Abstract
Background: Sick sinus syndrome (SSS) is a common disease and causes increased risk of death and cardiovascular disease in patients. When patients with SSS refuse pacemaker therapy because of contraindications or financial or personal reasons, drug treatment is needed, especially in developing countries.
Objective: The study assessed the therapeutic effects of calcium dibutyryladenosine cyclophosphate (CDC) on patients with SSS.
Method: We studied 65 inpatients with SSS who were without permanent pacemaker implantation and were treated with or without CDC at random. The patients who received intravenous injection with CDC in addition to conventional treatment were considered as treatment group. The patients who only received conventional treatment were considered as control group. After 12 days administration, manifestations, 12-lead electrocardiographic and 24-hour Holter monitor were compared respectively.
Result: After the treatment with CDC, 91.2% of the patients reported a significant overall improvement of symptoms, while patients recovered clearly compared with the control group (P<0.01). CDC markedly improved heart rate measured by 24-hour Holter monitor in patients with SSS compared with the control group (P<0.01).
Conclusion: CDC showed significant therapeutic effects on patients with SSS and could be an affordable and expected alternative therapy.
Keywords: Calcium Dibutyryladenosine Cyclophosphate; Sick Sinus Syndrome; Therapy; Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate; Heart Rate
Abbreviations and Acronyms: cAMP: Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate; CDC: Calcium Dibutyryladenosine Cyclophosphate; ECG: Electrocardiographic; SSS: Sick Sinus Syndrome
Introduction
Sick sinus syndrome (SSS) is a common and prevalent disease characterized by symptomatic dysfunction of the sinoatrial node. Typical symptoms of SSS include dizziness, syncope, palpitations, exertional dyspnea, easy fatigability from chronotropic incompetence, heart failure, angina, or even sudden death. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), SSS usually manifests as sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, or sinoatrial block, and sometimes is accompanied by supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (“tachybrady” syndrome) [1,2]. SSS mostly occurs in the elder and causes increased risk of death and cardiovascular disease in patients [3]. The number of Americans with SSS will remarkably increase by the aging [4]. Despite pacemaker implantation is the effective treatment of SSS, parts of patients with SSS refuse pacemaker therapy because of contraindications or financial or personal reasons, especially in developing countries. Drug treatment for SSS has received little attention and is poorly understood. Here, we observed the treatment with calcium dibutyryladenosine cyclophosphate (CDC) on individuals hospitalized for SSS to investigate the therapeutic effects of CDC.
Methods
Patients
The open, non-interventional study comprised 65 hospitalized individuals with SSS aged 31 to 73 years (median age 46.5 years) when treated between 2008 and 2018 in the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China. The patients were diagnosed with SSS if symptoms or signs consistent with SSS (e.g., syncope, dizziness, bradycardia, sinus pauses), with no evidence of other conditions responsible for the episode, such as atrioventricular block or medication use. 12-lead ECG, 24-hour Holter monitor and transesophageal atrial pacing could confirm SSS cases. All of them refused pacemaker implantation because of different reasons. Patients were randomized, 31 to control and 34 to treatment. All the patients received conventional treatment of SSS without permanent pacemaker implantation. In addition to conventional treatment, the patients who received intravenous injection with CDC for injection (Shanghai No. 1 Biochemical & Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, 40mg CDC in 250 ml 5% glucose for injection per day) were considered as treatment group. The patients who only received conventional treatment were considered as control group. After 12 days administration, manifestations, 12- lead electrocardiographic (ECG) and 24-hour Holter monitor were compared respectively.
Assessments and Outcome Measures
The therapeutic effect of CDC injection with SSS patients was assessed at the beginning and the end of treatment and was evaluated as follows:
Excellent: The disappearance of clinical symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, syncope and other discomfort, heart rate > 70000 beats/24 h, heart rate ≥ 55 beats/min in 12-lead ECG, the improvement of average heart rate ≥ 10 beats/min in 24-hour Holter ECG.
Effective: Ameliorative clinical symptoms, heart rate 65000- 70000 beats/24 h, heart rate 45-55 beats/min in 12-lead ECG, the improvement of average heart rate 5-10 beats/min in 24-hour Holter ECG.
Null: Aggravation or no change in clinical symptoms, 12-lead ECG and 24-hour Holter ECG.
Statistical Analyses
All the statistical data were analyzed by the statistical program SPSS 10.0 (IBM Corporation, NY, USA). The percentage of effectiveness was analyzed by Chi-square test. The other statistical comparisons between two groups were analyzed by the Student’s t-test. All values were presented as mean ± standard deviation. A two-tailed P value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Result
Evaluation of Efficacy
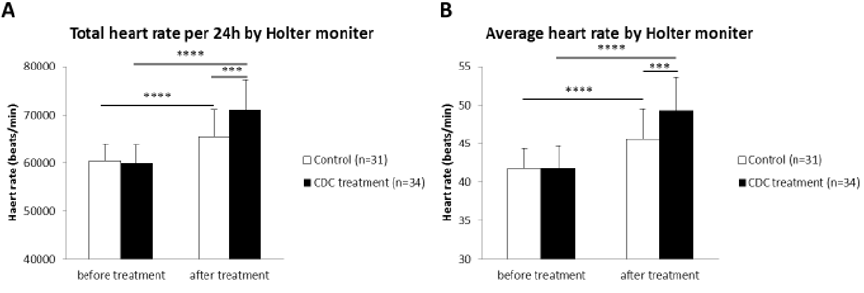
To analyze the effect of CDC on patients with SSS, patients were treated with or without CDC for injection, which has already been used in clinic in China for more than five years. We found that patients received CDC injection, compared with control group patients, experienced remarkably improvements in heart rate as well as clinical symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, syncope and other discomfort (Table 1). After the treatment with CDC, 91.2% of the patients reported a significant overall improvement of symptoms, while patients recovered clearly compared with control group patients (Table 1). CDC significantly increased the average heart rate and total heart rate per 24 hours measured by 24-hour Holter monitor in patients with SSS compared with control group patients (Figure 1).
Table 1: Comparison of curative effect between two groups.
Note: CDC = Calcium Dibutyryladenosine Cyclophosphate; *p<0.01
Figure 1: Heart rate was significantly improved after the treatment with CDC injection in patients with sick sinus syndrome.
A. Total heart rate per 24 hours measured by 24-hour Holter monitor in patients before and after treatment.
B. Average heart rate measured by 24-hour Holter monitor in patients before and after treatment. (Values are presented as mean ± SEM. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
Adverse Events
Most of patients rated CDC treatment as well tolerated. Overall, 2 out of 34 (5.9%) patients experienced nausea and vomiting during the intravenous injection with CDC. After medication, the 2 cases with adverse events were maintained and achieved remission of clinical symptoms. There is no adverse event appeared in the control group.
Discussion
SSS is a common and severe cardiovascular disease, and only parts of patients with SSS could accept and receive permanent pacemaker placement treatment which is the only effective treatment for chronic symptomatic SSS [5]. So far, there is no exactly effective alternative drug therapy reported, and the present study is the first observation to demonstrate the effectiveness of CDC injection in the treatment of SSS patients. CDC is a kind of derivatives of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) by chemical synthesis and belongs to protease activator. Within the heart, the channels which determine heart rate are found most abundantly in sinoatrial cardiomyocytes and modulated by local cAMP concentrations [6]. Here, we observed the treatment with CDC injection on patients hospitalized for SSS. We found that CDC injection markedly improved symptoms and heart rate of SSS patients, indicating the effectiveness of improved heart rate might be mediated by cAMP signaling pathway. The safety profile of CDC injection in SSS was also observed during the treatment of SSS. The CDC injection was safe as demonstrated by a low frequency of few adverse events, resulting in only two patients experienced nausea and vominting during the intravenous injection with CDC, while they recovered quickly after symptomatic therapy. Of consequence, CDC injection could be used in the SSS patients who refuse or cannot accept pacemaker implantation by the reasons of contraindications, financial or private aspects. CDC is safe and significantly improves clinical symptoms and heart rate in routine treated patients with SSS. CDC shows significant therapeutic effects on patients with SSS, and could be an affordable, efficacious and expected alternative therapy.
Clinical Perspectives
SSS is a common disease which causes increased risk of death and cardiovascular disease in patients. When patients refuse pacemaker therapy because of contraindications or financial or personal reasons, drug treatment is needed, especially in developing countries. We show that intravenous injection with CDC significantly promotes recovery on patients with SSS and could be an affordable and expected alternative therapy.
Acknowledgment
Thanks for all the co-authors’ help.
Conflict of Interest
No conflicts of interest.
References
- Ferrer MI (1973) The sick sinus syndrome. Circulation 47(3): 635-641.
- Adán V, Crown LA (2003) Diagnosis and treatment of sick sinus syndrome. Am Fam Physician 67(8):1725-1732.
- Alonso A, Jensen PN, Lopez FL, Chen LY, Psaty BM, et.al. (2014) Association of sick sinus syndrome with incident cardiovascular disease and mortality: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study and Cardiovascular Health Study. PLoS One 9(10): e109662.
- Jensen PN, Gronroos NN, Chen LY, Folsom AR, De Filippi C, et al. (2014) Incidence of and risk factors for sick sinus syndrome in the general population. J Am Coll Cardiol 64(6): 531-538.
- Semelka M, Gera J, Usman S (2013) Sick sinus syndrome: a review. Am Fam Physician 87(10): 691-696.
- Alig J, Marger L, Mesirca P, Ehmke H, Mangoni ME, et al. (2009) Control of heart rate by cAMP sensitivity of HCN channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(29): 12189-12194.

 Research Article
Research Article