anna University got thirteen rank in all over the India during the year of 2019 [3] and National Institute Ranking Framework [4] (NIRF) ranking, the Indian Institute of Technology Madras bagged the 1st ranks and Anna University got 13th rank among the overall institutions in India during the year of 2019 The first university was established in 1857 at Chennai (Madras) University of Madras, followed in 1929 by Annamalai University Annamalai Nagar. These two universities are our nation’s pre-independence universities [5]. In India, one of the most highly ranked institution available state was tamilnadu, by holding IITs, IIMs and leading medical and technical universities. Analyzing the scholarly research output of this Indian state will give an overview of the Indian research growth, further, to identify the gap in the research in different disciplines and research growth this study will give a greater benefit to all the researchers.
Review of Literature
Manuelaj Peter, Spurgeon Anandraj, Mohamed Idhris, Abdurahiman Pattukuthu and Arun Vijay Subbarayalu [6] analyzed Bibliometric study in Health Care Professionals in Saudi Arabia the journal “PLoS One” was the most effective journal published in 2014-18, with 680 of its publishing followed by the Saudi medical journal.
Mohamed Idhris, Manuelraj Peter, Abdurahiman Pattukuthu and Spurgeon Anandraj Samuel [7], the study reveals a gradual increase in work on LUPUS between 2010 and 2017. Highest number of publications related to the year 2016. During 2010-2017, the United States is the top contributor. PETRI M is the lead author with 394 papers comprising 1,017% of the overall publications. Siwach AK et al. [8] research explores Maharshi Dayanand University, Rohtak’s research contributions in terms of publishing output over the period 2000-2013 as reflected in the Scopus database. The research evaluates the year - to-year efficacy of research, its effects on citations, national and international partnerships, top collaborative institutions, subject-matter distribution of articles, journals used for correspondence, most popular journals for publishing, most prolific authors, number of citations earned and top-quoted University papers during the study period.
N Geetha et al. [9] analyzed that her paper on Research Output of Anna University: A Bibliometric Study Based on Scopus Database stated her study shows that there is substantial research output and a steady increase in publications among Anna University academics and the dominance of collaborative work between Anna University. Venkatakrishnan CJ [10] Analysis of the growth trend was carried out and predictions are presented. Prosthodontist exhibited a tendency to publish case reports in general dental journals in international newspapers. Poorni S, et al. [11] analyzed that Most of the 33 papers have been published in the Indian Journal of Dental Research and 25 in the Conservative Dentistry Review. Of these papers, 66 are based on the authors ‘ original research. Kumaragurupari R, et al. [12] revealed that research quality, as reflected in both the number of publications in peer-reviewed journals and those journals ‘ qualitative indicators, improved during the duration of this study.
Methodology
The chosen data were downloaded from Scopus database. The following search terms have been used to retrieve the records from database “AFFILCITY (Tamilnadu) OR AFFILCITY(Tamilnadu) OR AFFILCITY(Chennai) OR AFFILCITY(Vellore) OR AFFILCITY(Tiruvannamalai) OR AFFILCITY(Cuddalore) OR AFFILCITY(Villuppuram) OR AFFILCITY(Kancheepuram) OR AFFILCITY(Tiruvallur) OR AFFILCITY(Kallakurich) OR AFFILCITY(Chengalpattu) OR AFFILCITY(Tirupattur) OR AFFILCITY(Ranipettai) OR AFFILCITY( Coimbatore) OR AFFILCITY(Nilgiris) OR AFFILCITY(Salem AND india) OR AFFILCITY(Dharmapuri) OR AFFILCITY(Erode) OR AFFILCITY(Dindigul) OR AFFILCITY(Karur) OR AFFILCITY(Namakkal) OR AFFILCITY(Krishnagiri) OR AFFILCITY(Tirupur) OR AFFILCITY(Thanjavur) OR AFFILCITY(Tiruchirappalli) OR AFFILCITY( Trichy) OR AFFILCITY(Pudukkottai) OR AFFILCITY(Nagapattinam) OR AFFILCITY(Tiruvarur) OR AFFILCITY(Perambalur) OR AFFILCITY(Ariyalur) OR AFFILCITY(Kanyakumari) OR AFFILCITY( Madurai) OR AFFILCITY(Ramanathapuram) OR AFFILCITY( Tirunelveli) OR AFFILCITY(Virudhunagar) OR AFFILCITY(Sivagangai) OR AFFILCITY(Thoothukudi) OR AFFILCITY(Theni) OR AFFILCITY(Tenkasi)” from 2009 to 2018. No journal or types of article restrictions have been established. All the publications that were displayed were taken into the analysis. In Excel, a data sheet was prepared to record the information and then the data was entered from the paper itself manually.
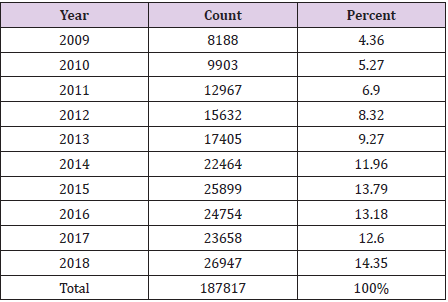
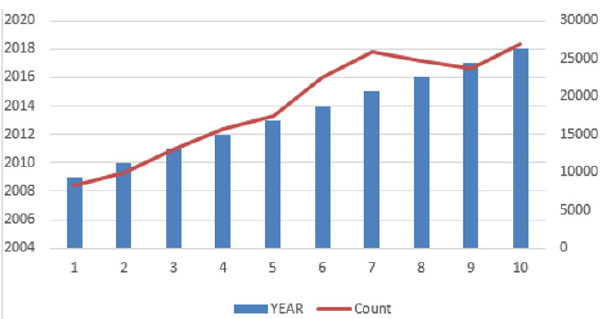
Table 1 shows the yearly publication of articles published by Tamil Nadu State based on Scopus results. When reviewing the last ten years of publishing results, it is observed that (14.35%) of articles n=26947 published in 2018 and the remaining 85 percent of articles published over a 9-year period. While 2015 has the second highest number of articles n=25899, (13.79 %), the lowest number of articles published in 2009 was n=8188 (4.36%). On an average, n=18781 articles were published per year. After 2014 research publication increased very rapid, and last five years contributed 68.88% of the research output. From Figure 1, we can see an upward trend in Tamil Nadu’s research output regarding the number of publications from the Scopus list (Tables 1 & 2) (Figure 1) [13,14].
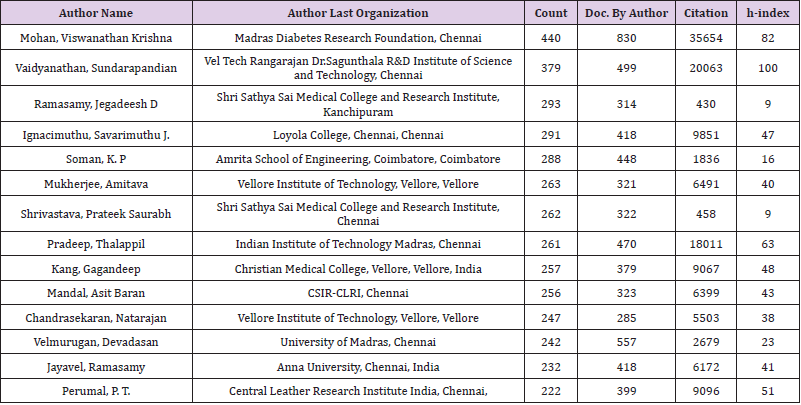
Table 2 indicates ranking of authors by number of publications. Mr. Mohan, Viswanathan Krishna, working at the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Chennai, got the first rank with 440 publications and also highest citation score among the top 15 authors, Mr. Vaidyanathan, Underspending, he is working in Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and Technology Chennai, ranked second with 379 publications, and he got highest h-index (n=100). Mr. Ramasamy Jegadeesh working in Shri Sathya Sai Medical College and Research Institute, Kanchipuram, ranked third with 293 publications. Most of authors are working in the Private institutions. Out of the 15 authors nine authors are working in the Chennai based institutions. The top 15 authors analysis also found that only Medical and Engineering subjects’ group were produced more scholarly research than the other subject disciples (Table 3).
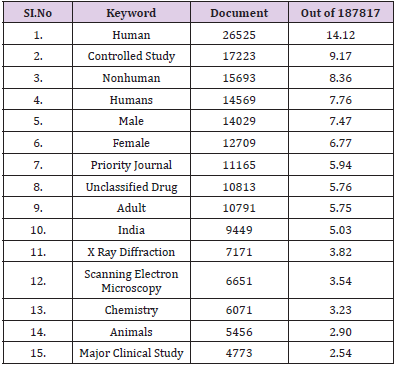
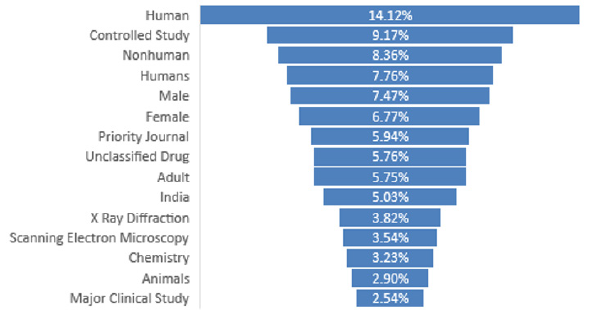
Table 3 shows the list of Journals ranked. The most productive journal is the International Journal of Applied Engineering Research with n=5949 articles, followed with n=2155 articles by the Indian Journal of Science and Technology, some of the journals cite score and citations data are not available in the Scopus database. The Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research published by (JCDR Research and Publications (Pvt) Limited) n=1053 got least number of publications among top 15 journals list (Table 4) (Figure 2). Another research we performed was to determine the top 15 keywords used in this Tamil Nadu publication. During the last decades from the n=187817 documents found. The top 15 keywords with high frequency of occurrence are “human” utilized n=26525 (14.12%) items, followed by “Controlled Study” n=17223 (9.17%) and “Nonhuman” n=15693(8.36%) items. It was identified that the top listed keywords are mostly from medical and Science background (Table 5) (Figure 3) [15].
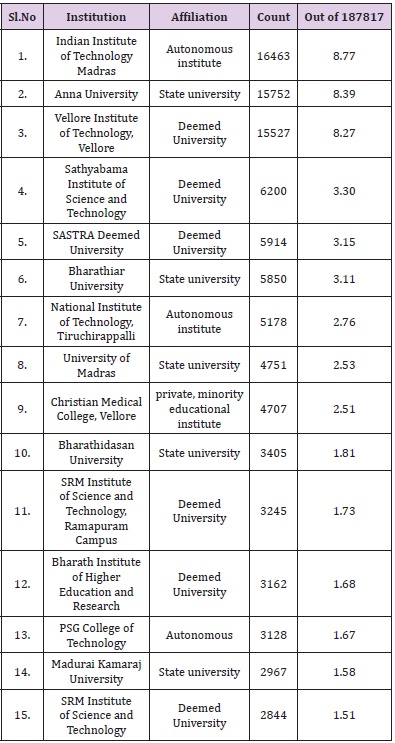
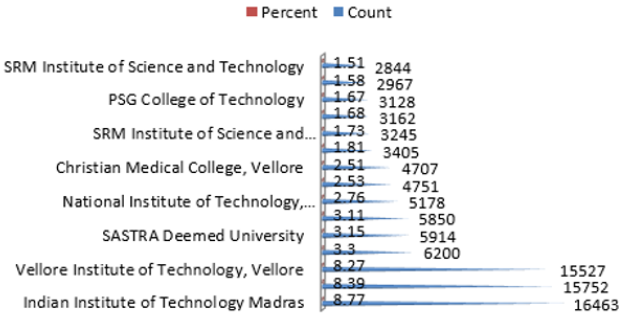
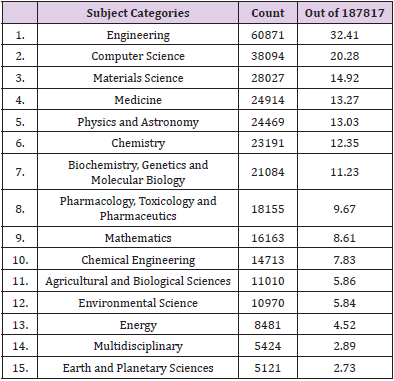
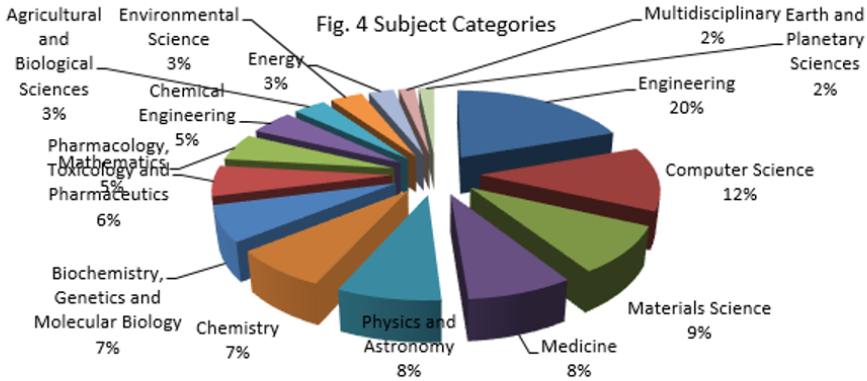
The fifteen highly productive Institutes get the highest publishing level in Tamil Nadu in Table 5, With n= 16463 (8.77%) papers, the Indian Institute of Technology Madras is in first place, followed by Anna University, in second position with n= 15752 (8.39%) documents, and Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore in third position with n=15527 (8.27%). In positions four are the Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology with n=6200 (3.30%), Finally SRM Institute of Science and Technology has n=2844 (1.51%). Increasing publications and ranking affiliations could be related to collaboration among authors. Most of the institutions are based on engineering and autonomous body (Table 6) (Figure 4). The number of publications was acquired from the Scopus database by each thematic field. The major thematic areas are represented by the distribution (Table 6). This figure 4 shows that the area with the highest percentage of documents was Engineering n=60871 (32.41) followed by Computer Science n=38094 (20.28%), Materials Science n=28027 (14.92%) and Medicine n=24914 (13.27%). Engineering and engineering related subject Categories are occupied one third of top 15 major subjects. This shows the need of improvement in the medical science research productivity (Table 7) (Figure 5) [16].
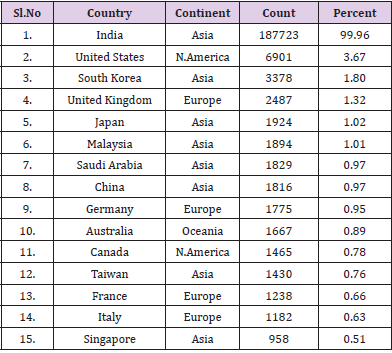
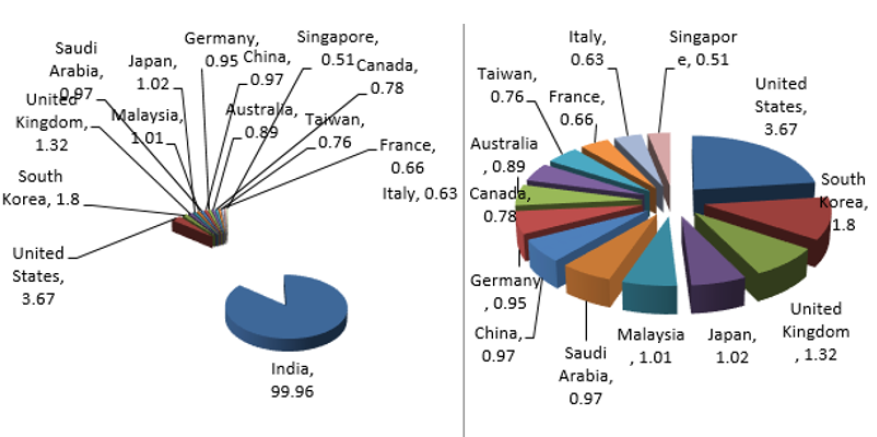
Number of publications ranked the top 15 countries / territories, including the number and percentage of single country articles and internationally collaborative articles (Table 7) Eight Asian countries, two North American countries, four European countries, and one country in Oceania are ranked among the top 15 of the publications. In the top 15 competitive countries, there are still no African or South American countries. The seven major industrial nations (G7: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States) have placed the top fifteen in the world. In addition, G7 had high productivity in independent papers, which included all independent papers n=16972 (9.03%). United states have contributed n=6901(3.67%) articles and stood first rank in the ranking of Country Collaborated with India followed by South Korea n=3378(1.80%) articles has received second highest position. However, United Kingdom contributed n=2487(1.32%) followed by Japan n=1924(1.02%) [17-20].
Conspectus
a) It is clear from the finding that n=26947(14.35%) maximum number of publications were published in the year 2018.
b) It indicates that Mr.Mohan, Viswanathan Krishna, working at the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Chennai, got the first rank with 440 publications and also highest citation score (n=35654).
c) It is cleared that the most productive journal is the International Journal of Applied Engineering Research with n=5949 articles.
d) It is clear from the study that the keyword “Human” n=26525(14.12%) is the most dominated keywords in this study.
e) It revealed that Indian Institute of Technology Madras has dominated the Top ranked Institute list by contributing n=16463(8.77%) articles alone.
f) It is clear from the study that the Subject Categories Engineering n=60871(32.41%) is the is the most dominated Subject Categories in this study.
g) United states have contributed n=6901(3.67%) articles and stood first rank in the ranking of Country Collaborated with India.
Conclusion
The study was conducted based on Scopus database during 2009-2018 of Tamil Nadu. Publication growth in Tamil Nadu is expanding rapidly in recent years. UGC is the major funding sponsor in Tamil Nadu publications and UGC funded publication count is increased year by year nevertheless after between 2015 to 2018 publication count is decreased it shows that lack of publication awareness among the researchers. The Scopus database covered only standard publications that is one of the reasons for it. Most of the top-ranking authors are working in the non-governmental organizations. Publication count has increased to force Nongovernmental organization authors to work under them. In recent years, the number of publication count is increased year by year.
References
- (2019) ENVIS Centre, M.OE.F., Govt. of India, ENVIS Centre.
- (2019) Tamil Nadu, in wikipedia.
- (2019) QS India University Ranking 2019.
- (2019) NIRF, National Institutional Ranking Framework, in India Ranking.
- (2019) University of Madras, in Wikipedia.
- M Peter SS, M Idhris, A Pattukuthu, AV Subbarayalu (2019) Bibliometric Analysis of Research Productivity of Health Care Professionals in Saudi Arabia: An Exploratory Study. Library Philosophy and Practice p. 1-21.
- Mohamed Idhris MP, Abdurahiman Pattukuthu (2019) Scientometric Analysis and Literature Research Growth of Lupus During 2010-2017. Library Philosophy and Practice (e-journal) p. 1-8.
- Siwach, Anil Kumar, Kumar Satish (2015) Bibliometric analysis of research publications of Maharshi Dayanand University (Rohtak) during 2000-2013. DESIDOC Journal of Library and Information Technology 35(1): 17-24.
- Geetha N, Kothainayaki S (2019) Research Output of Anna University: A Bibliometric Study Based on Scopus Database. Asian Journal of Information Science and Technology 9: 84-91.
- Venkatakrishnan CJ (2013) Bibliometric study of publication by Indian prosthodontists between 1996-2007: a medline approach. J Indian Prosthodont Soc 13(4): 536-540.
- Poorni S, Ramachandran S, Rooban T, Kumar PM (2010) Contributions of Indian conservative dentists and endodontists to the Medline database during 1996-2009: A bibliometric analysis. J Conserv Dent 13(4): 169-172.
- Kumaragurupari R, PC Sieving, P Lalitha (2010) A bibliometric study of publications by Indian ophthalmologists and vision researchers, 2001-06. Indian J Ophthalmol 58(4): 275-280.
- Shafiei K, Khazaneha M (2018) A bibliometric study of the movement disorder field by analyzing classic citation data on publication. Iran J Neurol 17(1): 53-55.
- Sheridan G, Wisken E, Hing CB, Smith TO (2018) A bibliometric analysis assessing temporal changes in publication and authorship characteristics in The Knee from 1996 to 2016. Knee 25(2): 213-218.
- Tellez H, Vadillo JM (2010) Bibliometric study of journal publications on analytical chemistry 2000-2007: publication productivity and journal preferences by country. Anal Bioanal Chem 397(4): 1477-1484.
- Thompson DF (2019) Publication Records and Bibliometric Indices of Pharmacy School Deans. Am J Pharm Educ 83(2): 6513.
- Van der Steen LP, Hage JJ, Loonen MP, Kon M (2004) Full publication of papers presented at the 1995 through 1999 European Association of Plastic Surgeons annual scientific meetings: a systemic bibliometric analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(1): 113-120.
- Kokulu K, Mutlu H, Sert ET (2019) Scientific Publication Productivity of Emergency Physicians: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Last Decade. J Emerg Med 57(1): 13-20.
- Liu CJ, Yeh TC, Hsu SH, Chu CM, Liu CK, et al. (2018) Bibliometric Analysis of Palliative Care-Related Publication Trends During 2001 to 2016. Am J Hosp Palliat Care 35(10): 1280-1286.
- López Muñoz F, Marín F, Boya J (1996) Bibliometric evaluation of the Spanish scientific output in neurosciences. Analysis of the publication with international readership between 1984 and 1993. Rev Neurol 24(128): 417-426.

 Research Article
Research Article