Abstract
Glioblastoma multiforme, a common highly malignant brain tumor is composed of invasive proliferating cancer cells, and a small population of glioblastoma stem cells characterized by relative quiescence, self-renewal, pluripotency, resistance to conventional chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiation. These glioblastoma stem cells if not eradicated following current standard of care, lead to tumor recurrence. By expressing a spectrum of phenotypic markers, associated competencies and a variety of growth patterns, tumor recurrence accounts for a lack of survival benefit . To remedy this recurrence issue, it is necessary to eliminate glioblastoma stem cells subsets. This will require a significant change in current therapeutic approach i.e. the application of Withaferin A or a combination of pleiotropic agents as suggested in a previous publication.
Keywords: Tumor Stem Cells; Glioblastoma Multiforme; Withaferin A; Pleiotropic Agents
Introduction
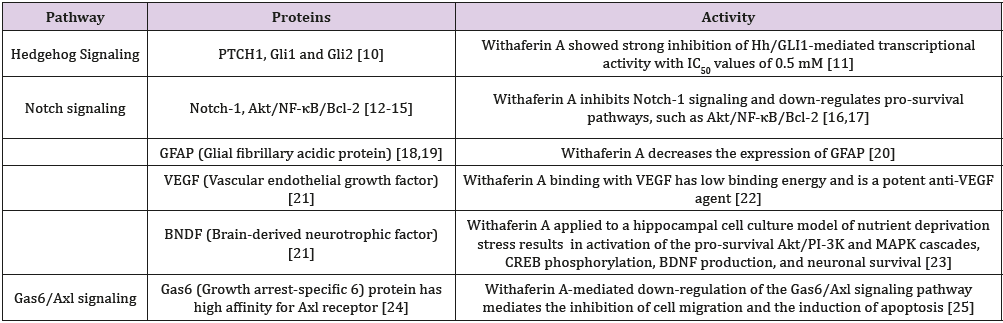
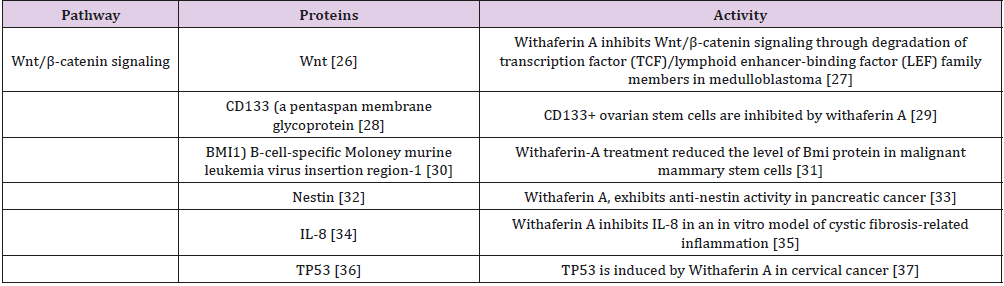
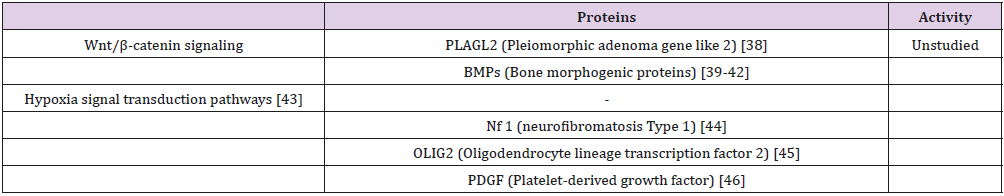
Glioblastoma multiforme is characterized by tumor cell heterogeneity, and by recurrent invasive tumors following conventional radiation, cytotoxic drugs, and limited ablative surgery [1-5]. The tumor originates from a stem cell population which exhibits properties of self-renewal and multi-lineage differentiation followed by clonal evolution, hierarchical stem cell development and bidirectional inter-conversion with nonstem cells [6]. These observations indicate that it is necessary to eradicate glioblastoma stem cells in order to abrogate the enhanced risk of tumor recurrence following conventional chemotherapy surgery, and radiation. The therapeutic focus should initially consist of applying pleiotropic medicinal (supplements, drugs) directed to the multiple molecular pathways promoting tumor stem cell genesis. Based on published pre-clinical research [7], pleiotropic compounds such as withaferin A, [8] and curcumin can be considered appropriate candidate agents [9]. There are several published withaferin A inhibitory interactions with critical molecular pathways in glioblastoma stem cells promoting tumor development (Table 1), There are also pre-clinical studies with withaferin A prohibiting tumor development in other tumors, but unexplored in glioblastoma stem cells (Tables 2 & 3).
Table 2: Published Withaferin an interaction with tumor stem cells other than glioblastoma stem cells.
Conclusion
Gliomagenesis and tumor stem cell heterogeneity are promoted by genetic alterations(driver mutations) and multiple factors in the surrounding tumor microenvironment [47,48] An additional mechanism for post-therapeutic reestablishment of an invasive and chemo/ radiation resistance population of differentiated glioblastoma cancer cells into cancer stem-like cells expressing markers associated with pluripotency and stemness such as CD133, SOX2, Oct4, and Nestin has been published [48]. These observations emphasize the importance of preclinical research studies with pleiotropic compounds interacting in a specific manner with tumor stem cells and avoiding interacting with normal stem cells. In the clinical setting, Withaferin A alone, or in combination with other pleiotropic approved drugs or supplements as initial therapy following diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme [49-53] may prohibit or delay tumor recurrence assuming these agents abrogate the effects of driver mutations, and micro-environmental factors.
References
- Loius DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella Branger D, et al. (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131(6): 803-820.
- Parajuli P, Mittal S (2018) Picture of glioma stem cells has become a Notch brighter. SCI Stem Cell Investigation 5: 42.
- Eramo A, Ricci Vitiani, L, Zeuner A, Pallini R, Lotti F, et al. (2006) Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Death and Differentiation 13(7): 1238-1241.
- Chen R, Nishimura MC, Bumbaca SM, Kharbanda S,Forrest WF, et al. (2010) A Hierarchy of Self-RenewingTumor-initiation Cell Types in Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 17(4): 362-375.
- Helson l, Majeed M (2019) Pleiotropic Chemotherapy to Abrogate Glioblastoma Multiforme Migration/Invasion. Anticancer Research 39(7): 3423-3427.
- Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ (2012) Cancer Stem Cells: Current Status and Evolving Cell Stem Cell 10(6): 717-728.
- Farnier D, Renoult O, Alves Fuerra MC, Paris F, Pacquer C, et al. (2019) Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells, Metabolic Strategy to Kill a Challenging Target. Front Oncol 9: 18.
- Vyas AR, Singh SV (2014) Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Cancer Prevention and Treatment by Withaferin A, A Naturally Occurring Steroidal Lactone, APS J 16(1): 1-10.
- Hatcher H, Planalp R, Cho J, Torti FM, Torti SV, et al. (2008) Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical trials. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(11): 1631-1652.
- Clement V,Sanchez P,de Tribolet N,Radovanovic I,Altaba AR, et al. (2007) HEDGEHOG-GLI1 Signaling Regulates Human Glioma Growth, Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal, and Tumorigenicity. Current Biology Cell Press 17(2): 165-172.
- Yoneyama T Arai MA, Sadhu SK, Ahmas F, Ishibashi M (2015) Hedgehog inhibitors from Withania somnifera. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 25(17): 3541-3544.
- Krishna BM, Jana S, Singhal J, Horne D, Awasthi S, et al. (2019) Notch signaling in breast cancer: From pathway analysis to therapy. Cancer Lett 461: 123-131.
- Wang J, Wakeman TP, Latha JD, Hjelmeland AB, Xiao Fan Wang X F, et al. (2010) Notch Promotes Radioresistance of Glioma Stem Cells, Stem Cells 28(1): 17-28.
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, et al. (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444(7120): 756-760.
- Olsauskas Kuprys R, Zlobin A, Osipo C (2013) Gamma secretase inhibitors of Notch signaling Onco Targets Ther 6:943-955.
- Koduru S, Kumar R, Srinivasan S, Evers MB, Damodaran C, et al. (2010) Notch-1 Inhibition by Withaferin-A: A Therapeutic Target against Colon Carcinogenesis Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 9(1): 202-210.
- Lee Y, LeeJ K, Ahn SH, Lee J, Nam DH, et al. (2016) Wnt signaling in glioblastoma and therapeutic opportunities. Laboratory Investigation 96(2): 137-150.
- Jacque CM, Vinner C, Kujas M, Raoul M, Racadot J, et al. (1978) Determination of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in human brain tumors. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 35(1): 147-155.
- Jung CS, Foerch C, Schänzer A, Heck A, Plate KH, et al. (2007) Serum GFAP is a diagnostic marker for glioblastoma multiforme Brain 130(12): 3336-3341.
- Guichet PO, Guelfi S, Ripoli C, Tiegell M, Sabourin JC, et al. (2016) Asymmetric Distribution of GFAP in Glioma Multipotent Cells PLOS ONE.
- Bargagna Mohan P, Hamza A, Kim YE, Khuan Abby Ho Y, Mor Vaknin N, et al. (2007) Withaferin A Targets Intermediate Filaments Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and Vimentin in a Model of Retinal Gliosis. Chem Biol 14(6): 623-634.
- Hamerlik P, Lathia JD, Rasmussen R, Wu Q, Bartkova J, et al. (2012) Autocrine VEGF–VEGFR2–Neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth. J Exp Med 209(3): 507-520.
- Saha S, Islam MK, Shilpi JA, Hasan S (2013) Inhibition of VEGF: a novel mechanism to control angiogenesis by Withania somnifera’s key metabolite Withaferin A 1: (11): In Silico Pharmacol 1: 11.
- Hwang D, Vasquez I, Galvez L, Do H, Lopez de Santa Ana A, et al. (2017) Ashwagandha and Its Active Ingredient, Withanolide A, Increase Activation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3’ Kinase/Akt Cascade in Hippocampal Neurons European Journal of Medicinal Plants 20(2): 1-19.
- Demarchi, F Verardo R, Varnum B, Brancolini C, Schneider C, et al. (2001) Gas6 anti-apoptotic signaling requires NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem 276(34): 31738-31744.
- Woo SM, Min KJ, Kim S, Park JW, Kim DE, et al. (2014) Axl is a novel target of withaferin A in the induction of apoptosis and the suppression of invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451(3): 455-460.
- Katoh M, Katoh M (2007) Wnt Signaling Pathway and Stem Cell Signaling Network. Clinical Cancer Research 13(14): 4042-4045.
- Grogan PT (2014) Withaferin A: A Novel therapeutic approach for Malignant Brain Tumors. Dissertation 2-242.
- Li Z (2013) CD133: a stem cell biomarker and beyond. Exp Hematol Oncol 2: 17.
- Kakar SS, Parte S, Carter K, Joshua IG, Worth C, et al. (2017) Withaferin A (WFA) inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting ovarian cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 8(43): 74494-74505.
- Abdouh M, Facchino S, Chatoo W, Balasingam V, Ferriera J, Bernier G, et al. (2009) BMI1 Sustains Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Stem Cell Renewal. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(28): 8884-8896.
- Liu S, Dontu G, Mantle ID, Patel S, Ahn NS, et al. (2006) Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res 66: 6063-6071.
- Ylivinkka I, Sihto H, Tynninen O, Hu Y, Laakso A, et al. (2017) Motility of glioblastoma cells is driven by netrin-1 induced gain of stemness. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1): 9.
- Su HT, Weng CC, Hsiao PJ, Chen LH, Kuo TL, et al. (2013) Stem Cell Marker Nestin Is Critical for TGF-b1-Mediated Tumor Progression in Pancreatic Cancer. Molecular Cancer Research 11(7): 768-779.
- Schraufstatter IU, Chung J, Burger M (2001) IL-8 activates endothelial cell CXCR1 and CXCR2 through Rho and Rac signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280: 1094-1103.
- Maitra R Porter MA, Huang S, Gilmour BP (2009) Inhibition of NFκB by the natural product Withaferin A in cellular models of Cystic Fibrosis inflammation. J Inflamm 6: 15.
- Hede SM, Nazarenko, Nister M, Lindstrom MS (2011) Novel Perspectives on p53 Function in Neural Stem Cells and Brain Tumors. J Oncol 2011: 852970.
- Munagala R, Kausar H, Munjal C, Gupta RC (2011) Withaferin A induces p53-dependent apoptosis by repression of HPV oncogenes and upregulation of tumor suppressor proteins in human cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 32 (11): 1697-1705.
- Zheng H, Ying H, Wiedemeyer R, Yan H, Quayle SN, et al. (2010) PLAGL2 Regulates Wnt Signaling to Impede Differentiation in Neural Stem Cells and Gliomas. Cancer Cell 17(5): 497-509.
- Kallioniemi A (2012) Bone morphogenetic protein 4-a fascinating regulator of cancer cell behavior. Cancer Genet 2205(6): 267-277.
- Li W Cogswell CA, LoTurco JJ (1998) Neuronal differentiation of precursors in the neocortical ventricular zone is triggered by BMP. J Neurosci 18(21): 8853-8862.
- Wi Q, Yao J (2013) BMP4 a new prognostic factor for glioma. World J Surg Oncol 11: 264.
- Piccolo S, Sasai Y, Lu B, De Robertis E (1996) Dorsoventral patterning in Xenopus: inhibition of ventral signals by direct binding of chordin to BMP4. Cell 86(4): 589-598.
- Panchision DM (2009) The role of oxygen in regulating neural stem cells in development and disease. Journal of Cellular Physiology 220(3): 562-568.
- Gutmann DH, Parada LF, Silva AJ, Ratner N (2012) Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Modeling CNS DysfunctionJ Neurosci 32(41): 14087-14093.
- Kupp R, Shtayer L, Tien AC, Szeto E, Sanai N, et al. (2016) Lineage-restricted OLIG2-RTK Signaling Governs the Molecular Subtype of Glioma Stem-like Cells. Cell Rep 16(11): 2838-2845.
- Nazarenko I, Hede SM, He X, Hedren A, Thompson J, et al. (2012) PDGF and PDGF receptors in glioma Ups J Med Sci 117(2): 99-112.
- Lathia JD, Heddelston JM, Venere M, Rich JN (2011) Deadly Teamwork: Neural Cancer Stem Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment Cell StemCell.8(5): 482-485.
- Auffinger B, Tobias AL, Han Y, Lee G, Guo D, et al. (2014) Conversion of differentiated cancer cells into cancer stem-like cells in a glioblastoma model after primary chemotherapy. Cell Death Differ 21(7):1119-1131.
- Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipellitti B, Gritti A, et al. (2004) Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 64: 7011-7021.
- Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Jeremy A Squire, Jane Bayani, et al. (2004) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432: 396-401.
- Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, et al. (2003) Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 63(18): 5821-5828.
- Ignatova TN, Kukekov VG, Laywell ED, Suslov (2002) Human cortical glial tumors contain neural stem-like cells expressing astroglial and neuronal markers in vitro. Glia 39(3): 193-206.
- Gong X, Schwartz PH, Linskey ME, Bota DA (2011) Neural stem/progenitors and glioma stem-like cells have differential sensitivity to chemotherapy. Neurology 76(13): 1126-1134.

 Review Article
Review Article