Abstract
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major public health problem globally. Female genital tuberculosis (FGT) occurs mostly secondary to pulmonary tuberculosis, commonly by the haematogenous route. The main difficulties in the monitoring of treatment efficacy are connected with the use of the same technologies both in the diagnosis and cure estimation of FGT. Articles in tuberculosis journals rarely featured by equations. The aim of the present study was to elaborate new analytical approaches, in form of equation concerning FGT treatment efficacy identification. The general conclusion was created towards the RCSR (red cells sedimentation rate), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and tuberculin skin-test, ultrasound and radial examinations: they are not reliable tools since both false–negative or false–positive cases were observed . Explanation of the mismatch of the most of identified alterations by means of ultrasound and radial examinations (CT and MRI) with the clinical status of women is explained by the prolonged maintenance of alterations caused by disease, up till several years after clinical recovery. Newly elaborated test based on 1H–NMR (T1, T2), relaxation times measurement in vitro being combined with the regression analysis models have a potential to assess the treatment efficacy of female genital tuberculosis in 70% of cases.
Keywords: Female Genital Tuberculosis; Severity; Diagnosis
Abbreviations: TB: Tuberculosis; FGT: Female Genital Tuberculosis; SSNFGT: Sputum Smear–Negative Not Seriously Ill Female Genital Tuberculosis; PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction; MBT: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis; CT: Computed Tomography; MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging; RCSR: Red Cells Sedimentation Rate; USG: Ultrasound Examination; HSG: Hysterosalpingography; 1H-NMR: Relaxation; T1: Spin–Latex Relaxation Time; T2: Spin-Spin Relaxation Time; P (%): Spin Population; A,B: Fractions of Spin Populations; PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease; WHO: World Health Organization; HU: Hounsfield Units
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is an increasing public health concern worldwide with about six million new cases a year. It is one of the most important causes of infectious morbidity and mortality. On a global scale, TB has a devastating impact on developing nations with 13 countries accounting for nearly 75% of all cases [1]. World health organization (WHO) classifies FGT as category III (extrapulmonary, sputum smear-negative, not seriously ill (SSNFGT)) [2]. FGT affects about 12% of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis [3] and represents 15-20% of extrapulmonary tuberculosis [4]. FGT occurs mostly secondary to pulmonary tuberculosis, commonly by the haematogenous route in a manner similar to spread to other extra-pulmonary sites like urinary tract, bones and joints etc.
Remarkably, despite of a wealth of information, clinical physicians and TB biologists possess virtually no comprehensive theoretical model which could serve as a framework for understanding, organizing and applying these data. Continuing search is needed for finding simpler and practicable methods for making diagnosis in respect of FGT easier and the use of therapeutic test should be avoided. Diagnosis of FGT is made by meticulous patients history study, thorough clinical examination and proper use of investigations, particularly endometrial aspirate for AFB (Acid Fast Bacilli :tuberculosis test: organisms (including mycobacteria) that resist decolorization with acid alcohol due to the lipid-rich mycolic acids in the cell wall thereby retaining the primary stain) culture, PCR and histopathology aided by endoscopy It may be mentioned that research is considerably hampered due to a non-availability of clear criteria for monitoring the treatment efficacy, unlike in pulmonary TB [5]. Therefore, more research is needed, so that delivery of therapy can become more certain and therapeutic effects get better defined in terms of the normalization of the pathologic process and the desirable reproductive function [6]. Therefore, all the available diagnostic techniques should be combined judiciously and correlated with the clinical profile prior to instituting the treatment of tuberculosis [7]. The main difficulties in the monitoring of treatment efficacy are connected with the use of the same technologies both in the diagnosis and cure estimation of TB. Articles in tuberculosis journals rarely featured by equations. Apparently, as a reason of it could be the fact that mathematical models in the case of medical application are becoming increasingly complex, and as a result some of the subtleties of interpretation are in danger of being overlooked. The aim of the present study was to elaborate new analytical approaches, in form of equation concerning FGT treatment efficacy revelation and estimate informative value of new approaches compared with the common laboratory, serological and instrumental methods.
Material and Methods
Objects: Cohort of 116 women was examined: in the status of severe FGT, SSNFGT, according to the International diseases classification X : A18.1 :57 women (17–56 years of age), recovered of the FGT: 41 women (18–48 years of age), healthy persons: 18 women (20-40 years of age).
Biological Specimens for Laboratory Analyses
Blood for the 1H–NMR (T1, T2) relaxation times measurements and polymerase chain reaction was yielded from the venum cubitalis by means of syringe and needle, oxaloacetate was used as a stabilizer, volume 5 mL; blood plasma was obtained by spinning of blood at 5000 rounds/per minute during 20 minutes. Vaginal lavage: vagina and vaginal part of the cervix uteri was dried by gauze plug, 5,0 mL of 0,86% NaCl sterilized solution was poured to the vagina, exposed there during 20 minutes, lavage was sucked by means of the sterilized syringe and put to the glass tube.
Laboratory Techniques
PCR was performed on the equipment of “DNA-technology” (Russia) using reagents of “Flash” (Russia). Tuberculin–skin–test was performed with the purified, liquid tuberculosis allergen, manufactured by “Biolek” (Ukraine), standard dilutions were used for the intradermal application. Tuberculosis allergen was injected to the arm, allergen’s IV (10 Tuberculosis units) and VI (0,01 Tuberculosis unit) dilutions were used. Tuberculin–test reaction was estimated by passing 72 hours. papule ≥5 mm was considered as a positive result. RCSR was revealed [7].
Radial Studies NMR.
NMR–relaxometer (19,0 MHz) was used. 1H–NMR relaxation times (T1a, T1b, T2a, T2b, T1, T2 (ms)) “fast” (a) and “slow” (b) water and theirs spin population were registered in the blood serum and vaginal lavage. T1 was measured by using pulse seguence 180°–τ –90°. T2 measurements were performed by using Carr- Përcell-Meubum-Gill pulse sequences. Registered parameters were recorded and mathematically approximated as the mono-or biexponential curves. CT. Computer tomography was performed on the equipment “CT Race” of “GE Medical Systems” (USA). MRI. MRI studies were performed by means of “Tomikon–BMT 100” (0,28 T, “Bruker”, Germany). Standard pulse seguences for T1, T2 weighted images were applied.
Statistical Calculations
Statistical calculations have been performed by means of “Microsoft Excel” and Statistica 6,0 (Manuguistic Group) programs. Comparison of two groups values has been performed according to U test Wilcoxon-Mann-Uhitny. Approximation of the FGT activity dependence upon the revealed parameters has been performed by the method of regression analysis [5]:
Linear*: 1. FGT activity (0→1) 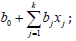 – equation value: ≥1, FGT is active; <1, FGT is inactive.
– equation value: ≥1, FGT is active; <1, FGT is inactive.
2. Binary logistic: 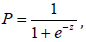 if P<0,5 FGT activity occurs;
if P<0,5 FGT activity occurs;
3. Nonlinear*: FGT activity 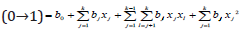
Informative value of the regression equations has been estimated according to R2 (determination coefficient) meaning, statistical significance was assessed according to Fisher’s F-factor. All the scientific researches fit to the rules of the Ethical Control Commission, sanitarian and regimes against infection.
Result and Discussion
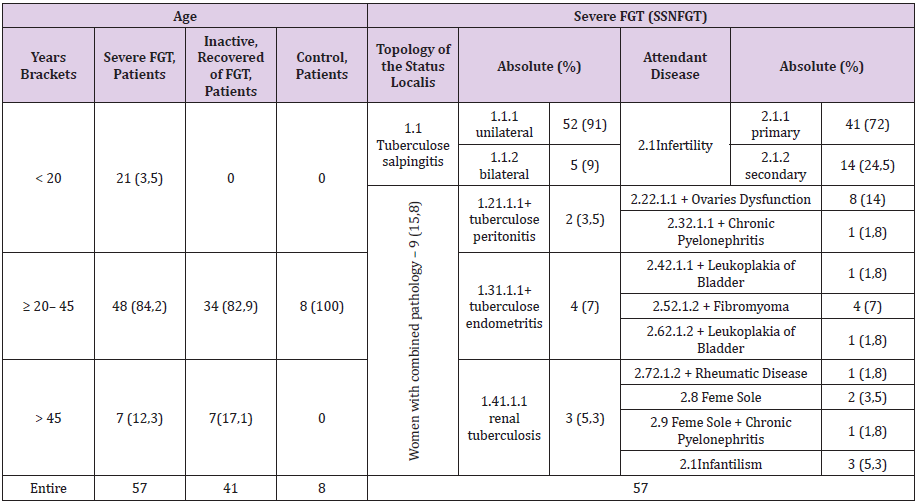
Although FGT can occur in any age group, the majority of patients are usually belonging to the reproductive group of age, 75% are in the 20–45 years age bracket, postmenopausal women account for 11% of cases of FGT [6]. In our investigations they amounted 84,2%, and 12,3% of cases respectively (Table 1).
Different parts of the female genital organs commonly are involved, andinclude (literature, % [4,6] & (Table 1), %): the fallopian tubes (95–100/100), endometrium (50–60/3), and ovaries (20–30/0), kidney (0/5,3), peritoneum (0/3,5), cervix (5– 15/0), vulva/vagina (≤1/0) and the myometrium (2,5/0) .FGT may be asymptomatic and the majority of women are diagnosed during examination on infertility (Table 1) & [8,9]. Systemic constitutional symptoms of the weight loss, feeling unwell and night sweats may be present. Attendant disease is very frequent, 96,5% (Table 1). In the postmenopausal women, FGT is combined with postmenopausal bleeding, persistent leucorrhoea.
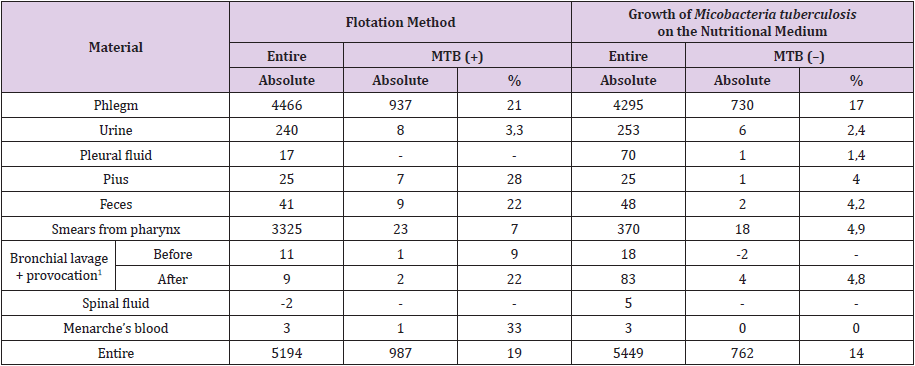
During the entire course of cure patient with TB is undergoing to more than 80 types of heamatological, cytological, biochemical, blood coagulation, immunological and microbiological analyses. This number is an indicator of both, of detailed knowledge concerning TB and lack of the reliable objective criterion of the cure efficacy assessment. At the same time MBT revelation is problematic, indeed. In patients with the different forms of TB positive revelation of MBT depending upon the substance of analysis occurs only in 1,4 :33% of cases (Table 2).
Table 2: Mycobacteria tuberculosis revelation frequency in the biological fluids in the tests performed in the diagnostic clinical laboratory of Kazan tubercular hospital.
Note:
a) Inhalation or intrabronchial infusion of the Tubazide;
b) Lack of the analyses.
Laboratory Tests
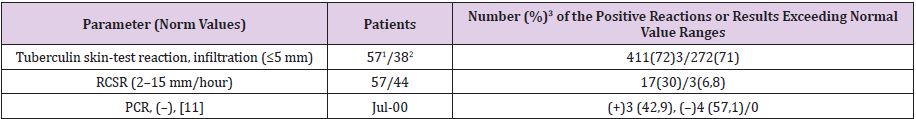
Other indirect common tests are used also. The full blood elements count is often normal but RCSR is usually raised [1] & (Table 3). Stimulation of T–cells cause release of cytokines from them, manifested by the positive tuberculin skin–test, which has a sensitivity 55% [10], 72% (Table 3) and specificity 80% 29% [10] & (Table 3). False-positive reactions occur, while false-negative reactions, although not uncommon, in at least 20% [1], 28% (Table 3) of patients with the confirmed active tuberculosis. Concerning FGT activity revelation, disadvantage of the widely shared tests is their positive value both in severe/inactive FGT (skin-test, RCSR), or combination of (+)/(–) cases in PCR analyses in severe FGT [11]: skin –test 72%/71%,RCSR 30%/6,8%, PCR positive 42,9%/false– negative 57,1% (Table 3).
Table 3: Laboratory and serological analyses of women with FGT.
Note:
a) Number of patients with severe FGT, sputum smear negative and
b) Inactive recovered FGT;
c) Number of analyses which exceeds normal value ranges.
Radial Studies In Vivo
USG. All the recovered patients were featured by the pathological changes of anatomical structures, some of these changes were revealed in 100% (Table 4). HSG. HSG is performed frequently as an investigation for infertility [7], what is a common complication of genital TB. It should not be performed when TB is diagnosed by other means, as it may result in dissemination and flare-up of disease. Tubal occlusion is the most frequent HSG finding in genital tuberculosis (Table 4).
Table 4: The radial studies of women with FGT.
Note: *Number of cases; **Density was measured in the Hounsfield units (HU), normal value brachets were +16,62→+26,75 (HU);
a) Severe FGT, sputum negative status;
b) Recovered of FGT;
c) Normal state;
d) Abnormal state;
e) No measurements were performed
The HSG of 43 women with FGT identified features of gained or reduced size of the uterus cavity in 24 women, impaired fallopian tubes in 33 women, an abnormal state of the ampoule part of fallopian tubes in 13 women (Table 4). Although the various features which HSG describes are not specific for genital tuberculosis, they are only highly suggestive of it. All these signs of USG and HSG scanning are not reliable because of false-positive and false-negative cases in both of women groups (Table 4). CT and MRI studies were performed only in SSNFGT patients.
CT. CT findings of abdominal tuberculosis may mimic diffuse peritoneal malignancy. These features include ascites, omental and mesenteric infiltration and smooth thickening of the parietal peritoneum [12]. None of the registered parameters was revealed in all the cases, what makes CT examination as a not reliable estimation tool in TB treatment monitoring (Table 4). MRI. MRI provides a valuable tool for visualizing common anatomical changes in soft tissues, to which female genitals belong also. MRI seems to be a useful modality for the tubes and ovarian masses changes induced by tuberculosis infection [6,13] & (Table 4).
The general conclusion was created towards the RCSR, PCR and tuberculin skin-test and radial examinations: they are not reliable tools since both false–negative or false–positive cases were observed. Explanation of the mismatch of the most of revealed alterations by means of radial examination with the clinical status of women is explained by the prolonged maintenance of alterations caused by disease, up till several years after clinical recovery. Further investigation has been focused on the radio spectroscopy parameters of 1H–NMR relaxation T1, T2 times measurements in vitro.
Radial Studies In Vitro
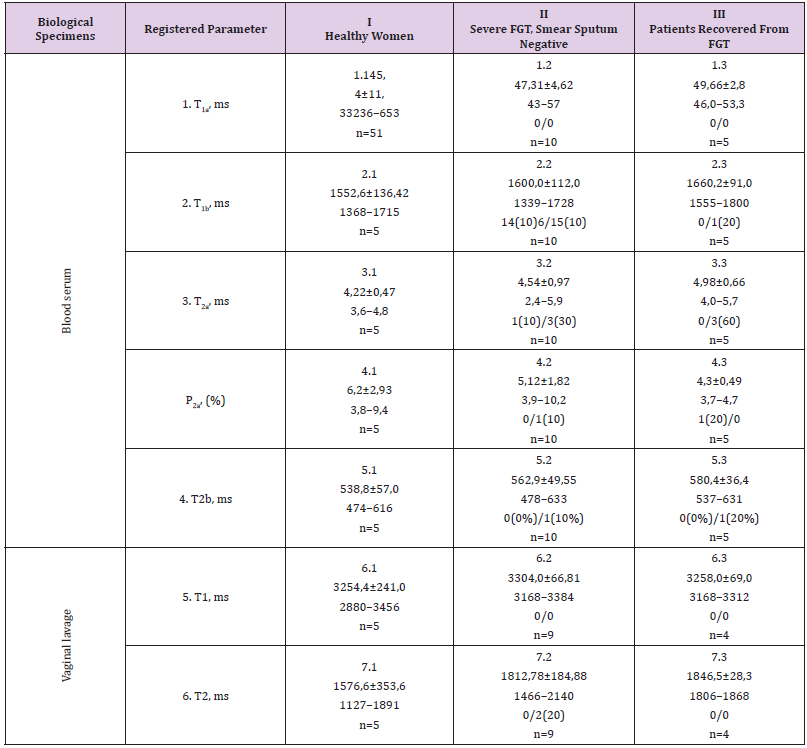
NMR. 1H–NMR (T1, T2) relaxation times reflects the change of metallic ions, diamagnetics, high molecular weight compounds and low molecular weight ligands contents. Additionally T1, T2 values are stipulated by the capacity of molecules, which are the constituents of tissues, to induce formation of the “hydration water”, the water shell, and by the thickness of shell, which in turn is stipulated by the conformation and the composition of the biochemical structures exposed to the water phase. The mostly probable molecular substrate of the nature of the water 1H–NMR relaxation times (T1, T2), gained in blood serum, in some of diseases, is seemed to be a fraction of the low molecular weight compounds with the mass approximately5000 Da. We have failed to yield statistical significant differences between I, II, III subgroups of women in NMR investigations, while deviations from the normal value ranges up to 60% have been observed (Table 5). Identification of FGT treatment efficacy according to direct T1, T2 measurements, based on the descriptive statistics, is not available.
Table 5: 1H–NMR relaxation (T1,T2) parameters of the blood serum and vaginal lavage in the women with FGT.
Note:
a) Number of patients;
b) MD±SD;
c) Value ranges;
d) Number of analyses which are less than norm;
e) Number of analyses which exceed norm; 6:Share (%) of analyses which deviate of norm. It has been revealed no statistical difference between subgroups.
Regressions Analyses
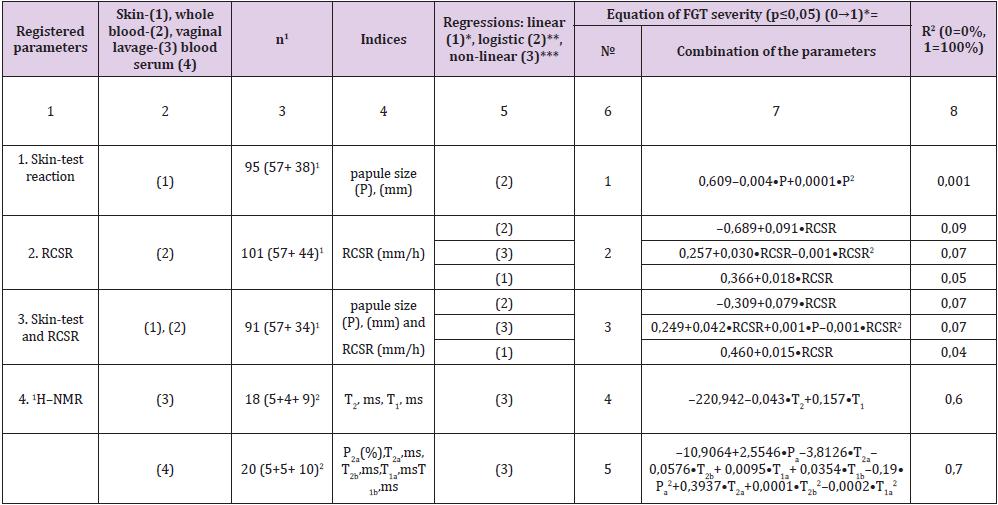
Preliminary all above investigated parameters have been considered in terms of the descriptive statistics (Tables 3-6). Common approach in the scientific researches, in the attempts to prove or deny patients diagnosis or clinical status, includes methods of descriptive statistics: type of the data distribution form (normal, Gauss etc.), comparison of two mean values, correlation coefficients etc. Informative value of certain laboratory or technological parameter in clinics is estimated from the extent of its deviation from the normal value ranges. For neither of the above considered laboratory and instrumental tests reliable criterion of FGT severity and treatment monitoring has been confirmed (Tables 2-6).
Table 6: Revelation of FGT activity according to the values of skin-test reaction, RCSR and 1H–NMR parameters.
Note: 1 – recovered of FGT+SSNFGT. 2 – control + recovered of
FGT+SSNFGT.
* – linear regression analysis, interpretation: ≥1
SSNFGT, is severe, active, <1–FGT is inactive.
** – bimodal logistic regression analysis, interpretation,
value of Z in the equation→, , active, SSNFGT occurs.
*** – non–linear regression analysis, interpretation: ≥1–
SSNFGT, severe, active, <1–FGT inactive.
n – number of patients P (%)–
spin population
FGT – female genital tuberculosis a, b –
components
T1, ms – spin–latex relaxation time T2, ms–
spin-spin relaxation time
The real reasonable linkage between the values of the registered parameters and the woman status can be proven by means of the regression analysis [14] & (Table 6). Convenience of the obtained equations includes two main items:
a) Technology of the treatment’s efficacy monitoring is based on the analytical representation of data, in form of the equations.
b) Collation of the equations is carried out by means of R2* value coefficients. R2 reflects the share of the examined individuals, both healthy and ones affected by TB, circumscribed by the appropriate equation (0%→100%).
RCSR, tuberculin skin–test and 1H–NMR registered parameters were arranged in a number of regression equations (Table 6). Depending upon the type of equation (linear, bimodal or nonlinear) and combination of the involved parameters R2 has been varied in a wide range, in a lower value of 0,001, skin-test (Equation No. 1), and in a highest one of 0,7 (Equation No. 2). So how can yielded equation help phthisiatrics of FGT? They can form the schematic framework for mechanistic, quantitative models that incorporate more realistic properties of biological systems such as stochasticity and nonlinearity. As the outcomes of such interactions cannot be determined by verbal reasoning alone, the treatment efficacy of FGT must be computed from general integral models of TB lesions healing.s
Conclusion
TB models can and do highlight major gaps in data and areas where greater empiric evidence is needed. Making these assumptions and therefore their uncertainties explicit provides benefit in itself. Newly elaborated test based on 1H–NMR (T1, T2), relaxation times measurement in vitro being combined with the regression analysis models have a potential to assess the treatment efficacy of female genital tuberculosis in 70% of cases.
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to O.A. Opanasyuk (Kazan Federal University) for the technical support and close cooperation.
References
- (2018) World Нealth Organization. WHO global tuberculosis report 2018, Geneva, Switzerland
- (2011) Global tuberculosis control 2011. WHO Report?
- Aka N, Vural TZE (1997) Evaluation of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis for genital involvement. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 23(4): 337-340.
- Rajamaheswari N, Pelvic tuberculosis.
- Arora R Rajaram P, Oumachigui A, Arora VK (1992) Prospective analysis of short course chemotherapy in female genital tuberculosis. Int J Gynecol Obstel 38(4): 311-314.
- Arora VK, Gupta R, Arora R (2003) Female genital tuberculosis need for more research. Ind J Tub 50: 9.
- Baikeev RF, Nefedova LN, Safina NF (2004) Immune status in the Tuberculosis of the female reproductive organs: Materials of the Scientifically practical conference Progenome epoch in the biology and problems of biotechnology, Kazan: 25-29.
- Mendenhall W, Sincich TL (1996) A second course in statistics: regression analysis. Prentice Hall, USA, p: 899.
- Qureshi RN, Sammad S, Hamd R, Lakha SF (2001) Female genital tuberculosis revisited. J Pak Med Assoc 51(1): 16-18.
- ОТЧЕТ КАМЕНКИ
- Zissin R, Gayer G, Chowers M, Sapiro-Feinberg M, Kots E, et al. (2001) Computerised tomography findings of abdominal tuberculosis: report of 19 cases Isr Med Assoc J 3(6): 414-418.
- Baikeev RF, Ziytdinov KM, Zalaliev RA, Ahmadeev IR (1997) Tissue destruction and blood coagulation initiation in the tuberculosis inflammation. Problemi Tuberculyeza, Russia 4: 44-50.
- Yapar EG, Ekici E, Karasahin E, Gokmen O (1995) Sonographic features of tuberculous peritonitis with female genital tuberculosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynaecol 6(2): 121-125.
- Chavhan GB, Hira P, Rathod K (2004) Female genital tuberculosis: hysterosalpingographic appearances. Br J Radiol 77(914): 164-169.
- Sharma JB, Karmakar D, Hari S, Singh N, Singh SP, et al. (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging findings among women with tubercular tubo-ovarian masses. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 113(1): 76-80.
- Baikeev RF, Ziytdinov KM, Ahmadeev IR (1992) Destructive changes revelation in the pulmonary and bone tuberculosis. Problemi Tuberculyeza, Russia 11-12: 28-31.

 Research Article
Research Article