Short Communication
In 2016 a very powerful AI (artificial intelligence) tool has been established for identifying RNA pseudouridine sites, which is one of the important post modifications in RNA [1]. To see how the webserver is working, please do the following.
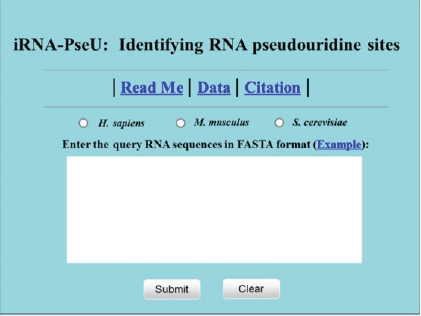
Step 1. Open the web server at http://lin-group.cn/server/ iRNA-PseU and you will see the top page of the iRNA-PseU predictor on your computer screen, as shown in Figure 1. Click on the Read Me button to see a brief introduction about the predictor and the caveat when using it.
Figure 1: A semi-screenshot for the top-page of the iRNAPseU web-server at http://lin-group.cn/server/iRNAPseU (Adapted from [1] with permission).
Step 2. Select the organism or species by checking on the corresponding open circle. Either type or copy/paste the query RNA sequences into the input box at the center of Figure 1. The input sequence should be in FASTA format. For the examples of RNA sequences in FASTA format, click the Example button right above the input box.
Step 3. Click on the Submit button to see the predicted result. For example, if using the three query RNA sequences from the H. sapiens species in the Example window as the input and checking on the H. sapiens button, after clicking the Submit button, you will see the following shown on the screen of your computer.
a. The 1st query sequence includes 5 U (uridine) residues, of which the one at position 11 can be modified to be of pseudouridine (Ψ site).
b. The 2nd query sequence includes 3U residues, of which none can be modified to be of pseudouridine.
c. The 3rd query sequence includes 7 U residues, of which the one at position 21 can be modified to be of pseudouridine. All these results are fully consistent with the experimental observations.
Note: to get the anticipated prediction accuracy, the species button must be consistent with the source of query sequences: if the query sequences are from H. sapiens, check on the H. sapiens button; from M. musculus, check on the M. musculus button; from S. cerevisiae, check on the S. cerevisiae button.
Step 4. Click on the Data button to download the datasets used to train and test the iRNA-PseU predictor.
Step 5. Click on the Citation button to find the relevant papers that document the detailed development and algorithm of iRNAPseU.
It is instructive to point out that the AI tool has been developed by strictly observing the guidelines of “Chou’s 5-steps rule” and hence have the following notable merits (see, e.g., [2-29] and three comprehensive review papers [30-32]):
a. Crystal clear in logic development,
b. Completely transparent in operation,
c. Easily to repeat the reported results by other investigators,
d. With high potential in stimulating other sequenceanalyzing methods, and
e. Very convenient to be used by most experimental scientists.
Also, it has not escaped our notice that during the development of iRNA-PseU AI tool, the approach of general pseudo amino acid components [33] or PseAAC [34] had been applied and hence its accuracy would be much higher than its counterparts, as concurred by many investigators [30, 33-281]. It is anticipated that iRNA-PseU may become a useful high throughput tool for conducting genome analysis as well as drug development. For the remarkable and awesome roles of the “5-steps rule” in driving proteome, genome analyses and drug development, see a series of recent papers [31, 32, 282-292] where the rule and its wide applications have been very impressively presented from various aspects or at different angles.
References
- W Chen, H Tang, J Ye, H Lin, KC Chou (2016) iRNA-PseU: Identifying RNA pseudouridine sites. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids 5: e332.
- Barukab, YD Khan, SA Khan, KC Chou (2019) iSulfoTyr-PseAAC: Identify tyrosine sulfation sites by incorporating statistical moments via Chou's 5-steps rule and pseudo components. Current Genomics 20(4).
- X Cheng, WZ Lin, X Xiao, KC Chou (2019) pLoc_bal-mAnimal: predict subcellular localization of animal proteins by balancing training dataset and PseAAC. Bioinformatics 35(3): 398-406.
- KC Chou, X Cheng, X Xiao (2019) pLoc_bal-mHum: predict subcellular localization of human proteins by PseAAC and quasi-balancing training dataset. Genomics 111(6): 1274-1282.
- KC Chou, X Cheng, X Xiao (2019) pLoc_bal-mEuk: predict subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins by general PseAAC and quasi-balancing training dataset. Med Chem 15(5): 472-485.
- A Ehsan, MK Mahmood, YD Khan, OM Barukab, SA Khan, et al. (2019) iHyd-PseAAC (EPSV): Identify hydroxylation sites in proteins by extracting enhanced position and sequence variant feature via Chou's 5-step rule and general pseudo amino acid composition. Current Genomics 20(2): 124-133.
- P Feng, H Yang, H Ding, H Lin, W Chen, et al. (2019) iDNA6mA-PseKNC: Identifying DNA N(6)-methyladenosine sites by incorporating nucleotide physicochemical properties into PseKNC. Genomics 111: 96-102.
- W Hussain, SD Khan, N Rasool, SA Khan, KC Chou (2019) SPalmitoylC-PseAAC: A sequence-based model developed via Chou's 5-steps rule and general PseAAC for identifying S-palmitoylation sites in proteins. Anal Biochem 568: 14-23.
- W Hussain, YD Khan, N Rasool, SA Khan, KC Chou (2019) SPrenylC-PseAAC: A sequence-based model developed via Chou's 5-steps rule and general PseAAC for identifying S-prenylation sites in proteins. J Theor Biol 468(7): 1-11.
- S Ilyas, W Hussain, A Ashraf, YD Khan, SA Khan, et al. (2019) iMethylK-PseAAC: Improving accuracy for lysine methylation sites identification by incorporating statistical moments and position relative features into general PseAAC via Chou’s 5-steps rule. Current Genomics 20(4).
- J Jia, X Li, W Qiu, X Xiao, KC Chou (2019) iPPI-PseAAC(CGR): Identify protein-protein interactions by incorporating chaos game representation into PseAAC. Journal of Theoretical Biology 460(7): 195-203.
- YD Khan, A Batool, N Rasool, A Khan, KC Chou (2019) Prediction of nitrosocysteine sites using position and composition variant features. Letters in Organic Chemistry 16(4): 283-293.
- YD Khan, M Jamil, W Hussain, N Rasool, SA Khan, et al. (2019) pSSbond-PseAAC: Prediction of disulfide bonding sites by integration of PseAAC and statistical moments. J Theor Biol 463(21): 47-55.
- Y Lu, S Wang, J Wang, G Zhou, Q Zhang, et al. (2019) An Epidemic Avian Influenza Prediction Model Based on Google Trends. Letters in Organic Chemistry 16(4): 303-310.
- B Niu, C Liang, Y Lu, M Zhao, Q Chen, et al. (2019) Glioma stages prediction based on machine learning algorithm combined with protein-protein interaction networks. Genomics.
- G Pugalenthi, V Nithya, KC Chou, G Archunan (2019) Nglyc: A random forest method for prediction of N-Glycosylation sites in eukaryotic protein sequence. Protein & Peptide Letters.
- Salman, M Khan, N Iqbal, T Hussain, S Afzal, et al. (2019) A two-level computation model based on deep learning algorithm for identification of piRNA and their functions via Chou's 5-steps rule. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (IJPRT).
- X Xiao, X Cheng, G Chen, Q Mao, KC Chou (2019) pLoc_bal-mGpos: predict subcellular localization of Gram-positive bacterial proteins by quasi-balancing training dataset and PseAAC. Genomics 111: 886-892.
- X Xiao, ZC Xu, WR Qiu, P Wang, HT Ge, et al. (2019) iPSW(2L)-PseKNC: A two-layer predictor for identifying promoters and their strength by hybrid features via pseudo K-tuple nucleotide composition. Genomics 111(6): 1785-1793.
- L Yang, Y Lv, S Wang, Q Zhang, Y Pan, et al. (2019) Identifying FL11 subtype by characterizing tumor immune microenvironment in prostate adenocarcinoma via Chou's 5-steps rule. Genomics.
- A Wiktorowicz, A Wit, A Dziewierz, L Rzeszutko, D Dudek, et al. (2019) Calcium Pattern Assessment in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis Via the Chou's 5-Steps Rule. Current Pharmaceutical Design 25(35): 3769-3775.
- S Vishnoi, P Garg, P Arora (2019) Physicochemical n-Grams Tool: A tool for protein physicochemical descriptor generation via Chou's 5-steps rule. Chem Biol Drug Des 95(1): 79-86.
- Y Liang, S Zhang (2019) Identifying DNase I hypersensitive sites using multi-features fusion and F-score features selection via Chou's 5-steps rule. Biophys Chem 253: 106227.
- R Liang, J Xie, C Zhang, M Zhang, H Huang, et al. (2019) Identifying Cancer Targets Based on Machine Learning Methods via Chou's 5-steps Rule and General Pseudo Components. Current Topics in Medicnal Chemistry 19(25): 2301-2317.
- J Lan, J Liu, C Liao, DJ Merkler, Q Han, et al. (2019) A Study for Therapeutic Treatment against Parkinson’s Disease via Chou's 5-steps Rule. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 19(25): 2318-2333.
- M Kabir, S Ahmad, M Iqbal, M Hayat (2019) iNR-2L: A two-level sequence-based predictor developed via Chou's 5-steps rule and general PseAAC for identifying nuclear receptors and their families. Genomics.
- Z Ju, SY Wang (2019) Prediction of lysine formylation sites using the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs via Chou's 5-steps rule and general pseudo components. Genomics.
- X Du, Y Diao, H Liu, S Li (2019) MsDBP: Exploring DNA-binding Proteins by Integrating Multi-scale Sequence Information via Chou's 5-steps Rule. Journal of Proteome Research 18(8): 3119-3132.
- Y Chen, X Fan (2019) Use of Chou's 5-Steps Rule to Reveal Active Compound and Mechanism of Shuangshen Pingfei San on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Current Molecular Medicine 20(3).
- KC Chou (2011) Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition (50th Anniversary Year Review, 5-steps rule). Journal of Theoretical Biology 273(1): 236-247.
- KC Chou (2019) Advance in predicting subcellular localization of multi-label proteins and its implication for developing multi-target drugs. Current Medicinal Chemistry 26: 4918-4943.
- KC Chou (2019) Impacts of pseudo amino acid components and 5-steps rule to proteomics and proteome analysis. Current Topics in Medicinak Chemistry (CTMC) (Special Issue ed. G.P Zhou) 19(25).
- KC Chou (2001) Prediction of protein cellular attributes using pseudo amino acid composition. PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Genetics (Erratum: ibid., 2001, Vol.44, 60) 43: 246-255.
- KC Chou (2005) Using amphiphilic pseudo amino acid composition to predict enzyme subfamily classes. Bioinformatics 21(1): 10-19.
- ZM Guo (2002) Prediction of membrane protein types by using pattern recognition method based on pseudo amino acid composition. Master Thesis, Bio-X Life Science Research Center, Shanghai Jiaotong University.
- YD Cai, KC Chou (2003) Nearest neighbour algorithm for predicting protein subcellular location by combining functional domain composition and pseudo amino acid composition. Biochem Biophys Res Comm (BBRC) 305(2): 407-411.
- KC Chou, YD Cai (2003) Predicting protein quaternary structure by pseudo amino acid composition. PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Genetics 53(2): 282-289.
- KC Chou, YD Cai (2003) Prediction and classification of protein subcellular location: sequence-order effect and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry (Addendum, ibid. 2004, 91, 1085) 90(6): 1250-1260.
- YX Pan, ZZ Zhang, ZM Guo, GY Feng, ZD Huang, et al. (2003) Application of pseudo amino acid composition for predicting protein subcellular location: stochastic signal processing approach. Journal of Protein Chemistry 22(4): 395-402.
- KC Chou, YD Cai (2004) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins by hybridizing functional domain composition and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 91(6): 1197-1203.
- M Wang, J Yang, GP Liu, ZJ Xu, KC Chou (2004) Weighted-support vector machines for predicting membrane protein types based on pseudo amino acid composition. Protein Engineering, Design, and Selection 17(6): 509-516.
- YD Cai, KC Chou (2005) Predicting enzyme subclass by functional domain composition and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Proteome Research 4(3): 967-971.
- YD Cai, GP Zhou, KC Chou (2005) Predicting enzyme family classes by hybridizing gene product composition and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 234(1): 145-149.
- Y Gao, SH Shao, X Xiao, YS Ding, YS Huang, et al. (2005) Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein subcellular location: approached with Lyapunov index, Bessel function, and Chebyshev filter. Amino Acids 28: 373-376.
- H Liu, J Yang, M Wang, L Xue, KC Chou (2005) Using Fourier spectrum analysis and pseudo amino acid composition for prediction of membrane protein types. The Protein Journal 24(6): 385-389.
- HB Shen, KC Chou (2005) Using optimized evidence-theoretic K-nearest neighbor classifier and pseudo amino acid composition to predict membrane protein types. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications (BBRC) 334(1): 288-292.
- HB Shen, KC Chou (2005) Predicting protein subnuclear location with optimized evidence-theoretic K-nearest classifier and pseudo amino acid composition. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. (BBRC) 337(3): 752-756.
- YD Cai, KC Chou (2006) Predicting membrane protein type by functional domain composition and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 238(2): 395-400.
- C Chen, YX Tian, XY Zou, PX Cai, JY Mo (2006) Using pseudo amino acid composition and support vector machine to predict protein structural class. J Theor Biol 243(1): 444-448.
- C Chen, X Zhou, Y Tian, X Zou, P Cai (2006) Predicting protein structural class with pseudo amino acid composition and support vector machine fusion network. Analytical Biochemistry 357(1): 116-121.
- P Du, Y Li (2006) Prediction of protein submitochondria locations by hybridizing pseudo amino acid composition with various physicochemical features of segmented sequence. BMC Bioinformatics 30(7): 518.
- S Mondal, R Bhavna, R Mohan Babu, S Ramakumar (2006) Pseudo amino acid composition and multi-class support vector machines approach for conotoxin superfamily classification. J Theor Biol 243(2): 252-260.
- HB Shen, J Yang, KC Chou (2006) Fuzzy KNN for predicting membrane protein types from pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 240(1): 9-13.
- SQ Wang, J Yang, KC Chou (2006) Using stacked generalization to predict membrane protein types based on pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 242(4): 941-946.
- X Xiao, SH Shao, YS Ding, ZD Huang, KC Chou (2006) Using cellular automata images and pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein subcellular location. Amino Acids 30(1): 49-54.
- X Xiao, SH Shao, ZD Huang, KC Chou (2006) Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein structural classes: approached with complexity measure factor. Journal of Computational Chemistry 27(4): 478-482.
- SW Zhang, Q Pan, HC Zhang, ZC Shao, JY Shi (2006) Prediction protein homo-oligomer types by pseudo amino acid composition: Approached with an improved feature extraction and naive Bayes feature fusion. Amino Acids 30(4): 461-468.
- GP Zhou, YD Cai (2006) Predicting protease types by hybridizing gene ontology and pseudo amino acid composition. PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 63(3): 681-684.
- YL Chen, QZ Li (2007) Prediction of apoptosis protein subcellular location using improved hybrid approach and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 248(2): 377-381.
- YS Ding, TL Zhang, KC Chou (2007) Prediction of protein structure classes with pseudo amino acid composition and fuzzy support vector machine network. Protein & Peptide Letters 14(8): 811-815.
- H Lin, QZ Li (2007) Predicting conotoxin superfamily and family by using pseudo amino acid composition and modified Mahalanobis discriminant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354(2): 548-551.
- H Lin, QZ Li (2007) Using Pseudo Amino Acid Composition to Predict Protein Structural Class: Approached by Incorporating 400 Dipeptide Components. Journal of Computational Chemistry 28(9): 1463-1466.
- P Mundra, M Kumar, KK Kumar, VK Jayaraman, BD Kulkarni (2007) Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein subnuclear localization: Approached with PSSM. Pattern Recognition Letters 28(13): 1610-1615.
- JY Shi, SW Zhang, Q Pan, YM Cheng, J Xie (2007) Prediction of protein subcellular localization by support vector machines using multi-scale energy and pseudo amino acid composition. Amino Acids 33(1): 69-74.
- TL Zhang, YS Ding (2007) Using pseudo amino acid composition and binary-tree support vector machines to predict protein structural classes. Amino Acids 33(4): 623-629.
- XB Zhou, C Chen, ZC Li, XY Zou (2007) Using Chou's amphiphilic pseudo amino acid composition and support vector machine for prediction of enzyme subfamily classes. Journal of Theoretical Biology 248(3): 546–551.
- Y Diao, D Ma, Z Wen, J Yin, J Xiang, M Li (2008) Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict transmembrane regions in protein: cellular automata and Lempel-Ziv complexity. Amino Acids 34: 111-117.
- YS Ding, TL Zhang (2008) Using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition to predict subcellular localization of apoptosis proteins: an approach with immune genetic algorithm-based ensemble classifier. Pattern Recognition Letters 29(13): 1887-1892.
- Y Fang, Y Guo, Y Feng, M Li (2008) Predicting DNA-binding proteins: approached from Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and other specific sequence features. Amino Acids 34(1): 103-109.
- Q Gu, Y Ding, T Zhang (2008) Prediction of G-protein-coupled receptor classes with pseudo amino acid composition. IEEE Xplore (iCBBE, Shanghai, China) 390(1): 68-73.
- X Jiang, R Wei, TL Zhang, Q Gu (2008) Using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition to predict apoptosis proteins subcellular location: an approach by approximate entropy. Protein & Peptide Letters 15(4): 392-396.
- X Jiang, R Wei, Y Zhao, T Zhang (2008) Using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition based on approximate entropy and an ensemble of AdaBoost classifiers to predict protein subnuclear location. Amino Acids 34: 669-675.
- FM Li, QZ Li (2008) Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein subnuclear location with improved hybrid approach. Amino Acids 34: 119-125.
- FM Li, QZ Li (2008) Predicting protein subcellular location using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and improved hybrid approach. Protein & Peptide Letters 15(6): 612-616.
- H Lin (2008) The modified Mahalanobis discriminant for predicting outer membrane proteins by using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 252(2): 350-356.
- H Lin, H Ding, FB Feng-Biao Guo, AY Zhang, J Huang (2008) Predicting subcellular localization of mycobacterial proteins by using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 15(7): 739-744.
- L Nanni, A Lumini (2008) Genetic programming for creating Chou's pseudo amino acid based features for submitochondria localization. Amino Acids 34(4): 653-660.
- HB Shen, KC Chou (2008) PseAAC: a flexible web-server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition. Analytical Biochemistry 373(2): 386-388.
- JY Shi, SW Zhang, Q Pan, GP Zhou (2008) Using Pseudo Amino Acid Composition to Predict Protein Subcellular Location: Approached with Amino Acid Composition Distribution. Amino Acids 35(2): 321-327.
- X Xiao, WZ Lin, KC Chou (2008) Using grey dynamic modeling and pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein structural classes. Journal of Computational Chemistry 29(12): 2018-2024.
- X Xiao, P Wang, KC Chou (2008) Predicting protein structural classes with pseudo amino acid composition: an approach using geometric moments of cellular automaton image. Journal of Theoretical Biology 254(3): 691-696.
- GY Zhang, BS Fang (2008) Predicting the cofactors of oxidoreductases based on amino acid composition distribution and Chou's amphiphilic pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 253(2): 310-315.
- GY Zhang, HC Li, JQ Gao, BS Fang (2008) Predicting lipase types by improved Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 15(10): 1132-1137.
- SW Zhang, W Chen, F Yang, Q Pan (2008) Using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein quaternary structure: a sequence-segmented PseAAC approach. Amino Acids 35(3): 591-598.
- SW Zhang, YL Zhang, HF Yang, CH Zhao, Q Pan (2008) Using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein subcellular localization: an approach by incorporating evolutionary information and von Neumann entropies. Amino Acids 34(4): 565-572.
- TL Zhang, YS Ding, KC Chou (2008) Prediction protein structural classes with pseudo amino acid composition: approximate entropy and hydrophobicity pattern. Journal of Theoretical Biology 250(1): 186-193.
- C Chen, L Chen, X Zou, P Cai (2009) Prediction of protein secondary structure content by using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and support vector machine. Protein & Peptide Letters 16(1): 27-31.
- KC Chou (2009) Pseudo amino acid composition and its applications in bioinformatics, proteomics and system biology. Current Proteomics 6(4): 262-274.
- H Ding, L Luo, H Lin (2009) Prediction of cell wall lytic enzymes using Chou's amphiphilic pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 16(4): 351-355.
- P Du, S Cao, Y Li (2009) SubChlo: predicting protein subchloroplast locations with pseudo amino acid composition and the evidence-theoretic K-nearest neighbor (ET-KNN) algorithm. Journal of Theoretical Biolology 261(2): 330-335.
- QB Gao, ZC Jin, XF Ye, C Wu, J He (2009) Prediction of nuclear receptors with optimal pseudo amino acid composition. Analytical Biochemistry 387(1): 54-59.
- DN Georgiou, TE Karakasidis, JJ Nieto, A Torres (2009) Use of fuzzy clustering technique and matrices to classify amino acids and its impact to Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 257(1): 17-26.
- (2009) Pseudo amino acid composition, Wikipedia.
- ZC Li, XB Zhou, Z Dai, XY Zou (2009) Prediction of protein structural classes by Chou's pseudo amino acid composition: approached using continuous wavelet transform and principal component analysis. Amino Acids 37(2): 415-425.
- H Lin, H Wang, H Ding, YL Chen, QZ Li (2009) Prediction of Subcellular Localization of Apoptosis Protein Using Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Acta Biotheoretica 57(3): 321-330.
- JD Qiu, JH Huang, RP Liang, XQ Lu (2009) Prediction of G-protein-coupled receptor classes based on the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition: an approach from discrete wavelet transform. Analytical Biochemistry 390(1): 68-73.
- X Xiao, P Wang, KC Chou (2009) Predicting protein quaternary structural attribute by hybridizing functional domain composition and pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Applied Crystallography 42: 169-173.
- YH Zeng, YZ Guo, RQ Xiao, L Yang, LZ Yu, et al. (2009) Using the augmented Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for predicting protein submitochondria locations based on auto covariance approach. Journal of Theoretical Biology 259(2): 366-372.
- M Esmaeili, H Mohabatkar, S Mohsenzadeh (2010) Using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for risk type prediction of human papillomaviruses. Journal of Theoretical Biology 263(2): 203-209.
- QB Gao, XF Ye, ZC Jin, J He (2010) Improving discrimination of outer membrane proteins by fusing different forms of pseudo amino acid composition. Analytical Biochemistry 398(1): 52-59.
- Q Gu, Y Ding, T Zhang, Y Shen (2010) Prediction of G-protein-coupled receptor classes with pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of biomedical engineering 27: 500-504.
- Q Gu, YS Ding, TL Zhang (2010) Prediction of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Classes in Low Homology Using Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition with Approximate Entropy and Hydrophobicity Patterns. Protein & Peptide Letters 17(5): 559-567.
- KK Kandaswamy, G Pugalenthi, S Moller, E Hartmann, KU Kalies, et al. (2010) Prediction of Apoptosis Protein Locations with Genetic Algorithms and Support Vector Machines Through a New Mode of Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Protein and Peptide Letters 17(12): 1473-1479.
- T Liu, X Zheng, C Wang, J Wang (2010) Prediction of Subcellular Location of Apoptosis Proteins using Pseudo Amino Acid Composition: An Approach from Auto Covariance Transformation. Protein & Peptide Letters 17(10): 1263-1269.
- H Mohabatkar (2010) Prediction of cyclin proteins using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 17(10): 1207-1214.
- L Nanni, S Brahnam, A Lumini (2010) High performance set of PseAAC and sequence based descriptors for protein classification. Journal of Theoretical Biology 266(1): 1-10.
- XH Niu, NN Li, F Shi, XH Hu, JB Xia, HJ Xiong (2010) Predicting protein solubility with a hybrid approach by pseudo amino Acid composition. Protein and Peptide Letters 17(12): 1466-1472.
- JD Qiu, JH Huang, SP Shi, RP Liang (2010) Using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition to predict enzyme family classes: an approach with support vector machine based on discrete wavelet transform. Protein & Peptide Letters 17(6): 715-722.
- SS Sahu, G Panda (2010) A novel feature representation method based on Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for protein structural class prediction. Computational Biology and Chemistry 34(5-6): 320-327.
- YC Wang, XB Wang, ZX Yang, NY Deng (2010) Prediction of enzyme subfamily class via pseudo amino acid composition by incorporating the conjoint triad feature. Protein & Peptide Letters 17(11): 1441-1449.
- J Wu, ML Li, LZ Yu, C Wang (2010) An ensemble classifier of support vector machines used to predict protein structural classes by fusing auto covariance and pseudo amino acid composition. Protein J 29: 62-67.
- L Yu, Y Guo, Y Li, G Li, M Li, et al. (2010) SecretP: Identifying bacterial secreted proteins by fusing new features into Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 267(1): 1-6.
- H Ding, L Liu, FB Guo, J Huang, H Lin (2011) Identify Golgi protein types with modified mahalanobis discriminant algorithm and pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(1): 58-63.
- J Guo, N Rao, G Liu, Y Yang, G Wang (2011) Predicting protein folding rates using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Computational Chemistry 32(8): 1612-1617.
- M Hayat, A Khan (2011) Predicting membrane protein types by fusing composite protein sequence features into pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 271(1): 10-17.
- L Hu, L Zheng, Z Wang, B Li, L Liu (2011) Using pseudo amino Acid composition to predict protease families by incorporating a series of protein biological features. Protein and Peptide Letters 18(6): 552-558.
- Y Huang, L Yang, T Wang (2011) Phylogenetic analysis of DNA sequences based on the generalized pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 269(1): 217-223.
- X Jingbo, Z Silan, S Feng, X Huijuan, H Xuehai, et al. (2011) Using the concept of pseudo amino acid composition to predict resistance gene against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice: An approach from chaos games representation. Journal of Theoretical Biology 284(1): 16-23.
- B Liao, JB Jiang, QG Zeng, W Zhu (2011) Predicting Apoptosis Protein Subcellular Location with PseAAC by Incorporating Tripeptide Composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(11): 1086-1092.
- H Lin, H Ding (2011) Predicting ion channels and their types by the dipeptide mode of pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 269(1): 64-69.
- J Lin, Y Wang (2011) Using a novel AdaBoost algorithm and Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for predicting protein subcellular localization. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(12): 1219-1225.
- J Lin, Y Wang, X Xu (2011) A novel ensemble and composite approach for classifying proteins based on Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. African Journal of Biotechnology 10(74): 16963-16968.
- XL Liu, JL Lu, XH Hu (2011) Predicting Thermophilic Proteins with Pseudo Amino Acid Composition: Approached from Chaos Game Representation and Principal Component Analysis. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(12): 1244-1250.
- A Mahdavi, S Jahandideh (2011) Application of density similarities to predict membrane protein types based on pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 276(1): 132-137.
- H Mohabatkar, M Mohammad Beigi, A Esmaeili (2011) Prediction of GABA(A) receptor proteins using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and support vector machine. Journal of Theoretical Biology 281(1): 18-23.
- BM Mohammad, M Behjati, H Mohabatkar (2011) Prediction of metalloproteinase family based on the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition using a machine learning approach. Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics 12(4): 191-197.
- JD Qiu, XY Sun, SB Suo, SP Shi, SY Huang, et al. (2011) Predicting homo-oligomers and hetero-oligomers by pseudo amino acid composition: an approach from discrete wavelet transformation. Biochimie 93(7): 1132-8.
- JD Qiu, SB Suo, XY Sun, SP Shi, RP Liang (2011) OligoPred: A web-server for predicting homo-oligomeric proteins by incorporating discrete wavelet transform into Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling 30: 129-134.
- R Shi, C Xu (2011) Prediction of rat protein subcellular localization with pseudo amino Acid composition based on multiple sequential features. Protein and Peptide Letters 18(6): 625-633.
- M Shu, X Cheng, Y Zhang, Y Wang, Y Lin, et al. (2011) Predicting the Activity of ACE Inhibitory Peptides with a Novel Mode of Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(12): 1233-1243.
- D Wang, L Yang, Z Fu, J Xia (2011) Prediction of thermophilic protein with pseudo amino Acid composition: an approach from combined feature selection and reduction. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(7): 684-689.
- W Wang, XB Geng, Y Dou, T Liu, X Zheng (2011) Predicting protein subcellular localization by pseudo amino Acid composition with a segment-weighted and features-combined approach. Protein and Peptide Letters 18(5): 480-487.
- X Xiao, KC Chou (2011) Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein attributes via cellular automata and other approaches. Current Bioinformatics 6(2): 251-260.
- X Xiao, P Wang, KC Chou (2011) GPCR-2L: Predicting G protein-coupled receptors and their types by hybridizing two different modes of pseudo amino acid compositions. Molecular Biosystems 7(3): 911-919.
- R Zia Ur, A Khan (2011) Prediction of GPCRs with Pseudo Amino Acid Composition: Employing Composite Features and Grey Incidence Degree Based Classification. Protein & Peptide Letters 18(9): 872-878.
- D Zou, Z He, J He, Y Xia (2011) Supersecondary structure prediction using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Computational Chemistry 32(2): 271-278.
- JZ Cao, WQ Liu, H Gu (2012) Predicting Viral Protein Subcellular Localization with Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition and Imbalance-Weighted Multi-Label K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm. Protein and Peptide Letters 19(11): 1163-1169.
- C Chen, ZB Shen, XY Zou (2012) Dual-Layer Wavelet SVM for Predicting Protein Structural Class Via the General Form of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(4): 422-429.
- YL Chen, QZ Li, LQ Zhang (2012) Using increment of diversity to predict mitochondrial proteins of malaria parasite: integrating pseudo amino acid composition and structural alphabet. Amino Acids 42(4): 1309-1316.
- P Du, X Wang, C Xu, Y Gao (2012) PseAAC-Builder: A cross-platform stand-alone program for generating various special Chou's pseudo amino acid compositions. Analytical Biochemistry 425(2): 117-119.
- GL Fan, QZ Li (2012) Predict mycobacterial proteins subcellular locations by incorporating pseudo-average chemical shift into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 304: 88-95.
- GL Fan, QZ Li (2012) Predicting protein submitochondria locations by combining different descriptors into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Amino Acids 43(2): 545-555.
- QB Gao, H Zhao, X Ye, J He (2012) Prediction of pattern recognition receptor family using pseudo amino acid composition. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 417(1): 73-77.
- M Hayat, A Khan (2012) Discriminating Outer Membrane Proteins with Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithms Based on the General Form of Chou's PseAAC. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(4): 411-421.
- LQ Li, Y Zhang, LY Zou, Y Zhou, XQ Zheng (2012) Prediction of Protein Subcellular Multi-Localization Based on the General form of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(4): 375-387.
- B Liao, Q Xiang, D Li (2012) Incorporating Secondary Features into the General form of Chou's PseAAC for Predicting Protein Structural Class. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(11): 1133-1138.
- WZ Lin, JA Fang, X Xiao, KC Chou (2012) Predicting Secretory Proteins of Malaria Parasite by Incorporating Sequence Evolution Information into Pseudo Amino Acid Composition via Grey System Model. PLoS One 7: e49040.
- L Liu, XZ Hu, XX Liu, Y Wang, SB Li (2012) Predicting Protein Fold Types by the General Form of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition: Approached from Optimal Feature Extractions. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(4): 439-449.
- S Mei (2012) Multi-kernel transfer learning based on Chou's PseAAC formulation for protein submitochondria localization. Journal of Theoretical Biology 293: 121-130.
- S Mei (2012) Predicting plant protein subcellular multi-localization by Chou's PseAAC formulation based multi-label homolog knowledge transfer learning. Journal of Theoretical Biology 310: 80-87.
- Nanni L, Brahnam S, Lumini A (2012) Wavelet images and Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for protein classification. Amino Acids 43(2): 657-665.
- Nanni L, Lumini A, Gupta D, Garg A (2012) Identifying bacterial virulent proteins by fusing a set of classifiers based on variants of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and on evolutionary information. IEEE-ACM Transaction on Computational Biolology and Bioinformatics 9(2): 467-475.
- Niu XH, Hu XH, Shi F, Xia JB (2012) Predicting Protein Solubility by the General Form of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition: Approached from Chaos Game Representation and Fractal Dimension. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(9): 940-948.
- Qin YF, Wang CH, Yu XQ, Zhu J, Liu TG, et al. (2012) Predicting Protein Structural Class by Incorporating Patterns of Over- Represented k-mers into the General form of Chou's PseAAC. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(4): 388-397.
- Ren LY, Zhang YS, Gutman I (2012) Predicting the Classification of Transcription Factors by Incorporating their Binding Site Properties into a Novel Mode of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(11): 1170-1176.
- Sun XY, Shi SP, Qiu JD, Suo SB, Huang SY, et al. (2012) Identifying protein quaternary structural attributes by incorporating physicochemical properties into the general form of Chou's PseAAC via discrete wavelet transform. Molecular BioSystems 8: 3178-3184.
- Wang J, Li Y, Wang Q, You X, Man J, et al. (2012) ProClusEnsem: predicting membrane protein types by fusing different modes of pseudo amino acid composition. Comput Biol Med 42(5): 564-574.
- Yu X, Zheng X, Liu T, Dou Y, Wang J (2012) Predicting subcellular location of apoptosis proteins with pseudo amino acid composition: approach from amino acid substitution matrix and auto covariance transformation. Amino Acids 42(5): 1619-1625.
- Zhao XW, Ma ZQ, Yin MH (2012) Predicting protein-protein interactions by combing various sequence- derived features into the general form of Chou's Pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(5): 492-500.
- Zia ur Rehman, Khan A (2012) Identifying GPCRs and their Types with Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition: An Approach from Multi-scale Energy Representation and Position Specific Scoring Matrix. Protein & Peptide Letters 19(8): 890-903.
- Cao DS, Xu QS, Liang YZ (2013) propy: a tool to generate various modes of Chou's PseAAC. Bioinformatics 29 (7): 960-962.
- Chang TH, Wu LC, Lee TY, Chen SP, Huang HD, et al. (2013) EuLoc: a web-server for accurately predict protein subcellular localization in eukaryotes by incorporating various features of sequence segments into the general form of Chou's PseAAC. Journal of Computer Aided Molecular Design 27(1): 91-103.
- Chen YK, Li KB (2013) Predicting membrane protein types by incorporating protein topology, domains, signal peptides, and physicochemical properties into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 318: 1-12.
- Fan GL, Li QZ, Zuo YC (2013) Predicting acidic and alkaline enzymes by incorporating the average chemical shift and gene ontology informations into the general form of Chou's PseAAC. Pocess Biochemistry 48(7): 1048-1053.
- Fan GL, Li QZ (2013) Discriminating bioluminescent proteins by incorporating average chemical shift and evolutionary information into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 334: 45-51.
- Georgiou DN, Karakasidis TE, Megaritis AC (2013) A short survey on genetic sequences, Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and its combination with fuzzy set theory. The Open Bioinformatics Journal 7: 41-48.
- Gupta MK, Niyogi R, Misra M (2013) An alignment-free method to find similarity among protein sequences via the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. SAR QSAR Environ Res 24: 597-609.
- Huang C, Yuan JQ(2013) Using radial basis function on the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and PSSM to predict subcellular locations of proteins with both single and multiple sites. Biosystems 113(1): 50-57.
- Huang C, Yuan JQ (2013) A multilabel model based on Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for identifying membrane proteins with both single and multiple functional types. J Membr Biol 246 (4): 327-34.
- Huang C, Yuan JQ (2013) Predicting protein subchloroplast locations with both single and multiple sites via three different modes of Chou's pseudo amino acid compositions. Journal of Theoretical Biology 335: 205-212.
- Khosravian M, Faramarzi FK, Beigi MM, Behbahani M, Mohabatkar H (2013) Predicting Antibacterial Peptides by the Concept of Chou's Pseudo amino Acid Composition and Machine Learning Methods. Protein & Peptide Letters 20(2): 180-186.
- Lin H, Ding C, Yuan LF, Chen W, Ding H, et al. (2013) Predicting subchloroplast locations of proteins based on the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition: Approached from optimal tripeptide composition. International Journal of Biomethmatics 6: 1350003.
- Lin H, Ding C, Yuan LF, Chen W, Ding H, et al. (2013) Predicting subchloroplast locations of proteins based on the general form of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition: approached from optimal tripeptide composition. International Journal of Biomathematics 6: Article Number: 1350003.
- Liu B, Wang X, Zou Q, Dong Q, Chen Q (2013) Protein remote homology detection by combining Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and profile-based protein representation. Molecular Informatics 32: 775-782.
- Mohabatkar H, Beigi MM, Abdolahi K, Mohsenzadeh S (2013) Prediction of Allergenic Proteins by Means of the Concept of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition and a Machine Learning Approach. Medicinal Chemistry 9(1): 133-137.
- Pacharawongsakda E, Theeramunkong T (2013) Predict Subcellular Locations of Singleplex and Multiplex Proteins by Semi-Supervised Learning and Dimension-Reducing General Mode of Chou's PseAAC. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience 12(4): 311-320.
- Qin YF, Zheng L, Huang J (2013) Locating apoptosis proteins by incorporating the signal peptide cleavage sites into the general form of Chou's Pseudo amino acid composition. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry 113: 1660-1667.
- Sarangi AN, Lohani M, Aggarwal R (2013) Prediction of Essential Proteins in Prokaryotes by Incorporating Various Physico-chemical Features into the General form of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Protein Pept Lett 20(7): 781-795.
- Wan S, Mak MW, Kung SY (2013) GOASVM: A subcellular location predictor by incorporating term-frequency gene ontology into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 323: 40-48.
- Wang X, Li GZ, Lu WC (2013) Virus-ECC-mPLoc: a multi-label predictor for predicting the subcellular localization of virus proteins with both single and multiple sites based on a general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Protein & Peptide Letters 20(3): 309-317.
- Xiao X, Min JL, Wang P, Chou KC (2013) iCDI-PseFpt: Identify the channel-drug interaction in cellular networking with PseAAC and molecular fingerprints. Journal of Theoretical Biology 337: 71-79.
- Xiaohui N, Nana L, Jingbo X, Dingyan C, Yuehua P, et al. (2013) Using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein solubility: An approach with entropies in information theory. Journal of Theoretical Biology 332: 211-217.
- Xie HL, Fu L, Nie XD (2013) Using ensemble SVM to identify human GPCRs N-linked glycosylation sites based on the general form of Chou's PseAAC. Protein Eng Des Sel 26(11): 735-742.
- Xu Y, Ding J, Wu LY, Chou KC (2013) iSNO-PseAAC: Predict cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins by incorporating position specific amino acid propensity into pseudo amino acid composition PLoS ONE 8(2): e55844.
- Xu Y, Shao XJ, Wu LY, Deng NY, Chou KC (2013) iSNO-AAPair: incorporating amino acid pairwise coupling into PseAAC for predicting cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins. PeerJ 1: e171.
- Du P, Gu S, Jiao Y (2014) PseAAC-General: Fast building various modes of general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition for large-scale protein datasets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15(3): 3495-3506.
- Hajisharifi Z, Piryaiee M, Mohammad Beigi M, Behbahani M, Mohabatkar H (2014) Predicting anticancer peptides with Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and investigating their mutagenicity via Ames test. Journal of Theoretical Biology 341: 34-40.
- Han GS, Yu ZG, Anh V (2014) A two-stage SVM method to predict membrane protein types by incorporating amino acid classifications and physicochemical properties into a general form of Chou's PseAAC. J Theor Biol 344: 31-39.
- Hayat M, Iqbal N (2014) Discriminating protein structure classes by incorporating Pseudo Average Chemical Shift to Chou's general PseAAC and Support Vector Machine. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 116: 184-192.
- Jia C, Lin X, Wang Z (2014) Prediction of Protein S-Nitrosylation Sites Based on Adapted Normal Distribution Bi-Profile Bayes and Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. Int J Mol Sci 15(6): 10410-10423.
- Kong L, Zhang L, Lv J (2014) Accurate prediction of protein structural classes by incorporating predicted secondary structure information into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 344: 12-18.
- Li L, Yu S, Xiao W, Li Y, Li M, et al. (2014) Prediction of bacterial protein subcellular localization by incorporating various features into Chou's PseAAC and a backward feature selection approach. Biochimie 104: 100-107.
- Liu B, Xu J, Lan X, Xu R, Zhou J, et al. (2014) iDNA-Prot|dis: identifying DNA-binding proteins by incorporating amino acid distance-pairs and reduced alphabet profile into the general pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS ONE 9: e106691.
- Mondal S, Pai PP (2014) Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition improves sequence-based antifreeze protein prediction. J Theor Biol 356: 30-35.
- Nanni L, Brahnam S, Lumini A (2014) Prediction of protein structure classes by incorporating different protein descriptors into general Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 360: 109-116.
- Qiu WR, Xiao X, Chou KC (2014) iRSpot-TNCPseAAC: Identify recombination spots with trinucleotide composition and pseudo amino acid components. Int J Mol Sci (IJMS) 15(2): 1746-1766.
- Qiu WR, Xiao X, Lin WZ, Chou KC (2014) iMethyl-PseAAC: Identification of Protein Methylation Sites via a Pseudo Amino Acid Composition Approach. Biomed Res Int (BMRI) 2014: 947416.
- Xu Y, Wen X, Shao XJ, Deng NY, Chou KC (2014) iHyd-PseAAC: Predicting hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine in proteins by incorporating dipeptide position-specific propensity into pseudo amino acid composition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences (IJMS) 15(5): 7594-7610.
- Xu Y, Wen X, Wen LS, Wu LY, Deng NY, et al. (2014) iNitro-Tyr: Prediction of nitrotyrosine sites in proteins with general pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS ONE 9: e105018.
- Zhang J, Sun P, Zhao X, Ma Z (2014) PECM: Prediction of extracellular matrix proteins using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. Journal of Theoretical Biology 363: 412-418.
- Zhang J, Zhao X, Sun P, Ma Z (2014) PSNO: Predicting Cysteine S-Nitrosylation Sites by Incorporating Various Sequence-Derived Features into the General Form of Chou's PseAAC. Int J Mol Sci 15(7): 11204-11219.
- Zhang L, Zhao X, Kong L (2014) Predict protein structural class for low-similarity sequences by evolutionary difference information into the general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 355: 105-110.
- Zuo YC, Peng Y, Liu L, Chen W, Yang L, et al. (2014) Predicting peroxidase subcellular location by hybridizing different descriptors of Chou's pseudo amino acid patterns. Anal Biochem 458: 14-19.
- Ahmad S, Kabir M, Hayat M (2015) Identification of Heat Shock Protein families and J-protein types by incorporating Dipeptide Composition into Chou's general PseAAC. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 122(2): 165-174.
- Ali F, Hayat M (2015) Classification of membrane protein types using Voting Feature Interval in combination with Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. J Theor Biol 384: 78-83.
- Chen L, Chu C, Huang T, Kong X, Cai YD (2015) Prediction and analysis of cell-penetrating peptides using pseudo amino acid composition and random forest models. Amino Acids 47(7):1485-1493.
- Dehzangi A, Heffernan R, Sharma A, Lyons J, Paliwal K, et al. (2015) Gram-positive and Gram-negative protein subcellular localization by incorporating evolutionary-based descriptors into Chou's general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 364: 284-294.
- Fan GL, Zhang XY, Liu YL, Nang Y, Wang H (2015) DSPMP: Discriminating secretory proteins of malaria parasite by hybridizing different descriptors of Chou's pseudo amino acid patterns. J Comput Chem 36: 2317-2327.
- Huang C, Yuan JQ (2015) Simultaneously Identify Three Different Attributes of Proteins by Fusing their Three Different Modes of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Compositions. Protein Pept Lett 22(6): 547-556.
- Jia J, Liu Z, Xiao, X Chou KC (2015) iPPI-Esml: an ensemble classifier for identifying the interactions of proteins by incorporating their physicochemical properties and wavelet transforms into PseAAC. J Theor Biol 377: 47-56.
- Ju Z, Cao JZ, Gu H (2015) iLM-2L: A two-level predictor for identifying protein lysine methylation sites and their methylation degrees by incorporating K-gap amino acid pairs into Chous general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 385: 50-57.
- Khan ZU, Hayat M, Khan MA (2015) Discrimination of acidic and alkaline enzyme using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition in conjunction with probabilistic neural network model. J Theor Biol 365: 197-203.
- Kumar R, Srivastava A, Kumari B, Kumar M (2015) Prediction of beta-lactamase and its class by Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and support vector machine. J Theor Biol 365: 96-103.
- Liu B, Chen J, Wang X (2015) Protein remote homology detection by combining Chou's distance-pair pseudo amino acid composition and principal component analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 290(5): 1919-31.
- Liu B, Xu J, Fan S, Xu R, Jiyun Zhou J, et al. (2015) PseDNA-Pro: DNA-binding protein identification by combining Chou's PseAAC and physicochemical distance transformation. Molecular Informatics 34: 8-17.
- Mandal M, Mukhopadhyay A, Maulik U (2015) Prediction of protein subcellular localization by incorporating multiobjective PSO-based feature subset selection into the general form of Chou's PseAAC. Med Biol Eng Comput 53(4): 331-44.
- Sanchez V, Peinado AM, Perez Cordoba JL, Gomez AM (2015) A new signal characterization and signal-based Chou's PseAAC representation of protein sequences. J Bioinform Comput Biol 13(5): 1550024.
- Sharma R, Dehzangi A, Lyons J, Paliwal K, Tsunoda T, et al. (2015) Predict Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Subcellular Localization via Incorporating Evolutionary Information and Physicochemical Features Into Chou's General PseAAC. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 14(8): 915-26.
- Wang X, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Li GZ (2015) MultiP-SChlo: multi-label protein subchloroplast localization prediction with Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and a novel multi-label classifier. Bioinformatics 31(16): 2639-2645.
- Xu R, Zhou J, Liu B, He YA, Zou Q, et al. (2015) Identification of DNA-binding proteins by incorporating evolutionary information into pseudo amino acid composition via the top-n-gram approach. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics (JBSD) 33: 1720-1730.
- Zhang M, Zhao B, Liu X (2015) Predicting industrial polymer melt index via incorporating chaotic characters into Chou's general PseAAC. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems (CHEMOLAB) 146: 232-240.
- Zhang SL (2015) Accurate prediction of protein structural classes by incorporating PSSS and PSSM into Chou's general PseAAC. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems (CHEMOLAB) 142: 28-35.
- Zhu PP, Li WC, Zhong ZJ, Deng EZ, Ding H, et al. (2015) Predicting the subcellular localization of mycobacterial proteins by incorporating the optimal tripeptides into the general form of pseudo amino acid composition. Mol Biosyst 11(2): 558-563.
- Ahmad K, Waris M, Hayat M (2016) Prediction of Protein Submitochondrial Locations by Incorporating Dipeptide Composition into Chou's General Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. J Membr Biol 249(3): 293-304.
- Behbahani M, Mohabatkar H, Nosrati M (2016) Analysis and comparison of lignin peroxidases between fungi and bacteria using three different modes of Chou's general pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 411: 1-5.
- Fan GL, Liu YL, Wang H (2016) Identification of thermophilic proteins by incorporating evolutionary and acid dissociation information into Chou's general pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 407: 138-142.
- Jia J, Liu Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Chou KC (2016) Identification of protein-protein binding sites by incorporating the physicochemical properties and stationary wavelet transforms into pseudo amino acid composition (iPPBS-PseAAC). J Biomol Struct Dyn (JBSD) 34: 1946-1961.
- Jia J, Liu Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Chou KC (2016) pSuc-Lys: Predict lysine succinylation sites in proteins with PseAAC and ensemble random forest approach. Journal of Theoretical Biology 394: 223-230.
- Jia J, Liu Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Chou KC (2016) iCar-PseCp: identify carbonylation sites in proteins by Monto Carlo sampling and incorporating sequence coupled effects into general PseAAC. Oncotarget 7(23): 34558-34570.
- Jia J, Zhang L, Liu Z, Xiao X, Chou KC (2016) pSumo-CD: Predicting sumoylation sites in proteins with covariance discriminant algorithm by incorporating sequence-coupled effects into general PseAAC. Bioinformatics 32(20): 3133-3141.
- Jiao YS, Du PF (2016) Prediction of Golgi-resident protein types using general form of Chou's pseudo amino acid compositions: Approaches with minimal redundancy maximal relevance feature selection. J Theor Biol 402: 38-44.
- Ju Z, Cao JZ, Gu H (2016) Predicting lysine phosphoglycerylation with fuzzy SVM by incorporating k-spaced amino acid pairs into Chou's general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 397: 145-150.
- Kabir M, Hayat M (2016) iRSpot-GAEnsC: identifing recombination spots via ensemble classifier and extending the concept of Chou's PseAAC to formulate DNA samples. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 291(1): 285-96.
- Qiu WR, Sun BQ, Xiao X, Xu ZC, Chou KC (2016) iHyd-PseCp: Identify hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine in proteins by incorporating sequence-coupled effects into general PseAAC. Oncotarget 7(28): 44310-44321.
- Tahir M, Hayat M (2016) iNuc-STNC: a sequence-based predictor for identification of nucleosome positioning in genomes by extending the concept of SAAC and Chou's PseAAC. Mol Biosyst 12(8): 2587-2593.
- Tang H, Chen W, Lin H (2016) Identification of immunoglobulins using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition with feature selection technique. Mol Biosyst 12(4): 1269-1275.
- Tiwari AK (2016) Prediction of G-protein coupled receptors and their subfamilies by incorporating various sequence features into Chou's general PseAAC. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 134: 197-213.
- Xu C, Sun D, Liu S, Zhang Y (2016) Protein Sequence Analysis by Incorporating Modified Chaos Game and Physicochemical Properties into Chou's General Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. J Theor Biol 406: 105-115.
- Zou HL, Xiao X (2016) Predicting the Functional Types of Singleplex and Multiplex Eukaryotic Membrane Proteins via Different Models of Chou's Pseudo Amino Acid Compositions. J Membr Biol 249(1-2): 23-29.
- Zou HL, Xiao X (2016) Classifying Multifunctional Enzymes by Incorporating Three Different Models into Chou's General Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. J Membr Biol 249(4): 561-567.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2017) pLoc-mPlant: predict subcellular localization of multi-location plant proteins via incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Molecular BioSystems 13(9): 1722-1727.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2017) pLoc-mVirus: predict subcellular localization of multi-location virus proteins via incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Gene 628: 315-321.
- Ju Z, He JJ (2017) Prediction of lysine propionylation sites using biased SVM and incorporating four different sequence features into Chou's PseAAC. J Mol Graph Model 76: 356-363.
- Ju Z, He JJ (2017) Prediction of lysine crotonylation sites by incorporating the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs into Chou's general PseAAC. J Mol Graph Model 77: 200-204.
- Khan M, Hayat M, Khan SA, Iqbal N (2017) Unb-DPC: Identify mycobacterial membrane protein types by incorporating un-biased dipeptide composition into Chou's general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 415: 13-19.
- Liang Y, Zhang S (2017) Predict protein structural class by incorporating two different modes of evolutionary information into Chou's general pseudo amino acid composition. J Mol Graph Model 78: 110-117.
- Liu LM, Y Xu, Chou KC (2017) iPGK-PseAAC: identify lysine phosphoglycerylation sites in proteins by incorporating four different tiers of amino acid pairwise coupling information into the general PseAAC. Med Chem 13(6): 552-559.
- Meher PK, Sahu TK, Saini V, Rao AR (2017) Predicting antimicrobial peptides with improved accuracy by incorporating the compositional, physico-chemical and structural features into Chou's general PseAAC. Sci Rep 7: 42362.
- Qiu WR, Sun BQ, Xiao X, Xu D, Chou KC (2017) iPhos-PseEvo: Identifying human phosphorylated proteins by incorporating evolutionary information into general PseAAC via grey system theory. Molecular Informatics 36: UNSP 1600010.
- Qiu WR, Zheng QS, Sun BQ, Xiao X (2017) Multi-iPPseEvo: A Multi-label Classifier for Identifying Human Phosphorylated Proteins by Incorporating Evolutionary Information into Chou's General PseAAC via Grey System Theory. Mol Inform 36: UNSP 1600085.
- Rahimi M, Bakhtiarizadeh MR, Mohammadi Sangcheshmeh A (2017) OOgenesis_Pred: A sequence-based method for predicting oogenesis proteins by six different modes of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 414: 128-136.
- Tripathi P, Pandey PN (2017) A novel alignment-free method to classify protein folding types by combining spectral graph clustering with Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 424: 49-54.
- Xiao X, Cheng X, Su S, Nao Q, Chou KC (2017) pLoc-mGpos: Incorporate key gene ontology information into general PseAAC for predicting subcellular localization of Gram-positive bacterial proteins. Natural Science 9(9): 331-349.
- Xu C, Ge L, Zhang Y, Dehmer V, Gutman V (2017) Prediction of therapeutic peptides by incorporating q-Wiener index into Chou's general PseAAC. J Biomed Inform.
- Xu Y, Li C, Chou KC (2017) iPreny-PseAAC: identify C-terminal cysteine prenylation sites in proteins by incorporating two tiers of sequence couplings into PseAAC. Med Chem 13(6): 544-551.
- Yu B, Li S, Qiu WY, Chen C, Chen RX, et al. (2017) Accurate prediction of subcellular location of apoptosis proteins combining Chou's PseAAC and PsePSSM based on wavelet denoising. Oncotarget 8(64): 107640-107665.
- Yu B, Lou L, Li S, Zhang Y, Qiu W, et al. (2017) Prediction of protein structural class for low-similarity sequences using Chou's pseudo amino acid composition and wavelet denoising. J Mol Graph Model 76: 260-273.
- Ahmad J, Hayat M (2018) MFSC: Multi-voting based Feature Selection for Classification of Golgi Proteins by Adopting the General form of Chou's PseAAC components. J Theor Biol 463: 99-109.
- Akbar S, Hayat M (2018) iMethyl-STTNC: Identification of N(6)-methyladenosine sites by extending the Idea of SAAC into Chou's PseAAC to formulate RNA sequences. J Theor Biol 455: 205-211.
- Arif M, Hayat M, Jan Z (2018) iMem-2LSAAC: A two-level model for discrimination of membrane proteins and their types by extending the notion of SAAC into Chou's pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 442: 11-21.
- Butt AH, Rasool N, Khan YD (2018) Predicting membrane proteins and their types by extracting various sequence features into Chou's general PseAAC. Mol Biol Rep.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2018) pLoc-mEuk: Predict subcellular localization of multi-label eukaryotic proteins by extracting the key GO information into general PseAAC. Genomics 110(1): 50-58.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2018) pLoc-mGneg: Predict subcellular localization of Gram-negative bacterial proteins by deep gene ontology learning via general PseAAC. Genomics 110: 231-239.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2018) pLoc-mHum: predict subcellular localization of multi-location human proteins via general PseAAC to winnow out the crucial GO information. Bioinformatics 34(9): 1448-1456.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2018) pLoc_bal-mGneg: predict subcellular localization of Gram-negative bacterial proteins by quasi-balancing training dataset and general PseAAC. Journal of Theoretical Biology 458: 92-102.
- Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou KC (2018) pLoc_bal-mPlant: predict subcellular localization of plant proteins by general PseAAC and balancing training dataset Curr Pharm Des 24(34): 4013-4022.
- Contreras Torres E (2018) Predicting structural classes of proteins by incorporating their global and local physicochemical and conformational properties into general Chou's PseAAC. J Theor Biol 454: 139-145.
- Fu X, Zhu W, Liso B, Cai L, Peng L, et al. (2018) Improved DNA-binding protein identification by incorporating evolutionary information into the Chou's PseAAC. IEEE Access 20.
- Ghauri AW, Khan YD, Rasool N, Khan SA, Chou KC (2018) pNitro-Tyr-PseAAC: Predict nitrotyrosine sites in proteins by incorporating five features into Chou's general PseAAC. Curr Pharm Des 24(34): 4034-4043.
- Javed F, Hayat M (2018) Predicting subcellular localizations of multi-label proteins by incorporating the sequence features into Chou's PseAAC. Genomics 111(6): 1325-1332.
- Ju Z, Wang SY (2018) Prediction of citrullination sites by incorporating k-spaced amino acid pairs into Chou's general pseudo amino acid composition. Gene 664: 78-83.
- Khan YD, Rasool N, Hussain W, Khan SA, Chou KC (2018) iPhosT-PseAAC: Identify phosphothreonine sites by incorporating sequence statistical moments into PseAAC. Analytical Biochemistry 550: 109-116.
- Khan YD, Rasool N, Hussain W, Khan SA, Chou KC (2018) iPhosY-PseAAC: identify phosphotyrosine sites by incorporating sequence statistical moments into PseAAC. Mol Biol Rep 45(6): 2501-2509.
- Krishnan MS (2018) Using Chou's general PseAAC to analyze the evolutionary relationship of receptor associated proteins (RAP) with various folding patterns of protein domains. J Theor Biol 445: 62-74.
- Liang Y, Zhang S (2018) Identify Gram-negative bacterial secreted protein types by incorporating different modes of PSSM into Chou's general PseAAC via Kullback-Leibler divergence. J Theor Biol 454: 22-29.
- Mei J, Y. Fu, Zhao J (2018) Analysis and prediction of ion channel inhibitors by using feature selection and Chou's general pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 456: 41-48.
- Mei J, Zhao J (2018) Prediction of HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteins by using Chou's pseudo amino acid compositions and different classifiers. Sci Rep 8(1): 2359.
- Mei J, Zhao J (2018) Analysis and prediction of presynaptic and postsynaptic neurotoxins by Chou's general pseudo amino acid composition and motif features. J Theor Biol 427: 147-153.
- Mousavizadegan M, Mohabatkar H (2018) Computational prediction of antifungal peptides via Chou's PseAAC and SVM. J Bioinform Comput Biol 16(4): 1850016.
- Rahman SM, Shatabda S, Saha S, Kaykobad M, Sohel Rahman M (2018) DPP-PseAAC: A DNA-binding Protein Prediction model using Chou's general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 452: 22-34.
- Sankari ES, Manimegalai DD (2018) Predicting membrane protein types by incorporating a novel feature set into Chou's general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 455: 319-328.
- Chou KC (2019) Two kinds of metrics for computational biology. Genomics.
- Chou KC (2019) Proposing pseudo amino acid components is an important milestone for proteome and genome analyses. International Journal for Peptide Research and Therapeutics (IJPRT).
- Chou KC (2019) An insightful recollection for predicting protein subcellular locations in multi-label systems. Genomics.
- Chou KC (2019) Progresses in predicting post-translational modification. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (IJPRT).
- Chou KC (2019) Recent Progresses in Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization with Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools Developed Via the 5-Steps Rule. Japanese Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
- Chou KC (2019) An insightful recollection since the distorted key theory was born about 23 years ago. Genomics.
- Chou KC (2019) Artificial intelligence (AI) tools constructed via the 5-steps rule for predicting post-translational modifications. Trends in Artificial Inttelengence (TIA) 3: 60-74.
- Chou KC (2020) Distorted Key Theory and Its Implication for Drug Development. Current Genomics.
- Chou KC (2019) An Insightful 10-year Recollection Since the Emergence of the 5-steps Rule. Current Pharmaceutical Design 25(4): 4223-4234.
- Chou KC (2019) An insightful recollection since the birth of Gordon Life Science Institute about 17 years ago. Advancement in Scientific and Engineering Research 4: 31-36.
- Chou KC (2019) Gordon Life Science Institute: Its philosophy, achievements, and perspective. Annals of Cancer Therapy and Pharmacology 2: 01-26.

 Short Communication
Short Communication