Abstract
Neisseria meningitidis is a causal agent of human meningitis. Twelve serogroups exist base in their polysaccharide compositions, six of them cause meningococcal disease, plane and covalently conjugated parenteral vaccines are available. The serum IgG cross reactivity between pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains is a fact. It is consequence of their high protein homology. Nevertheless, the mucosal IgA cross response against polysaccharides are unknown. So, the response induce by polysaccharide C from N. meningitidis alone of adjuvantated with AFCo1 adjuvant in Balb/c mice was addressed. Three intranasal doses did not induce serum IgG responses against A, Y nor W135N. meningitidis serogroups. Contrary, polysaccharide C alone and better when it is formulated with AFCo1 induce mucosal IgA cross reactive response against all polysaccharide tested. The possible use of SinTimVaS approaches for vaccine development is suggested
Abbreviations: OD: Optical Density, CTL: Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte, BSA: Bovine Seroalbumin
Introduction
Neisseria is a mucosal obligate pathogen or non-pathogen species where N. meningitidis has 13 serogroups. This classification is based in its polysaccharide expression and they are: A, B, C, D, E, H, I, K, L, W135, X, Y y Z. Of them, the A, B, C, W135 and Y serogroups are the most disease causing agents. As polysaccharides are thymus-independent antigens the current approach for vaccines purpose is the covalent conjugation to some proteins and theirs use as parenteral vaccines [1]. Nevertheless, in not immunodeficient human the occurrence of a disease by N. meningitidis infection is only one time and it arrives by mucosal route. In addition, the mucosal IgA response induce by N. meningitidis infections have been less explored. The IgA response could be induced as a thymus-dependent and -independent manner [2]. The former is mainly induced against proteins antigens and it is more specific. The latter is not totally clear which antigen is the main responsible for its induction and might be more cross reactive. Consequently, we would like to explore the possible cross reactivity induce by polysaccharides applied by mucosal route in mice. Although N. meningitidis infects through mucosal surfaces where IgA is the main protecting antibody, systemic vaccination is currently used which did not induce mucosal response. At present antigen delivery to mucosal surfaces is very interesting especially for protection against infectious agent that are mediated by local immune response. However, mucosal immunization has been limited by important aspects as safety and immunogenicity. An approach to improve this route of vaccination is the use of safe and effective adjuvants. Cross reactivity at serum IgG level between species of Neisseria genus, in particular with N. gonorrhoeae have been described [3]. However, its main explanation is by their structural homology between commons proteins in those species. One of the shortcomings of parenteral immunization is its relatively poor ability to induce specific IgA [4,5]. Nevertheless, cross reactivity at mucosal IgA level against polysaccharides between N. meningitidis serogroups have been less explored [6]. The first vaccine against N. meningitidis serogroups B and C is base in the outer membrane detergent extractions of a Proteoliposome (PL) form the B serogroup [7] which contains several proteins [8,9]. It is bivalent as it contains also the C polysaccharide adsorbed onto Al(OH)3 (Alum). Our group have been demonstrated that PL in addition to the protective antigens function as a potent adjuvant [10,11], and using this polysaccharide covalent conjugation, the hallmark of polysaccharide vaccines, is not required [12-14]. This vaccine is use by parenteral route overcoming the polysaccharide C thymus-independence also in human toddlers [15]. Nevertheless, as PL is absorbed onto alum it could not be use as mucosal adjuvant. So, we have developed a PL-derived cochleate (AFCo1) adjuvant. AFCo1 is a multilayer microparticle formed by the interaction of the lipid bilayer of the PL and Ca2+, which contains similar proteins and pathogen-associated molecular pattern as the PL [10,11] inducing systemic specific IgG and in addition mucosal specific IgA. AFCo1 applied by nasal route induces mucosal at regional and distal places (specific IgA) and systemic immune responses (serum specific IgG, specific IgG2a subclass, and IFN-γ) polarizing to a Th1 pattern [16]. The mucosal approach has being applied to several antigens [17,18].
Materials and Methods
Animals
Female Balb/c mice, six to eight weeks old, supplied by Cenpalab, Cuba were used for all the experiments. All the experiments were performed with the approval from the Ethical Committee for Laboratory at Finlay Institute, Cuba. The studies were performed at least twice.
Preparation of Proteoliposome (PL) and AFCo1
PLs from outer membrane vesicles detergent-extracted from N. meningitidis serogroup B were prepared and supplied as an ethanol precipitate, as well as the C polysaccharide, by the vaccine production unit of the Finlay Institute, Havana, Cuba, for N. meningitidis serogroup B vaccine as previously described. PLderived AFCo1 was prepared as previously described [11].
Animal Immunization and Sample Collection
Mice were immunized intranasal (i.n) with 3 doses of AFCo1 + C polysaccharide; polysaccharide alone or naive as negative control with 7 days intervals. In all groups the blood was obtained from the retrorbital vein at 21 days after the last dose. Saliva samples were collected at 7 days after the last immunization by Pilocarpine 0.5% intraperitoneal stimulation. These were immediately inactivated at 56ºC for 15 min and the supernatants after centrifugation (9000 g) were stored as well the sera at -20°C.
Analysis of Mouse Antibody Response by ELISA
Maxisorp 96-well plates (Nunc) were coated with 100 μL of Neisseria meningitidis polysaccharide A, C, Y or W135 (10 μg/ mL) in 0.05M carbonate buffer, pH 9.6 for 4 h at room temperature, followed by overnight incubation at 4oC. The plates were blocked with 2% Bovine Seroalbumin (BSA) in Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS) for 30 min at 37ºC. The serial dilutions of sera or vaginal washes obtained were incubated for 1 h at 37ºC. After washing with 0.05% Tween-20, plates were incubated 1h at 37ºC with goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin (Ig) G, (Southern Biotechnology Associates, Inc., Birmingham, AL), or -mouse IgA (Southern Biotechnology Associates, Inc., Birmingham, AL) coupled to horseradish peroxidase in 1% BSA-PBS buffer. The plates were then washed with 0.05% Tween-20 and developed using 100 μL of 1 mg/mL o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (Sigma) in 0.1 M citrate buffer (pH 4.5) in the presence of 0.04% H2O2. The reaction was stopped with H2SO4. The absorbance was read at 492 nm and was expressed as Optical Density (OD).
Statistical Análisis
Statistical analyses were done by two way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post test using Graph Pad Prism 5 software (CA, USA).
Results and Discussion
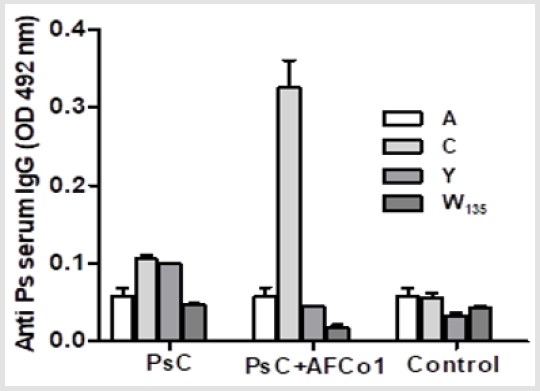
Neither C Polysaccharide Alone nor Adjuvantated With AFCo1 by Nasal Route Induce Cross Reactive Serum Igg Against Heterologous Neisseria Meningitidis Polysaccharides
Low serum anti Polysaccharide C IgG was obtained immunizing mice with it alone. This response was significantly increase by the adjuvantation with AFCo1. No serum specific IgG responses were obtained against heterologous polysaccharides with both formulation (Figure 1). These results are in agreement with the strong adjuvant capacity of AFCo1 against proteins [18,19].and non-covalently conjugated polysaccharides [19,20]. Our previous results have been confirmed that VA-MENGOC-BC™ vaccines as well as its derivates AFPL1 and AFCo1 induce a preferential Th (helper) 1 pattern of immune response characterized by: induction of IgG and IgG1 (in human, IgG2a in mice) with opsonophagocyte and some bactericidal activities; delayed-type hypersensitivity; and IL- 12 and IFN-γ, but neither Th2 (IL-4, IL-5) cytokine production nor mucosal specific IgA response. They also change the Th2 pattern normally induced by AL(OH)3 to a preferential Th1 immune response in mice and human. Beside, cross-priming and Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte (CTL) responses were induced in mice. Nevertheless, the transformation in AFCo1 meanwhile conserving its component increases the immunogenicity of the antigens of the formulations [10,21,22]. Overall, only the AFCo1 containing formulation increase the systemic IgG anti polysaccharide C response by nasal immunization.
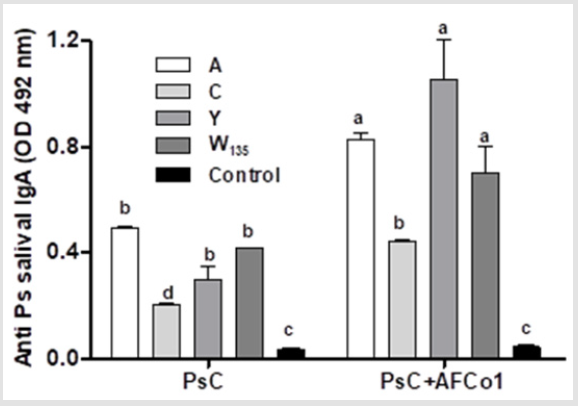
The C Polysaccharide Alone Immunized by Nasal Route Induces Cross Reactive Saliva Iga Against Heterologous Polysaccharides Which is Increased by AFCo1 Adjuvantation
To explore the mucosal IgA response induced by polysaccharide C containing formulations and their possible cross response over heterologous N. meningitidis polysaccharides mice were immunized mice with 3 i.n doses of polysaccharide C or adjuvantated with AFCo1. The polysaccaride C alone induces IgA responses that recognized the homologous and heterologous polysaccharides (Figure 2). These response are only at mucosal IgA level because it neither induce systemic specific nor heterologous cross reactive IgG (Figure 1). The adjuvantation with AFCo1 significant increases the specific homologosus and the cross reactive heterologosus IgA anti polysaccharide responses (Figure 2). These results confirm our previous results that a potent adjuvant, like AFCo1, overcome the thymus-independence of polysaccharide C without the requirement of covalent conjugation12,13,14. In addition, AFCo1 also significantly increses the cross reactive IgA induction againts heterologous polycacchaides (Figure 2).
Figure 1: Neither C polysaccharide alone nor adjuvantated with AFCo1 by nasal route induce cross reactive serum IgG against heterologous Neisseria meningitidis polysaccharides. A, C, Y and W135 are N. meningitidis serogroups; PsC N. meningitidis polysaccharide used in immunizations, OD, optical density determined by ELISA.
Figure 2: The C polysaccharide alone immunized by nasal route induces cross reactive saliva IgA against heterologous polysaccharides which is increased by AFCo1 adjuvantation. A, C, Y, and W135 are N. meningitidis serogroups; PsC, N. meningitidis polysaccharide used in immunizations, OD, optical density determined by ELISA. Different letters mean significant different value determined by Two way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test.
This IgA cross reactivity could not be explaine by polysacchaides structural homology as occurs with the systemic anti proteins IgG response between diferentes Neisseria species and serogrups2. So, these results open a new window of mucosal vaccination againts Neisseria serogroups. Neverthless, as it only induce IgA, but not IgG cross reactive responses the mucosal vaccination appraches is not enoght to protect against the different menigoccocal sergogroups that require bactericidal and opsonophagocitic serum antibodies to protection. So, one alternative could be the use of sigle time vaccination strategy (SinTimVaS) that combine at the same time two priming, one parenteral and another mucosal. SinTimVaS induces specific mucosal IgA and systemic IgG responses [21-25]. We are exploring this strategy for the induction of both mucosal and systemic cross reactive responses agains differents Neisseria meningitidis serogroups.
Acknowledgement
The research was supported by Instituto de Ciencias Básicas y Preclínicas “Victoria de Girón”, Medical University of Havana and Finlay Institute.
References
- Pérez O, Batista Duharte A, González E, Zayas C, Balboa J, et al. (2012) Human prophylactic vaccine adjuvants and their determinant role in new vaccine formulations. Brazilian J Med and Biol Res 45(8): 681-692.
- Wang D (2001) T independent IgA responses to microbial polysaccharides. The molecular Immunology of Complex Carbohydrates pp. 2485-2504.
- Griftiths F (1993) Th2 NH2 terminal (20 aa) of transferring-binding proteins (TBP)1 and TBP2 are corss-reactive between three Neisseria meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae. FEMS Microbiological Lett 109(1): 85-91.
- Bouvet JP, Bélec L, René Pirès, Pilot J (1994) Immunoglobulin G antibodies in human vaginal secretions after parenteral vaccination. Infect. Immun 62: 3957-3961.
- Nardelli-Haefliger D, Roden R, Balmelli C, Potts A, Shiller J, et al. (1999) Mucosal but not parenteral immunization with purified human papillomavirus type 16 virus-like particles induce neutralizing titles of antibodies throughout the estrous cycle of mice. J Virol 73: 9609-9613.
- Perez O, Del Campo J, Cuello M, González E, Núñez N, et al. (2009) Mucosal approaches in Neisseria Vaccinology. VacciMonitor 18(2): 53-55.
- Sierra GV, Campa HC, Varcacel NM, García IL, Izquierdo PL (1991) Vaccine against group B Neisseria meningitidis: protection trial and mass vaccination results in Cuba. NIPH Ann 14(2): 195-207.
- Uli L, Castellanos Serra L, Betancourt L, Domínguez F, Barberá R, et al. (2006) Outer membrane vesicles of the VA-MENGOC-BC® vaccine against serogroup B of Neisseria meningitidis: Analysis of protein components by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 6(11): 3389-3399.
- Gil J, Betancourt LZ, Sardiñas G, Yero D, Niebla O (2009) Proteomic study via a non-gel based approach of meningococcal outer membrane vesicle vaccine obtained from strain CU385: A road map for discovering new antigens. Hum Vaccin 5(5): 347-356.
- Pérez O, Romeu B, Del Campo J, Zayas C, Lastre M (2013) Proteoliposome and Polysaccharide-Based Meningococcal Vaccine Are Immunogenic in Infants and Toddlers and Primes for Memory against Serogroup C Polysaccharide. World Journal of Vaccines 3: 77-87.
- Pérez O, Bracho G, Lastre M, Del Campo J, Gil D, et al. (2004) Novel adjuvant based on a proteoliposome-derived cochleate structure containing native lipopolysaccharide as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern. Immunology and Cell Biology 82: 603-610.
- Romeu B, Lastre M, Reyes L, González E, Borrero Y, et al. (2014) Nasal immunization of mice with AFCo1 or AFPL1 plus capsular polysaccharide Vi from Salmonella typhi induces cellular response and memory B and T cell responses. Vaccine 5: 6971-6978.
- Romeu B, Gonzalez E, Lastre M, Pérez O (2012) Can mucosal adjuvants contribute to the induction of immunological memory induced via unconjugated T-cell-independent antigens? J Drug Target 20(6): 502-508.
- Romeu B, Lastre M, García L, Cedré B, Mandariote A (2013) Combined meningococcal serogroup A and W135 outer-membrane vesicles activate cell-mediated immunity and long-term memory responses against non-covalent capsular polysaccharide A. Immunol Res.
- Pérez O, Romeu B, del Campo J, Zayas C, Lastre M (2013) Proteoliposome and Polysaccharide-Based Meningococcal Vaccine Are Immunogenic in Infants and Toddlers and Primes for Memory against Serogroup C Polysaccharide. World Journal of Vaccines 3: 77-87.
- Cuello M, Cabrera O, Acevedo R, Nuñez N, del Campo J, et al. (2009) Nasal immunization with AFCo1 induces immune response to N. gonorrhoea in mice. VacciMonitor 18(2): 76-78.
- Del Campo J, Lindqvist M, Cuello M, Bäckström M, Cabrerra O, et al. (2010) Intranasal immunization with a proteoliposome-derived cochleate containing recombinant gD protein confers protective immunity against genital herpes in mice. Vaccine 28(6): 1193-1200.
- Robles-Reyes L, Lastre-González M, Reyes-Díaz LM, Borrego-González Y, Ramos Pupo R, et al. (2019) Vacuna antitetánica adyuvada en alúmina en inmunización simultánea por vías mucosa y parenteral. VacciMonitor 28(3): 85-90.
- Romeu B, González E, Zayas C, del Campo J, Acevedo R, et al. (2011) AFCo1 as nasal adjuvant of capsular polysaccharide from Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C induces systemic and mucosal immune responses. Scand J Infect Dis 43: 809-813.
- Romeu B, González E, del Campo J, Acevedo R, Zayas C, et al. (2011) Mucosal and systemic immune response of mice to tetanus toxoid coadministered nasally with AFCo1. Cand J Microbiol 57: 256-261.
- Pérez O, Lastre M, Lapinet J, Bracho G, Padrón J, et al. (2001) Immune Response Induction and New Effector Mechanisms Possibly Involved in Protection of Cuban Anti-Meningococcal BC Vaccine. Infect Immun 69(72001): 4502-4508.
- Rodríguez T, Pérez O, Menager N, Ugrinovic S, Bracho G et al. (2005) Interactions of proteoliposome from serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis with bone marrow-derived dendritic cells and macrophages: adjuvants and antigen delivery. Vaccine 23: 1312-1321.
- González E, Romeu B, del Campo J, Acevedo R, Lastre M, et al. (2009) Single Time Vaccination Strategy. VacciMonitor 18(2): 75-77.
- Pérez Martín OG, González Aznar E, Romeu Alvarez B, del Campo Alonso JM, Acevedo GroguesR, et al. (2010) Single-Time Vaccines.
- González Aznar E, Romeu B, Lastre M, Zayas C, Cuello M, et al. (2015) Mucosal and systemic immune responses induced by a single time vaccination strategy in mice. Can J Microbiol 61: 531-538.

 Short Communication
Short Communication